文章目录
- 141. 环形链表
- 142. 环形链表 II
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 160. 相交链表
141. 环形链表
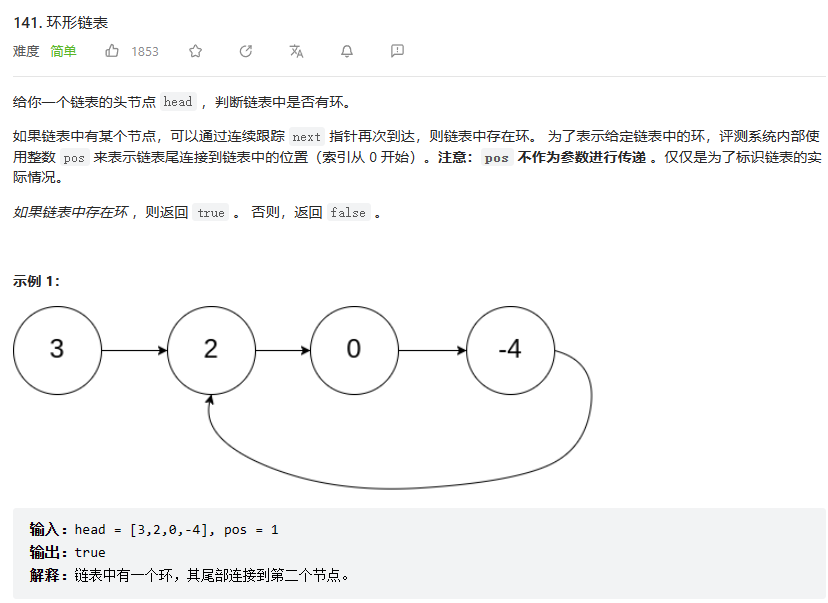
设置两个速度不一样的链表,如果其中他们两个在经过一定的步数(进入环之后,在
n
×
∣
环的大小
∣
n \times |环的大小|
n×∣环的大小∣ 步后会重合)之后会重合,则说明有环。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
head_i = head
head_j = head
while(head_i is not None and head_j is not None):
head_i = head_i.next
head_j = head_j.next
if head_j is None:
return False
else:
head_j = head_j.next
total += 1
if head_i == head_j:
return True
return False
142. 环形链表 II
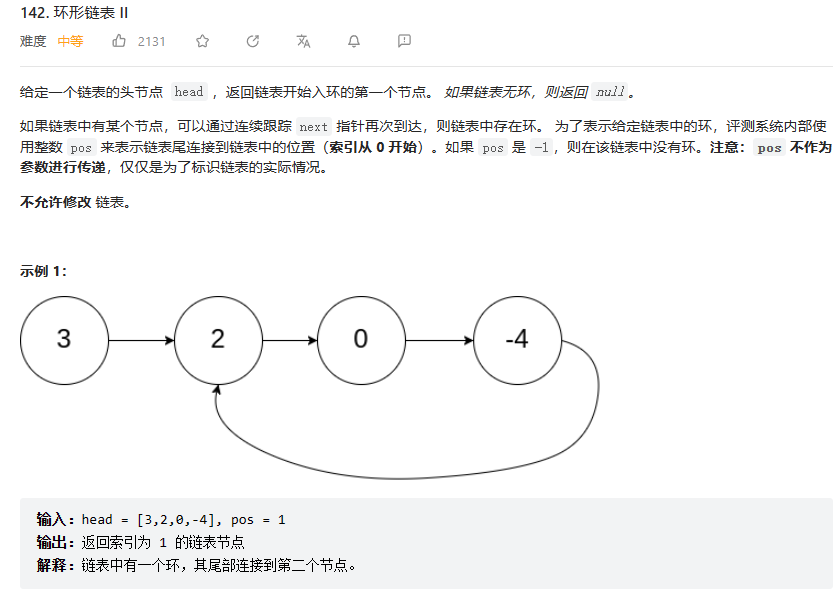
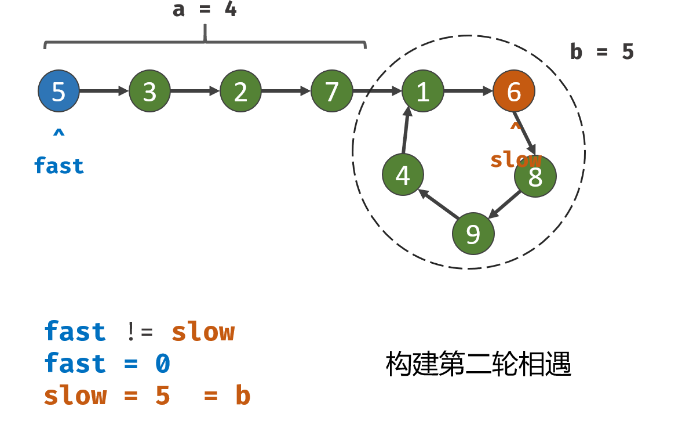
这里与上一题不同的地方在于需要求得环的入口。
设慢指针的步数为s,则第一次相遇时,快指针的步数为2s=s+nb,其中b为环的长度。化简可以得到s=nb。
在二者相遇之后,我们将快指针回退到head的位置。假设快指针又经过a步到达环的入口,此时慢指针步数为a+s=a+nb,一定也会到达环口。因此只需要再求出这时二者相遇的位置即可。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
if not head:
return None
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
head_slow = head
head_fast = head
while(True):
if not head_fast.next or not head_fast.next.next:
return None
head_slow, head_fast = head_slow.next, head_fast.next.next
if head_slow == head_fast:
# 第一次相遇
break
head_fast = head
while(head_fast != head_slow):
head_fast, head_slow = head_fast.next, head_slow.next
return head_fast
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点

这个让快指针先走n步就可以了。需要注意的是可以设置一个dummy head以处理只有一个node的情况。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(next=head)
# 设置一个dummy head可以帮助处理只有一个节点的情况
fast, slow = dummy, dummy
for i in range(n):
fast = fast.next
while(fast.next != None):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next
160. 相交链表

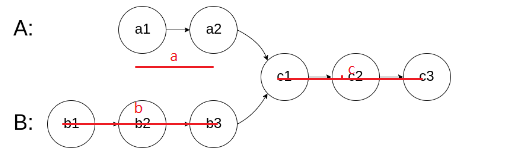
这一题的主要思路是两个head均设置一个指针,当某一个指针到达终点之后,去到对方的head重新开始走,走到交叉点一定会相遇,因为这时两个指针的路径长度都是a+b+c。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]:
pointerA = headA
pointerB = headB
# 当某一个指针到达终点之后,去到对方的head重新开始走,走到交叉点一定会相遇
# 因为这时两个指针的路径长度都是a+b+c
while(pointerA != pointerB):
pointerA = pointerA.next if pointerA else headB
pointerB = pointerB.next if pointerB else headA
if pointerA == pointerB and pointerB is not None:
return pointerA
return None