分数 30
全屏浏览题目
切换布局
作者 陈越
单位 浙江大学
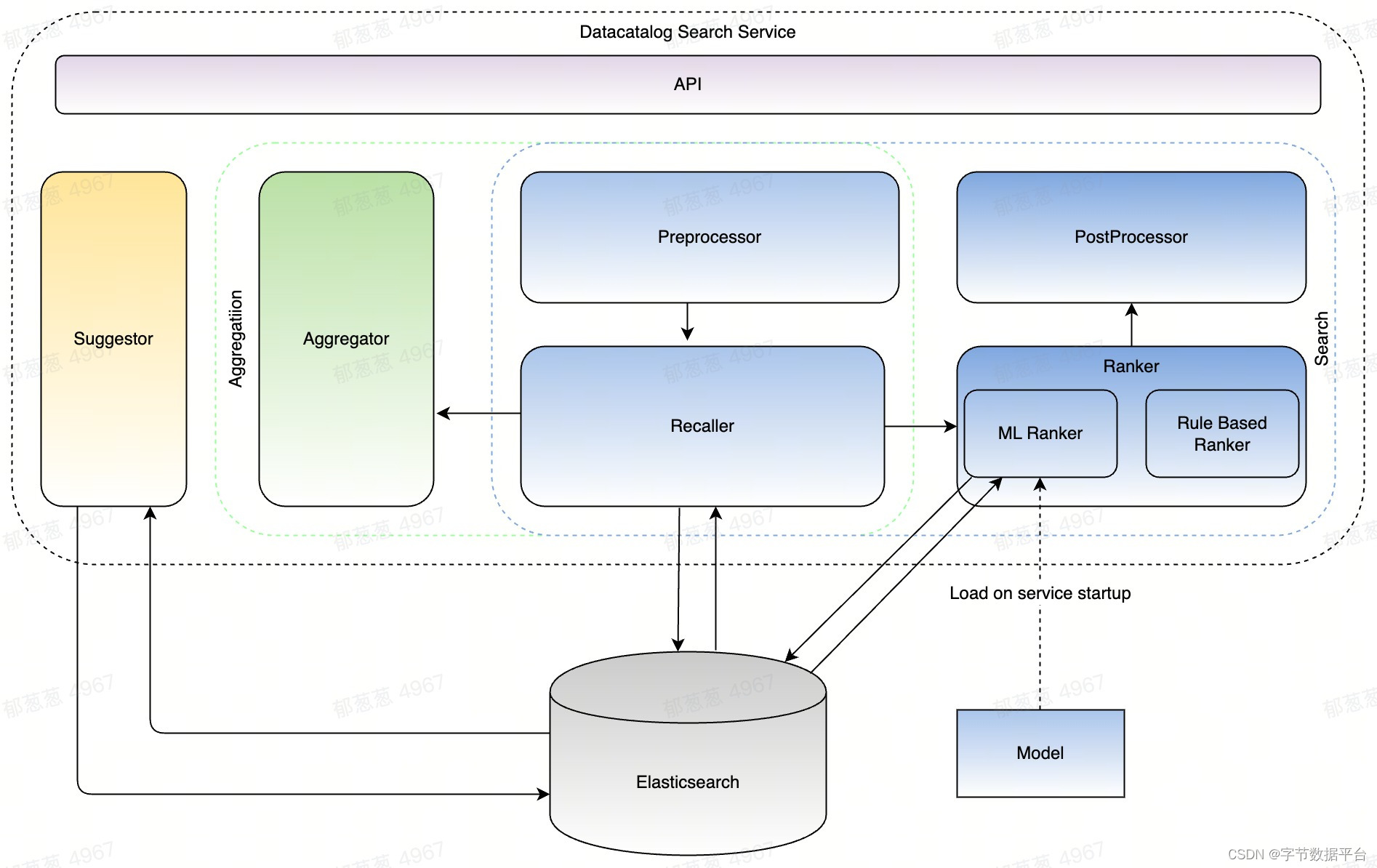
A Cartesian tree is a binary tree constructed from a sequence of distinct numbers. The tree is heap-ordered, and an inorder traversal returns the original sequence. For example, given the sequence { 8, 15, 3, 4, 1, 5, 12, 10, 18, 6 }, the min-heap Cartesian tree is shown by the figure.
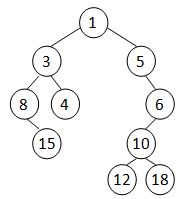
Your job is to output the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts from giving a positive integer N (≤30), and then N distinct numbers in the next line, separated by a space. All the numbers are in the range of int.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input:
10
8 15 3 4 1 5 12 10 18 6
Sample Output:
1 3 5 8 4 6 15 10 12 18
代码长度限制
16 KB
时间限制
400 ms
内存限制
64 MB
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,in[40];
map<int,int>l,r,pos;
int findmin(int il,int ir){//找到在il和ir之间最小的元素
int min=0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int i=il;i<=ir;i++){
if(min>in[i])min=in[i];
}
return min;
}
int build(int il,int ir){
int root=findmin(il,ir);//找到根结点
int k=pos[root];//根结点在中序遍历的下标
if(il<k)l[root]=build(il,k-1);//若有左子树,递归
if(ir>k)r[root]=build(k+1,ir);//若有右子树,递归
return root;//返回根结点
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){//输入中序遍历并记录各元素的位置
cin>>in[i];
pos[in[i]]=i;
}
int root=build(0,n-1);//建树
queue<int>q;
q.push(root);//插入根结点
while(q.size()){//层序遍历
int t=q.front();
q.pop();
if(l.count(t))q.push(l[t]);
if(r.count(t))q.push(r[t]);
cout<<t;
if(q.size())cout<<' ';
}
return 0;
}