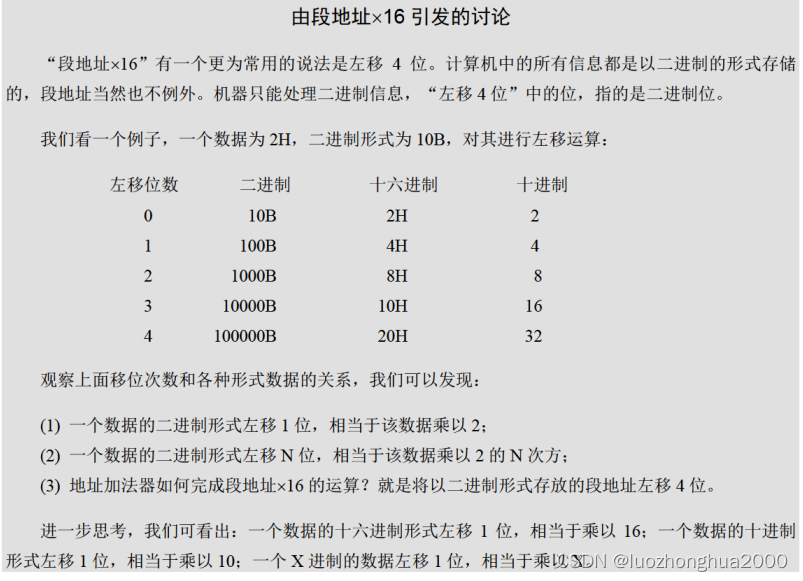
后端优化是指将一段时间内相机所有关键帧的位姿、内参、每个点3维坐标作为参数进行优化,得到最优的内、外参;利用的方法主要是Bundle Adjustment。
所谓Bundle Adjustment可以理解为从任意特征点发射出来的几束光线,它们会在几个相机的成像平面上变成像素或是检测到的特征点。如果我们调整各相机姿态和各特征点的空间位置,使得这些光线最终收束到相机光心,简称BA。
相机投影模型和BA代价函数
相机投影过程是从一个世界坐标系中的点p出发,把相机的内外参数和畸变考虑进来,最后投影成像素坐标。具体步骤:
世界坐标 -> 相机坐标系 -> 相机归一化坐标系 -> 成像平面归一化坐标系 -> 像素坐标系
转换方式:
除以Z方向距离
于是,整个过程构建出了观测方程,即
具体,这里的x指代此时相机的位姿,即外参R,t,对应的李群为T,李代数。y为路标,即三维点p,而z为观测数据,即
。将整体观测数据都考虑进行,得到如下代价函数:
对这个最小二乘进行求解,相当于对位姿和路标同时做了调整,也就是所谓的BA。这里的优化量可分为两部分,一部分是相机姿态、一部分是空间点;
于是,增加自变量增量:
最后将转化为线性方程:
基于ceres的计算代码,参看视觉slam十四讲:
#ifndef SnavelyReprojection_H
#define SnavelyReprojection_H
#include <iostream>
#include "ceres/ceres.h"
#include "rotation.h"
class SnavelyReprojectionError {
public:
SnavelyReprojectionError(double observation_x, double observation_y) : observed_x(observation_x),
observed_y(observation_y) {}
template<typename T>
bool operator()(const T *const camera,
const T *const point,
T *residuals) const {
// camera[0,1,2] are the angle-axis rotation
T predictions[2];
CamProjectionWithDistortion(camera, point, predictions);
residuals[0] = predictions[0] - T(observed_x);
residuals[1] = predictions[1] - T(observed_y);
return true;
}
// camera : 9 dims array
// [0-2] : angle-axis rotation
// [3-5] : translateion
// [6-8] : camera parameter, [6] focal length, [7-8] second and forth order radial distortion
// point : 3D location.
// predictions : 2D predictions with center of the image plane.
template<typename T>
static inline bool CamProjectionWithDistortion(const T *camera, const T *point, T *predictions) {
// Rodrigues' formula
T p[3];
AngleAxisRotatePoint(camera, point, p);
// camera[3,4,5] are the translation
p[0] += camera[3];
p[1] += camera[4];
p[2] += camera[5];
// Compute the center fo distortion
T xp = -p[0] / p[2];
T yp = -p[1] / p[2];
// Apply second and fourth order radial distortion
const T &l1 = camera[7];
const T &l2 = camera[8];
T r2 = xp * xp + yp * yp;
T distortion = T(1.0) + r2 * (l1 + l2 * r2);
const T &focal = camera[6];
predictions[0] = focal * distortion * xp;
predictions[1] = focal * distortion * yp;
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction *Create(const double observed_x, const double observed_y) {
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<SnavelyReprojectionError, 2, 9, 3>(
new SnavelyReprojectionError(observed_x, observed_y)));
}
private:
double observed_x;
double observed_y;
};
#endif // SnavelyReprojection.h
#include <iostream>
#include <ceres/ceres.h>
#include "common.h"
#include "SnavelyReprojectionError.h"
using namespace std;
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "usage: bundle_adjustment_ceres bal_data.txt" << endl;
return 1;
}
BALProblem bal_problem(argv[1]);
bal_problem.Normalize();
bal_problem.Perturb(0.1, 0.5, 0.5);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("initial.ply");
SolveBA(bal_problem);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("final.ply");
return 0;
}
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points();
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();
// Observations is 2 * num_observations long array observations
// [u_1, u_2, ... u_n], where each u_i is two dimensional, the x
// and y position of the observation.
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations();
ceres::Problem problem;
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) {
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function;
// Each Residual block takes a point and a camera as input
// and outputs a 2 dimensional Residual
cost_function = SnavelyReprojectionError::Create(observations[2 * i + 0], observations[2 * i + 1]);
// If enabled use Huber's loss function.
ceres::LossFunction *loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(1.0);
// Each observation corresponds to a pair of a camera and a point
// which are identified by camera_index()[i] and point_index()[i]
// respectively.
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * bal_problem.camera_index()[i];
double *point = points + point_block_size * bal_problem.point_index()[i];
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, camera, point);
}
// show some information here ...
std::cout << "bal problem file loaded..." << std::endl;
std::cout << "bal problem have " << bal_problem.num_cameras() << " cameras and "
<< bal_problem.num_points() << " points. " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Forming " << bal_problem.num_observations() << " observations. " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Solving ceres BA ... " << endl;
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::LinearSolverType::SPARSE_SCHUR;
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
std::cout << summary.FullReport() << "\n";
}基于g2o算法:
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel_impl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "common.h"
#include "sophus/se3.hpp"
using namespace Sophus;
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace std;
/// 姿态和内参的结构
struct PoseAndIntrinsics {
PoseAndIntrinsics() {}
/// set from given data address
explicit PoseAndIntrinsics(double *data_addr) {
rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(data_addr[0], data_addr[1], data_addr[2]));
translation = Vector3d(data_addr[3], data_addr[4], data_addr[5]);
focal = data_addr[6];
k1 = data_addr[7];
k2 = data_addr[8];
}
/// 将估计值放入内存
void set_to(double *data_addr) {
auto r = rotation.log();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i] = r[i];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i + 3] = translation[i];
data_addr[6] = focal;
data_addr[7] = k1;
data_addr[8] = k2;
}
SO3d rotation;
Vector3d translation = Vector3d::Zero();
double focal = 0;
double k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
};
/// 位姿加相机内参的顶点,9维,前三维为so3,接下去为t, f, k1, k2
class VertexPoseAndIntrinsics : public g2o::BaseVertex<9, PoseAndIntrinsics> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics() {}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = PoseAndIntrinsics();
}
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate.rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2])) * _estimate.rotation;
_estimate.translation += Vector3d(update[3], update[4], update[5]);
_estimate.focal += update[6];
_estimate.k1 += update[7];
_estimate.k2 += update[8];
}
/// 根据估计值投影一个点
Vector2d project(const Vector3d &point) {
Vector3d pc = _estimate.rotation * point + _estimate.translation;
pc = -pc / pc[2];
double r2 = pc.squaredNorm();
double distortion = 1.0 + r2 * (_estimate.k1 + _estimate.k2 * r2);
return Vector2d(_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[0],
_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[1]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
class VertexPoint : public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Vector3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoint() {}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
}
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate += Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
class EdgeProjection :
public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2d, VertexPoseAndIntrinsics, VertexPoint> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
virtual void computeError() override {
auto v0 = (VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *) _vertices[0];
auto v1 = (VertexPoint *) _vertices[1];
auto proj = v0->project(v1->estimate());
_error = proj - _measurement;
}
// use numeric derivatives
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "usage: bundle_adjustment_g2o bal_data.txt" << endl;
return 1;
}
BALProblem bal_problem(argv[1]);
bal_problem.Normalize();
bal_problem.Perturb(0.1, 0.5, 0.5);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("initial.ply");
SolveBA(bal_problem);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("final.ply");
return 0;
}
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points();
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();
// pose dimension 9, landmark is 3
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<9, 3>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
// use LM
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
/// build g2o problem
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations();
// vertex
vector<VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *> vertex_pose_intrinsics;
vector<VertexPoint *> vertex_points;
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *v = new VertexPoseAndIntrinsics();
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
v->setId(i);
v->setEstimate(PoseAndIntrinsics(camera));
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_pose_intrinsics.push_back(v);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
VertexPoint *v = new VertexPoint();
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
v->setId(i + bal_problem.num_cameras());
v->setEstimate(Vector3d(point[0], point[1], point[2]));
// g2o在BA中需要手动设置待Marg的顶点
v->setMarginalized(true);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_points.push_back(v);
}
// edge
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) {
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection;
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose_intrinsics[bal_problem.camera_index()[i]]);
edge->setVertex(1, vertex_points[bal_problem.point_index()[i]]);
edge->setMeasurement(Vector2d(observations[2 * i + 0], observations[2 * i + 1]));
edge->setInformation(Matrix2d::Identity());
edge->setRobustKernel(new g2o::RobustKernelHuber());
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(40);
// set to bal problem
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_pose_intrinsics[i];
auto estimate = vertex->estimate();
estimate.set_to(camera);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_points[i];
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k) point[k] = vertex->estimate()[k];
}
}