一个多功能(聚合)查询接口,实现模糊、分页、主键、排序以及多条件查询
前言
写的啰嗦了点,看效果请直接忽略中间,直接看后半部分。
引个流,公众号:小简聊开发
概念
瞎编的名字,哈哈哈,我就勉强称之为聚合查询吧,不知道概念符不符合。
大家好,我是小简,很久没写文章了,确实是太忙了,今天我异想天开(其实也有很多类似的实现,只不过没去封装)的想去实现一个查询接口,不同条件不同查询的功能,简单的玩玩,如果大家有更好的思路或者见解,可以评论区互动一下,我很菜,还请理解,大佬勿喷。
在日常开发中,我们基本上是使用RESTful接口,也就是一个接口对应一个功能,这很方便前端开发的对接,具体优势我想我就不必说了,大家都在使用。
但是RESTful如果功能过多,对应的接口也会随之增多,比如后台的查询接口和前台可能数据有区别需要额外写一个,可能前台查询数据某一个要模糊查询,某一个又要走主键查询,有的又是多条件查询。
那我就在想,要不试试一个查询接口,聚合N个实现?不同数据去不同实现然后不同拼合。
那其实这时候,GraphQL这个玩意,其实就很符合我的预想,这玩意的接口查询就是一个接口实现的,大概意思和大致想法都是一样的。
但是GraphQL的开发和使用复杂度要高一些,而且我还是喜欢RESTful一些,这里不做过多介绍与对比,有兴趣可以前往浏览器搜索一些,了解了解。
预想
那该怎么去实现呢?我的项目使用的是MyBatisPlus作为ORM框架,每一个实体都是去映射数据库表的,我要想这一个功能方便通用,那我肯定要去进行部分封装的。
首先考虑一下目前项目理想状态:
- 实体映射数据库
- 数据库字段规范的采用蛇形命名,无一例外
- 实体类采用驼峰命名映射,无一例外
这种情况下,我只需要通过反射,将一个传过来的实体类的字段从驼峰转换为蛇形命名,作为查询条件的Key,也就是数据库字段名。
然后获取对应的值,作为条件拼接,然后将查询条件对象丢到MyBatisPlus的service里面就可以了。
那么…开干!
查询条件拼接
我们MP是使用QueryWrapper来构建条件查询对象的,总共有四种情况:
- 基本查询条件:
queryWrapper.eq()- 模糊查询条件:
queryWrapper.like()- 排序查询条件:
queryWrapper.orderByXXX()
至于主键查询,我预想是创建一个注解作为标识,如果在逻辑处理时候发现主键标识注解的字段值不为空,我就直接抛弃所有其他条件,直接走主键查询,ById。
但是因为时间原因,我就没去具体实现了。
获取对象字段与值
-
先通过反射获取对象所有属性并遍历。
-
如果属性值不为
null就拼接。 -
使用
Hutool中的StrUtil.toUnderlineCase将属性名称转换蛇形。
拼接条件
代码如下:
/**
* 聚合查询对象拼接
*
* @param queries 查询对象
* @param obj 聚合查询属性对象
* @return 查询对象
*/
public static <Q> QueryWrapper<Q> splicingQueries(QueryWrapper<Q> queries, Object obj) {
Field[] declaredFields = obj.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
String underlineCase = StrUtil.toUnderlineCase(field.getName());
try {
if (field.get(obj) != null) {
queries.eq(underlineCase, field.get(obj));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return queries;
}
大概代码就是这样的,然后我给了个泛型,为了约束查询对象的类型。
那有人就说了:“那这样,模糊查询怎么办?排序怎么办?分页怎么办?”
哎哎哎,别急嘛,且听我娓娓道来。
拼接模糊
同理,去实现这个模糊查询的拼接方法封装。
/**
* 模糊查询对象拼接
*
* @param queries 查询对象
* @param obj 模糊查询属性对象
* @return 查询对象
*/
public static <Q> QueryWrapper<Q> splicingFuzzyQueries(QueryWrapper<Q> queries, Object obj) {
Field[] declaredFields = obj.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
String underlineCase = StrUtil.toUnderlineCase(field.getName());
try {
if (field.get(obj) != null) {
queries.like(underlineCase, field.get(obj));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return queries;
}
拼接排序
/**
* 排序
*
* @param wrapper 查询对象
* @param sortField 排序字段
* @param sortType 排序类型
*/
private static <Q> void applySort(QueryWrapper<Q> wrapper, String sortField, int sortType) {
String field = StrUtil.toUnderlineCase(sortField);
if (sortType == 1) {
wrapper.orderByDesc(field);
} else {
wrapper.orderByAsc(field);
}
}
这里其实可以优化sortType为枚举,不过…嘿嘿,我比较懒,算了算了吧。
分页实现
分页先留在后面了,客官先往下看。
逻辑处理
到目前,功能的方法封装好了,整理一下业务的逻辑。
在排除主键(没时间写啦)查询的情况下,逻辑总结如下:
如果存在绝对查询条件情况,如:ID查询、手机号查询、邮箱查询,直接性查询,就不拼接模糊查询了。
然后,基本查询条件,可以与绝对条件查询互补,也可以与模糊查询条件互补。
对于模糊查询,如果没有绝对查询条件的情况下,才会去拼接,模糊可与基本条件互补。
对于排序条件,只要数据存在就需要拼接,并且如果排序方式为
null,默认升序。对于分页条件,我设置的是必传项,并且没去设置默认值(懒…)。
那将这个逻辑串联起来,就可以实现一个通用方法。
但是!!!
在实现这个方法之前,我如何区分数据是要模糊还是基本条件或者又是绝对查询条件?
所以,我们需要先封装一个实体类,这个实体我们可能每一个对象都有自己不一样的属性,所以我们不能写死,直接泛化即可。
实体封装
先看我的注释,截个图:
再贴所有的代码:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2023. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
* Morbi non lorem porttitor neque feugiat blandit. Ut vitae ipsum eget quam lacinia accumsan.
* Etiam sed turpis ac ipsum condimentum fringilla. Maecenas magna.
* Proin dapibus sapien vel ante. Aliquam erat volutpat. Pellentesque sagittis ligula eget metus.
* Vestibulum commodo. Ut rhoncus gravida arcu.
* © JanYork 2023年6月2日 23点37分
*/
/**
* <p>
* 泛型说明:
* <ul>
* <li>T:直接性查询条件对象</li>
* <li>C:基本查询条件对象</li>
* <li>R:模糊查询条件对象</li>
* <li>泛型对象可以为空,为空时不进行查询</li>
* <li>泛型对象必须是一个Bean</li>
* <li>泛型对象的属性<b>必须是基本数据类型</b></li>
* </ul>
* </p>
*
* @author JanYork
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2023/06/02
* @description 聚合查询对象
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Data
@ApiModel(value = "聚合查询对象")
public class AggregateQueries<T, C, R> {
/**
* 直接性查询条件对象(T是一个Bean)
* <p>
* 直接性查询对象如果存在,<b>模块查询条件直接失效</b>,场景如:<br/> <b>ID直接查询</b>、<b>手机号直接查询</b>
* </p>
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "直接性查询条件对象")
private T queries;
/**
* 分页信息对象
* <p>
* 分页对象包含分页信息,<b>分页信息必须存在</b>,场景如:<br/> <b>分页查询</b>
* </p>
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "分页信息对象")
private PaginationDTO pagination;
/**
* 基本查询条件对象(C是一个Bean)
* <p>
* 基本查询对象与直接性查询可以同时存在,<b>基本查询条件对象的查询条件会与直接性查询条件对象的查询条件进行组合</b>,场景如:<br/>
* <b>直接性查询ID为10001的用户</b>,<b>基本性查询状态为true的用户</b>,结合后的查询条件为:<br/>
* <b>查询ID为10001且状态为true的用户</b>
* </p>
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "基本查询条件对象")
private C condition;
/**
* 模糊查询条件对象(R是一个Bean)
* <p>
* 模糊查询与直接性条件查询互斥,与基本查询条件对象互补,<b>模糊查询条件对象的查询条件会与基本查询条件对象的查询条件进行组合</b>,场景如:<br/>
* <b>基本性查询状态为true的用户</b>,<b>模糊性查询用户名为张三的用户</b>,结合后的查询条件为:<br/>
* <b>查询状态为true且用户名包含张三的用户</b>
* </p>
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "模糊查询条件对象")
private R fuzzyQueries;
/**
* 排序字段
* <p>
* 排序字段可以为空,为空时不进行排序
* </p>
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "排序字段")
private String sortField;
/**
* 排序方式
* <p>
* 排序方式可以为空,为空时默认为升序,0:升序,1:降序
* </p>
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "排序方式")
private Integer sortType;
/**
* 是否存在直接性查询条件对象
*
* @return boolean true:存在,false:不存在
*/
public boolean hasQueries() {
return queries != null;
}
/**
* 是否存在分页信息对象
*
* @return boolean true:存在,false:不存在
*/
public boolean hasPagination() {
return pagination != null;
}
/**
* 是否存在基本查询条件对象
*
* @return boolean true:存在,false:不存在
*/
public boolean hasCondition() {
return condition != null;
}
/**
* 是否存在模糊查询条件对象
*
* @return boolean true:存在,false:不存在
*/
public boolean hasFuzzyQueries() {
return fuzzyQueries != null;
}
/**
* 是否存在排序字段
*
* @return boolean true:存在,false:不存在
*/
public boolean hasSortField() {
return sortField != null;
}
/**
* 是否存在排序方式
*
* @return boolean true:存在,false:不存在
*/
public boolean hasSortType() {
return sortType != null;
}
}
这里面有一个PaginationDTO,是一个分页信息对象,我也贴出来:
/**
* @author JanYork
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2023/06/02
* @description 分页DTO
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Data
@ApiModel(value = "分页数据对象")
public class PaginationDTO {
/**
* 页码
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "页码")
private Integer page;
/**
* 每页大小
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "每页大小")
private Integer size;
}
那这样我们就封装成实体类了。
三个泛型?
三个泛型对象其实我在注释中已经说了:
泛型说明:
- T:直接性查询条件对象
- C:基本查询条件对象
- R:模糊查询条件对象
- 泛型对象可以为空,为空时不进行查询(不拼接)
- 泛型对象必须是一个Bean(实体),并且实体必须映射数据表,字段必须规范命名
- 泛型对象的属性必须是基本数据类型
然后对于这三个泛型,我们要创建不同的实体(麻烦归麻烦,规范还是要),所以,接下来看看我怎么用的。
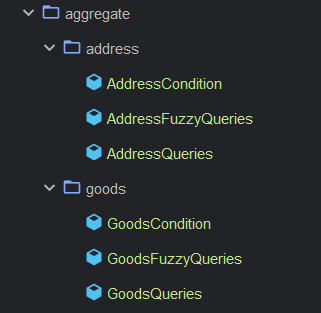
我这里一个地址聚合查询和一个商品聚合查询。
构建实体?
Condition结尾的是基本查询条件对象,如:
/**
* @author JanYork
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2023/06/02
* @description 地址基本条件查询对象
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Data
@ApiModel("(地址)基本条件查询对象")
public class AddressCondition {
/**
* 省
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "省")
private String province;
/**
* 城市
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "城市")
private String city;
/**
* 县/区
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "县/区")
private String district;
}
这里面的条件,如果存在,那就必定会拼接,与绝对查询条件或者模糊查询条件互补。
FuzzyQueries结尾的是模糊查询条件,如:
/**
* @author JanYork
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2023/06/02
* @description 地址模糊查询对象
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Data
@ApiModel("(地址)模糊查询对象")
public class AddressFuzzyQueries {
/**
* 用户手机号
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户手机号(可模糊)")
private String phone;
/**
* 用户姓名
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户姓名(可模糊)")
private String name;
/**
* 详细地址
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "详细地址(可模糊)")
private String address;
}
这个实体里面的条件与绝对查询条件互斥,且优先级低于绝对查询条件!
Queries结尾的是绝对查询条件,如:
/**
* @author JanYork
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2023/06/02
* @description 地址直接性查询对象
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Data
@ApiModel("(地址)直接性查询对象")
public class AddressQueries {
/**
* 用户ID
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户ID")
private Long userId;
/**
* 用户手机号
*/
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户手机号")
private String phone;
}
这个实体条件优先级最高,如果存在必定拼接。
然后三个实体都有了,我们还需要将上面逻辑处理段落总结的逻辑串联起来,实现一个通用方法。
通用方法实现
我们开始已经封装了模糊、条件、排序的拼接方法,所以我们可以直接调用封装好的方法去实现拼接的逻辑处理。
直接丢代码了:
/**
* 聚合查询对象拼接
*
* @param queries 查询对象
* @param aggregate 聚合查询对象
* @return {@link QueryWrapper}<{@link Q}>
*/
public static <Q, T, C, R> QueryWrapper<Q> splicingAggregateQueries(QueryWrapper<Q> queries, AggregateQueries<T, C, R> aggregate) {
if (aggregate.hasQueries()) {
splicingQueries(queries, aggregate.getQueries());
}
if (aggregate.hasCondition()) {
splicingQueries(queries, aggregate.getCondition());
}
if (aggregate.hasFuzzyQueries() && !aggregate.hasQueries()) {
splicingFuzzyQueries(queries, aggregate.getFuzzyQueries());
}
if (aggregate.hasSortField()) {
aggregate.setSortType(aggregate.hasSortType() ? aggregate.getSortType() : 0);
applySort(queries, aggregate.getSortField(), aggregate.getSortType());
}
return queries;
}
这个通用方法,主要就是实现通用性和逻辑贯穿处理,这里没写过多注释,aggregate.hasXXXX方法是判断是否存在条件实体对象或者字段值,逻辑还需要请各位亲自捋一下了,毕竟也就几个if。
使用聚合方法与分页操作
先看代码后讲解:
/**
* 聚合查询
*
* @param aggregate 聚合查询对象
* @return {@link ApiResponse}<{@link List}<{@link Address}>>
*/
@PostMapping("/get")
public ApiResponse<List<Address>> get(@RequestBody AggregateQueries<AddressQueries, AddressCondition, AddressFuzzyQueries> aggregate) {
if (!aggregate.hasPagination()) {
return ApiResponse.fail(null);
}
PaginationDTO pagination = aggregate.getPagination();
QueryWrapper<Address> wrapper = AggregateQueriesUtil.splicingAggregateQueries(new QueryWrapper<>(), aggregate);
Page<Address> page = new Page<>(pagination.getPage(), pagination.getSize());
return ApiResponse.ok(
addressService.page(page, wrapper).getRecords()
);
}
这里,接口接收的参数就是映射我们封装的聚合条件对象:AggregateQueries<AddressQueries, AddressCondition, AddressFuzzyQueries> aggregate了。
这三个泛型就是我们对于不同数据库实体的不同条件字段封装的不同POJO。
分页
先前说了,分页是必须的,所以我们判断一下,分页对象不存在直接返回失败。
if (!aggregate.hasPagination()) {
return ApiResponse.fail(null);
}
如果存在我们获取分页信息,利用MP的分页插件,直接进行分页查询操作,这个插件就不多说了。
处理
这里我们直接利用我们封装好的通用方法去获取拼接条件后的QueryWrapper对象:
QueryWrapper<Address> wrapper = AggregateQueriesUtil.splicingAggregateQueries(new QueryWrapper<>(), aggregate);
因为是后台管理端的数据,我就懒得去Bean拷贝到VO对象了,直接就是实体返回。
效果演示
调试工具用什么好呢?上postman吧。

数据库数据展示
1000 1658741489930473472 江西省 南昌市 南昌县 江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫 16688880818 小简 28.68333 115.88333 0
1001 1658741489930473472 江西省 南市 南昌县 江西省南昌市南昌县东湖区ABCD6栋 16670080818 小简 28.68333 115.88333 0
1002 1658741489930473472 江西省 昌市 南昌县 江西省南昌市南昌县CCC写字楼 16676080818 小简 28.68333 115.88333 1

测试JSON数据:
{
"queries": {
"phone":"16688880818"
},
"pagination": {
"page": 1,
"size": 3
},
"condition":{
"city":"南市"
},
"fuzzyQueries": {
"phone": "166",
"address": "CCC写字楼"
},
"sortField": "id",
"sortType": 1
}
绝对条件查询
数据:
{
"queries": {
"phone":"16688880818"
},
"pagination": {
"page": 1,
"size": 3
}
}
SQL日志:
SELECT id,user_id,province,city,district,address,phone,name,latitude,longitude,is_default FROM address WHERE (phone = ?) LIMIT ?
MP完整日志:
Creating a new SqlSession
SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@164276c] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active
JDBC Connection [com.alibaba.druid.proxy.jdbc.ConnectionProxyImpl@71237c20] will not be managed by Spring
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM address WHERE (phone = ?)
==> Parameters: 16688880818(String)
<== Columns: total
<== Row: 1
<== Total: 1
==> Preparing: SELECT id,user_id,province,city,district,address,phone,name,latitude,longitude,is_default FROM address WHERE (phone = ?) LIMIT ?
==> Parameters: 16688880818(String), 3(Long)
<== Columns: id, user_id, province, city, district, address, phone, name, latitude, longitude, is_default
<== Row: 1000, 1658741489930473472, 江西省, 南昌市, 南昌县, 江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫, 16688880818, 小简, 28.68333, 115.88333, 0
<== Total: 1
回调数据:
{
"code": 200,
"message": "success",
"data": [
{
"id": 1000,
"userId": 1658741489930473472,
"province": "江西省",
"city": "南昌市",
"district": "南昌县",
"address": "江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫",
"phone": "16688880818",
"name": "小简",
"latitude": "28.68333",
"longitude": "115.88333",
"isDefault": false
}
]
}
绝对+基本
数据:
{
"queries": {
"phone":"16688880818"
},
"pagination": {
"page": 1,
"size": 3
},
"condition":{
"city":"南昌市"
}
}
SQL日志:
SELECT id,user_id,province,city,district,address,phone,name,latitude,longitude,is_default FROM address WHERE (phone = ? AND city = ?) LIMIT ?
MP日志:
Creating a new SqlSession
SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@2e00c6c9] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active
JDBC Connection [com.alibaba.druid.proxy.jdbc.ConnectionProxyImpl@5e68f14e] will not be managed by Spring
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM address WHERE (phone = ? AND city = ?)
==> Parameters: 16688880818(String), 南昌市(String)
<== Columns: total
<== Row: 1
<== Total: 1
==> Preparing: SELECT id,user_id,province,city,district,address,phone,name,latitude,longitude,is_default FROM address WHERE (phone = ? AND city = ?) LIMIT ?
==> Parameters: 16688880818(String), 南昌市(String), 3(Long)
<== Columns: id, user_id, province, city, district, address, phone, name, latitude, longitude, is_default
<== Row: 1000, 1658741489930473472, 江西省, 南昌市, 南昌县, 江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫, 16688880818, 小简, 28.68333, 115.88333, 0
<== Total: 1
Closing non transactional SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@2e00c6c9]
回调数据:
{
"code": 200,
"message": "success",
"data": [
{
"id": 1000,
"userId": 1658741489930473472,
"province": "江西省",
"city": "南昌市",
"district": "南昌县",
"address": "江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫",
"phone": "16688880818",
"name": "小简",
"latitude": "28.68333",
"longitude": "115.88333",
"isDefault": false
}
]
}
模糊
数据:
{
"pagination": {
"page": 1,
"size": 3
},
"fuzzyQueries": {
"phone": "166"
// "address": "CCC写字楼"
}
}
SQL日志:
SELECT id,user_id,province,city,district,address,phone,name,latitude,longitude,is_default FROM address WHERE (phone LIKE ?) LIMIT ?
MP日志:
Creating a new SqlSession
SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@3646a7c1] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active
JDBC Connection [com.alibaba.druid.proxy.jdbc.ConnectionProxyImpl@3e66a291] will not be managed by Spring
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM address WHERE (phone LIKE ?)
==> Parameters: %166%(String)
<== Columns: total
<== Row: 3
<== Total: 1
==> Preparing: SELECT id,user_id,province,city,district,address,phone,name,latitude,longitude,is_default FROM address WHERE (phone LIKE ?) LIMIT ?
==> Parameters: %166%(String), 3(Long)
<== Columns: id, user_id, province, city, district, address, phone, name, latitude, longitude, is_default
<== Row: 1000, 1658741489930473472, 江西省, 南昌市, 南昌县, 江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫, 16688880818, 小简, 28.68333, 115.88333, 0
<== Row: 1001, 1658741489930473472, 江西省, 南市, 南昌县, 江西省南昌市南昌县东湖区ABCD6栋, 16670080818, 小简, 28.68333, 115.88333, 0
<== Row: 1002, 1658741489930473472, 江西省, 昌市, 南昌县, 江西省南昌市南昌县CCC写字楼, 16676080818, 小简, 28.68333, 115.88333, 1
<== Total: 3
Closing non transactional SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@3646a7c1]
回调数据:
{
"code": 200,
"message": "success",
"data": [
{
"id": 1000,
"userId": 1658741489930473472,
"province": "江西省",
"city": "南昌市",
"district": "南昌县",
"address": "江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫",
"phone": "16688880818",
"name": "小简",
"latitude": "28.68333",
"longitude": "115.88333",
"isDefault": false
},
{
"id": 1001,
"userId": 1658741489930473472,
"province": "江西省",
"city": "南市",
"district": "南昌县",
"address": "江西省南昌市南昌县东湖区ABCD6栋",
"phone": "16670080818",
"name": "小简",
"latitude": "28.68333",
"longitude": "115.88333",
"isDefault": false
},
{
"id": 1002,
"userId": 1658741489930473472,
"province": "江西省",
"city": "昌市",
"district": "南昌县",
"address": "江西省南昌市南昌县CCC写字楼",
"phone": "16676080818",
"name": "小简",
"latitude": "28.68333",
"longitude": "115.88333",
"isDefault": true
}
]
}
排序+模糊
数据:
{
"pagination": {
"page": 1,
"size": 3
},
"fuzzyQueries": {
"phone": "166"
},
"sortField": "id",
"sortType": 1
}
SQL日志:
SELECT id,user_id,province,city,district,address,phone,name,latitude,longitude,is_default FROM address WHERE (phone LIKE ?) ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT ?
MP日志:
Creating a new SqlSession
SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@26a0b246] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active
JDBC Connection [com.alibaba.druid.proxy.jdbc.ConnectionProxyImpl@3deaaebe] will not be managed by Spring
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM address WHERE (phone LIKE ?)
==> Parameters: %166%(String)
<== Columns: total
<== Row: 3
<== Total: 1
==> Preparing: SELECT id,user_id,province,city,district,address,phone,name,latitude,longitude,is_default FROM address WHERE (phone LIKE ?) ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT ?
==> Parameters: %166%(String), 3(Long)
<== Columns: id, user_id, province, city, district, address, phone, name, latitude, longitude, is_default
<== Row: 1002, 1658741489930473472, 江西省, 昌市, 南昌县, 江西省南昌市南昌县CCC写字楼, 16676080818, 小简, 28.68333, 115.88333, 1
<== Row: 1001, 1658741489930473472, 江西省, 南市, 南昌县, 江西省南昌市南昌县东湖区ABCD6栋, 16670080818, 小简, 28.68333, 115.88333, 0
<== Row: 1000, 1658741489930473472, 江西省, 南昌市, 南昌县, 江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫, 16688880818, 小简, 28.68333, 115.88333, 0
<== Total: 3
Closing non transactional SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@26a0b246]
回调数据:
{
"code": 200,
"message": "success",
"data": [
{
"id": 1002,
"userId": 1658741489930473472,
"province": "江西省",
"city": "昌市",
"district": "南昌县",
"address": "江西省南昌市南昌县CCC写字楼",
"phone": "16676080818",
"name": "小简",
"latitude": "28.68333",
"longitude": "115.88333",
"isDefault": true
},
{
"id": 1001,
"userId": 1658741489930473472,
"province": "江西省",
"city": "南市",
"district": "南昌县",
"address": "江西省南昌市南昌县东湖区ABCD6栋",
"phone": "16670080818",
"name": "小简",
"latitude": "28.68333",
"longitude": "115.88333",
"isDefault": false
},
{
"id": 1000,
"userId": 1658741489930473472,
"province": "江西省",
"city": "南昌市",
"district": "南昌县",
"address": "江西省南昌市南昌县万寿宫",
"phone": "16688880818",
"name": "小简",
"latitude": "28.68333",
"longitude": "115.88333",
"isDefault": false
}
]
}
其他效果
都可以自由组合,单排序、单分页、单模糊、排序+分页+模糊、排序+基本…
都是可以自由组合的,方法太多就不都去尝试了,大家也可以去试试,痛苦的封装也会带来一定的好处。
也可以在此基础上,去创造一些新鲜的玩法和业务实现,感谢大家阅读,下期再见啦!
我是小简,下期再会(不知道下期是多久了唉)。
尾述
为什么要去写一些七里八里的东东呢?
因为,创造性才是本质,我不希望被CRUD的工作丢失我的兴趣与活跃的思维。
我认为,赚钱的永远是思维和大脑,而非单纯的、一味的技术。