官网:https://grpc-ecosystem.github.io/grpc-gateway/
github:https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway
grpc gateway的原理官网有介绍。总结一下就是:
gRPC-Gateway帮助你同时以gRPC和RESTful风格提供你的API。grpc-gateway旨在为您的gRPC服务提供HTTP+JSON接口。 做法就是:在服务中附加HTTP语义的少量配置就是使用该库生成反向代理所需的全部内容。客户端的restful Api请求通过反向代理自动转换成grpc可识别的请求去调用grpc服务端。
具体实现步骤:
1、新增echo.proto文件,定义好http接口:
syntax = "proto3";
package pb;
option go_package = "go_grpc/grpc_gateway/proto/hello";
// 导入google/api/annotations.proto
import "google/api/annotations.proto"; //🌙这里在goland会提示:proto/hello/echo.proto: Import "google/api/annotations.proto" was not found or had errors.神奇的是:当我换vscode编辑器就没有这个问题。
service EchoService {
rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {
// // 这里添加了google.api.http注释
option (google.api.http) = {
post: "/v1/echo"
body: "*"
};
}
}
message StringMessage {
string value = 1;
}
2、生成对应的pb文件:
2.1 普通方式(推荐第二种方式:Buf工具)
执行目录是在项目根目录下,即go_grpc目录下:
protoc -I=proto --grpc-gateway_out=./proto --grpc-gateway_opt=paths=source_relative --go_out=proto --go_opt=paths=source_relative --go-grpc_out=proto --go-grpc_opt=paths=source_relative .\proto\hello\echo.proto
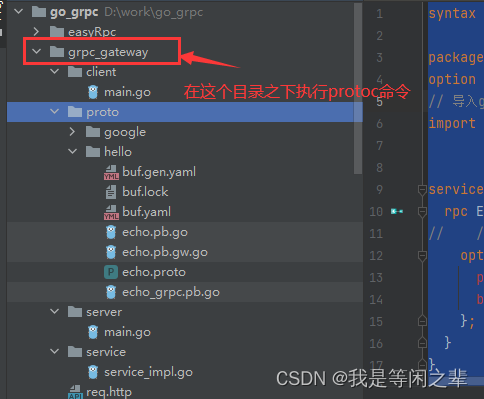
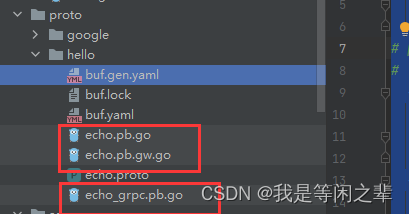
执行完毕后,就在如上图所示,在proto/hello目录下生成三个文件:
echo.pb.go
echo_grpc.pb.go
echo.pb.gw.go
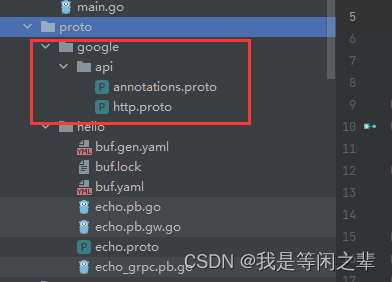
如果会提示:

需要在本地目录引入下面两个文件(目录保持一致),点击下面链接进行下载:
https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis/tree/master/google/api
2.2 使用buf工具生成pb文件
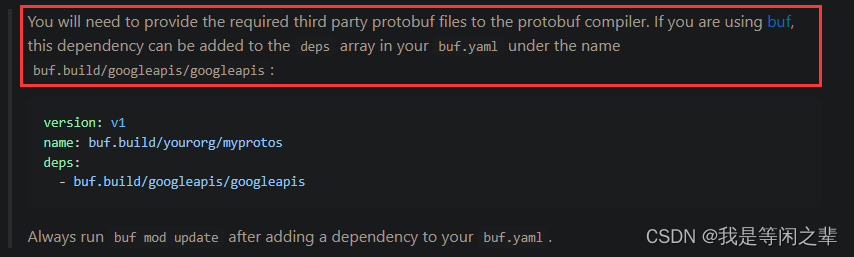
grpc-gateway项目的readme文件有推荐一款工具:Buf(官网链接),这个工具使我们不需要手动下载google/api/annotations.proto这些依赖包到我们的项目中。而且对于生成pb文件也会更加简单方便。
安装Buf:
https://github.com/bufbuild/buf/releases
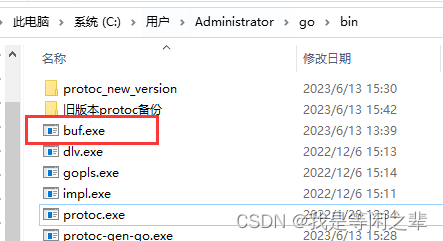
点击选择window版本下载,下载后的文件名是buf-Windows-x86_64.exe。将其重命名为buf.exe。然后放到$GOPATH/bin目录下,其实就是和protoc.exe同个目录。
Buf的用法:
1. 先在proto/hello目录下(即放proto文件的目录下),初始化buf:
go mod init
执行该命令后会生成buf.yaml。
然后在buf.yaml引入第三方依赖:
version: v1
breaking:
use:
- FILE
lint:
use:
- DEFAULT
name: buf.build/mygrpc/gateway
deps:
- buf.build/googleapis/googleapis
- buf.build/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway
其中,name参数第一个值buf.build是固定的,后面两个单词可以自定义。
加入依赖后,记得执行 buf mod update -v 更新一下。(每次对buf.yaml修改都要执行update)
2. 定义buf.gen.yaml文件
version: v1
plugins:
- plugin: go
out: ./
opt:
- paths=source_relative
# protoc_path可以指定不同版本的protoc工具,但是我在window测试无效。
# protoc_path: /c/Users/Administrator/go/bin/protoc_new_version/protoc
- plugin: go-grpc
out: ./
opt:
- paths=source_relative
- plugin: grpc-gateway
out: ./
opt:
- paths=source_relative
# protoc_path: /c/Users/Administrator/go/bin/protoc_new_version
- 执行下面命令,生成pb文件
buf generate -v --debug
执行成功后,会在proto文件的目录下生成三个pb文件:
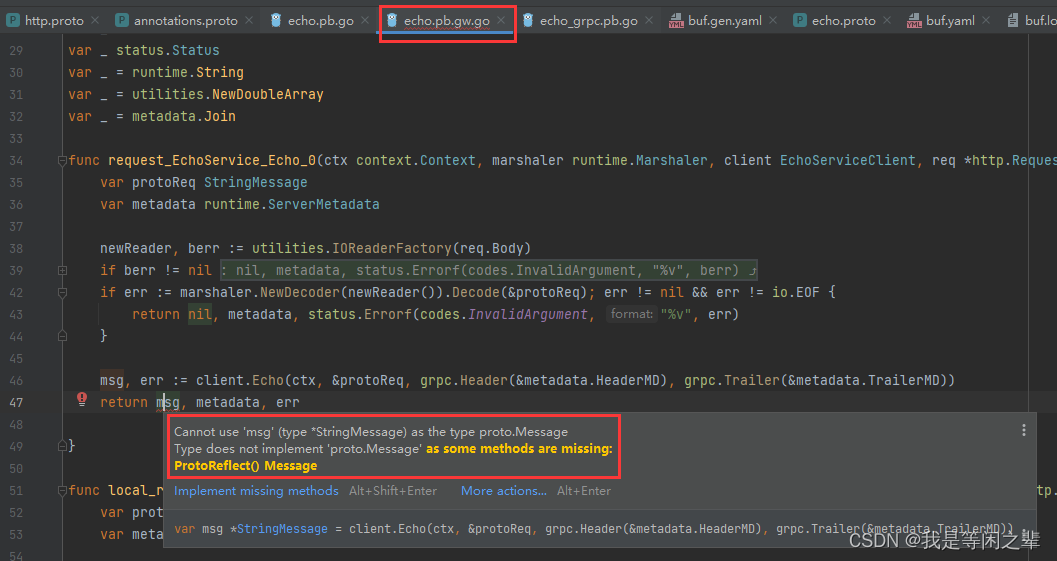
遇到的bug:
因为我的电脑的protoc.exe和protoc-gen-go.exe用的是老版本,导致我生成的echo.pb.gw.go文件报错(这里应该是echo.pb.go文件有误影响到了gw文件):
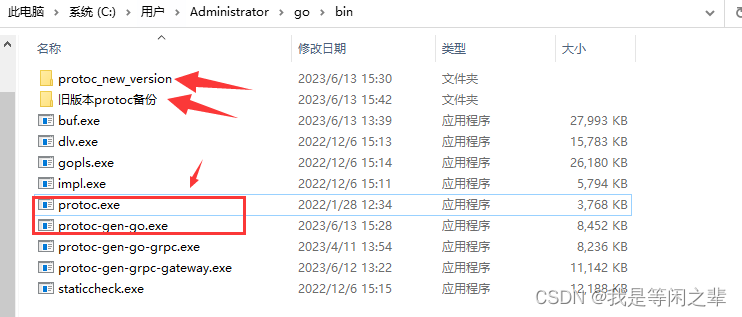
所以去gopath/bin目录下,把旧版本先备份后移除,然后下载比较新的版本。再执行puf generate就能生成正确无误的文件。
接下来就是测试http post请求是否成功。
这里我们需要启动rpc服务,再启动http服务。
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
pb "go_grpc/grpc_gateway/proto/hello"
"github.com/golang/glog"
"github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/v2/runtime"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials/insecure"
)
const port = ":4399"
type EchoService struct {
*pb.UnimplementedEchoServiceServer
}
func NewEchoService() *EchoService {
return &EchoService{}
}
func (c *EchoService) Echo(ctx context.Context, msg *pb.StringMessage) (*pb.StringMessage, error) {
reply := fmt.Sprintf("我收到你的信息了,你发送的信息是:%s", msg)
return &pb.StringMessage{Value: reply}, nil
}
//启动 http server
func runHttpService() error {
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
// Register gRPC server endpoint
// Note: Make sure the gRPC server is running properly and accessible
mux := runtime.NewServeMux()
opts := []grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())}
err := pb.RegisterEchoServiceHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, mux, "localhost:4399", opts)
if err != nil {
return err
}
println("http service start!")
// Start HTTP server (and proxy calls to gRPC server endpoint)
return http.ListenAndServe(":8081", mux)
}
//启动 rpc service
func runRpcService() error {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", port)
if err != nil {
return err
}
srv := NewEchoService()
rpcServer := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterEchoServiceServer(rpcServer, srv)
log.Println("start gRPC listen on port " + port)
return rpcServer.Serve(listener)
}
func main() {
//flag.Parse()
defer glog.Flush()
//得用一个协程启动rpc服务,不能先启动rpc服务,再启动http服务。不然启动rpc服务后会阻塞住
go func() {
if err := runRpcService(); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("runRpcService err:%#v\n", err)
glog.Fatal(err)
}
}()
println("cowboy very busy")
//再启动http service
if err := runHttpService(); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("runHttpService err:%#v\n", err)
glog.Fatal(err)
}
}
注意这里,rpc服务用的是4399端口,http服务用的是8081端口。
接下来启动service/main.go。然后用goland快速建立一个post请求:
File => New => HTTP Request
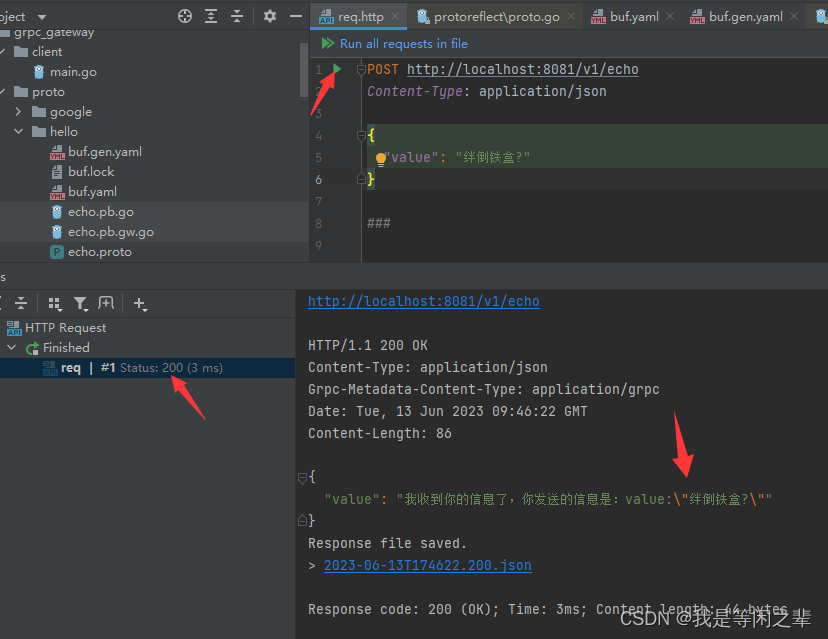
我们也用rpc客户端进行测试调用:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
pb "go_grpc/grpc_gateway/proto/hello"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials/insecure"
"log"
)
const (
address = "localhost:4399"
)
func main() {
conn, err := grpc.Dial(address, grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
if err != nil {
log.Println("did not connect.", err)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
client := pb.NewEchoServiceClient(conn)
ctx := context.Background()
req := &pb.StringMessage{Value: "Crazy Thursday"}
reply, err := client.Echo(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
log.Println("fail:", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("reply:%#v\n", reply)
}
同样,请求也是成功:

说明grpc网关实现成功了!!!