文章目录
- 一【题目类别】
- 二【题目难度】
- 三【题目编号】
- 四【题目描述】
- 五【题目示例】
- 六【解题思路】
- 七【题目提示】
- 八【题目进阶】
- 九【时间频度】
- 十【代码实现】
- 十一【提交结果】
一【题目类别】
- 链表
二【题目难度】
- 简单
三【题目编号】
- 141.环形链表
四【题目描述】
- 给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
- 如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
- 如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
五【题目示例】
-
示例 1:
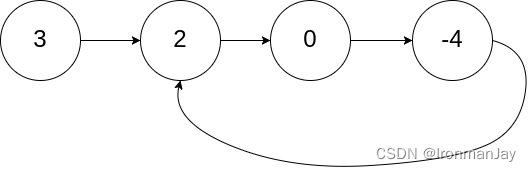
- 输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
- 输出:true
- 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
-
示例 2:
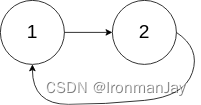
- 输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
- 输出:true
- 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
-
示例 3:
- 输入:head = [1], pos = -1
- 输出:false
- 解释:链表中没有环。
六【解题思路】
- 经典的快慢指针的问题
- 慢指针走一步,快指针走两步
- 如果由环,那么快指针和慢指针都会在这个环内“跑”,但是快指针走的快,所以说如果有环,快慢指针一定会相遇
- 如果快慢指针相遇说明有环,否则说明没环
- 如果有环返回true,否则返回false即可
七【题目提示】
- 链 表 中 节 点 的 数 目 范 围 是 [ 0 , 1 0 4 ] 链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 10^4] 链表中节点的数目范围是[0,104]
- − 1 0 5 < = N o d e . v a l < = 1 0 5 -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5 −105<=Node.val<=105
- p o s 为 − 1 或 者 链 表 中 的 一 个 有 效 索 引 。 pos 为 -1 或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。 pos为−1或者链表中的一个有效索引。
八【题目进阶】
- 你能用 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
九【时间频度】
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n为链表的长度
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
十【代码实现】
- Java语言版
package LinkedList;
/**
* @Author: IronmanJay
* @Description: 141.环形链表
* @CreateTime: 2022-12-05 15:39
*/
public class p141_LinkedListCycle {
int val;
p141_LinkedListCycle next;
public p141_LinkedListCycle(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public p141_LinkedListCycle(int val, p141_LinkedListCycle next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
p141_LinkedListCycle node1 = new p141_LinkedListCycle(3);
p141_LinkedListCycle node2 = new p141_LinkedListCycle(2);
p141_LinkedListCycle node3 = new p141_LinkedListCycle(0);
p141_LinkedListCycle node4 = new p141_LinkedListCycle(-4);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node2;
boolean res = hasCycle(node1);
System.out.println("res = " + res);
}
public static boolean hasCycle(p141_LinkedListCycle head) {
p141_LinkedListCycle slow = head;
p141_LinkedListCycle fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
- C语言版
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
};
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*主函数省略*/
十一【提交结果】
-
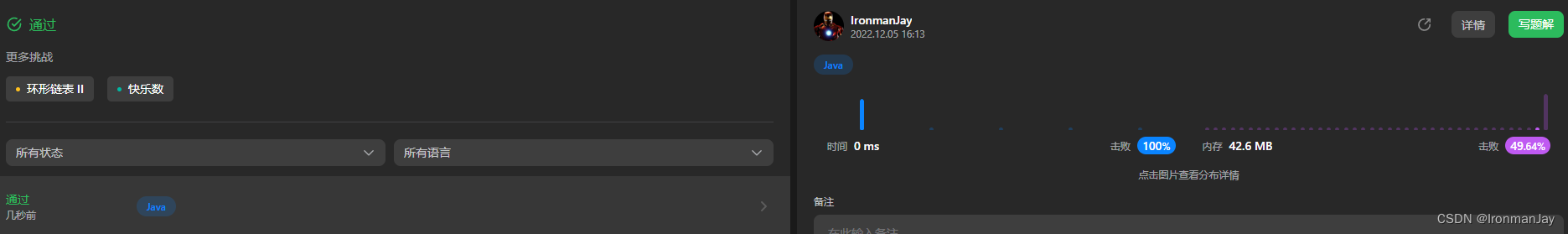
Java语言版
-
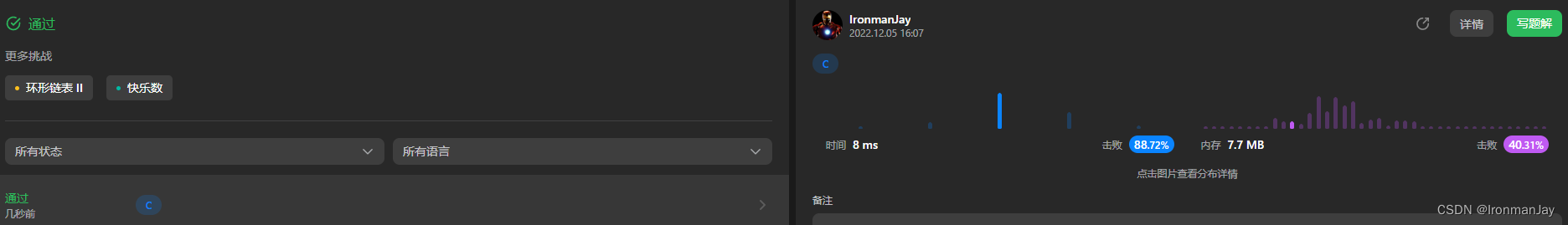
C语言版








![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计论文管理系统(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/250c6e6dd5c04fc5be22d23c01824097.png)