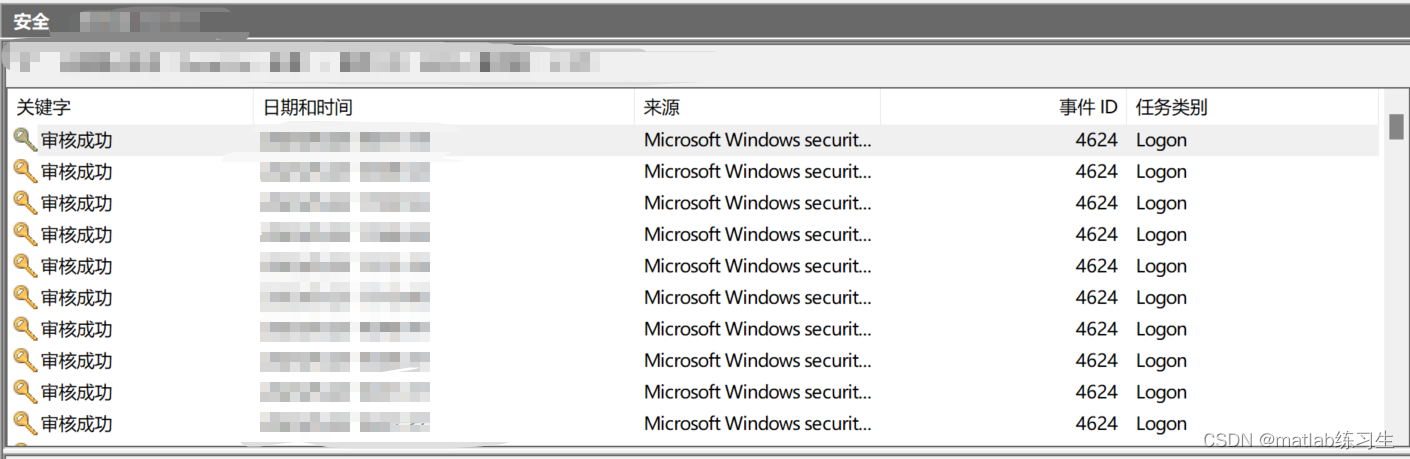
粘包产生
public class HelloWordServer {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWordServer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap()
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.group(boss, worker)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("connected{}", ctx.channel());
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("disconnected{}", ctx.channel());
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080);
channelFuture.sync();
log.debug("{} bing",channelFuture.channel());
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("server error",e);
}
}
}public class HelloWordClient {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWordServer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup work = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.group(work)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.debug("connetred");
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("sending");
Random r = new Random();
char c = 'a';
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4,5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15});
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("client error...");
}finally {
work.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
如上服务器端的某次输出,可以看到一次就接收了 160 个字节,而非分 10 次接收
半包产生
客户端代码希望发送 1 个消息,这个消息是 160 字节,代码改为
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15});
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);为现象明显,服务端修改一下接收缓冲区,其它代码不变
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10);服务器端的某次输出,可以看到接收的消息被分为两节,第一次 20 字节,第二次 140 字节

注意
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10) 影响的底层接收缓冲区(即滑动窗口)大小,仅决定了 netty 读取的最小单位,netty 实际每次读取的一般是它的整数倍
现象分析
粘包
- 现象,发送 abc def,接收 abcdef
- 原因
- 应用层:接收方 ByteBuf 设置太大(Netty 默认 1024)
- 滑动窗口:假设发送方 256 bytes 表示一个完整报文,但由于接收方处理不及时且窗口大小足够大,这 256 bytes 字节就会缓冲在接收方的滑动窗口中,当滑动窗口中缓冲了多个报文就会粘包
- Nagle 算法:会造成粘包
半包
- 现象,发送 abcdef,接收 abc def
- 原因
- 应用层:接收方 ByteBuf 小于实际发送数据量
- 滑动窗口:假设接收方的窗口只剩了 128 bytes,发送方的报文大小是 256 bytes,这时放不下了,只能先发送前 128 bytes,等待 ack 后才能发送剩余部分,这就造成了半包
- MSS 限制:当发送的数据超过 MSS 限制后,会将数据切分发送,就会造成半包
本质是因为 TCP 是流式协议,消息无边界
滑动窗口
TCP 以一个段(segment)为单位,每发送一个段就需要进行一次确认应答(ack)处理,但如果这么做,缺点是包的往返时间越长性能就越差
为了解决此问题,引入了窗口概念,窗口大小即决定了无需等待应答而可以继续发送的数据最大值
窗口实际就起到一个缓冲区的作用,同时也能起到流量控制的作用
- 图中深色的部分即要发送的数据,高亮的部分即窗口
- 窗口内的数据才允许被发送,当应答未到达前,窗口必须停止滑动
- 如果 1001~2000 这个段的数据 ack 回来了,窗口就可以向前滑动
- 接收方也会维护一个窗口,只有落在窗口内的数据才能允许接收
MSS 限制
链路层对一次能够发送的最大数据有限制,这个限制称之为 MTU(maximum transmission unit),不同的链路设备的 MTU 值也有所不同,例如
以太网的 MTU 是 1500
FDDI(光纤分布式数据接口)的 MTU 是 4352
本地回环地址的 MTU 是 65535 - 本地测试不走网卡
MSS 是最大段长度(maximum segment size),它是 MTU 刨去 tcp 头和 ip 头后剩余能够作为数据传输的字节数
ipv4 tcp 头占用 20 bytes,ip 头占用 20 bytes,因此以太网 MSS 的值为 1500 - 40 = 1460
TCP 在传递大量数据时,会按照 MSS 大小将数据进行分割发送
MSS 的值在三次握手时通知对方自己 MSS 的值,然后在两者之间选择一个小值作为 MSS
Nagle 算法
- 即使发送一个字节,也需要加入 tcp 头和 ip 头,也就是总字节数会使用 41 bytes,非常不经济。因此为了提高网络利用率,tcp 希望尽可能发送足够大的数据,这就是 Nagle 算法产生的缘由
- 该算法是指发送端即使还有应该发送的数据,但如果这部分数据很少的话,则进行延迟发送
- 如果 SO_SNDBUF 的数据达到 MSS,则需要发送
- 如果 SO_SNDBUF 中含有 FIN(表示需要连接关闭)这时将剩余数据发送,再关闭
- 如果 TCP_NODELAY = true,则需要发送
- 已发送的数据都收到 ack 时,则需要发送
- 上述条件不满足,但发生超时(一般为 200ms)则需要发送
- 除上述情况,延迟发送
解决方案
- 短链接,发一个包建立一次连接,这样连接建立到连接断开之间就是消息的边界,缺点效率太低
- 每一条消息采用固定长度,缺点浪费空间
- 每一条消息采用分隔符,例如 \n,缺点需要转义
- 每一条消息分为 head 和 body,head 中包含 body 的长度
短链接
发完马上关闭,下一次发送再次重新连接
public class HelloWorldClient {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldClient.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 分 10 次发送
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
send();
}
}
private static void send() {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.debug("conneted...");
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("sending...");
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15});
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
// 发完即关
ctx.close();
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
但是对于半包这种是不好解决掉的,因为接收方的缓冲区大小它是有限的
固定长度
让所有数据包长度固定(假设长度为 8 字节),服务器端加入
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(8));

FixedLengthFrameDecoder
一种解码器,用于按固定的字节数拆分接收到的 ByteBufs。例如,如果您收到以下四个分段数据包:
+---+----+------+----+
| A | BC | DEFG | HI |
+---+----+------+----+
A FixedLengthFrameDecoder(3) 会将它们解码为以下三个具有固定长度的数据包:
+-----+-----+-----+
| ABC | DEF | GHI |
+-----+-----+-----+
修改客户端,客户端代码如下
public class HelloWorldClient {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldClient.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.debug("conneted...");
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("sending...");
Random r = new Random();
char c = 'a';
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
byte[] bytes=new byte[8];
for (int j = 0; j < r.nextInt(8); j++) {
bytes[j]=(byte)c;
}
c++;
buffer.writeBytes(bytes);
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
} 这里可以看到客户端是一口气发送完的,但在服务端的解析如下:
这里可以看到客户端是一口气发送完的,但在服务端的解析如下:

缺点是,数据包的大小不好把握
- 长度定的太大,浪费
- 长度定的太小,对某些数据包又显得不够
固定分隔符
服务端加入,默认以 \n 或 \r\n 作为分隔符,如果超出指定长度仍未出现分隔符,则抛出异常
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));LineBasedFrameDecoder
一个解码器,用于在行尾拆分收到的 ByteBuf。
两者和"\n""\r\n"处理。
字节流应采用 UTF-8 字符编码或 ASCII。当前的实现使用直接byte强制char转换,然后将其与一些低范围的 ASCII 字符(如 '\n' or '\r')进行比较char。UTF-8 未对多字节代码点表示形式使用低范围 [0..0x7F] 字节值,因此此实现完全支持。
客户端在每条消息之后,加入 \n 分隔符
public class HelloWorldClient {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldClient.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.debug("connetted...");
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("sending...");
Random r = new Random();
char c = 'a';
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= r.nextInt(16)+1; j++) {
buffer.writeByte((byte) c);
}
buffer.writeByte(10);//换行
c++;
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}客户端发送的数据

服务器端解析的数据
 缺点,处理字符数据比较合适,但如果内容本身包含了分隔符(字节数据常常会有此情况),那么就会解析错误
缺点,处理字符数据比较合适,但如果内容本身包含了分隔符(字节数据常常会有此情况),那么就会解析错误
预设长度
在发送消息前,先约定用定长字节表示接下来数据的长度
// 最大长度,长度偏移,长度占用字节,长度调整,剥离字节数
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 0, 1, 0, 1));LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
一种解码器,它按消息中长度字段的值动态拆分收到的 ByteBufs。当您解码二进制消息时,它特别有用,该二进制消息具有表示消息正文或整个消息长度的整数标头字段。
经典构造办法:
public LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder( int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength, int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip) { this( maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength, lengthAdjustment, initialBytesToStrip, true); }创建新实例。
参数:
maxFrameLength:最大帧长度 ― 帧的最大长度。如果帧的长度大于此值, TooLongFrameException 将被抛出。
lengthFieldOffset:长度字段偏移量 – 长度字段的偏移量
lengthFieldLength:长度字段长度 – 长度字段的长度
lengthAdjustment:长度调整 – 要添加到长度字段值的补偿值
initialBytesToStrip :剥离字节数 ― 从解码帧中剥离的第一个字节数
调整客户端代码
public class HelloWorldClient {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldClient.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.debug("connetted...");
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("sending...");
Random r = new Random();
char c = 'a';
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
byte length = (byte) (r.nextInt(16) + 1);
// 先写入长度
buffer.writeByte(length);
// 再
for (int j = 1; j <= length; j++) {
buffer.writeByte((byte) c);
}
c++;
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
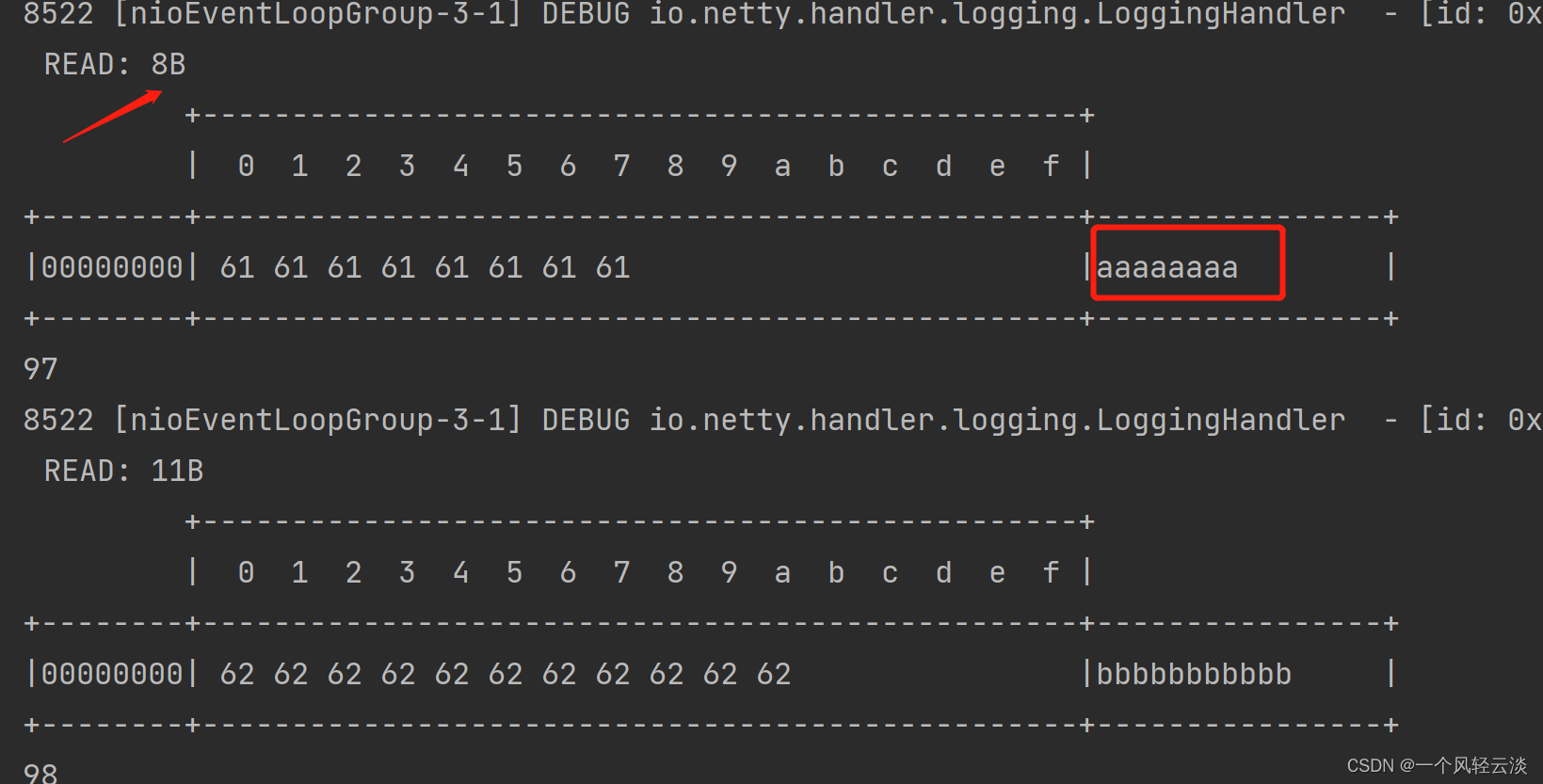
}客户端发送的数据

服务端接收的数据
偏移量为 0 处的 2 字节长度字段,不剥离标头 此示例中长度字段的值为 12 (0x0C), 表示“HELLO, WORLD”的长度。 默认情况下,解码器假定长度字段表示长度字段后面的字节数。 因此,可以使用简单的参数组合对其进行解码。 lengthFieldOffset = 0 lengthFieldLength = 2 lengthAdjustment = 0 initialBytesToStrip = 0 (= do not strip header) BEFORE DECODE (14 bytes) AFTER DECODE (14 bytes) +--------+----------------+ +--------+----------------+ | Length | Actual Content |----->| Length | Actual Content | | 0x000C | "HELLO, WORLD" | | 0x000C | "HELLO, WORLD" | +--------+----------------+ +--------+----------------+
偏移量为 0 处的 2 字节长度字段,条带标头 因为我们可以通过调用 ByteBuf.readableBytes()来获取内容的长度, 所以你可能希望通过指定 initialBytesToStrip来去除长度字段。 在此示例中,我们指定了 2,与长度字段的长度相同,以去除前两个字节。 lengthFieldOffset = 0 lengthFieldLength = 2 lengthAdjustment = 0 initialBytesToStrip = 2 (= the length of the Length field) BEFORE DECODE (14 bytes) AFTER DECODE (12 bytes) +--------+----------------+ +----------------+ | Length | Actual Content |----->| Actual Content | | 0x000C | "HELLO, WORLD" | | "HELLO, WORLD" | +--------+----------------+ +----------------+
偏移量为 0 处的 2 字节长度字段,不要剥离标头,长度字段表示整个消息的长度 在大多数情况下,长度字段仅表示消息正文的长度,如前面的示例所示。 但是,在某些协议中,长度字段表示整个消息的长度,包括消息标头。在这种情况下, 我们指定一个非零长度调整。由于此示例消息中的长度值始终大于正文长度 2, 因此我们将 -2 指定为 lengthAdjust 以进行补偿。 lengthFieldOffset = 0 lengthFieldLength = 2 lengthAdjustment = -2 (= the length of the Length field) initialBytesToStrip = 0 BEFORE DECODE (14 bytes) AFTER DECODE (14 bytes) +--------+----------------+ +--------+----------------+ | Length | Actual Content |----->| Length | Actual Content | | 0x000E | "HELLO, WORLD" | | 0x000E | "HELLO, WORLD" | +--------+----------------+ +--------+----------------+
字节标头末尾的 3 字节长度字段,不要剥离标头 以下消息是第一个示例的简单变体。消息前面附加了一个额外的标头值。 lengthAdjust 再次为零,因为解码器在计算帧长度时始终考虑预置数据的长度。 lengthFieldOffset = 2 (= the length of Header 1) lengthFieldLength = 3 lengthAdjustment = 0 initialBytesToStrip = 0 BEFORE DECODE (17 bytes) +----------+----------+----------------+ | Header 1 | Length | Actual Content | | 0xCAFE | 0x00000C | "HELLO, WORLD" | +----------+----------+----------------+ AFTER DECODE (17 bytes) +----------+----------+----------------+ | Header 1 | Length | Actual Content | | 0xCAFE | 0x00000C | "HELLO, WORLD" | +----------+----------+----------------+
字节标头开头的 3 字节长度字段,不要剥离标头 这是一个高级示例,显示了长度字段和消息正文之间有一个额外标头的情况。 您必须指定正 lengthAdjust, 以便解码器将额外的标头计入帧长度计算中。 lengthFieldOffset = 0 lengthFieldLength = 3 lengthAdjustment = 2 (= the length of Header 1) initialBytesToStrip = 0 BEFORE DECODE (17 bytes) +----------+----------+----------------+ | Length | Header 1 | Actual Content | | 0x00000C | 0xCAFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | +----------+----------+----------------+ AFTER DECODE (17 bytes) +----------+----------+----------------+ | Length | Header 1 | Actual Content | | 0x00000C | 0xCAFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | +----------+----------+----------------+
字节长度字段位于 4 字节标头中间的偏移量 1,去除第一个标头字段和长度字段 这是上述所有示例的组合。长度字段之前有前缀标头,长度字段之后有额外的标头。前面的标头会影响 lengthFieldOffset,而额外的标头会影响 lengthAdjust。我们还指定了一个非零的 initialBytesToStrip 来从帧中去除长度字段和前置标头。如果不想去除前面的标头,可以为 initialBytesToSkip 指定 0。 lengthFieldOffset = 1 (= the length of HDR1) lengthFieldLength = 2 lengthAdjustment = 1 (= the length of HDR2) initialBytesToStrip = 3 (= the length of HDR1 + LEN) BEFORE DECODE (16 bytes) +------+--------+------+----------------+ | HDR1 | Length | HDR2 | Actual Content | | 0xCA | 0x000C | 0xFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | +------+--------+------+----------------+ AFTER DECODE (13 bytes) +------+----------------+ | HDR2 | Actual Content | | 0xFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | +------+----------------+
字节长度字段在偏移量1处4字节头的中间, 去掉第一个头字段和长度字段,长度字段代表整个消息的长度 让我们对前面的例子再做一个转折。与前面的示例的唯一区别是, 长度字段表示整个消息的长度,而不是消息正文,就像第三个示例一样。 我们必须将 HDR1 和长度的长度计算成 长度调整。 请注意,我们不需要考虑 HDR2 的长度,因为长度字段已经包含整个标头长度。 lengthFieldOffset = 1 lengthFieldLength = 2 lengthAdjustment = -3 (= the length of HDR1 + LEN, negative) initialBytesToStrip = 3 BEFORE DECODE (16 bytes) +------+--------+------+----------------+ | HDR1 | Length | HDR2 | Actual Content | | 0xCA | 0x0010 | 0xFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | +------+--------+------+----------------+ AFTER DECODE (13 bytes) +------+----------------+ | HDR2 | Actual Content | | 0xFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | +------+----------------+