最远点采样FPS代码解析
注意:一般深度学习框架中都会使用批操作,来加速收敛。
因此采样函数的输入输出应当也要包含批。
def farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint):
"""
Input:
xyz: pointcloud data, [B, N, C]
npoint: number of samples
Return:
centroids: sampled pointcloud data, [B, npoint, C]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
S = npoint
centroids = torch.zeros(B, S, dtype=torch.long).to(device)
distance = torch.ones(B, N).to(device) * 1e10
farthest = torch.randint(0, N, (B,), dtype=torch.long).to(device)
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device)
for i in range(S):
centroids[:, i] = farthest
centroid = xyz[batch_indices, farthest, :].view(B, 1, 3)
dist = torch.sum((xyz - centroid) ** 2, -1)
mask = dist < distance
distance[mask] = dist[mask]
farthest = torch.max(distance, -1)[1]
return centroids
知识储备
pytorch、python知识点
- nn.BatchNorm1d:批数据的归一化,详细说明可参考这里。
最远点采样 ( Farthest Point Sampling )
本质:一句话概括就是不断迭代地选择距离已有采样点集合的最远点。
最远点采样(Farthest Point Sampling)是一种常用的采样算法,特别是在激光雷达3D点云数据中。这篇文章介绍最远点采样方法在一维、二维、三维点集中的使用。附有numpy写的代码和实例。
FPS算法原理步骤:
- 输入点云有N个点,从点云中选取一个点P0作为起始点,得到采样点集合S={P0}。
- 计算所有点到P0的距离,构成N维数组L,从中选择最大值对应的点作为P1,更新采样点集合S={P0,P1}。
- 计算所有点到P1的距离,对于每一个点Pi,其距离P1的距离如果小于L[i],则更新L[i] = d(Pi, P1),因此,数组L中存储的 一直是每一个点到采样点集合S的最近距离。
- 选取L中最大值对应的点作为P2,更新采样点集合S={P0,P1,P2}。
- 重复2-4步,一直采样到N’个目标采样点为止。
原理和实现代码(python)
ModelNet40数据集介绍
ModelNet40数据集是用于分类的点云数据集,包含了40个类别,训练集有9843个点云数据,验证集有2468个点云数据,数据集目录结构如下:

更多介绍请点击
代码实现(基于pytorch)
源码地址
环境配置
(1)Windows系统
python 3.8 cuda 11.1 pytorch 1.8.0 torchvision 0.9.0
(2)ubuntu系统
python 3.7 cuda 11.1 pytorch 1.8.0 torchvision 0.9.0
代码解析
可参考
目录结构
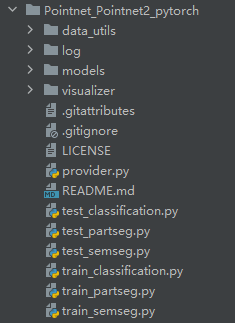
models:网络模型,如分割模型,分类模型,pointNet模型,pointNet++模型等
log??
data_utils??
visualizer:可视化
README
对于版本迭代的说明。
略…
工具链的安装
The latest codes are tested on Ubuntu 16.04, CUDA10.1, PyTorch 1.6 and Python 3.7:
conda install pytorch==1.6.0 cudatoolkit=10.1 -c pytorch
分类任务运行指南
下载数据集
- Data Preparation
Download alignment ModelNet here and save in data/modelnet40_normal_resampled/.