创建配置文件 config.ini
[MySQL]
host = 172.xxx.xxx.xxx
port = 3306
user = root
password = ******
db = bgp_routing
charset = utf8
创建读取配置文件 readConfig.py
import configparser
from pathlib import Path
class ReadConfig():
def __init__(self):
configDir = Path.cwd().parent.joinpath("config.ini") # 配置文件地址
self.cfg = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.cfg.read(configDir) # cfg.get()默认返回str
def getDBValue(self, name):
value = self.cfg.get("MySQL", name) # [MySQL]为需要获取的section名称
return value
import configparser
configparser模块定义了一个ConfigParser类,该类的作用是使用配置文件生效,配置文件的格式和windows的INI文件的格式相同。
该模块的作用 就是使用模块中的RawConfigParser()、ConfigParser()、 SafeConfigParser()这三个方法,创建一个对象使用对象的方法对指定的配置文件做增删改查操作。
Python中configparser的使用:https://blog.csdn.net/u012856866/article/details/131071552
创建数据库文件 configDB.py
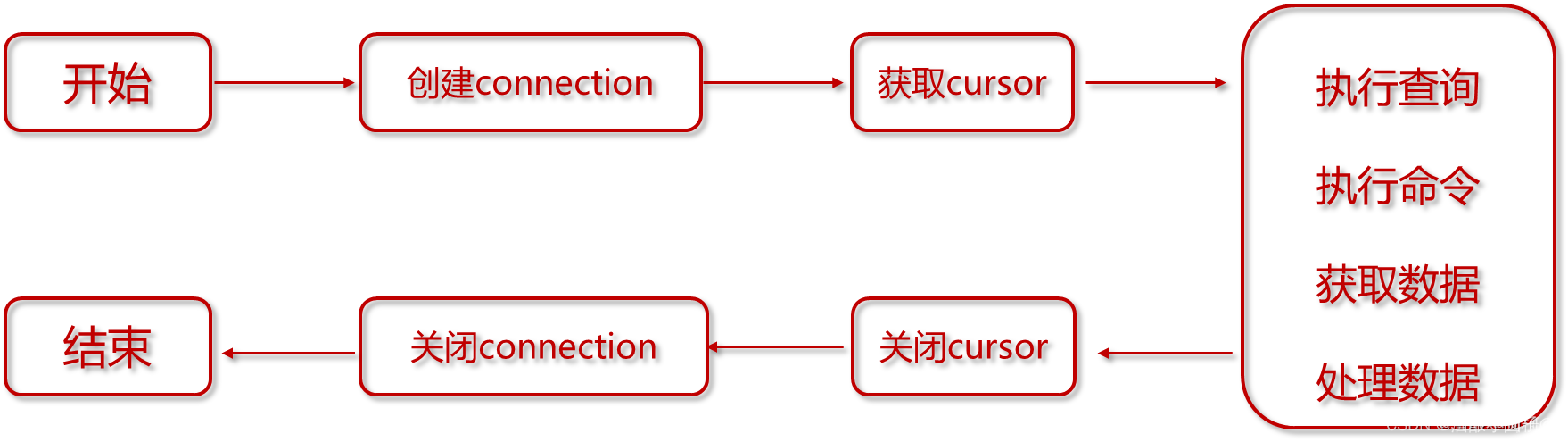
使用Python DB-API访问数据库的流程如下:
import pymysql
import readConfig
localReadConfig = readConfig.ReadConfig()
class myDB:
def __init__(self):
self.host = localReadConfig.getDBValue("host") # cfg.get()默认返回str
self.port = int(localReadConfig.getDBValue("port")) # 将port转化为int型
self.username = localReadConfig.getDBValue("user")
self.password = localReadConfig.getDBValue("password")
self.database = localReadConfig.getDBValue("db")
def connect_mysql(self):
#连接数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.host, port=self.port, user=self.user, password=self.password, db=self.db)
#使用cursor()方法创建一个游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
#使用execute()方法执行SQL语句
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM HT_VIRTUAL_GIFT")
#使用fetall()获取全部数据
data = cursor.fetchall()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return data
test = myDB()
data = test.connect_mysql()
print(data)
参考资料
- Python 数据库配置文件:https://www.cnblogs.com/QingshanY/p/16089725.html