文章目录
- 🔺一、video_device分析
- (1-1)struct video_device结构
- (1-2)struct v4l2_ioctl_ops结构
- (1-3)v4l2_file_operations结构
- 🔺二、注册video设备
- 🔺三、卸载清除video设备
- 🔺四、调试video设备
👀👉本文基于Linux内核版本
4.1.15分析V4L2框架下的video_device。
🔺一、video_device分析
如果视频驱动加载成功,则会向/dev目录下导出设备节点。那么在用户空间/dev目录中的实际设备节点是使用video_device结构(v4l2-dev.h)创建的,结构组成框图如下图所示:
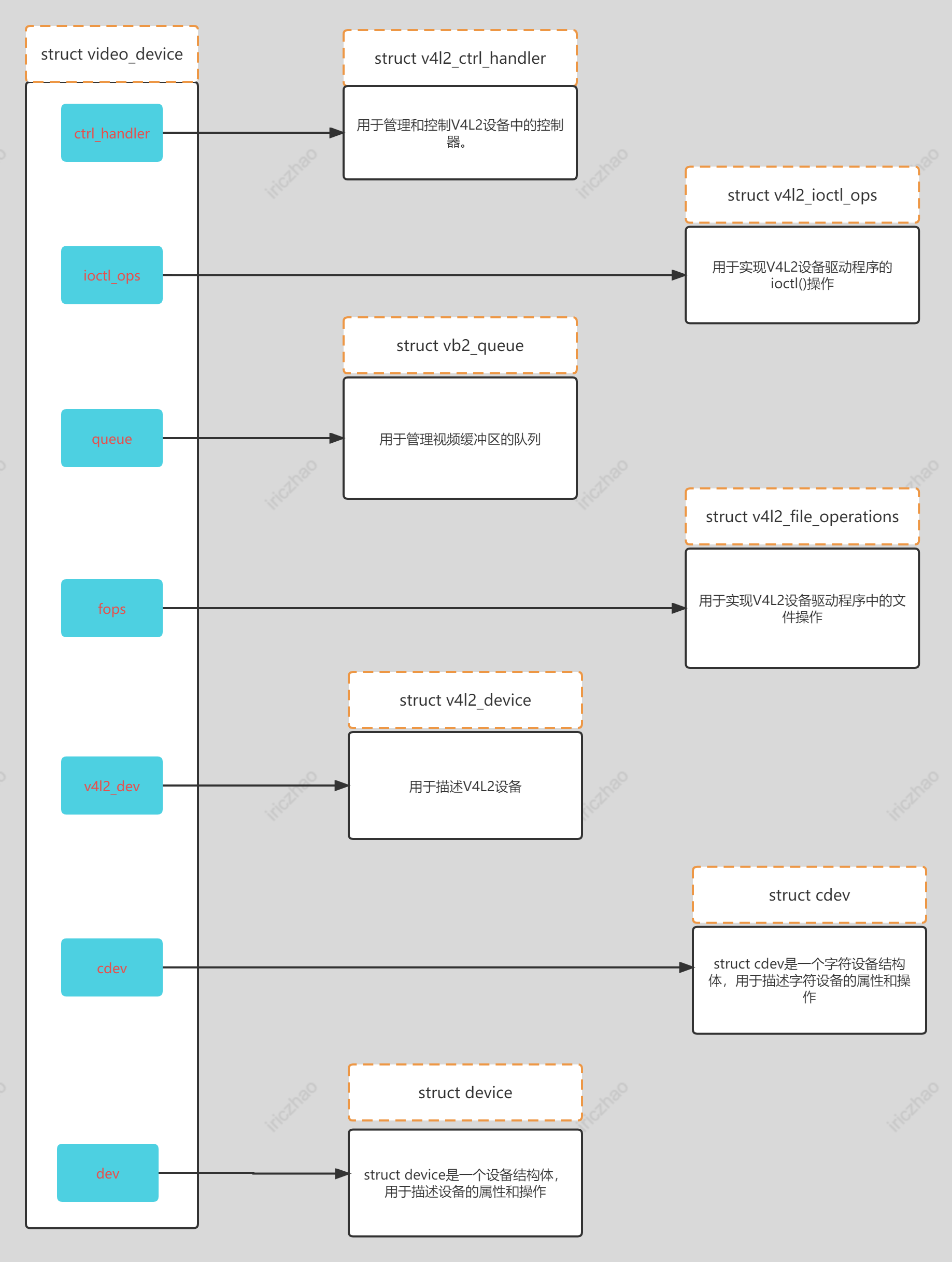
(1-1)struct video_device结构
struct video_device定义如下:
struct video_device {
#if defined(CONFIG_MEDIA_CONTROLLER);
struct media_entity entity; //表示media实例图形对象
struct media_intf_devnode *intf_devnode; //指向media_intf_devnode结构的指针,media_intf_devnode是一个通过设备节点的media接口
struct media_pipeline pipe; //表示media_pipeline,media_pipeline用于描述media管道相关的信息。
#endif;
const struct v4l2_file_operations *fops; //指向视频设备的v4l2_file_operations结构体的指针,v4l2_file_operations用于描述V4L2设备使用的fs操作。
u32 device_caps; //v4l2_capabilities中使用的设备功能。
struct device dev; //用于描述视频设备的device。
struct cdev *cdev; //字符设备
struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev; //指向v4l2_device父结构的指针,v4l2_device用于描述V4L2设备驱动程序的主要数据结构。
struct device *dev_parent; //指向device父结构的指针。
struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler; //描述与此设备节点关联的control处理程序,该元素可能为NULL。
struct vb2_queue *queue; // 描述与此设备节点关联的vb2_queue结构,该元素可能为NULL。
struct v4l2_prio_state *prio; //指向带有设备优先级状态的v4l2_prio_state结构体的指针,如果为NULL,则使用v4l2_dev->prio。
char name[32]; //video设备的名称。
enum vfl_devnode_type vfl_type; //V4L设备类型,由enum vfl_devnode_type定义。
enum vfl_devnode_direction vfl_dir; //表示V4L接收机,发射机或m2m。
int minor; //设备次要节点,如果设备注册失败,该参数设置为-1。
u16 num; //视频设备节点号
unsigned long flags; //视频设备标志,使用bitops来设置/clear/test标志,包含一组enum v4l2_video_device_flags。
int index; //该属性用于区分同一物理设备上的多个索引。
spinlock_t fh_lock; //自旋锁,用于锁定所有的v4l2_fh。
struct list_head fh_list; //struct v4l2_fh链表。
int dev_debug; //内部设备调试标志,该标志不供驱动程序使用。
v4l2_std_id tvnorms; //支持的电视规格。
void (*release)(struct video_device *vdev); //视频设备release()回调函数。
const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ioctl_ops; //指向具有ioctl回调函数的struct v4l2_ioctl_ops的指针。
unsigned long valid_ioctls[BITS_TO_LONGS(BASE_VIDIOC_PRIVATE)]; //具有此设备有效ioctls的位图。
struct mutex *lock; //指向struct mutex序列化互斥锁的指针。
};
video_device结构可以动态分配,也可以将其嵌入到更大的结构中。使用video_device_alloc()动态分配video_device结构,例如下列代码:
struct video_device *vdev = video_device_alloc();
if (vdev == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
//此处必须设置release()回调函数,当使用该视频设备的最后一个用户退出时会调用这个callback。
vdev->release = video_device_release;
默认video_device_release()回调函数目前只调用kfree来释放分配的内存。
(1-2)struct v4l2_ioctl_ops结构
在struct video_device中包含一个struct v4l2_ioctl_ops,用于描述每个V4L2 ioctl(IO控制)的操作,该操作集合中元素较多,在实现V4L2驱动程序的时候,需要填充该结构体下的callback,v4l2_ioctl_ops用于实现与视频设备相关的ioctl操作。ioctl操作是Linux内核中用于设备控制的系统调用之一,它允许用户空间程序与设备驱动程序进行交互,以实现对设备的控制、配置和查询等操作,在v4l2中,ioctl操作用于控制视频捕获设备、视频输出设备和视频处理设备等。v4l2_ioctl_ops结构体中包含了一组函数指针,这些函数指针定义了各种ioctl操作的实现,这些函数指针定义如下:
struct v4l2_ioctl_ops {
int (*vidioc_querycap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_capability *cap);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_sdr_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_sdr_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_meta_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_meta_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_sliced_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_sliced_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_sdr_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_sdr_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_meta_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_meta_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_out_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_sliced_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_sliced_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_out_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_sdr_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_sdr_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_meta_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_meta_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_out_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_sliced_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_sliced_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_cap_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_out_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_sdr_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_sdr_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_meta_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_meta_out)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_reqbufs)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_requestbuffers *b);
int (*vidioc_querybuf)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_buffer *b);
int (*vidioc_qbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_buffer *b);
int (*vidioc_expbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_exportbuffer *e);
int (*vidioc_dqbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_buffer *b);
int (*vidioc_create_bufs)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_create_buffers *b);
int (*vidioc_prepare_buf)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_buffer *b);
int (*vidioc_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int i);
int (*vidioc_g_fbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_framebuffer *a);
int (*vidioc_s_fbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_framebuffer *a);
int (*vidioc_streamon)(struct file *file, void *fh, enum v4l2_buf_type i);
int (*vidioc_streamoff)(struct file *file, void *fh, enum v4l2_buf_type i);
int (*vidioc_g_std)(struct file *file, void *fh, v4l2_std_id *norm);
int (*vidioc_s_std)(struct file *file, void *fh, v4l2_std_id norm);
int (*vidioc_querystd)(struct file *file, void *fh, v4l2_std_id *a);
int (*vidioc_enum_input)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_input *inp);
int (*vidioc_g_input)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int *i);
int (*vidioc_s_input)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int i);
int (*vidioc_enum_output)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_output *a);
int (*vidioc_g_output)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int *i);
int (*vidioc_s_output)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int i);
int (*vidioc_queryctrl)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_queryctrl *a);
int (*vidioc_query_ext_ctrl)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_query_ext_ctrl *a);
int (*vidioc_g_ctrl)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_control *a);
int (*vidioc_s_ctrl)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_control *a);
int (*vidioc_g_ext_ctrls)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_ext_controls *a);
int (*vidioc_s_ext_ctrls)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_ext_controls *a);
int (*vidioc_try_ext_ctrls)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_ext_controls *a);
int (*vidioc_querymenu)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_querymenu *a);
int (*vidioc_enumaudio)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_audio *a);
int (*vidioc_g_audio)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_audio *a);
int (*vidioc_s_audio)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_audio *a);
int (*vidioc_enumaudout)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_audioout *a);
int (*vidioc_g_audout)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_audioout *a);
int (*vidioc_s_audout)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_audioout *a);
int (*vidioc_g_modulator)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_modulator *a);
int (*vidioc_s_modulator)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_modulator *a);
int (*vidioc_g_pixelaspect)(struct file *file, void *fh, int buf_type, struct v4l2_fract *aspect);
int (*vidioc_g_selection)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_selection *s);
int (*vidioc_s_selection)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_selection *s);
int (*vidioc_g_jpegcomp)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_jpegcompression *a);
int (*vidioc_s_jpegcomp)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_jpegcompression *a);
int (*vidioc_g_enc_index)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_enc_idx *a);
int (*vidioc_encoder_cmd)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_encoder_cmd *a);
int (*vidioc_try_encoder_cmd)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_encoder_cmd *a);
int (*vidioc_decoder_cmd)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_decoder_cmd *a);
int (*vidioc_try_decoder_cmd)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_decoder_cmd *a);
int (*vidioc_g_parm)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_streamparm *a);
int (*vidioc_s_parm)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_streamparm *a);
int (*vidioc_g_tuner)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_tuner *a);
int (*vidioc_s_tuner)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_tuner *a);
int (*vidioc_g_frequency)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_frequency *a);
int (*vidioc_s_frequency)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_frequency *a);
int (*vidioc_enum_freq_bands)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_frequency_band *band);
int (*vidioc_g_sliced_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_sliced_vbi_cap *a);
int (*vidioc_log_status)(struct file *file, void *fh);
int (*vidioc_s_hw_freq_seek)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_hw_freq_seek *a);
#ifdef CONFIG_VIDEO_ADV_DEBUG;
int (*vidioc_g_register)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dbg_register *reg);
int (*vidioc_s_register)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_dbg_register *reg);
int (*vidioc_g_chip_info)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dbg_chip_info *chip);
#endif;
int (*vidioc_enum_framesizes)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_frmsizeenum *fsize);
int (*vidioc_enum_frameintervals)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_frmivalenum *fival);
int (*vidioc_s_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);
int (*vidioc_g_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);
int (*vidioc_query_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);
int (*vidioc_enum_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_enum_dv_timings *timings);
int (*vidioc_dv_timings_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dv_timings_cap *cap);
int (*vidioc_g_edid)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_edid *edid);
int (*vidioc_s_edid)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_edid *edid);
int (*vidioc_subscribe_event)(struct v4l2_fh *fh, const struct v4l2_event_subscription *sub);
int (*vidioc_unsubscribe_event)(struct v4l2_fh *fh, const struct v4l2_event_subscription *sub);
long (*vidioc_default)(struct file *file, void *fh, bool valid_prio, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
};
struct v4l2_ioctl_ops结构中元素真的太多,从内核源码目录下的各驱动程序的实现上分析可知,各种基于V4L2的驱动程序在实现中,几乎都会创建v4l2_ioctl_ops结构实列,然后逐一选择性的实现其中的callback,最后将其关联到struct video_device实列的.ioctl_ops元素。
(1-3)v4l2_file_operations结构
在V4l2框架中提供了一个v4l2_file_operations结构,用于表示一个V4L2设备的文件系统操作,struct v4l2_file_operations定义如下:
struct v4l2_file_operations {
struct module *owner; //指向struct module的指针。
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); //实现read()系统调用所需的操作。
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); //实现write()系统调用所需的操作。
__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); //实现poll()系统调用所需的操作。
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); //实现ioctl()系统调用所需的操作。
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT;
long (*compat_ioctl32) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); //在内核使用64位指令,而用户空间使用32位指令的特殊情况下,实现ioctl()系统调用所需的操作。
#endif;
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area) (struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);//在%!CONFIG_MMU下由mmap()系统调用调用。
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); //实现mmap()系统调用所需的操作。
int (*open) (struct file *); //实现open()系统调用所需的操作。
int (*release) (struct file *); //实现release()系统调用所需的操作。
};
在设计基于V4L2的video驱动程序时,需要创建
v4l2_file_operations结构实例,并实现其中的callback。然后将其设置到struct video_device实列的.fops元素。
🔺二、注册video设备
在创建video_device结构后,需使用video_register_device()向linux内核注册视频设备,在该函数中将创建字符设备。例如下列代码:
err = video_register_device(vdev, VFL_TYPE_VIDEO, -1);
if (err) {
video_device_release(vdev); /* or kfree(my_vdev); */
return err;
}
如果v4l2_device父设备有一个非NULL的mdev字段,视频设备实体将会自动注册到媒体设备。
使用video_register_device()函数注册哪个设备取决于type参数。可选类型参数如下表所示:
| vfl_devnode_type | Device名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| VFL_TYPE_VIDEO | /dev/videoX | 用于视频输入/输出设备 |
| VFL_TYPE_VBI | /dev/vbiX | 用于垂直空白数据 |
| VFL_TYPE_RADIO | /dev/radioX | 用于音频信号 |
| VFL_TYPE_SUBDEV | /dev/v4l-subdevX | 用于V4L2子设备 |
| VFL_TYPE_SDR | /dev/swradioX | 用于软件定义的音频信号 |
| VFL_TYPE_TOUCH | /dev/v4l-touchX | 用于触摸传感器 |
video_register_device()函数原型如下:
static inline int __must_check video_register_device(struct video_device *vdev,
int type, int nr)
{
return __video_register_device(vdev, type, nr, 1, vdev->fops->owner);
}
在上述函数中,本质上会调用__video_register_device()函数向注册一个视频设备,该函数间接调用device_register()实现核心注册功能,且在该函数中将执行以下几个连续操作:
(1)检查设备v类型。
(2)寻找一个空闲的次要设备,设备节点号和设备索引。
(3)初始化字符设备。
(4)向sysfs注册这个设备。
(5)注册一个media_controller。
(6)激活minor,以便使用这个char设备。
🔺三、卸载清除video设备
当视频设备节点必须被删除时,无论是在卸载驱动程序过程中还是因为USB设备断开了连接,都应该调用video_unregister_device(vdev);注销已注册的视频设备。该函数将从sysfs中移除该设备节点,从而移除在/dev目录下的设备节点。
当使用该视频设备节点的最后一个用户退出的时候,系统将调用vdev->release()回调函数,在该回调函数中执行最后的清理操作。
如果视频设备已经初始化,还需要调用media_entity_cleanup (&vdev->entity);清理与视频设备相关的media实例,该操作可以在release回调中完成。
🔺四、调试video设备
在/sys/class/video4linux/\<devX>/目录中,为每个video、vbi、radio或swradio设备创建了dev_debug属性(如果存在这些设备),可以通过该属性来启用文件操作的日志记录。该参数是一个位掩码,可设置的参数如下表所示:
| 掩码 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 0x01 | 记录ioctl名称和错误代码。vidoc_(D)QBUF ioctl仅在位0x08也被设置时才被记录。 |
| 0x02 | 记录ioctl名称参数和错误代码。vidoc_ (D)QBUF ioctl仅在位0x08也被设置时才被记录。 |
| 0x04 | 记录文件open、release、read、write、mmap和get_unmapped_area的操作,如果也设置了位0x08,则只记录读写操作。 |
| 0x08 | 记录文件的读写操作以及VIDIOC_QBUF和VIDIOC_DQBUF ioctls。 |
| 0x10 | 记录poll文件操作。 |
| 0x20 | 记录control操作中的错误和消息。 |
在v4l2框架初始化过程中,会在sysfs中创建video4linux目录,这个过程由videodev_init()完成:
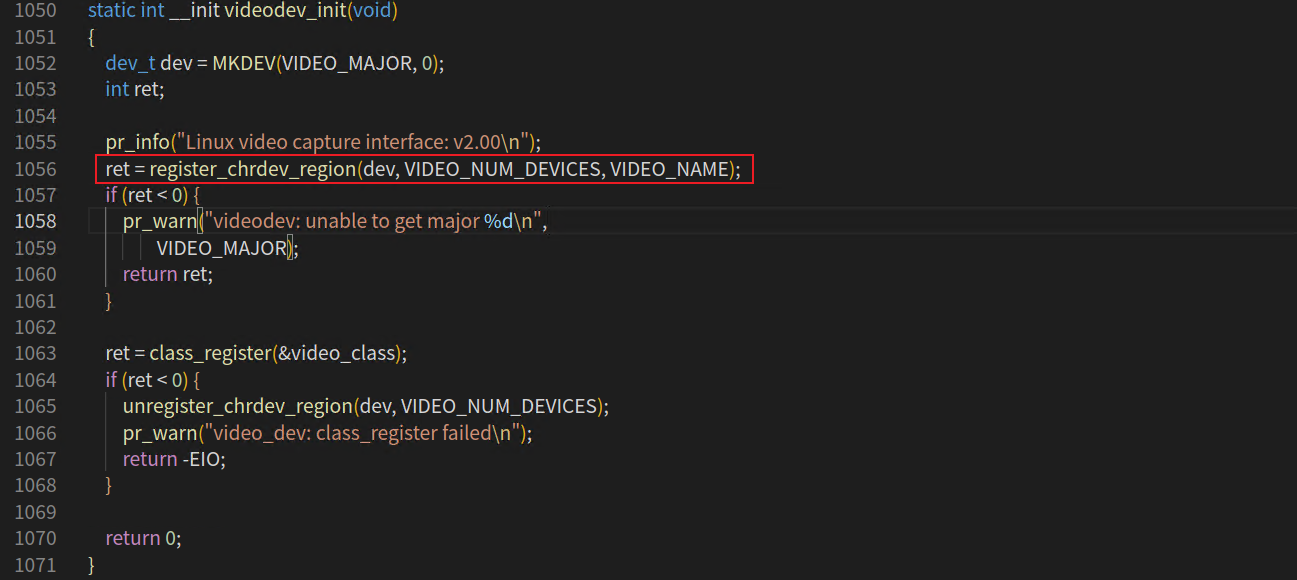
后续关于video设备的重要参数则会自动导入到sysfs文件系统的
video4linux目录下,因此可以通过sysfs下的video4linux下的目录和文件获知和调试video设备。





![[创业之路-73] :如何判断一个公司或团队是熵增:一盘散沙、乌合之众,还是,熵减:凝聚力强、上下一心?](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2f6b4562c3ef468e8e327a32df5ef5af.png)