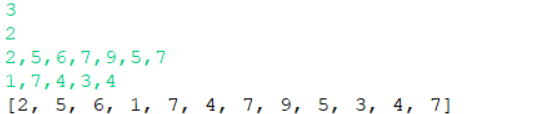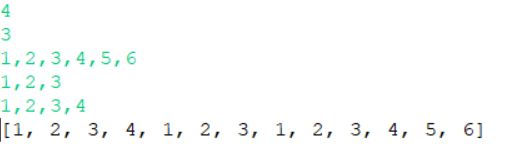数组拼接
题目描述
现在有多组整数数组,需要将它们合并成一个新的数组。
合并规则,从每个数组里按顺序取出固定长度的内容合并到新的数组中,取完的内容会删除掉,如果该行不足固定长度或者已经为空,则直接取出剩余部分的内容放到新的数组中,继续下一行。
输入描述
第一行是每次读取的固定长度,0 < 长度 < 10
第二行是整数数组的数目,0 < 数目 < 1000
第3-n行是需要合并的数组,不同的数组用回车换行分隔,数组内部用逗号分隔,最大不超过100个元素。
输出描述
输出一个新的数组,用逗号分隔。
用例
| 输入 | 3 |
| 输出 | 2,5,6,1,7,4,7,9,5,3,4,7 |
| 说明 | 1、获得长度3和数组数目2 2、先遍历第一行,获得2,5,6 3、再遍历第二行,获得1,7,4 4、再循环回到第一行,获得7,9,5 5、再遍历第二行,获得3,4 6、再回到第一行,获得7,按顺序拼接成最终结果 |
| 输入 | 4 3 1,2,3,4,5,6 1,2,3 1,2,3,4 |
| 输出 | 1,2,3,4,1,2,3,1,2,3,4,5,6 |
| 说明 | 无 |
题目解析
- 使用List 内部装入一个List类型的集合。这样就可以将所有数据装入一个List中,其结构体现为[ [],[],[],[],[] ]
- 遍历外层的List,每次取出从一个集合中取出对应的n个数据,如果该子列表的数据被取完,那么就将其从外层List中移出。
- 直到所有子列表都移出完成,即外层List的长度为0,那么就结束程序。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
//3
//2
//2,5,6,7,9,5,7
//1,7,4,3,4
public class T55 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int line = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
List<List<Integer>> numList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < line; i++) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Arrays.stream(sc.nextLine().split(",")).forEach(n -> {
list.add(Integer.parseInt(n));
});
numList.add(list);
}
List<Integer> resList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while (numList.size() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < numList.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> itemList = numList.get(i);
int count = 0;
while (count < num) {
resList.add(itemList.get(0));
itemList.remove(0);
count++;
if (itemList.size() == 0)
break;
}
if (itemList.isEmpty()) {
numList.remove(itemList);
i--;// 注意 移除后集合的大小会少一个,因此i--,再i++之后,正好是移除后的下一个
}
}
}
System.out.println(resList);
}
}
代码运行示意图