前言

本文为Json简介与基本使用相关知识,下边具体将对什么是JSON,XML与JSON的区别,JSON的语法格式,JSON数据的转换(包括:Java对象转换为JSON格式、JSON格式转换为Java对象)等进行详尽介绍~
📌博主主页:小新要变强 的主页
👉Java全栈学习路线可参考:【Java全栈学习路线】最全的Java学习路线及知识清单,Java自学方向指引,内含最全Java全栈学习技术清单~
👉算法刷题路线可参考:算法刷题路线总结与相关资料分享,内含最详尽的算法刷题路线指南及相关资料分享~
👉Java微服务开源项目可参考:企业级Java微服务开源项目(开源框架,用于学习、毕设、公司项目、私活等,减少开发工作,让您只关注业务!)

目录
文章标题
- 前言
- 目录
- 一、什么是JSON
- 二、XML与JSON的区别
- 三、JSON的语法格式
- 1️⃣JSON语法介绍
- 2️⃣JSON案例
- 四、JSON数据的转换
- 1️⃣FastJson介绍
- 2️⃣FastJson的使用
- 3️⃣Java对象转换为JSON格式
- 4️⃣JSON格式转换为Java对象
- 后记

一、什么是JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation,JS对象简谱)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。它基于ECMAScript (欧洲计算机协会制定的JS规范〉的一个子集,采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。简洁和清晰的层次结构使得JSON成为理想的数据交换语言。易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率。
JSON的特点︰
- JSON是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。
- JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,就是说不同的编程语言JSON数据是一致的。
- JSON易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成(一般用于提升网络传输速率)
二、XML与JSON的区别
(1)XML: 可扩展标记语言,是一种用于标记电子文件使其具有结构性的标记语言。
(2)JSON: JSON (JavaScript Object Notation,JS对象简谱)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。
(3)相同点: 它们都可以作为一种数据交换格式。
(4)区别:
- XML是重量级的,JSON是轻量级的,XML在传输过程中比较占带宽,JSON占带宽少,易于压缩。
- XML和JSON都用在项目交互下,XML多用于做配置文件,JSON用于数据交互。
三、JSON的语法格式
1️⃣JSON语法介绍
我们先来看一下JSON数据︰
{
"id": 001,
"name": "小新",
"age": 24
}
语法注意:
- (1)外面由括起来
- (2)数据以"键:值"对的形式出现(其中键多以字符串形式出现,值可取字符串,数值,甚至其他JSON对象)
- (3)每两个"键:值"对以逗号分隔(最后一个"键:值"对省略逗号)
- (4)参数值如果是string类型,就必须加引号,如果是数字类型,引号可加可不加遵守上面4点,便可以形成一个JSON对象
2️⃣JSON案例
- (1)创建一个Maven类型的项目,项目名称: json_demo。
- (2)在json_demo项目的src/main下创建一个webapp目录。
- (3)在File - Project Structure - Facets选项下配置项目的web.xml文件。
- (4)声明JSON格式的对象、数组以及集合的数据格式。在项目的webapp目录下创建一个json_demo.html的页面。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang= "en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>JSON</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//自定义JSoN数据格式(Java中的对象)
var person = {
"eid" : 0001,
"username" : "Jenny",
"sex" :"女",
"age" : 12
};
console.log(person);
//数组来接收JSON数据
let persons = {
"persons": [
{
"eid" : 0002,
"username" : "Jams",
"sex" :"男",
"age" : 20
},
{
"eid" : 0003,
"username" : "Coco",
"sex" :"女",
"age" : 22
}
]
};
console.log(persons);
// 集合存储JSON数据
let list = [
{
"eid" : 0004,
"username" : "Mary",
"sex" :"女",
"age" : 24
},
{
"eid" : 0005,
"username" : "Jack",
"sex" :"男",
"age" : 23
}
];
console.log(list);
</script>
</body>
</html>
四、JSON数据的转换
目前,前后端的AJAX通讯几乎用的都是JSON格式的数据,所以在开发的过程中,我们经常会涉及到JSON数据的转换。
JSON数据与Java对象的转换,见下图:

1️⃣FastJson介绍
(1)FastJson是一个Java库,可以将Java对象转换为JSON格式,当然它也可以将JSON字符串转换为Java对象。
(2)FastJson特点如下︰
- 能够支持将Java Bean序列化成JSON字符串,也能够将JSON字符串反序列化成Java Bean。
- 顾名思义,FastJson操作JSON的速度是非常快的。·
- FastJson无其他包的依赖,使用比较方便。
2️⃣FastJson的使用
在Maven项目中使用FastJson库,需要提前在Maven的配置文件中添加此FastJson包的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.colobu</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson-jaxrs-json-provider</artifactId>
<version>0.3.1</version>
</dependency>
3️⃣Java对象转换为JSON格式
🍀(1)项目配置
创建一个JavaWeb企业级项目,并添加上边FastJson包的依赖。
🍀(2)代码实现
Person.java:
package com.wang.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Person implements Serializable{
private int eid;
private String username;
private int age;
private String birthday;
public Person(){
}
public Person(int eid, String username, int age, String birthday) {
this.eid = eid;
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public int getEid() {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"eid=" + eid +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
FastJsonTests.java:
package com.wang.json_demo;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.wang.model.Person;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class FastJsonTests {
@Test
public void javaBeanToJSON() {
Person person = new Person(001,"小新",23,"1999-01-01");
//JSON类中有静态方法直接调用可以将JavaBean对象转化成JSON串
//第二个参数是规定是否按Json格式输出
String jsonStr1 = JSON.toJSONString(person,true);
System.out.println("jsonStr1:" + jsonStr1);
}
@Test
//Java Bean对象的数组转换为JSON数组
public void arrayToJSON() {
Person person1 = new Person(001,"小新",23,"1999-01-01");
Person person2 = new Person(002,"李白",20,"2002-05-01");
Person person3 = new Person(003,"王五",21,"2001-10-01");
Person [] persons = {person1, person2, person3};
// 数组转换成JSON格式的数组
String jsonStr2 = JSON.toJSONString(persons,true);
System.out.println("jsonStr2:" + jsonStr2);
}
@Test
//list集合转换为JSON格式的数据
public void listToJSON() {
Person person1 = new Person(001,"小新",23,"1999-01-01");
Person person2 = new Person(002,"李白",20,"2002-05-01");
Person person3 = new Person(003,"王五",21,"2001-10-01");
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, person1, person2, person3);
String jsonStr3 = JSON.toJSONString(list,true);
System.out.println("jsonStr3:" + jsonStr3);
}
}
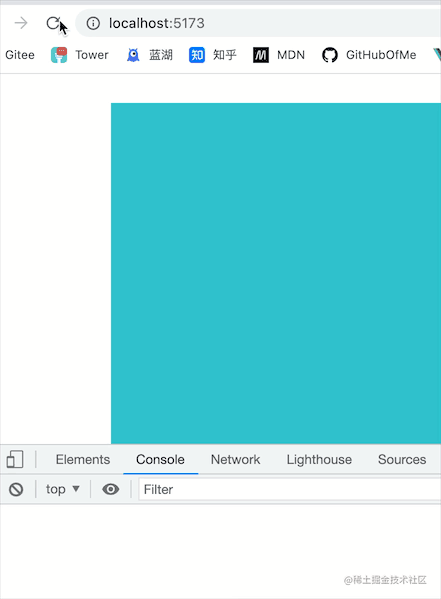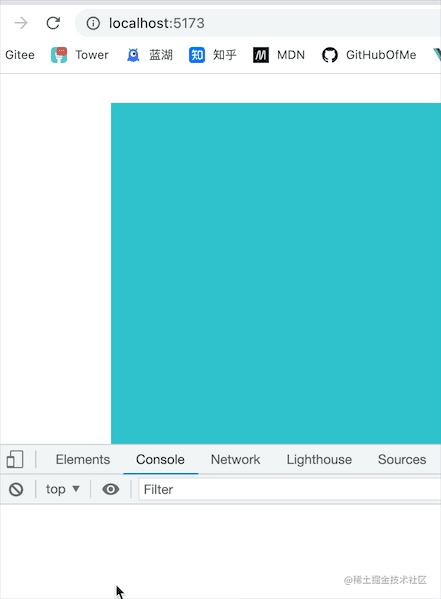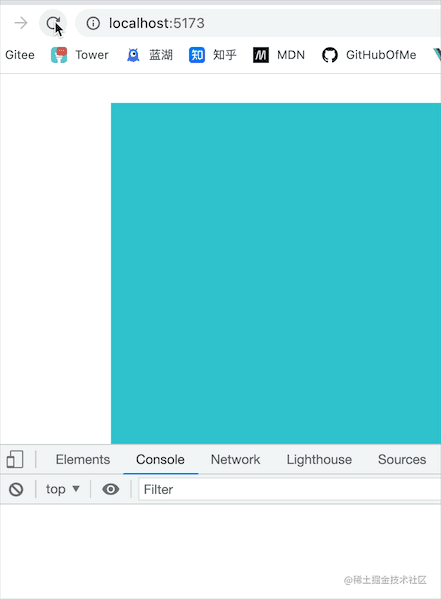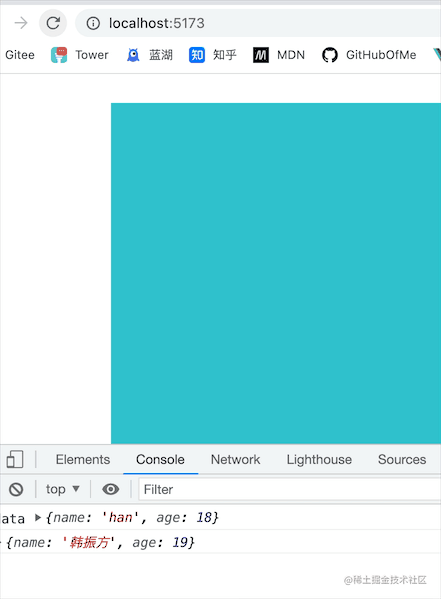
🍀(3)运行结果



🍀(4)JSONField注解用法
JSONField注解中:ordinal字段用于自定义字段的输出顺序;name字段用于表示字段转换成JSON串的字段名字。
Person.java:
package com.wang.model;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* ordinal:表示具体字段的顺序,取数字
* name: 表示字段转换成JSON串的字段名字
*/
public class Person implements Serializable{
// 自定义字段的输出顺序
@JSONField(ordinal = 1)
private int eid;
@JSONField(ordinal = 2, name="user")
private String username;
@JSONField(ordinal = 3)
private int age;
@JSONField(ordinal = 4)
private String birthday;
public Person(){
}
public Person(int eid, String username, int age, String birthday) {
this.eid = eid;
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public int getEid() {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"eid=" + eid +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
FastJsonTests.java:还是上边的代码不变
运行结果:



JSONField注解中serialize字段设为false可使某一字段不参与序列化
Person.java:
package com.wang.model;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* ordinal:表示具体字段的顺序,取数字
* name: 表示字段转换成JSON串的字段名字
* serialize: 值为false表示指定的字段不参与序列化
*/
public class Person implements Serializable{
@JSONField(ordinal = 1)
private int eid;
@JSONField(ordinal = 2, name="user")
private String username;
@JSONField(ordinal = 3, serialize=false)
private int age;
@JSONField(ordinal = 4, serialize=false)
private String birthday;
public Person(){
}
public Person(int eid, String username, int age, String birthday) {
this.eid = eid;
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public int getEid() {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"eid=" + eid +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
FastJsonTests.java:还是上边的代码不变
运行结果:



4️⃣JSON格式转换为Java对象
🍀(1)常用方法
(1)JSON.parseObject()
- 可以使用JSON.parseObject()将JSON字符串转换为Java对象。
- 注意反序列化时为对象时,必须要有默认无参的构造方法,否则会报异常。
(2)JSON.parseArray()
- 可以使用JSON.parseArray()将JSON字符串转换为集合对象。
🍀(2)代码实现
(1)在Person类中添加无参构造方法。
package com.wang.model;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* ordinal:表示具体字段的顺序,取数字
* name: 表示字段转换成JSON串的字段名字
* serialize: 值为false表示指定的字段不参与序列化
*/
public class Person implements Serializable{
@JSONField(ordinal = 1)
private int eid;
@JSONField(ordinal = 2)
private String username;
@JSONField(ordinal = 3)
private int age;
@JSONField(ordinal = 4)
private String birthday;
public Person(){
}
public Person(int eid, String username, int age, String birthday) {
this.eid = eid;
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public int getEid() {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"eid=" + eid +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
(2)在FastJsonTests测试类中添加JSON格式转换为Java对象的相应方法。
package com.wang.json_demo;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.wang.model.Person;
import org.junit.Test;
public class FastJsonTests {
@Test
public void jsonToJavaBean() {
String json = "{\"eid\":1, \"username\":\"小新\", \"age\":23, \"birthday\":\"1999-01-01\"}";
Person person = JSON.parseObject(json,Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
@Test
public void jsonToJavaList() {
String json = "[" +
"{\"eid\":1, \"username\":\"小新\", \"age\":23, \"birthday\":\"1999-01-01\"}, " +
"{\"eid\":2, \"username\":\"李白\", \"age\":20, \"birthday\":\"2002-05-01\"}, " +
"{\"eid\":3, \"username\":\"王五\", \"age\":21, \"birthday\":\"2001-10-01\"}" +
"]";
List<Person> list = JSON.parseArray(json,Person.class);
System.out.println("personList:" + list);
}
}
运行结果:

后记

👉Java全栈学习路线可参考:【Java全栈学习路线】最全的Java学习路线及知识清单,Java自学方向指引,内含最全Java全栈学习技术清单~
👉算法刷题路线可参考:算法刷题路线总结与相关资料分享,内含最详尽的算法刷题路线指南及相关资料分享~






![[附源码]计算机毕业设计物业管理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1339edec060a4fb489b6e6274fa3a994.png)



![[黑马程序员C++笔记]P168-P173模板-函数模板](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bc0cb7397545498fa20ee389f954ef82.png)