一、自定义线程池
1. 简易线程池
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool") public class TestPool { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { int j =i; threadPool.execute(() -> { log.debug("{}",j); }); } } } @Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool") class ThreadPool { // 任务队列 private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue; // 线程集合 private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>(); // 核心线程数 private int coreSize; // 获取任务时的超时时间 private long timeout; private TimeUnit timeUnit; public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapcity) { this.coreSize = coreSize; this.timeout = timeout; this.timeUnit = timeUnit; this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapcity); } // 执行任务 public void execute(Runnable task) { // 当任务数没有超过 coreSize 时,直接交给 worker 对象执行 // 如果任务数超过 coreSize 时,加入任务队列暂存 synchronized (workers) { if (workers.size() < coreSize) { Worker worker = new Worker(task); log.debug("新增 worker{}, {}", worker, task); workers.add(worker); worker.start(); } else { taskQueue.put(task); } } } class Worker extends Thread { private Runnable task; public Worker(Runnable task) { this.task = task; } @Override public void run() { // 执行任务 // 1) 当 task 不为空,执行任务 // 2) 当 task 执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行 // while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) { while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, timeUnit)) != null) { try { log.debug("正在执行...{}", task); task.run(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { task = null; } } synchronized (workers) { log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this); workers.remove(this); } } } } // 阻塞队列 @Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue") class BlockingQueue<T> { // 1. 任务队列 private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(); // 2. 锁 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // 3. 生产者条件变量 private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition(); // 4. 消费者条件变量 private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition(); // 5. 容量 private int capcity; public BlockingQueue(int capcity) { this.capcity = capcity; } // 带超时阻塞获取 public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) { lock.lock(); try { // 将 timeout 统一转换为 纳秒 long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); while (queue.isEmpty()) { try { if (nanos <= 0) { return null; } // 返回值是剩余时间 nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } T t = queue.removeFirst(); fullWaitSet.signal(); return t; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } // 阻塞获取 public T take() { lock.lock(); try { while (queue.isEmpty()) { try { emptyWaitSet.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } T t = queue.removeFirst(); fullWaitSet.signal(); return t; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } // 阻塞添加 public void put(T task) { lock.lock(); try { while (queue.size() == capcity) { try { log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ...", task); fullWaitSet.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task); queue.addLast(task); emptyWaitSet.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public int size() { lock.lock(); try { return queue.size(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
2. 拒绝策略
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool") public class TestPool { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(1, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 1, (queue, task)->{ // 1. 死等 // queue.put(task); // 2) 带超时等待 // queue.offer(task, 1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 3) 让调用者放弃任务执行 // log.debug("放弃{}", task); // 4) 让调用者抛出异常 // throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败 " + task); // 5) 让调用者自己执行任务 task.run(); }); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int j = i; threadPool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.debug("{}", j); }); } } } @FunctionalInterface // 拒绝策略 interface RejectPolicy<T> { void reject(BlockingQueue<T> queue, T task); } @Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool") class ThreadPool { // 任务队列 private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue; // 线程集合 private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>(); // 核心线程数 private int coreSize; // 获取任务时的超时时间 private long timeout; private TimeUnit timeUnit; private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy; // 执行任务 public void execute(Runnable task) { // 当任务数没有超过 coreSize 时,直接交给 worker 对象执行 // 如果任务数超过 coreSize 时,加入任务队列暂存 synchronized (workers) { if(workers.size() < coreSize) { Worker worker = new Worker(task); log.debug("新增 worker{}, {}", worker, task); workers.add(worker); worker.start(); } else { // taskQueue.put(task); // 1) 死等 // 2) 带超时等待 // 3) 让调用者放弃任务执行 // 4) 让调用者抛出异常 // 5) 让调用者自己执行任务 taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy, task); } } } public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapcity, RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) { this.coreSize = coreSize; this.timeout = timeout; this.timeUnit = timeUnit; this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapcity); this.rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy; } class Worker extends Thread{ private Runnable task; public Worker(Runnable task) { this.task = task; } @Override public void run() { // 执行任务 // 1) 当 task 不为空,执行任务 // 2) 当 task 执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行 // while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) { while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, timeUnit)) != null) { try { log.debug("正在执行...{}", task); task.run(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { task = null; } } synchronized (workers) { log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this); workers.remove(this); } } } } @Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue") class BlockingQueue<T> { // 1. 任务队列 private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(); // 2. 锁 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // 3. 生产者条件变量 private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition(); // 4. 消费者条件变量 private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition(); // 5. 容量 private int capcity; public BlockingQueue(int capcity) { this.capcity = capcity; } // 带超时阻塞获取 public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) { lock.lock(); try { // 将 timeout 统一转换为 纳秒 long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); while (queue.isEmpty()) { try { // 返回值是剩余时间 if (nanos <= 0) { return null; } nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } T t = queue.removeFirst(); fullWaitSet.signal(); return t; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } // 阻塞获取 public T take() { lock.lock(); try { while (queue.isEmpty()) { try { emptyWaitSet.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } T t = queue.removeFirst(); fullWaitSet.signal(); return t; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } // 阻塞添加 public void put(T task) { lock.lock(); try { while (queue.size() == capcity) { try { log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ...", task); fullWaitSet.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task); queue.addLast(task); emptyWaitSet.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } // 带超时时间阻塞添加 public boolean offer(T task, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) { lock.lock(); try { long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeout); while (queue.size() == capcity) { try { if(nanos <= 0) { return false; } log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ...", task); nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task); queue.addLast(task); emptyWaitSet.signal(); return true; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public int size() { lock.lock(); try { return queue.size(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void tryPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy, T task) { lock.lock(); try { // 判断队列是否满 if(queue.size() == capcity) { rejectPolicy.reject(this, task); } else { // 有空闲 log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task); queue.addLast(task); emptyWaitSet.signal(); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
二、ThreadPoolExecutor
1. 线程池状态
ThreadPoolExecutor 使用 int 的 高 3 位来表示线程池状态,低 29 位表示线程数量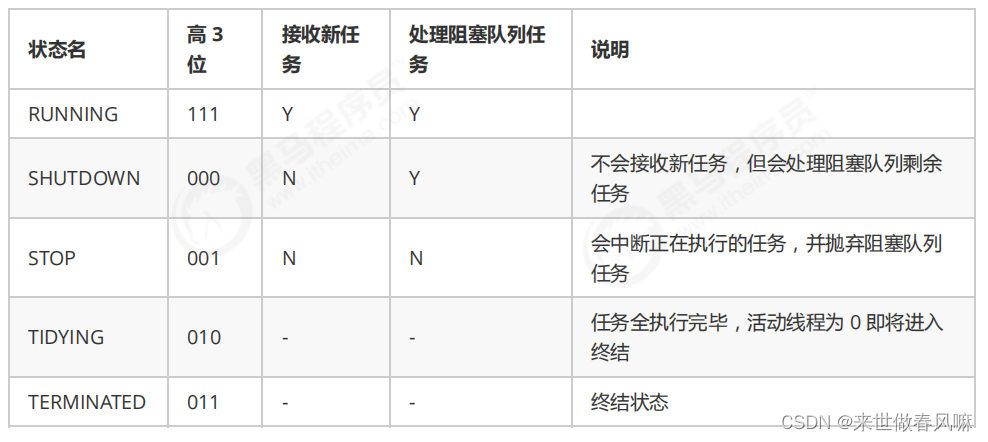
从数字上比较,TERMINATED > TIDYING > STOP > SHUTDOWN > RUNNING
这些信息存储在一个原子变量 ctl 中,目的是将线程池状态与线程个数合二为一,这样就可以用一次 cas 原子操作进行赋值
2. 构造方法(***)
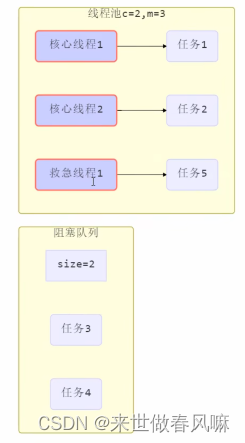
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)(1)corePoolSize 核心线程数目 ( 最多保留的线程数 )(2)maximumPoolSize 最大线程数目(3)keepAliveTime 生存时间 - 针对救急线程(4)unit 时间单位 - 针对救急线程(5)workQueue 阻塞队列(6)threadFactory 线程工厂 - 可以为线程创建时起个好名字(7)handler 拒绝策略
工作方式:
(1)线程池中刚开始没有线程,当一个任务提交给线程池后,线程池会创建一个新线程来执行任务。
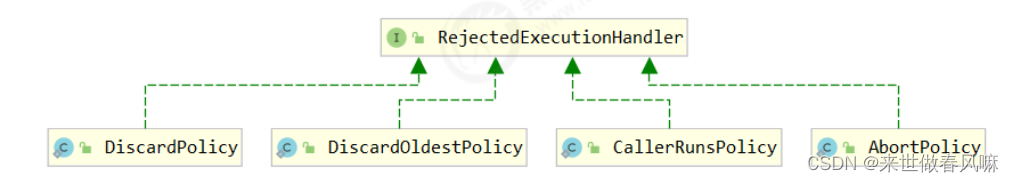
(2)当线程数达到 corePoolSize 并没有线程空闲,这时再加入任务,新加的任务会被加入 workQueue 队列排队,直到有空闲的线程。(3)如果队列选择了有界队列,那么任务超过了队列大小时,会创建 maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize 数目的线程来救急。(4)如果线程到达 maximumPoolSize 仍然有新任务这时会执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略 jdk 提供了 4 种实现,其它著名框架也提供了实现1️⃣AbortPolicy 让调用者抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,这是 默认策略2️⃣CallerRunsPolicy 让调用者运行任务3️⃣DiscardPolicy 放弃本次任务4️⃣DiscardOldestPolicy 放弃队列中最早的任务,本任务取而代之5️⃣Dubbo 的实现,在抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常之前会记录日志,并 dump 线程栈信息,方便定位问题6️⃣Netty 的实现,是创建一个新线程来执行任务7️⃣ActiveMQ 的实现,带超时等待( 60s )尝试放入队列,类似我们之前自定义的拒绝策略8️⃣PinPoint 的实现,它使用了一个拒绝策略链,会逐一尝试策略链中每种拒绝策略(5) 当高峰过去后,超过 corePoolSize 的救急线程如果一段时间没有任务做,需要结束节省资源,这个时间由 keepAliveTime 和 unit 来控制。
拒绝策略
根据这个构造方法, JDK Executors 类中提供了众多工厂方法来创建各种用途的线程池
3. newFixedThreadPool(固定大小线程池)
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }特点:(1)核心线程数 == 最大线程数(没有救急线程被创建),因此也无需超时时间(2)阻塞队列是无界的,可以放任意数量的任务
评价 适用于任务量已知,相对耗时的任务
public class TestThreadPoolExecutors { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); ExecutorService pool2 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2, new ThreadFactory() { private AtomicInteger t = new AtomicInteger(1); @Override public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { return new Thread(r, "mypool_t" + t.getAndIncrement()); } }); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("1"); }); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("1"); }); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("1"); }); } }
4. newCachedThreadPool(带缓冲功能线程池)
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }特点:(1) 核心线程数是 0, 最大线程数是 Integer.MAX_VALUE ,救急线程的空闲生存时间是 60s ,意味着1️⃣全部都是救急线程( 60s 后可以回收)2️⃣ 救急线程可以无限创建(2) 队列采用了 SynchronousQueue 实现特点是,它没有容量,没有线程来取是放不进去的(一手交钱、一手交 货)@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSynchronousQueue") public class TestSynchronousQueue { public static void main(String[] args) { SynchronousQueue<Integer> integers = new SynchronousQueue<>(); new Thread(() -> { try { log.debug("putting {} ", 1); integers.put(1); log.debug("{} putted...", 1); log.debug("putting...{} ", 2); integers.put(2); log.debug("{} putted...", 2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"t1").start(); sleep(1); new Thread(() -> { try { log.debug("taking {}", 1); integers.take(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"t2").start(); sleep(1); new Thread(() -> { try { log.debug("taking {}", 2); integers.take(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"t3").start(); } }
评价
(1)整个线程池表现为线程数会根据任务量不断增长,没有上限,当任务执行完毕,空闲 1分钟后释放线程。(2)适合任务数比较密集,但每个任务执行时间较短的情况
5. newSingleThreadExecutor(单线程线程池)
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }使用场景:希望多个任务排队执行。线程数固定为 1 ,任务数多于 1 时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这唯一的线程也不会被释放。
区别:(1) 自己创建一个单线程串行执行任务,如果任务执行失败而终止那么没有任何补救措施,而线程池还会新建一个线程,保证池的正常工作(2) Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() 线程个数始终为 1 ,不能修改1️⃣FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService 应用的是装饰器模式,只对外暴露了 ExecutorService 接口,因此不能调用 ThreadPoolExecutor 中特有的方法(3) Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1) 初始时为 1 ,以后还可以修改1️⃣ 对外暴露的是 ThreadPoolExecutor 对象,可以强转后调用 setCorePoolSize 等方法进行修改@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestExecutors") public class TestExecutors { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { test2(); } public static void test2() { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("1"); int i = 1 / 0; log.debug("111"); }); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("2"); }); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("3"); }); } }
6. 提交任务
// 执行任务 void execute(Runnable command); // 提交任务 task,用返回值 Future 获得任务执行结果 <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task); // 提交 tasks 中所有任务 <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException; // 提交 tasks 中所有任务,带超时时间 <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; // 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消 <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; // 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消,带超时时间 <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException; }
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSubmit") public class TestSubmit { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1); } private static void method3(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { String result = pool.invokeAny(Arrays.asList( () -> { log.debug("begin 1"); Thread.sleep(1000); log.debug("end 1"); return "1"; }, () -> { log.debug("begin 2"); Thread.sleep(500); log.debug("end 2"); return "2"; }, () -> { log.debug("begin 3"); Thread.sleep(2000); log.debug("end 3"); return "3"; } )); log.debug("{}", result); } private static void method2(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException { List<Future<String>> futures = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList( () -> { log.debug("begin"); Thread.sleep(1000); return "1"; }, () -> { log.debug("begin"); Thread.sleep(500); return "2"; }, () -> { log.debug("begin"); Thread.sleep(2000); return "3"; } )); futures.forEach( f -> { try { log.debug("{}", f.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } private static void method1(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { // new Callable<>() Future<String> future = pool.submit(() -> { log.debug("running"); Thread.sleep(1000); return "ok"; }); log.debug("{}", future.get()); } }
7. 关闭线程池
7.1 shutdown
/* 线程池状态变为 SHUTDOWN - 不会接收新任务 - 但已提交任务会执行完 - 此方法不会阻塞调用线程的执行 */ void shutdown();public void shutdown() { final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock; mainLock.lock(); try { checkShutdownAccess(); // 修改线程池状态 advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN); // 仅会打断空闲线程 interruptIdleWorkers(); onShutdown(); // 扩展点 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor } finally { mainLock.unlock(); } // 尝试终结(没有运行的线程可以立刻终结,如果还有运行的线程也不会等) tryTerminate(); }
7.2 shutdownNow
/* 线程池状态变为 STOP - 不会接收新任务 - 会将队列中的任务返回 - 并用 interrupt 的方式中断正在执行的任务 */ List<Runnable> shutdownNow();public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {List<Runnable> tasks; final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock; mainLock.lock(); try { checkShutdownAccess(); // 修改线程池状态 advanceRunState(STOP); // 打断所有线程 interruptWorkers(); // 获取队列中剩余任务 tasks = drainQueue(); } finally { mainLock.unlock(); } // 尝试终结 tryTerminate(); return tasks; }
7.3 其他方法
// 不在 RUNNING 状态的线程池,此方法就返回 true boolean isShutdown(); // 线程池状态是否是 TERMINATED boolean isTerminated(); // 调用 shutdown 后,由于调用线程并不会等待所有任务运行结束,因此如果它想在线程池 TERMINATED 后做些事情,可以利用此方法等待 boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
7.4 演示
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestShutDown") public class TestShutDown { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); Future<Integer> result1 = pool.submit(() -> { log.debug("task 1 running..."); Thread.sleep(1000); log.debug("task 1 finish..."); return 1; }); Future<Integer> result2 = pool.submit(() -> { log.debug("task 2 running..."); Thread.sleep(1000); log.debug("task 2 finish..."); return 2; }); Future<Integer> result3 = pool.submit(() -> { log.debug("task 3 running..."); Thread.sleep(1000); log.debug("task 3 finish..."); return 3; }); log.debug("shutdown"); // pool.shutdown(); // pool.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); List<Runnable> runnables = pool.shutdownNow(); log.debug("other.... {}" , runnables); } }



![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django社区人员信息管理系统设计与实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f4a0f47d67c4468d98a534397809a6b9.png)


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django甜品购物网站](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fdfc756dec994bd7b6bf7323bb8d70ca.png)