代码随想录算法训练营day60 | 84.柱状图中最大的矩形
- 84.柱状图中最大的矩形
- 解法一:单调栈
- 解法二:暴力双指针(会超时)
- 解法三:优化双指针
- 总结
最后一天打卡留念!
84.柱状图中最大的矩形
教程视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ns4y1o7uB
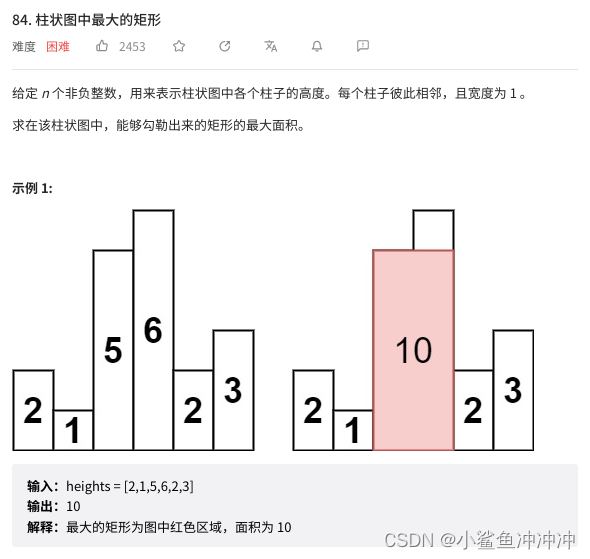
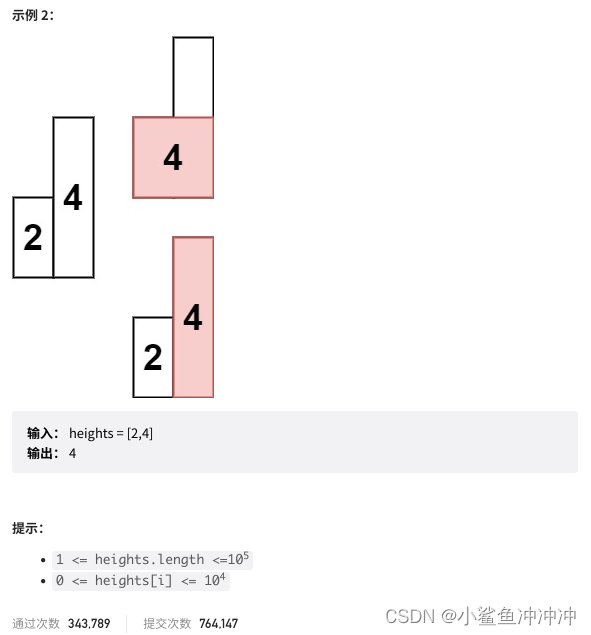
包含索引i中部分面积的最大矩形面积取决于该索引两侧第一个小于height[i]的值,以及这两个索引之间的距离。
因此本题需要找到索引两侧第一个小于height[i]的值,适合用单调栈来解决。
解法一:单调栈
因为本题是要找每个柱子左右两边第一个小于该柱子的柱子,从栈头(元素从栈头弹出)到栈底的顺序应该是从大到小的顺序!
栈顶决定了最大面积的高度,和栈顶的下一个元素以及要入栈的三个元素决定了最大面积的宽度。
分析清楚如下三种情况:
情况一:当前遍历的元素heights[i]大于栈顶元素heights[stack.peek()]的情况
情况二:当前遍历的元素heights[i]等于栈顶元素heights[stack.peek()]的情况
情况三:当前遍历的元素heights[i]小于栈顶元素heights[stack.peek()]的情况
【注意】
为了保证一定存在左边界,需要再数组开头加个0;
为了保证一定存在右边界,需要再数组末尾加个0,这样才能保证对每个数值都计算对应最大面积(即最后弹出所有元素)。
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
// 数组扩容,在头和尾各加入一个元素0
int [] newHeights = new int[heights.length + 2];
newHeights[0] = 0;
newHeights[newHeights.length - 1] = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < heights.length; index++){
newHeights[index + 1] = heights[index];
}
int result = 0;
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(0);
for(int i=1;i<newHeights.length;i++){
if(newHeights[i]>newHeights[stack.peek()]){
stack.push(i);
}else if(newHeights[i]==newHeights[stack.peek()]){
stack.pop();
stack.push(i);
}else{
while(!stack.isEmpty() && newHeights[i]<newHeights[stack.peek()]){
int mid = stack.pop();
if(!stack.isEmpty()){
int left = stack.peek();
result = Math.max(result, newHeights[mid]*(i-left-1));
}
}
stack.push(i);
}
}
return result;
}
}
//精简版
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int[] newHeight = new int[heights.length + 2];
System.arraycopy(heights, 0, newHeight, 1, heights.length);
newHeight[heights.length+1] = 0;
newHeight[0] = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(0);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < newHeight.length; i++) {
while (newHeight[i] < newHeight[stack.peek()]) {
int mid = stack.pop();
int w = i - stack.peek() - 1;
int h = newHeight[mid];
res = Math.max(res, w * h);
}
stack.push(i);
}
return res;
}
}
解法二:暴力双指针(会超时)
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int result=0;
for(int i=0;i<heights.length;i++){
int left=i-1;
while(left>=0){
if(heights[left]>heights[i])continue;
left--;
}
if(left==-1)left=0;
int right=i+1;
while(right<heights.length){
if(heights[right]>heights[i])continue;
right++;
}
if(right==heights.length)right=heights.length-1;
result=Math.max(result, (right-left-1)*heights[i]);
}
return result;
}
}
解法三:优化双指针
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int length = heights.length;
int[] leftMin = new int[length];
int[] rightMin = new int[length];
// 记录左边第一个小于该柱子的下标
leftMin[0] = -1 ;
for(int i=1;i<length;i++){
int temp=i-1;
while(temp>=0 && heights[temp]>=heights[i]){// 这里不断向左寻找的过程
temp=leftMin[temp];
}
leftMin[i]=temp;
}
// 记录每个柱子右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
rightMin[length-1]=length;
for(int i=length-2;i>=0;i--){
int temp=i+1;
while(temp<length && heights[temp]>=heights[i]){// 这里不断向左寻找的过程
temp=rightMin[temp];
}
rightMin[i]=temp;
}
// 求和
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int sum = heights[i] * (rightMin[i] - leftMin[i] - 1);
result = Math.max(sum, result);
}
return result;
}
}
总结
单调栈首先需要考虑栈内是递增还是递减,找左右第一个大于当前的元素用递增,找小于的用递减。
第二步是考虑要入栈的元素、栈顶元素三种关系下的处理逻辑。
如果要求两侧元素的话还需要考虑栈顶下一个元素,同时需要考虑首尾加0来处理边界问题。