文章目录
- 涉及float和double的问题:
- 它们的存储方式:
- 有效位?
- 链式结构
涉及float和double的问题:
它们的存储方式:

它们会分成小数部分和指数部分分别存储。小数部分的有效位数越多,精度就越高,指数部分占位越多,能表示的数值范围越大。
- 一般float是4个字节,double是8个字节。
- 一般float的精度比double的大一些。
- double的数值表示范围远远大于float。
- 该结论来源于谭浩强《C语言设计》的例子。
有效位?
[来源于百度百科]从一个数的左边第一个非0数字起,到末位数字止,所有的数字都是这个数的有效数字。
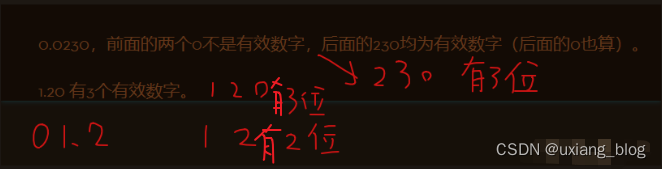
问:float的有效位数是六位,指的是小数点之后的六位还是包括小数点前的数总共六位?
答:float的有效位数指的是小数点后的六位,不包括符号位的数字。
链式结构
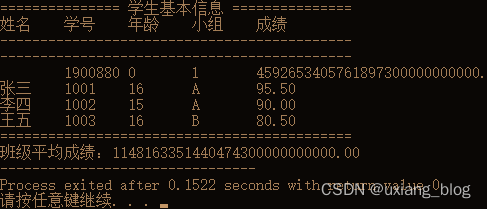
定义一个学生结构体,并创建一个链表用于保存一个班级所有学生的基本信息,最后输出所有学生基本信息,以及班级的学生平均成绩。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Student
{
char *name;
int id;
unsigned int age;
char group;
float score;
struct Student *next;
} Student, *M_Class;
M_Class init_class()
{
M_Class head;
head = (Student *)malloc(sizeof(Student));
if (!head)
return NULL;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void insert_student(M_Class cls, char *name, int id, unsigned int age, char group, float score)
{
M_Class p;
p = (Student *)malloc(sizeof(Student));
p->name = name, p->id = id, p->age = age, p->group = group, p->score = score;
p->next = cls->next;
cls->next = p;
}
void print_class(const M_Class cls)
{
M_Class prt = NULL;
float total = 0, average = 0;
int num_stu = 0;
printf("=============== 学生基本信息 ===============\n");
printf("姓名\t学号\t年龄\t小组\t成绩\n");
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
for (prt = cls; prt; prt = prt->next)
{
printf("%s\t%d\t%d\t%c\t%.2f\n",
prt->name, prt->id, prt->age, prt->group, prt->score);
total += prt->score;
++num_stu;
}
printf("============================================\n");
average = total / num_stu;
printf("班级平均成绩:%.2f", average);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
M_Class cls = init_class();
insert_student(cls, "王五", 1003, 16, 'B', 80.50);
insert_student(cls, "李四", 1002, 15, 'A', 90.00);
insert_student(cls, "张三", 1001, 16, 'A', 95.50);
print_class(cls);
return 0;
}