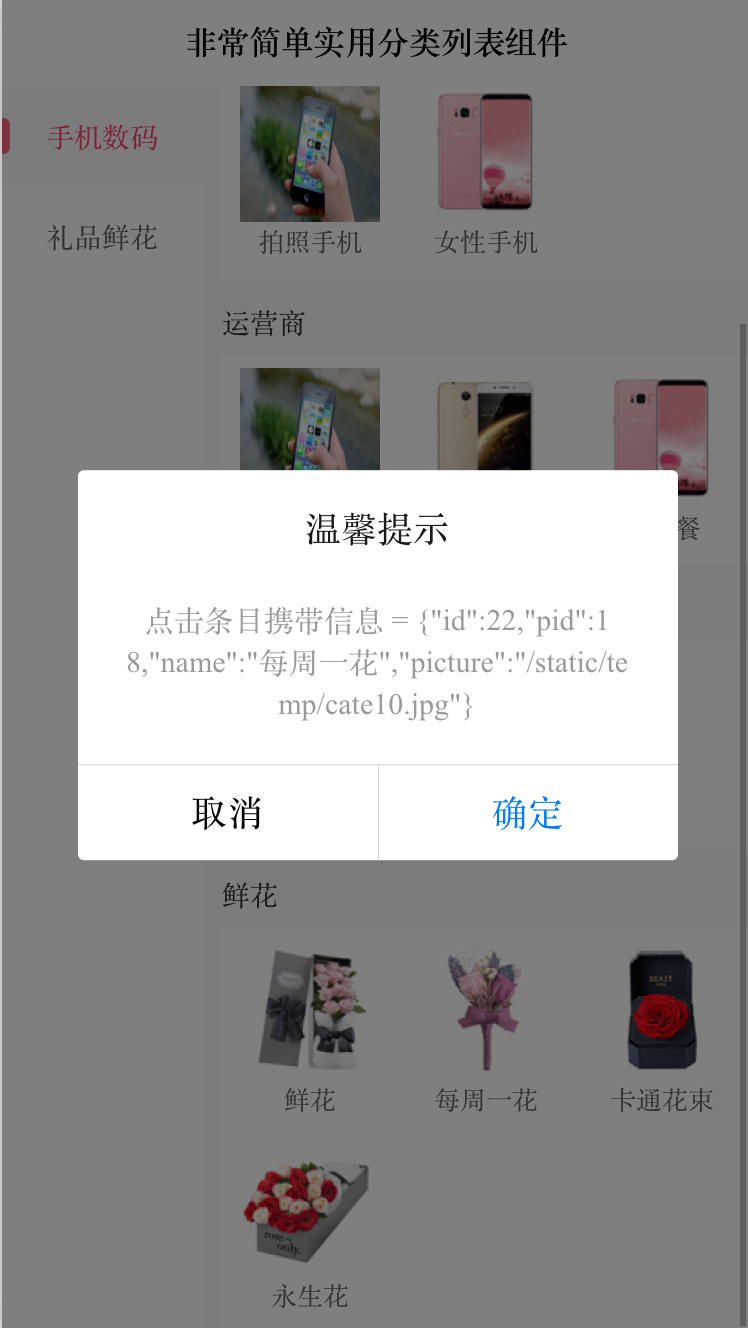
文章目录
- 1. 目的
- 2. 原理
- 3. 实现
- 3.1 获得直方图 `int hist[256]`
- 3.2 获得累积分布 `int cdf[256]`
- 3.3 均衡化公式
- 3.4 遍历原图,逐点均衡化,得到结果
- 4. 完整代码和结果
- 4.1 例子1
- 4.2 例子2
- 4.3 例子3
- 4.4 完整代码
- 5. References
1. 目的
用 C 语言实现直方图均衡化。
没有调用第三方依赖库, 没有使用 C++。图像加载和保存时使用的 .pgm 这一格式。
2. 原理
首先得到单通道灰度图的直方图这一统计量 int hist[256], 然后得到累积分布函数 cdf (cumulated distribution function), 也就是统计量 int cdf[256], 最后根据均衡化公式遍历原始图像每个像素得到均衡化后的图像像素,得到最终结果。
3. 实现
3.1 获得直方图 int hist[256]
获得直方图的过程不在赘述, 见 scratch lenet(2): C语言实现图像直方图的计算。
3.2 获得累积分布 int cdf[256]
获得 cdf 的过程很简单, 遍历 hist 每个元素并累加即可。由于后续的均衡化公式需要用到 cdf 的最小、最大值, 这里也一并统计算出:
int cdf[256] = { 0 };
cdf[0] = hist[0];
bool found_min = false;
int min_cdf = -1;
for (int i = 1; i < 256; i++)
{
cdf[i] = hist[i] + cdf[i-1];
if (!found_min && cdf[i] > 0)
{
min_cdf = cdf[i];
found_min = true;
}
}
int max_cdf = cdf[255];
3.3 均衡化公式
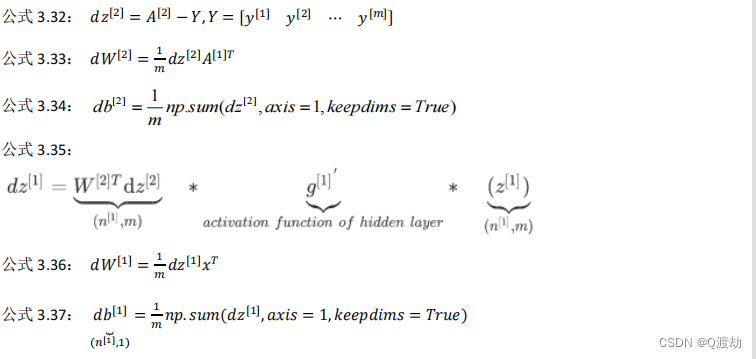
对于原始像素取值为 v 的情况, 均衡化后的值为 h(v), 公式为:
h
(
v
)
=
r
o
u
n
d
(
cdf
(
v
)
−
cdf
(
m
i
n
)
cdf
(
m
a
x
)
−
cdf
(
m
i
n
)
∗
(
L
−
1
)
)
h(v) = round(\frac{\text{cdf}(v) - \text{cdf}(min)}{\text{cdf}(max) - \text{cdf}(min)} * (L-1))
h(v)=round(cdf(max)−cdf(min)cdf(v)−cdf(min)∗(L−1))
对于图像任务来说, 通常 L = 256 L=256 L=256. 容易写出对应的 C 实现
int equalize(uchar v, int min_cdf, int max_cdf, int cdf[256])
{
int up = cdf[v] - min_cdf;
int down = max_cdf - min_cdf;
float frac = up * 255.f / down;
int equalized_v = (int)(frac + 0.5);
return equalized_v;
}
3.4 遍历原图,逐点均衡化,得到结果
uchar* equalized_image = (uchar*)malloc(height * width);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
int idx = i * width + j;
uchar v = image[idx];
uchar equalized_v = equalize(v, min_cdf, max_cdf, cdf);
equalized_image[idx] = equalized_v;
}
}
4. 完整代码和结果
4.1 例子1
原图:

原图和直方图 vs 均衡化后的图像:

原图的直方图 vs 直方图均衡化后的直方图

4.2 例子2
原图: 很模糊, 是 28x28 大小的手写数字 3 执行了 5x5 kernel 为全1的卷积计算后的结果:

直方图均衡化后的结果图:

原图的直方图 vs 结果图的直方图:

4.3 例子3
原图:

直方图均衡化之后的结果图:

原图的直方图 vs 结果图的直方图:

4.4 完整代码
// Author: Zhuo Zhang <imzhuo@foxmail.com>
// Homepage: https://github.com/zchrissirhcz
// Date: 2023.06.17
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef unsigned char uchar;
typedef struct GrayImage
{
int width;
int height;
uchar* data;
} GrayImage;
GrayImage read_pgm_image(const char* filepath)
{
FILE* fin = fopen(filepath, "rb");
char magic[3];
int width, height;
int nscan = fscanf(fin, "%2s\n%d %d\n255\n", magic, &width, &height);
uchar* image = NULL;
if (nscan == 3 && magic[0] == 'P' && magic[1] == '5')
{
image = (uchar*)malloc(width * height);
fread(image, width * height, 1, fin);
}
else
{
printf("Error: failed to read pgm file %s\n", filepath);
}
fclose(fin);
GrayImage gray;
gray.width = width;
gray.height = height;
gray.data = image;
return gray;
}
void write_pgm_image(uchar* image, int width, int height, const char* filename)
{
FILE* fout = fopen(filename, "wb");
fprintf(fout, "P5\n%d %d\n255\n", width, height);
fwrite(image, width * height, 1, fout);
fclose(fout);
}
void* memset(void* s, int c, size_t n)
{
char x = c & 0xff;
char* p = (char*)s;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
p[i] = x;
}
return s;
}
void* memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t n)
{
char* dp = (char*)dest;
char* sp = (char*)src;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
*dp = *sp;
dp++;
sp++;
}
return dest;
}
int equalize(uchar v, int min_cdf, int max_cdf, int cdf[256])
{
int up = cdf[v] - min_cdf;
int down = max_cdf - min_cdf;
float frac = up * 255.f / down;
int equalized_v = (int)(frac + 0.5);
return equalized_v;
}
void calculate_histogram(uchar* image, int width, int height, int hist[256])
{
memset(hist, 0, 256 * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
int idx = i * width + j;
uchar v = image[idx];
hist[v]++;
}
}
}
GrayImage create_gray_image_from_histogram(int hist[256])
{
// draw histogram as image
int max_hist = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
if (hist[i] > max_hist)
{
max_hist = hist[i];
}
}
int hist_height = max_hist;
int hist_width = 256;
uchar* image = (uchar*)malloc(hist_height * hist_width);
for (int i = 0; i < hist_height; i++)
{
int inv_i = hist_height - 1 - i;
for (int j = 0; j < hist_width; j++)
{
int idx = i * hist_width + j;
if (inv_i > hist[j])
{
image[idx] = 255;
}
else
{
image[idx] = 0;
}
}
}
GrayImage hist_image;
hist_image.width = hist_width;
hist_image.height = hist_height;
hist_image.data = image;
return hist_image;
}
uchar* equalize_histogram(uchar* image, int width, int height, int hist[256])
{
// get CDF
int cdf[256] = { 0 };
cdf[0] = hist[0];
bool found_min = false;
int min_cdf = -1;
for (int i = 1; i < 256; i++)
{
cdf[i] = hist[i] + cdf[i-1];
if (!found_min && cdf[i] > 0)
{
min_cdf = cdf[i];
found_min = true;
}
}
int max_cdf = cdf[255];
// calculate equalized histogram
uchar* equalized_image = (uchar*)malloc(height * width);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
int idx = i * width + j;
uchar v = image[idx];
uchar equalized_v = equalize(v, min_cdf, max_cdf, cdf);
equalized_image[idx] = equalized_v;
}
}
return equalized_image;
}
void test_histogram()
{
GrayImage gray = read_pgm_image("/home/zz/work/lenet_c/2.pgm");
uchar* image = gray.data;
int width = gray.width;
int height = gray.height;
int hist[256] = { 0 };
calculate_histogram(image, width, height, hist);
calculate_histogram(image, width, height, hist);
GrayImage hist_image = create_gray_image_from_histogram(hist);
write_pgm_image(hist_image.data, hist_image.width, hist_image.height, "res_histogram.pgm");
free(hist_image.data);
uchar* equalized_image = equalize_histogram(image, width, height, hist);
write_pgm_image(equalized_image, width, height, "res_equalized_image.pgm");
int eq_hist[256] = { 0 };
calculate_histogram(equalized_image, width, height, eq_hist);
GrayImage eq_hist_image = create_gray_image_from_histogram(eq_hist);
write_pgm_image(eq_hist_image.data, eq_hist_image.width, eq_hist_image.height, "res_eq_histogram.pgm");
free(eq_hist_image.data);
free(equalized_image);
free(gray.data);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
test_histogram();
return 0;
}
5. References
- 直方图均衡化(HE)
- scratch lenet(2): C语言实现图像直方图的计算