打开文件流程
本文基本Linux5.15
当应用层通过open api打开一个文件,内核中究竟如何处理? 本身用来描述内核中对应open 系统调用的处理流程。
数据结构
fdtable
一个进程可以打开很多文件, 内核用fdtable来管理这些文件。
include/linux/fdtable.h
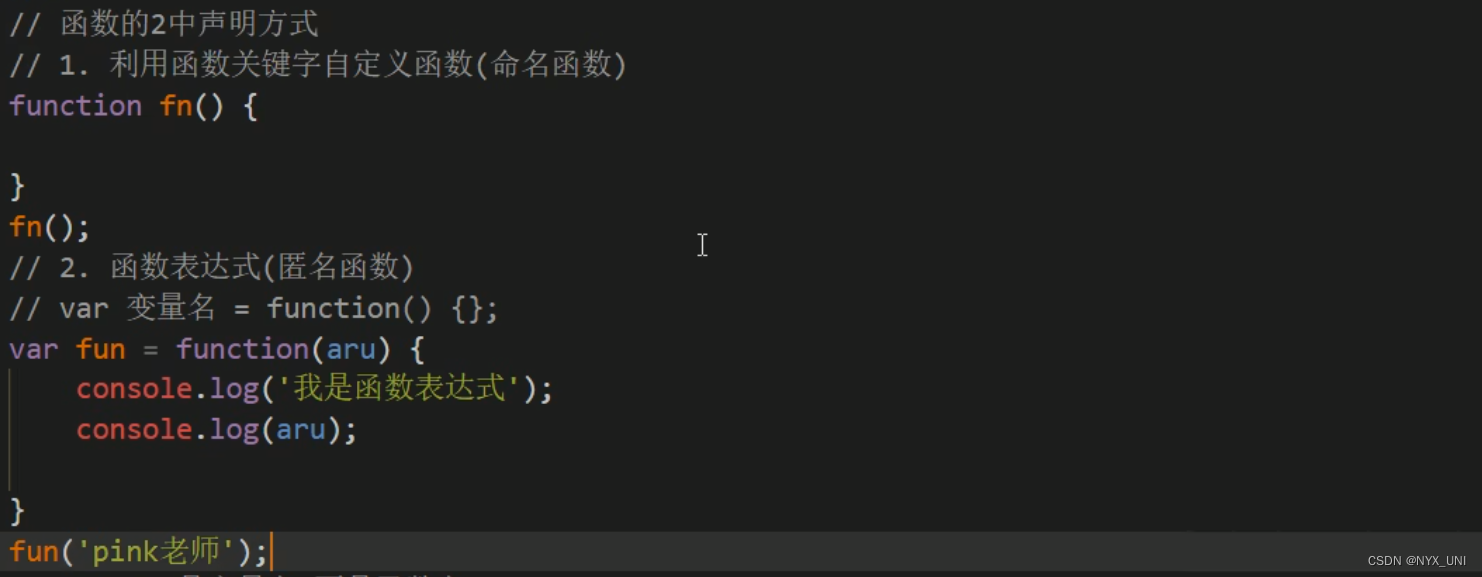
struct fdtable {
unsigned int max_fds;
struct file __rcu **fd; /* current fd array */
unsigned long *close_on_exec;
unsigned long *open_fds;
unsigned long *full_fds_bits;
struct rcu_head rcu;
};fd: 文件描述符数组
open_fds: 为方便查找数组中的空闲项, 为该数组建立的位图
close_on_exec: 在打开的文件中, 有些文件时用于执行目的, 在执行完成之后应该自动关闭
files_struct
对于大多数进程, 打开文件的数量是有限的,一种优化的设计方式是为每个进程内置分配少量数目的文件描述符指针数组, 但进程需要更多的指针时, 再动态扩展。 为此, 进程并不直接使用fdtable, 而是使用files_struct结构体, 作为task_struct的一个域
/*
* Open file table structure
*/
struct files_struct {
/*
* read mostly part
*/
atomic_t count;
bool resize_in_progress;
wait_queue_head_t resize_wait;
struct fdtable __rcu *fdt;
struct fdtable fdtab;
/*
* written part on a separate cache line in SMP
*/
spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
unsigned int next_fd;
unsigned long close_on_exec_init[1];
unsigned long open_fds_init[1];
unsigned long full_fds_bits_init[1];
struct file __rcu * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];
};fdt指向进程实际使用的fdtable。 对于大多数进程来说, 打开文件的梳理并不会很多, 这时候无需另外分配空间, 直接指向内嵌的结构, 即fdtab域。
file
每个打开的文件都会对应一个file结构体, 进程通过它对文件进行操作。
include/linux/fs.h
struct file {
union {
struct llist_node fu_llist;
struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;
} f_u;
struct path f_path;
struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */
const struct file_operations *f_op;
/*
* Protects f_ep_links, f_flags.
* Must not be taken from IRQ context.
*/
spinlock_t f_lock;
enum rw_hint f_write_hint;
atomic_long_t f_count;
unsigned int f_flags;
fmode_t f_mode;
struct mutex f_pos_lock;
loff_t f_pos;
struct fown_struct f_owner;
const struct cred *f_cred;
struct file_ra_state f_ra;
u64 f_version;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *f_security;
#endif
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
struct list_head f_ep_links;
struct list_head f_tfile_llink;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
struct address_space *f_mapping;
errseq_t f_wb_err;
errseq_t f_sb_err; /* for syncfs */
} __randomize_layoutf_path: 文件路径
f_op: 指向文件操作表, read/write等操作都会调用这里的回调
f_mapping: 指向文件地址空间描述符
f_pos: 当前文件的偏移值
处理流程
open系统调用

整体系统调用栈如下:
#3 0xffffffff81218174 in do_filp_open (dfd=dfd@entry=-100, pathname=pathname@entry=0xffff888004950000, op=op@entry=0xffffc90000173ee4) at fs/namei.c:3396
#4 0xffffffff81203cfd in do_sys_openat2 (dfd=-100, filename=<optimized out>, how=how@entry=0xffffc90000173f20) at fs/open.c:1168
#5 0xffffffff81205135 in do_sys_open (dfd=<optimized out>, filename=<optimized out>, flags=<optimized out>, mode=<optimized out>) at fs/open.c:1184
#6 0xffffffff819bf903 in do_syscall_64 (nr=<optimized out>, regs=0xffffc90000173f58) at arch/x86/entry/common.c:46
#7 0xffffffff81a0007c in entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:120open 系统调用的入口函数定义如下:
long do_sys_open(int dfd, const char __user *filename, int flags, umode_t mode)
{
struct open_how how = build_open_how(flags, mode);
return do_sys_openat2(dfd, filename, &how);
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(open, const char __user *, filename, int, flags, umode_t, mode)
{
if (force_o_largefile())
flags |= O_LARGEFILE;
return do_sys_open(AT_FDCWD, filename, flags, mode);
}do_sys_open 函数调用了do_sys_openat2, 其处理流程如下:
static long do_sys_openat2(int dfd, const char __user *filename,
struct open_how *how)
{
struct open_flags op;
int fd = build_open_flags(how, &op);
struct filename *tmp;
if (fd)
return fd;
tmp = getname(filename);
if (IS_ERR(tmp))
return PTR_ERR(tmp);
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(how->flags); /* 1 */
if (fd >= 0) {
struct file *f = do_filp_open(dfd, tmp, &op); /* 2 */
if (IS_ERR(f)) {
put_unused_fd(fd);
fd = PTR_ERR(f);
} else {
fsnotify_open(f);
fd_install(fd, f); /* 3 */
}
}
putname(tmp);
return fd;
}(1) 获取一个空闲的fd
(2) 执行真正的open 流程, 是后面需要分析的重点
(3) open 成功后, 将fd 链接到当前进程的task_struct 结构体中
fd_install 的处理流程如下:
fs/file.c
void fd_install(unsigned int fd, struct file *file)
{
__fd_install(current->files, fd, file);
}
void __fd_install(struct files_struct *files, unsigned int fd,
struct file *file)
{
struct fdtable *fdt;
rcu_read_lock_sched();
if (unlikely(files->resize_in_progress)) {
rcu_read_unlock_sched();
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
BUG_ON(fdt->fd[fd] != NULL);
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file);
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
return;
}
/* coupled with smp_wmb() in expand_fdtable() */
smp_rmb();
fdt = rcu_dereference_sched(files->fdt); /* 1 */
BUG_ON(fdt->fd[fd] != NULL);
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file); /* 2 */
rcu_read_unlock_sched();
}(1) 找到进程对应的fdt table
(2) 将file结构体赋值到对应的fdt中
do_file_open 函数的处理如下, 主要调用了path_openat 函数去执行真正的open 流程:
fs/namei.c
do_sys_open->do_sys_openat2->do_filp_open
struct file *do_filp_open(int dfd, struct filename *pathname,
const struct open_flags *op)
{
struct nameidata nd;
int flags = op->lookup_flags;
struct file *filp;
set_nameidata(&nd, dfd, pathname);
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_RCU);
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ECHILD)))
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags);
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ESTALE)))
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_REVAL);
restore_nameidata();
return filp;
}path_openat: 执行open的核心流程
fs/namei.c
do_sys_open->do_sys_openat2->do_filp_open->path_openat
static struct file *path_openat(struct nameidata *nd,
const struct open_flags *op, unsigned flags)
{
struct file *file;
int error;
file = alloc_empty_file(op->open_flag, current_cred()); /* 1 */
if (IS_ERR(file))
return file;
if (unlikely(file->f_flags & __O_TMPFILE)) {
error = do_tmpfile(nd, flags, op, file);
} else if (unlikely(file->f_flags & O_PATH)) {
error = do_o_path(nd, flags, file);
} else {
const char *s = path_init(nd, flags);
while (!(error = link_path_walk(s, nd)) && /* 2 */
(s = open_last_lookups(nd, file, op)) != NULL) /* 3 */
;
if (!error)
error = do_open(nd, file, op); /* 4 */
terminate_walk(nd);
}
if (likely(!error)) {
if (likely(file->f_mode & FMODE_OPENED))
return file;
WARN_ON(1);
error = -EINVAL;
}
fput(file);
if (error == -EOPENSTALE) {
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU)
error = -ECHILD;
else
error = -ESTALE;
}
return ERR_PTR(error);
}(1) 申请 file 结构体, 并做初始化
(2) 找到路径的最后一个分量
(3) 对于最后一个分量进行处理, 这里面会去查找文件是否存在,如果不存在则看条件创建
(4) 执行open的最后步骤, 例如调用open 回调
下面分别针对上述的2,3,4 步做详细说明
link_path_walk
link_path_walk的内部实现有点复杂, 大致逻辑是,反复调用walk_component函数, 直到找到路径的最后一个分量。
open_last_lookups
open_lask_lookups 调用lookup_open函数执行 lookup and maybe create 操作
fs/namei.c
do_sys_open->do_sys_openat2->do_filp_open->path_openat->open_last_lookups->lookup_open
static struct dentry *lookup_open(struct nameidata *nd, struct file *file,
const struct open_flags *op,
bool got_write)
{
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry;
struct inode *dir_inode = dir->d_inode;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
struct dentry *dentry;
int error, create_error = 0;
umode_t mode = op->mode;
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(wq);
if (unlikely(IS_DEADDIR(dir_inode)))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
file->f_mode &= ~FMODE_CREATED;
dentry = d_lookup(dir, &nd->last); /* 1 */
for (;;) {
if (!dentry) {
dentry = d_alloc_parallel(dir, &nd->last, &wq);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return dentry;
}
if (d_in_lookup(dentry))
break;
error = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
if (likely(error > 0))
break;
if (error)
goto out_dput;
d_invalidate(dentry);
dput(dentry);
dentry = NULL;
}
if (dentry->d_inode) {
/* Cached positive dentry: will open in f_op->open */
return dentry;
}
/*
* Checking write permission is tricky, bacuse we don't know if we are
* going to actually need it: O_CREAT opens should work as long as the
* file exists. But checking existence breaks atomicity. The trick is
* to check access and if not granted clear O_CREAT from the flags.
*
* Another problem is returing the "right" error value (e.g. for an
* O_EXCL open we want to return EEXIST not EROFS).
*/
if (unlikely(!got_write))
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
if (open_flag & O_CREAT) {
if (open_flag & O_EXCL)
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
if (!IS_POSIXACL(dir->d_inode))
mode &= ~current_umask();
if (likely(got_write))
create_error = may_o_create(&nd->path, dentry, mode);
else
create_error = -EROFS;
}
if (create_error)
open_flag &= ~O_CREAT;
if (dir_inode->i_op->atomic_open) {
dentry = atomic_open(nd, dentry, file, open_flag, mode);
if (unlikely(create_error) && dentry == ERR_PTR(-ENOENT))
dentry = ERR_PTR(create_error);
return dentry;
}
if (d_in_lookup(dentry)) {
struct dentry *res = dir_inode->i_op->lookup(dir_inode, dentry,
nd->flags); /* 2 */
d_lookup_done(dentry);
if (unlikely(res)) {
if (IS_ERR(res)) {
error = PTR_ERR(res);
goto out_dput;
}
dput(dentry);
dentry = res;
}
}
/* Negative dentry, just create the file */
if (!dentry->d_inode && (open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
file->f_mode |= FMODE_CREATED;
audit_inode_child(dir_inode, dentry, AUDIT_TYPE_CHILD_CREATE);
if (!dir_inode->i_op->create) {
error = -EACCES;
goto out_dput;
}
error = dir_inode->i_op->create(dir_inode, dentry, mode,
open_flag & O_EXCL); /* 3 */
if (error)
goto out_dput;
}
if (unlikely(create_error) && !dentry->d_inode) {
error = create_error;
goto out_dput;
}
return dentry;
out_dput:
dput(dentry);
return ERR_PTR(error);
}(1) 从缓存中查找dentry
(2) 如果没有找到, 调用文件系统的lookup 方法进行查找
(3) 如果没有找到且O_CREAT, 调用文件系统的create方法进行创建
do_open
在找到对应的文件后,do_open对其进行最后的收尾工作。
fs/namei.c
do_sys_open->do_sys_openat2->do_filp_open->path_openat->do_open
static int do_open(struct nameidata *nd,
struct file *file, const struct open_flags *op)
{
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
bool do_truncate;
int acc_mode;
int error;
if (!(file->f_mode & (FMODE_OPENED | FMODE_CREATED))) {
error = complete_walk(nd);
if (error)
return error;
}
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CREATED))
audit_inode(nd->name, nd->path.dentry, 0);
if (open_flag & O_CREAT) {
if ((open_flag & O_EXCL) && !(file->f_mode & FMODE_CREATED))
return -EEXIST;
if (d_is_dir(nd->path.dentry))
return -EISDIR;
error = may_create_in_sticky(nd->dir_mode, nd->dir_uid,
d_backing_inode(nd->path.dentry));
if (unlikely(error))
return error;
}
if ((nd->flags & LOOKUP_DIRECTORY) && !d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))
return -ENOTDIR;
do_truncate = false;
acc_mode = op->acc_mode;
if (file->f_mode & FMODE_CREATED) {
/* Don't check for write permission, don't truncate */
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
acc_mode = 0;
} else if (d_is_reg(nd->path.dentry) && open_flag & O_TRUNC) {
error = mnt_want_write(nd->path.mnt);
if (error)
return error;
do_truncate = true;
}
error = may_open(&nd->path, acc_mode, open_flag); /* 1 */
if (!error && !(file->f_mode & FMODE_OPENED))
error = vfs_open(&nd->path, file); /* 2 */
if (!error)
error = ima_file_check(file, op->acc_mode);
if (!error && do_truncate)
error = handle_truncate(file);
if (unlikely(error > 0)) {
WARN_ON(1);
error = -EINVAL;
}
if (do_truncate)
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
return error;
}(1) map_open 里面会做一些权限检查, 比如检测文件系统是否是readonly
(2) 调用vfs_open执行最后的open 流程
fs/open.c
do_sys_open->do_sys_openat2->do_filp_open->path_openat->do_open->vfs_open
int vfs_open(const struct path *path, struct file *file)
{
file->f_path = *path;
return do_dentry_open(file, d_backing_inode(path->dentry), NULL);
}
static int do_dentry_open(struct file *f,
struct inode *inode,
int (*open)(struct inode *, struct file *))
{
static const struct file_operations empty_fops = {};
int error;
path_get(&f->f_path);
f->f_inode = inode;
f->f_mapping = inode->i_mapping;
f->f_wb_err = filemap_sample_wb_err(f->f_mapping);
f->f_sb_err = file_sample_sb_err(f); /* 1 */
if (unlikely(f->f_flags & O_PATH)) {
f->f_mode = FMODE_PATH | FMODE_OPENED;
f->f_op = &empty_fops;
return 0;
}
if (f->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE && !special_file(inode->i_mode)) {
error = get_write_access(inode);
if (unlikely(error))
goto cleanup_file;
error = __mnt_want_write(f->f_path.mnt);
if (unlikely(error)) {
put_write_access(inode);
goto cleanup_file;
}
f->f_mode |= FMODE_WRITER;
}
/* POSIX.1-2008/SUSv4 Section XSI 2.9.7 */
if (S_ISREG(inode->i_mode) || S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode))
f->f_mode |= FMODE_ATOMIC_POS;
f->f_op = fops_get(inode->i_fop); /* 2 */
if (WARN_ON(!f->f_op)) {
error = -ENODEV;
goto cleanup_all;
}
error = security_file_open(f);
if (error)
goto cleanup_all;
error = break_lease(locks_inode(f), f->f_flags);
if (error)
goto cleanup_all;
/* normally all 3 are set; ->open() can clear them if needed */
f->f_mode |= FMODE_LSEEK | FMODE_PREAD | FMODE_PWRITE;
if (!open)
open = f->f_op->open;
if (open) {
error = open(inode, f); /* 3 */
if (error)
goto cleanup_all;
}
f->f_mode |= FMODE_OPENED;
if ((f->f_mode & (FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE)) == FMODE_READ)
i_readcount_inc(inode);
if ((f->f_mode & FMODE_READ) &&
likely(f->f_op->read || f->f_op->read_iter))
f->f_mode |= FMODE_CAN_READ;
if ((f->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE) &&
likely(f->f_op->write || f->f_op->write_iter))
f->f_mode |= FMODE_CAN_WRITE;
f->f_write_hint = WRITE_LIFE_NOT_SET;
f->f_flags &= ~(O_CREAT | O_EXCL | O_NOCTTY | O_TRUNC);
file_ra_state_init(&f->f_ra, f->f_mapping->host->i_mapping);
/* NB: we're sure to have correct a_ops only after f_op->open */
if (f->f_flags & O_DIRECT) {
if (!f->f_mapping->a_ops || !f->f_mapping->a_ops->direct_IO)
return -EINVAL;
}
/*
* XXX: Huge page cache doesn't support writing yet. Drop all page
* cache for this file before processing writes.
*/
if ((f->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE) && filemap_nr_thps(inode->i_mapping))
truncate_pagecache(inode, 0);
return 0;
cleanup_all:
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(error > 0))
error = -EINVAL;
fops_put(f->f_op);
if (f->f_mode & FMODE_WRITER) {
put_write_access(inode);
__mnt_drop_write(f->f_path.mnt);
}
cleanup_file:
path_put(&f->f_path);
f->f_path.mnt = NULL;
f->f_path.dentry = NULL;
f->f_inode = NULL;
return error;
}(1) (2) 设置file结构体的一些成员
(3) 找到open 回调, 并执行
exfat 相关回调
下面以exfat 文件系统为例, 介绍一下open 流程中相关回调的具体实现。
open 流程中,涉及到三个具体回调: lookup, create, open
其中lookup 和 create 位于inode_operations, open
struct inode_operations {
****
struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, unsigned int);
int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, umode_t, bool);
****
}
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
*****
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
*****
}其中, exfat 没有实现open函数, 只实现了create和lookup 函数。
exfat_lookup
static struct dentry *exfat_lookup(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry,
unsigned int flags)
{
struct super_block *sb = dir->i_sb;
struct inode *inode;
struct dentry *alias;
struct exfat_dir_entry info;
int err;
loff_t i_pos;
mode_t i_mode;
mutex_lock(&EXFAT_SB(sb)->s_lock);
err = exfat_find(dir, &dentry->d_name, &info); /* 1 */
if (err) {
if (err == -ENOENT) {
inode = NULL;
goto out;
}
goto unlock;
}
i_pos = exfat_make_i_pos(&info);
inode = exfat_build_inode(sb, &info, i_pos); /* 2 */
err = PTR_ERR_OR_ZERO(inode);
if (err)
goto unlock;
i_mode = inode->i_mode;
alias = d_find_alias(inode);
/*
* Checking "alias->d_parent == dentry->d_parent" to make sure
* FS is not corrupted (especially double linked dir).
*/
if (alias && alias->d_parent == dentry->d_parent &&
!exfat_d_anon_disconn(alias)) {
/*
* Unhashed alias is able to exist because of revalidate()
* called by lookup_fast. You can easily make this status
* by calling create and lookup concurrently
* In such case, we reuse an alias instead of new dentry
*/
if (d_unhashed(alias)) {
WARN_ON(alias->d_name.hash_len !=
dentry->d_name.hash_len);
exfat_info(sb, "rehashed a dentry(%p) in read lookup",
alias);
d_drop(dentry);
d_rehash(alias);
} else if (!S_ISDIR(i_mode)) {
/*
* This inode has non anonymous-DCACHE_DISCONNECTED
* dentry. This means, the user did ->lookup() by an
* another name (longname vs 8.3 alias of it) in past.
*
* Switch to new one for reason of locality if possible.
*/
d_move(alias, dentry);
}
iput(inode);
mutex_unlock(&EXFAT_SB(sb)->s_lock);
return alias;
}
dput(alias);
out:
mutex_unlock(&EXFAT_SB(sb)->s_lock);
if (!inode)
exfat_d_version_set(dentry, inode_query_iversion(dir));
return d_splice_alias(inode, dentry); /* 3 */
unlock:
mutex_unlock(&EXFAT_SB(sb)->s_lock);
return ERR_PTR(err);
}lookup 函数的入参定义为:
dir: 父目录对应的inode
dentry: 所需要找的文件对应的dentry
返回值为所找文件对应的dentry。
在调用这个函数之前, 已经为子节点分配了dentry, 并将它关联到父目录的dentry, 但是它还没有被关联到inode。
这个函数应该在父目录中找到文件, 并分配inode, 关联到对用的dentry上。
(1) 根据name, 在父目录中,找对对应的entry
(2) 建立对应的inode
(3) 建立inode 和dentry之间的联系
其中, exfat_find的流程如下:
/* lookup a file */
static int exfat_find(struct inode *dir, struct qstr *qname,
struct exfat_dir_entry *info)
{
int ret, dentry, num_entries, count;
struct exfat_chain cdir;
struct exfat_uni_name uni_name;
struct super_block *sb = dir->i_sb;
struct exfat_sb_info *sbi = EXFAT_SB(sb);
struct exfat_inode_info *ei = EXFAT_I(dir);
struct exfat_dentry *ep, *ep2;
struct exfat_entry_set_cache *es;
if (qname->len == 0)
return -ENOENT;
/* check the validity of directory name in the given pathname */
ret = exfat_resolve_path_for_lookup(dir, qname->name, &cdir, &uni_name);
if (ret)
return ret;
num_entries = exfat_calc_num_entries(&uni_name);
if (num_entries < 0)
return num_entries;
/* check the validation of hint_stat and initialize it if required */
if (ei->version != (inode_peek_iversion_raw(dir) & 0xffffffff)) {
ei->hint_stat.clu = cdir.dir;
ei->hint_stat.eidx = 0;
ei->version = (inode_peek_iversion_raw(dir) & 0xffffffff);
ei->hint_femp.eidx = EXFAT_HINT_NONE;
}
/* search the file name for directories */
dentry = exfat_find_dir_entry(sb, ei, &cdir, &uni_name,
num_entries, TYPE_ALL); /* 1 */
if (dentry < 0)
return dentry; /* -error value */
info->dir = cdir;
info->entry = dentry;
info->num_subdirs = 0;
es = exfat_get_dentry_set(sb, &cdir, dentry, ES_2_ENTRIES);
if (!es)
return -EIO;
ep = exfat_get_dentry_cached(es, 0);
ep2 = exfat_get_dentry_cached(es, 1);
info->type = exfat_get_entry_type(ep); /* 2 */
info->attr = le16_to_cpu(ep->dentry.file.attr);
info->size = le64_to_cpu(ep2->dentry.stream.valid_size);
if ((info->type == TYPE_FILE) && (info->size == 0)) {
info->flags = ALLOC_NO_FAT_CHAIN;
info->start_clu = EXFAT_EOF_CLUSTER;
} else {
info->flags = ep2->dentry.stream.flags;
info->start_clu =
le32_to_cpu(ep2->dentry.stream.start_clu);
}
exfat_get_entry_time(sbi, &info->crtime,
ep->dentry.file.create_tz,
ep->dentry.file.create_time,
ep->dentry.file.create_date,
ep->dentry.file.create_time_cs);
exfat_get_entry_time(sbi, &info->mtime,
ep->dentry.file.modify_tz,
ep->dentry.file.modify_time,
ep->dentry.file.modify_date,
ep->dentry.file.modify_time_cs);
exfat_get_entry_time(sbi, &info->atime,
ep->dentry.file.access_tz,
ep->dentry.file.access_time,
ep->dentry.file.access_date,
0);
exfat_free_dentry_set(es, false);
if (ei->start_clu == EXFAT_FREE_CLUSTER) {
exfat_fs_error(sb,
"non-zero size file starts with zero cluster (size : %llu, p_dir : %u, entry : 0x%08x)",
i_size_read(dir), ei->dir.dir, ei->entry);
return -EIO;
}
if (info->type == TYPE_DIR) {
exfat_chain_set(&cdir, info->start_clu,
EXFAT_B_TO_CLU(info->size, sbi), info->flags);
count = exfat_count_dir_entries(sb, &cdir);
if (count < 0)
return -EIO;
info->num_subdirs = count + EXFAT_MIN_SUBDIR;
}
return 0;
}从逻辑上讲, 这个函数要做的事情,应该是遍历这个父目录的cluster, 根据name找到匹配的那个entry。
(1) 根据name找到对应的entry
(2) entry中记录的相关信息记录到struct exfat_dir_entry *info 这个结构体中
exfat_create
static int exfat_create(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry, umode_t mode,
bool excl)
{
struct super_block *sb = dir->i_sb;
struct inode *inode;
struct exfat_chain cdir;
struct exfat_dir_entry info;
loff_t i_pos;
int err;
mutex_lock(&EXFAT_SB(sb)->s_lock);
exfat_set_volume_dirty(sb);
err = exfat_add_entry(dir, dentry->d_name.name, &cdir, TYPE_FILE,
&info); /* 1 */
exfat_clear_volume_dirty(sb);
if (err)
goto unlock;
inode_inc_iversion(dir);
dir->i_ctime = dir->i_mtime = current_time(dir);
if (IS_DIRSYNC(dir))
exfat_sync_inode(dir);
else
mark_inode_dirty(dir);
i_pos = exfat_make_i_pos(&info);
inode = exfat_build_inode(sb, &info, i_pos); /* 2 */
err = PTR_ERR_OR_ZERO(inode);
if (err)
goto unlock;
inode_inc_iversion(inode);
inode->i_mtime = inode->i_atime = inode->i_ctime =
EXFAT_I(inode)->i_crtime = current_time(inode);
exfat_truncate_atime(&inode->i_atime);
/* timestamp is already written, so mark_inode_dirty() is unneeded. */
d_instantiate(dentry, inode); /* 3 */
unlock:
mutex_unlock(&EXFAT_SB(sb)->s_lock);
return err;
}exfat_create用于在目录下创建文件。 第一个参数为目录对应的inode, 第二个参数为需要创建的文件对应的dentry。
这个函数应该做的是, 在文件系统中创建一个新的文件, 并建立inode, 关联到对应的dentry上。
(1) 在目录中添加一个entry
(2) 建立inode
(3) 管理inode和denty
其中exfat_add_entry的主要流程如下:
static int exfat_add_entry(struct inode *inode, const char *path,
struct exfat_chain *p_dir, unsigned int type,
struct exfat_dir_entry *info)
{
int ret, dentry, num_entries;
struct super_block *sb = inode->i_sb;
struct exfat_sb_info *sbi = EXFAT_SB(sb);
struct exfat_uni_name uniname;
struct exfat_chain clu;
int clu_size = 0;
unsigned int start_clu = EXFAT_FREE_CLUSTER;
ret = exfat_resolve_path(inode, path, p_dir, &uniname);
if (ret)
goto out;
num_entries = exfat_calc_num_entries(&uniname);
if (num_entries < 0) {
ret = num_entries;
goto out;
}
/* exfat_find_empty_entry must be called before alloc_cluster() */
dentry = exfat_find_empty_entry(inode, p_dir, num_entries); /* 1 */
if (dentry < 0) {
ret = dentry; /* -EIO or -ENOSPC */
goto out;
}
if (type == TYPE_DIR) {
ret = exfat_alloc_new_dir(inode, &clu);
if (ret)
goto out;
start_clu = clu.dir;
clu_size = sbi->cluster_size;
}
/* update the directory entry */
/* fill the dos name directory entry information of the created file.
* the first cluster is not determined yet. (0)
*/
ret = exfat_init_dir_entry(inode, p_dir, dentry, type,
start_clu, clu_size); /* 2 */
if (ret)
goto out;
ret = exfat_init_ext_entry(inode, p_dir, dentry, num_entries, &uniname);
if (ret)
goto out;
info->dir = *p_dir;
info->entry = dentry;
info->flags = ALLOC_NO_FAT_CHAIN;
info->type = type;
if (type == TYPE_FILE) {
info->attr = ATTR_ARCHIVE;
info->start_clu = EXFAT_EOF_CLUSTER;
info->size = 0;
info->num_subdirs = 0;
} else {
info->attr = ATTR_SUBDIR;
info->start_clu = start_clu;
info->size = clu_size;
info->num_subdirs = EXFAT_MIN_SUBDIR;
}
memset(&info->crtime, 0, sizeof(info->crtime));
memset(&info->mtime, 0, sizeof(info->mtime));
memset(&info->atime, 0, sizeof(info->atime));
out:
return ret;
}(1) 在目录中找到一个空闲的entry。这个里面会去遍历整个目录的cluster, 直到找到没有使用的entry
(2) 根据找到的entry, 初始化相关的元数据