NGINX与Apache对比
- 轻量级,Nginx比apache 占用更少的内存及资源;
- 静态处理,Nginx 静态处理性能比 Apache 高 ;
- Nginx可以实现无缓存的反向代理加速,提高网站运行速度;
- Nginx的性能和可伸缩性不依赖于硬件,Apache依赖于硬件;
- Nginx支持热部署,启动速度迅速,可以在不间断服务的情况下,对软件版本或者配置进行升级;
- nginx(异步不阻塞)是异步进程,多个连接可以对应一个进程 ;apache是同步多进程,一个连接对应一个进程;
- Nginx高度模块化,编写模块相对简单,且组件比Apache少
- 高并发下nginx 能保持低资源低消耗高性能;
- Nginx 配置简洁, Apache配置复杂;
通俗的讲,就是
nginx 是轻量级web应用,apache 相比较则更重量
nginx 占用内存等资源更少
nginx 处理静态页面请求性能更好
nginx 模块配置相对简单,简洁,apache 则配置复杂
nginx 处理请求是异步非阻塞,apache 则是阻塞的
nginc 基于事件的web服务器, apache 是基于流程的web服务器
nginx 所有请求由一个线程处理,apache 单个线程处理单个请求
nginx 使用场景更多(web服务器,反向代理服务器与负载均衡,缓存服务器等)NGINX单台服务器可支持30000-50000个并发(面试题)
(实际上大约20000-30000。Apache只有几千不到10000,大概差2-3倍)
nginx 的最大并发能力怎么看?
worker_processes x worker_connections
(工作进程数,通常设置与cpu数量一致,或auto)* (每个worker进程能够处理的连接数)
并且需要设置NGINX的worker_rlimit_nofile(设置所有worker进程最大可以打开的文件数,匹配上worker_connections)
还需要配置系统的最大打开文件数
ulimit -n XXX(xxx为文件打开数量)(临时设置)
或vim /etc/security/limits.conf --> nofile 进程能够打开的文件数(文件描述符、文件句柄) (永久设置)
nginx 当前并发连接数怎么看?
方法1.开启 --with-http_stub_status_module 状态统计模块,配置文件 开启状态统计功能 stub_status on;
访问状态统计页面,看 Active connections:
方法2.netstat/ss -natp | grep nginx | grep -c ESTABLISHED
--------编译安装Nginx服务--------
1.关闭防火墙,将安装nginx所需软件包传到/opt目录下
nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz
关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld setenforce 0vim /etc/selinux/config disable 永久关闭selinux
2.安装依赖包
nginx的配置及运行需要pcre、zlib、openssl等软件包的支持,因此需要安装这些软件的开发包,以便提供相应的库和头文件。
yum -y install pcre-devel zlib-devel openssl-devel gcc gcc-c++ make
3.创建运行用户、组
Nginx 服务程序默认以 nobody 身份运行,建议为其创建专门的用户账号,以便更准确地控制其访问权限)
useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
4.编译安装Nginx
cd /opt tar zxvf nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz -C /opt/配置软件
cd nginx-1.12.0/ ./configure \ --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \ #指定nginx的安装路径 --user=nginx \ #指定用户名 --group=nginx \ #指定组名 --with-http_stub_status_module #启用 http_stub_status_module 模块以支持状态统计 ···················································· cd nginx-1.12.0/ ./configure \ --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \ --user=nginx \ --group=nginx \ --with-http_stub_status_module编译安装
make -j 8 make install让系统识别nginx的操作命令
ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/ #让系统识别nginx的操作命令安装完成后查看
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx ./nginx -v #版本 ./nginx -V #版本和配置
5.检查、启动、重启、停止 nginx服务
检查配置文件是否配置正确
nginx -t启动nginx
可以直接输入nginx,但是完整路径启动更好(生产环境多用完整路径)
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx停止nginx
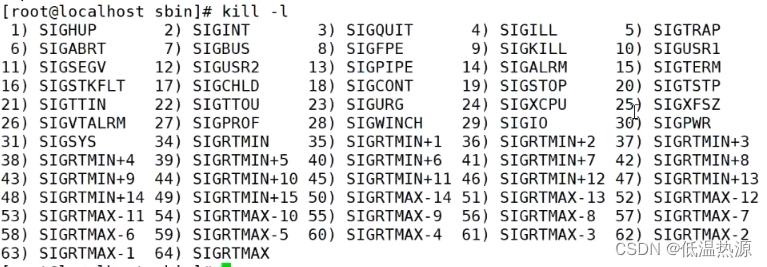
cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid #先查看nginx的PID号 kill -3 <PID号> kill -s QUIT <PID号> kill -s QUIT $(cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid) #kill -s QUIT = kill -3 留下日志关闭 killall -3 nginx killall -s QUIT nginx #不建议,killall根据名字会误杀kill -l
9 SIGKILL 强关
15 SIGTERM 自行关(默认)
3 SIGQUIT 留下日志关闭
1 SIGNHUP 重载配置
重载nginxkill -1 <PID号> killall -1 nginx kill -s HUP <PID号> killall -s HUP nginx #-1重载配置
日志分割
重新打开日志文件
kill -USR1 <PID号>平滑升级
kill -USR2 <PID号>执行make update就相当于kill -USR2(平滑升级)
验证nginx进程是否存在
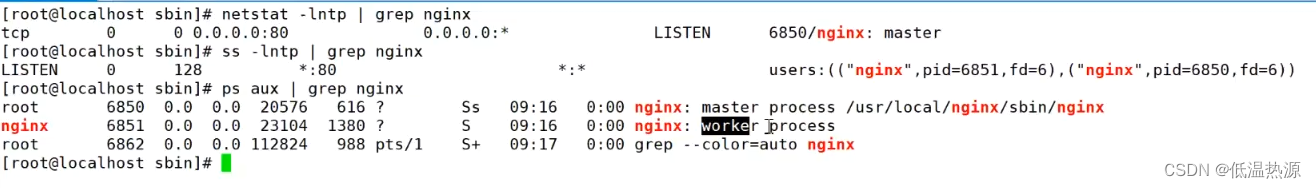
netstat -lntp | grep nginx #查看nginx进程是否存在 方法1 通过端口号/网络 ss -lntp | grep nginxkillall -0 nginx #查看nginx进程是否存在 方法2 通过killall -0检测进程存在 echo $? #获取执行结果(存在为0且不提示 不存在为1且no process found)ps aux | grep nginx #检测nginx进程是否存在 方法3 ps aux显示进程grep筛选
nginx两种进程(面试题)
master管理work进程,启动nginx读取配置文件
work真正的处理用户请求的进程
新版本升级
解压新版本包
tar -zxvf nginx-1.xx.xx.tar.gz cd nginx-1.xx.xx更新前查看当前配置,以便增加配置
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx ./nginx -v #版本 ./nginx -V #版本和配置配置软件
./configure \ --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \ --user=nginx \ --group=nginx \ --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module备份文件
mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx_old cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx升级
make upgrade #执行make update就相当于kill -USR2(平滑升级)#要保证当前 nginx 进程是通过 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 启动的,而不是通过查找环境变量中那个 nginx 命令启动的
#或者先 killall nginx ,再/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
6.添加 Nginx 系统服务
方法一
创建/etc/init.d/nginx执行脚本
vim /etc/init.d/nginx #!/bin/bash #chkconfig: - 99 20 #description:Nginx Service Control Script COM="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx" PID="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid" case "$1" in start) $COM ;; stop) kill -s QUIT $(cat $PID) ;; restart) $0 stop $0 start ;; reload) kill -s HUP $(cat $PID) ;; *) echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|reload}" exit 1 esac exit 0完善脚本,添加if判断输出状态
vim /etc/init.d/nginx #!/bin/bash #chkconfig: - 99 20 #description:Nginx Service Control Script CMD="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx" PIDFILE="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid" COUNT=$(ps -ef | egrep -v "service|grep|$$" | grep -c "nginx") # ps -ef获得进程 # 用egrep -v排除service|$$|grep # 添加service过滤(由于service命令启动nginx时会有一个service nginx start进程,会被误判) # 添加$$过滤 $$为获取当前脚本进程pid(由于脚本叫nginx.sh会误当成nginx进程,会被误判) # 添加grep过滤(由于grep筛选也会有grep nginx进程,会被误判) # 最后grep -c过滤出nginx进程数量。大于0即为存在nginx。 #检测nginx是否启动另外两种方法如下 上面通过查看进程 #killall -0 nginx 通过killall命令 #netstat -lntp | grep nginx 、$? 通过网络 case "$1" in start) #netstat -lntp | grep nginx #if [ $? -eq 0 ] if [ $COUNT -ge 1 ] then echo "NGINX 已经启动" else echo "NGINX 正在启动" $CMD fi ;; stop) kill -s QUIT $(cat $PIDFILE) ;; restart) $0 stop $0 start ;; reload) kill -s HUP $(cat $PIDFILE) ;; status) if killall -0 nginx &> /dev/null then echo "NGINX 正在运行" else echo "NGINX 未启动" fi ;; *) echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|reload|status}" exit 1 esac exit 0添加为系统服务
增加权限(看情况可以不用)
chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginxchkconfig 添加服务以便systemctl命令调用
chkconfig --add nginx #这里的nginx为/etc/init.d/nginx刚刚编写的脚本文件此时可用service systemctl命令对nginx进行操作
systemctl start nginx systemctl stop nginx方法二
创建/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service 服务文件
vim /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service [Unit] Description=nginx After=network.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID PrivateTmp=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target --------------------------------------------------------- [Unit]:服务的说明 Description:描述服务 After:依赖,当依赖的服务启动之后再启动自定义的服务 [Service]服务运行参数的设置 Type=forking是后台运行的形式,使用此启动类型应同时指定PIDFile=,以便systemd能够跟踪服务的主进程。 ExecStart为服务的具体运行命令 ExecReload为重启命令 ExecStop为停止命令 PrivateTmp=True表示给服务分配独立的临时空间 注意:启动、重启、停止命令全部要求使用绝对路径 [Install]服务安装的相关设置,可设置为多用户 ---------------------------------------------------------添加权限(看情况可以不用)
chmod 754 /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service重载systemd配置
systemctl daemon-reload此时可用systemctl对nginx进行设置
systemctl start nginx.service systemctl enable nginx.service查看 nginx 是否打开
netstat -lntp | grep nginx
--------认识Nginx服务的主配置文件 nginx.conf--------
查看nginx.conf文件 去除注释行
cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf | egrep -v "^$|^/s*#" egrep -v ^$ 去除空白行 egrep -v ^/s*# 去除 ^开头 /s空格字符 *n次空白空格 #后面加上# ///去除开头多次空白空格#的行/// 不用^.*#因为遇到 keepalive——timeout 65# 此类的行会因为匹配任意字符任意次#被吞掉。.任意字符替换为/s任意行1、全局块:全局配置,对全局生效;
2、events块:配置影响 Nginx 服务器与用户的网络连接;
3、http块:配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置;
4、server块:配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个 http 块中可以有多个 server 块;
5、location块:用于配置匹配的 uri ;
6、upstream:配置后端服务器具体地址,负载均衡配置不可或缺的部分。
nginx.conf 配置文件
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
1.全局配置
#user nobody; #运行用户,若编译时未指定则默认为 nobody worker_processes 8; #✨工作进程数量,一般设置为和 CPU 核数一样;设置为auto,nginx将会自己获取这个数值 #error_log logs/error.log; #错误日志文件的位置 #pid logs/nginx.pid; #PID 文件的位置 worker_rlimit_nofile 60000; #✨设置所有worker进程最大可以打开的文件数,默认为1024工作进程设置多少?(面试题)
与服务器CPU核心数量对应(16核心 worker_processes=16),
或者设置auto让nginx自行调整
查看CPU核心数量
lscpu top cat /proc/cpuinfo打开文件数修改
可以设置worker_rlimit_nofile 60000,但是系统可能不支持。
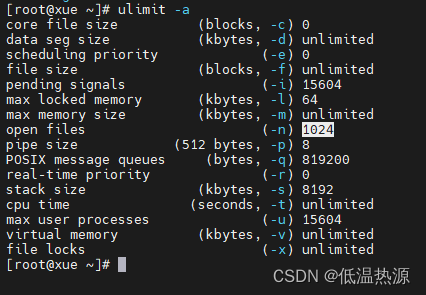
使用 ulimit -a 命令查看系统可打开最大文件数,ulimit -n临时修改,/etc/security/limits.conf永久修改。
ulimit -a
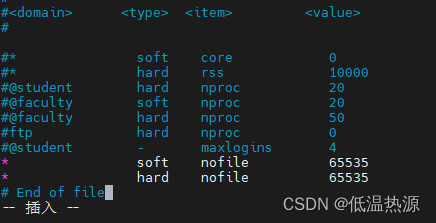
临时修改 ulimit -n 60000永久修改 重启生效 vim /etc/security/limits.conf * soft nofile 65535 * hard nofile 65535 #任意用户 软/硬限制 一个进程可打开最大文件数65535
2.I/O 事件配置
events { use epoll; #使用 epoll I/O模型,2.6及以上版本的系统内核,建议使用epoll模型以提高性能 worker_connections 60000; #✨每个进程处理 60000 个连接 与上一步全局配置设置的最大文件数相同即可(别忘了修改系统配置的最大文件数) multi_accept on; #是否一次性将监听到的连接全接收进来,默认为off,关闭时一次接收一条连接 accept_mutex on; #默认为on,开启时表示以串行方式接入新连接,否则将通报给所有worker。这可能会浪费资源并产生不可预计的后果,例如惊群问题 }
- 如提高每个进程的连接数还需执行“ulimit -n 65535”命令临时修改本地每个进程可以同时打开的最大文件数。
- 在Linux平台上,在进行高并发TCP连接处理时,最高的并发数量都要受到系统对用户单一进程同时可打开文件数量的限制(这是因为系统为每个TCP连接都要创建一个socket句柄,每个socket句柄同时也是一个文件句柄)。
- 可使用ulimit -a命令查看系统允许当前用户进程打开的文件数限制。
- epoll是Linux内核为处理大批句柄而作改进的poll,是Linux下多路复用IO接口select/poll的增强版本,它能显著的减少程序在大量并发连接中只有少量活跃的情况下的系统CPU利用率。epoll模型 用于异步非阻塞 (阻塞就注册事件,去处理其他任务,而不是傻等。等上游服务器返回响应再继续处理)
- worker_processes的值和work_connections的值决定了最大并发数量,最大并发数计算方式为:worker_processes*worker_connections。但在反向代理场景中计算方法不同,因为nginx既要维持和客户端的连接,又要维持和后端服务器的连接,因此处理一次连接要占用2个连接,所以最大并发数计算方式为:worker_processes*worker_connections/2。
3.HTTP 配置
http { ##文件扩展名与文件类型映射表 include mime.types; ##默认文件类型 default_type application/octet-stream; ##日志格式设定 #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; ##访问日志位置 #access_log logs/access.log main; ##开启文件传输模式 sendfile on; ##只在sendfile on时有效。调用tcp_cork方法,让数据包不会马上传送出去,等到数据包最大时,一次性的传输出去,这样有助于解决网络堵塞。默认为off。 #tcp_nopush on; ##连接保持超时时间,单位是秒 #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; ##gzip模块设置,设置是否开启gzip压缩输出 #gzip on; ##Web 服务的监听配置 server { ##监听地址及端口 listen 80; ##站点域名,可以有多个,用空格隔开 server_name www.xue.com; ##网页的默认字符集 charset utf-8; ##根目录配置 location / { ##nginx在磁盘中目录为 /usr/local/nginx root html; ##网站相对路径/html 根目录绝对路径则为/usr/local/nginx/html ##默认首页文件名 index index.html index.php; } ##内部错误的反馈页面 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; ##错误页面配置 location = /50x.html { root html; } } }location常见配置指令,root、alias、proxy_pass
locate块 根据用户访问url匹配路径,跳转到相应的html文件路径
注意 location /file 诸如此类的路径不要加上斜杠写成 location /file/ 否则转化完的网站也会多出斜杠变成//导致错误
location / { ##网站根目录的位置/usr/local/nginx/html root html; ##默认首页文件名 index index.html index.php; }root alias 路径区别(面试题)
root(根路径配置)
root /var/www/html
请求www.xue.com/test/1.html,会返回文件/var/www/html/test/1.html/test 的根目录是 /var/www/html ,跟在后面
location /test { #如果浏览器访问/test/1.html root /var/www/html; #则Linux文件系统中访问/var/www/html文件夹下 /test/1.html文件 }alias(别名配置)
alias /var/www/html
请求www.xue.com/test/1.html,会返回文件/var/www/html/1.html/test 的别名就是 /var/www/html ,直接替代
location /test { #如果浏览器访问/test/1.html alias /var/www/html; #则Linux文件系统中访问/var/www/html文件夹下 /1.html文件 }proxy_pass(反向代理配置)
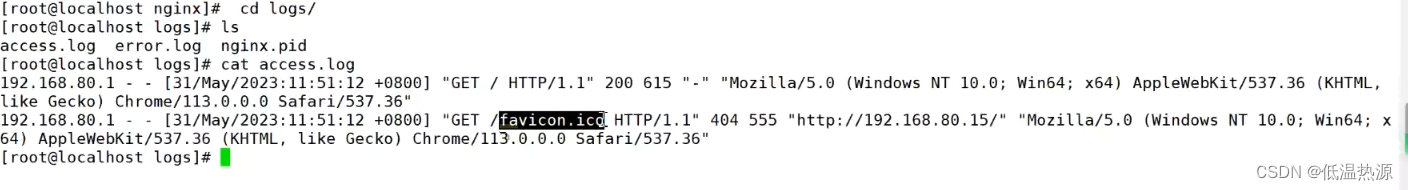
日志格式设定
$remote_addr(上一个服务器地址 可能是代理服务器地址)与$http_x_forwarded_for(最初发出请求的服务器地址 无视代理服务器)用以记录客户端的ip地址; $remote_user:用来记录客户端用户名称; $time_local: 用来记录访问时间与时区; $request: 用来记录请求的url与http协议; $status: 用来记录请求状态;成功是200, $body_bytes_sent :记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小; $http_referer:用来记录从哪个页面链接访问过来的(可以依此做防盗链); $http_user_agent:记录客户浏览器的相关信息;通常web服务器放在反向代理的后面,这样就不能获取到客户的IP地址了,通过$remote_add拿到的IP地址是反向代理服务器的iP地址。
反向代理服务器在转发请求的http头信息中,可以增加x_forwarded_for信息,用以记录原有客户端的IP地址和原来客户端的请求的服务器地址。
--------访问状态统计配置--------
1.先使用命令/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V 查看已安装的 Nginx 是否包含 HTTP_STUB_STATUS 模块
cat /opt/nginx-1.12.0/auto/options #可查看 nginx 已安装的所有模块 包括开启关闭方法 cat /opt/nginx-1.12.0/auto/options | grep YES
模块默认开启
若要关闭./configure时加上 --without-http-cache参数关闭
如果模块关闭
需要开启./configure时加上 --with-http-cache参数开启
vim /opt/nginx-1.12.0/auto/options
2.修改 nginx.conf 配置文件,指定访问位置并添加 stub_status 配置
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf cp nginx.conf nginx.conf.bakvim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ...... http { ...... server { listen 80; server_name www.xue.com; charset utf-8; location / { root html; index index.html index.php; } ##添加 stub_status 配置## location /status { #访问位置为/status stub_status on; #打开状态统计功能 access_log off; #关闭此位置的日志记录 } } }
3.重启服务,访问测试
systemctl restart nginx浏览器访问
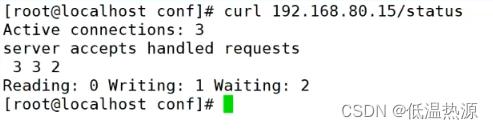
http://192.168.80.101/status
Active connections:表示当前的活动连接数,即当前与 Nginx 服务器建立的连接数。
server accepts handled requests :表示已经处理的连接信息
三个数字依次表示服务器已接收的连接数;服务器成功处理的连接数;服务器累计处理的总请求数(在保持连接模式下,请求数量可能会大于连接数量)
Reading:表示当前正在从客户端读取数据的连接数。
Writing:表示当前正在向客户端写入数据的连接数。
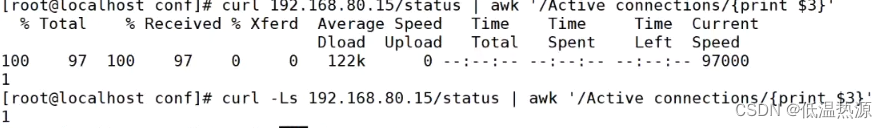
Waiting:表示当前空闲并等待请求的连接数。可以curl http://192.168.80.101/status 文本获取网页,并且结合 awk与if 语句进行性能监控。
curl -Ls http://192.168.80.101/status | awk '/Active connections/{print $3}' -Ls 将curl改为静态显示 awk匹配Active connections行获取第三段连接数
编写脚本,连接数超过1000个报警 ,10秒检测一次

--------访问控制--------
---基于授权的访问控制---
1.生成用户密码认证文件
安装工具
yum install -y httpd-tools创建密码文件
htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db zhangsan #-c为第一次创建密码文件需要加上 htpasswd /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db lisi更改密码文件权限 由于之前设置过NGINX服务由nginx用户运行,设置只有nginx用户才能使用此密码文件
chown nginx /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db chmod 400 /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db
2.修改主配置文件相对应目录,添加认证配置项
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ...... server { location / { ...... ##添加认证配置## auth_basic "hello world"; #设置密码提示框文字信息 auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db; } }
3.重启服务,访问测试
nginx -t systemctl reload nginx #systemctl restart nginx #reload不行再restart浏览器访问
http://192.168.80.101
---基于客户端的访问控制---
访问控制规则如下
- deny IP/IP 段:拒绝某个 IP 或 IP 段的客户端访问。
- allow IP/IP 段:允许某个 IP 或 IP 段的客户端访问。
规则从上往下执行,如匹配则停止,不再往下匹配。
白名单
allow IP/网段;
deny IP/网段;黑名单
deny IP/网段;
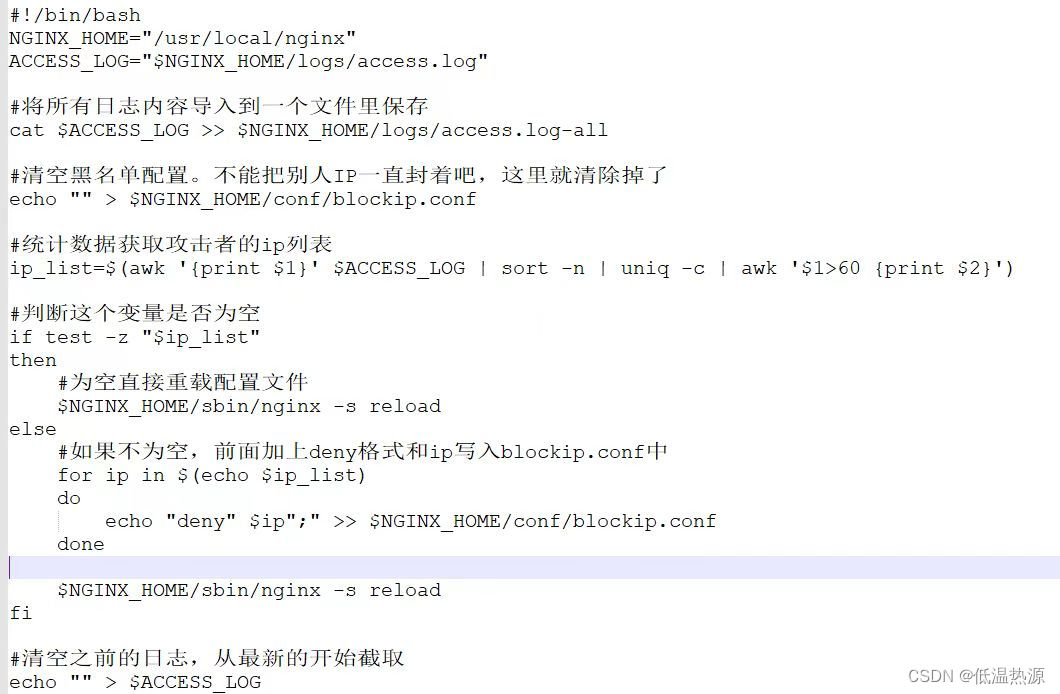
一个防DDoS的实例 1分钟内访问60次以上封禁 (此处脚本是对这个网站内shell脚本的优化)
详细部署步骤可以参考这个网站 服务又被攻击?Nginx + 简单脚本,轻松拦截
-------Nginx 虚拟主机-------
---基于域名的 Nginx 虚拟主机---
1.为虚拟主机提供域名解析(准备不同域名)
echo "192.168.80.101 www.xue.com www.benet.com" >> /etc/hosts
2.为虚拟主机准备网页文档
mkdir -p /var/www/html/benet mkdir -p /var/www/html/xue echo "<h1>www.xue.com</h1>" > /var/www/html/xue/index.html echo "<h1>www.benet.com</h1>" > /var/www/html/benet/index.html
3.修改Nginx的配置文件(不同域名)
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ...... http { ...... server { listen 80; server_name www.xue.com; #设置域名www.kgc.com charset utf-8; access_log logs/www.xue.access.log; #设置日志名 location / { root /var/www/html/xue; #设置www.kgc.com 的工作目录 index index.html index.php; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = 50x.html{ root html; } } server { listen 80; server_name www.benet.com; #设置域名www.benet.com charset utf-8; access_log logs/www.benet.access.log; location / { root /var/www/html/benet; index index.html index.php; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = 50x.html{ root html; } } }
4.重启服务,访问测试
systemctl restart nginx浏览器访问
http://www.xue.com
http://www.benet.com
---基于IP 的 Nginx 虚拟主机---
1.配置虚拟网卡区分IP(准备不同IP)
ifconfig ens33:0 192.168.80.111 netmask 255.255.255.0
2.为虚拟主机准备网页文档 (刚刚已经做过)
mkdir -p /var/www/html/benet mkdir -p /var/www/html/xue echo "<h1>www.xue.com</h1>" > /var/www/html/xue/index.html echo "<h1>www.benet.com</h1>" > /var/www/html/benet/index.html
3.修改Nginx的配置文件(不同IP)
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ...... http { ...... server { listen 192.168.80.101:80; #设置监听地址192.168.80.101 server_name www.xue.com; charset utf-8; access_log logs/www.xue.access.log; location / { root /var/www/html/xue; index index.html index.php; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = 50x.html{ root html; } } server { listen 192.168.80.111:80; #设置监听地址192.168.80.111 server_name www.benet.com; charset utf-8; access_log logs/www.benet.access.log; location / { root /var/www/html/benet; index index.html index.php; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = 50x.html{ root html; } } }:35,79 co 80 快速复制
4.重启服务,访问测试
systemctl restart nginx浏览器访问
http://192.168.80.101
http://192.168.80.111
---基于端口的 Nginx 虚拟主机----
1.为虚拟主机准备网页文档 (刚刚已经做过)
mkdir -p /var/www/html/benet mkdir -p /var/www/html/xue echo "<h1>www.xue.com</h1>" > /var/www/html/xue/index.html echo "<h1>www.benet.com</h1>" > /var/www/html/benet/index.html
2.修改Nginx的配置文件(不同端口)
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ...... http { ...... server { listen 192.168.80.101:8080; #设置监听 8080 端口 server_name www.xue.com; charset utf-8; access_log logs/www.xue.access.log; location / { root /var/www/html/xue; index index.html index.php; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = 50x.html{ root html; } } server { listen 192.168.80.101:8888; #设置监听 8888 端口 server_name www.benet.com; charset utf-8; access_log logs/www.benet.access.log; location / { root /var/www/html/benet; index index.html index.php; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = 50x.html{ root html; } } }
3.重启服务,访问测试
systemctl restart nginx浏览器访问
http://192.168.80.101:8080
http://192.168.80.101:8888