文章目录
- 1、自定义类型作为map的key
- 2、自定义类型作为unordered_map的key
1、自定义类型作为map的key

map中有4个参数,前两个参数是key和val的类型,第三个参数表示比较的仿函数,用于对键值进行比较,默认情况下采用less<Key>,第四个参数表示分配器的类型,用于分配和管理内存。

如果key是内置类型,比如char,int等,使用默认的less<Key>不会错。
如果Key不是内置类型,在插入数据时就会产生一个编译错误
例如:
class Student
{
public:
Student() = default;
Student(string _name) :name(_name){}
private:
string name;
};
int main()
{
map<Student, Student> treeMap;
Student stu("fl");
treeMap[stu] = stu;
return 0;
}


要保证编译通过,需要在自定义类中重载<运算符或者显示的传入一个比较仿函数,或者普通函数,或者定义一个lambda表达式
方法1:在自定义类中重载<运算符
class Student
{
public:
Student() = default;
Student(string _name) :name(_name){}
bool operator<(const Student& stu) const
{
return name < stu.name;
}
string name;
};
int main()
{
map<Student, Student> treeMap;
Student stu("fl");
treeMap[stu] = stu;
return 0;
}
方法2:自定义比较函数
class Student
{
public:
Student() = default;
Student(string _name) :name(_name){}
string name;
};
bool StudentCmp(const Student& stu1, const Student& stu2)
{
return stu1.name < stu2.name;
}
int main()
{
map<Student, Student, decltype(StudentCmp)*> treeMap;
Student stu("fl");
treeMap[stu] = stu;
return 0;
}
方法3:自定义比较仿函数
class Student
{
public:
Student() = default;
Student(string _name) :name(_name){}
string name;
};
class StudentCmp
{
public:
bool operator()(const Student& stu1, const Student& stu2) const
{
return stu1.name < stu2.name;
}
};
int main()
{
map<Student, Student, StudentCmp> treeMap;
Student stu("fl");
treeMap[stu] = stu;
return 0;
}
方法4:使用lambda表达式
class Student
{
public:
Student() = default;
Student(string _name) :name(_name){}
string name;
};
int main()
{
auto cmp = [&](const Student& stu1, const Student& stu2) {
return stu1.name < stu2.name;
};
map<Student, Student, decltype(cmp)> treeMap(cmp);
Student stu("fl");
treeMap[stu] = stu;
return 0;
}
2、自定义类型作为unordered_map的key
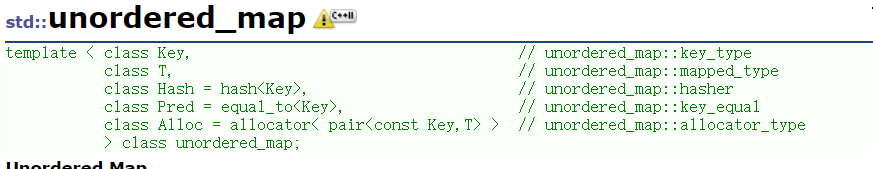
unordered_map有5个参数,前两个参数是key和val的类型,第三个参数是一个哈希函数,表示用于计算哈希值,第四个参数是比较函数,用于判断两个键是否相等,第五个参数是分配器类型。
对于hash,可以支持任何的内置类型
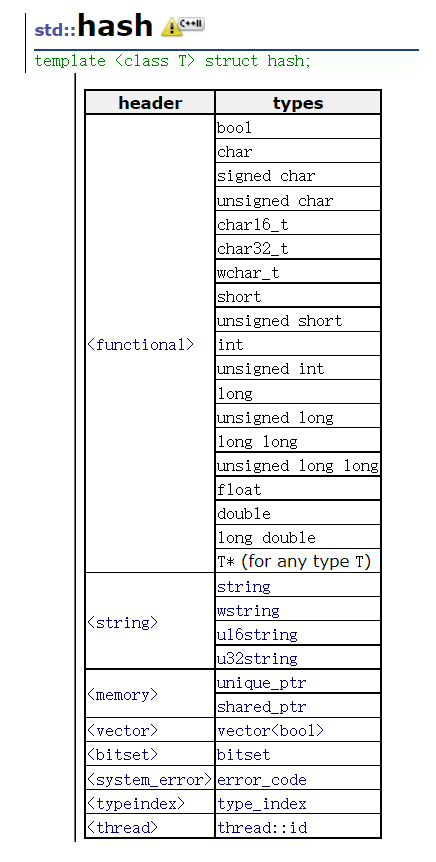
对于比较函数equal_to,也支持任何的内置类型的比较
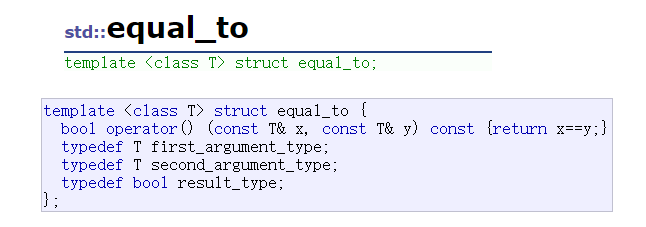
如果key是内置类型,对应默认的hash和equal_to完全够用,不会不错。
如果key是自定义类型,在插入数据时就会产生一个编译错误。
例如:
class Student
{
public:
Student() = default;
Student(string _name) :name(_name){}
string name;
};
int main()
{
unordered_map<Student, Student> hashMap;
Student stu("fl");
hashMap[stu] = stu;
return 0;
}


要保证编译通过,则需要在类中重载==操作符并且自定哈希函数或者自定义比较(可以是普通的函数,仿函数,lambda表达式)并且自定义哈希函数
方法1:在类中重载==操作符并且自定哈希函数
class Student
{
public:
Student() = default;
Student(string _name) :name(_name){}
string name;
bool operator==(const Student& stu) const
{
return name == stu.name;
}
};
class Studenthash
{
public:
size_t operator()(const Student& stu) const
{
return std::hash<string>()(stu.name);
}
};
int main()
{
unordered_map<Student, Student, Studenthash> hashMap;
Student stu("fl");
hashMap[stu] = stu;
return 0;
}
方法2:自定义比较(可以是普通的函数,仿函数,lambda表达式)并且自定义哈希函数
class Student
{
public:
Student() = default;
Student(string _name) :name(_name){}
string name;
};
//我这里就写一个比较函数,除此之外还可以是仿函数,lambda表达式
bool StudentEqual(const Student& stu1, const Student& stu2)
{
return stu1.name == stu2.name;
}
class Studenthash
{
public:
size_t operator()(const Student& stu) const
{
return std::hash<string>()(stu.name);
}
};
int main()
{
unordered_map<Student, Student, Studenthash, decltype(StudentEqual)*> hashMap;
Student stu("fl");
hashMap[stu] = stu;
return 0;
}