文章目录
- 为什么需要加密?
- 加盐加密
- MD5+盐值加密
- Spring Security加盐
为什么需要加密?
从下面的图片中,可以看到用户的密码在数据库中存储时,如果不对密码加密,则是以明文的方式存储的,如果被别人获取到数据库的信息,那将会将用户的密码泄露,从而造成安全隐患

我们可以使用MD5加密方式对用户的密码进行加密存储,但是传统的MD5有规则可循,可以破解
String s = "12345";
String mds1 = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(s.getBytes()).toString();
System.out.println(mds1);
String mds2 = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(s.getBytes()).toString();
System.out.println(mds2);
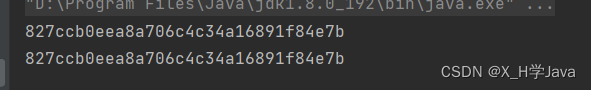
我们从上述代码及打印结果看,使用MD5对同一个字符串加密,加密后的结果不变,MD5加密是单向不可逆(不能从密文获取明文),此时呢针对MD5这种加密方式可以使用暴力破解的方式进行破解
加盐加密
加盐加密算法(Salt Encryption)是一种对称密钥加密算法,它使用一个随机生成的盐(salt)作为加密和解密的关键参数,在加密过程中,将明文和盐作为输入,通过哈希函数计算出一个密文和一个盐值,在解密过程中,使用相同的盐值和密文计算哈希值,然后再用哈希值和盐值进行解密操作,以获取原始的明文
MD5+盐值加密
加密:我们可以使用一个随机字符串(盐值)和明文密码组合起来,作为带盐值的明文密码,再使用MD5对带盐值的密码进行加密
解密:解密其实就是判断用户需要校验密码的正确性
此时需要用到加密使用的盐值,这个盐值如何获取呢?
我们在数据库存储密码时存储盐值+密文,使用一个特定的分割符将盐值和密文分隔开,我们从数据库获取到密码的密文后,也使用同样的规则获取到盐值,使用该盐值和校验的密码重新使用MD5生成密文,判断新生成的密文和数据库保存的密文是否一致,如果是一致说明密码正确,否则密码错误
加密解密的代码实现:
public class PasswordTools {
/**
*加盐加密
* @param password
* @return 加密后的密码
*/
public static String encrypt(String password){
//生成盐值,使用随机字符串UUID,UUID为32位的
String salt = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-","");
//(盐值+密码)进行MD5加密,DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex参数为字节数组,生成一个十六进制32位的字符串
String finalPassword = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex((salt+password).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//将盐值和加密的密码组合返回,最终存储到数据库中的密码
String dbPassword = salt + "$" + finalPassword;
return dbPassword;
}
/**
* 校验密码
* @param password
* @param dbPassword
* @return
*/
public static boolean decrypt(String password,String dbPassword){
if(StringUtils.hasLength(password) && StringUtils.hasLength(dbPassword)
&& dbPassword.length()==65 && dbPassword.contains("$")){
String[] arr = dbPassword.split("\\$");
String salt = arr[0];
//根据获取的盐值生成校验的密码
String checkPassword = salt + "$" + DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex((salt+password).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//用校验密码与数据库保存的密码进行校验
if(checkPassword.equals(dbPassword)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String dbPassword = encrypt("12345");
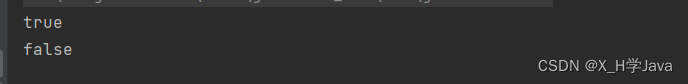
System.out.println(decrypt("12345",dbPassword)); //true
System.out.println(decrypt("45678",dbPassword)); //false
}
}
Spring Security加盐
- 添加Spring Security依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 关闭Spring Security的认证
在启动类上的注解添加排除,禁止Spring boot启动时自动加载Spring Security框架
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {SecurityAutoConfiguration.class})
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 使用
BCryptPasswordEncoder对象提供的encode(String password)加密,和matches(String password,String dbPassword)解密方法
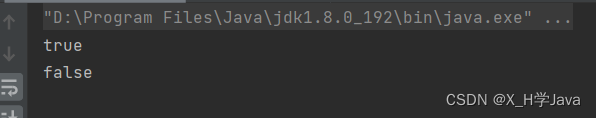
BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String password = "123456";
System.out.println(passwordEncoder.encode(password));
System.out.println(passwordEncoder.encode(password));
System.out.println(passwordEncoder.encode(password));
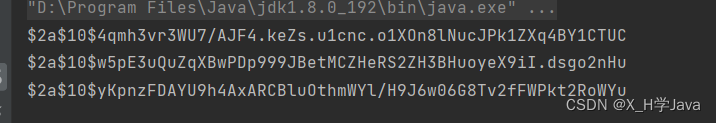
BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String password = "123456";
String dbPassword = passwordEncoder.encode(password);
boolean result1 = passwordEncoder.matches(password,dbPassword); //正确的密码
boolean result2 = passwordEncoder.matches("12345",dbPassword); //错误的密码
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2);