本文为RNN做古诗生成的一个小demo,只要是为了完成课上的作业(由于训练比较慢,所以周期仅设置为3,大一点性能可能会更好),如有需要可以在这基础之上进行加工,数据集没办法上传,如有需要,可以私信我。
LSTM:

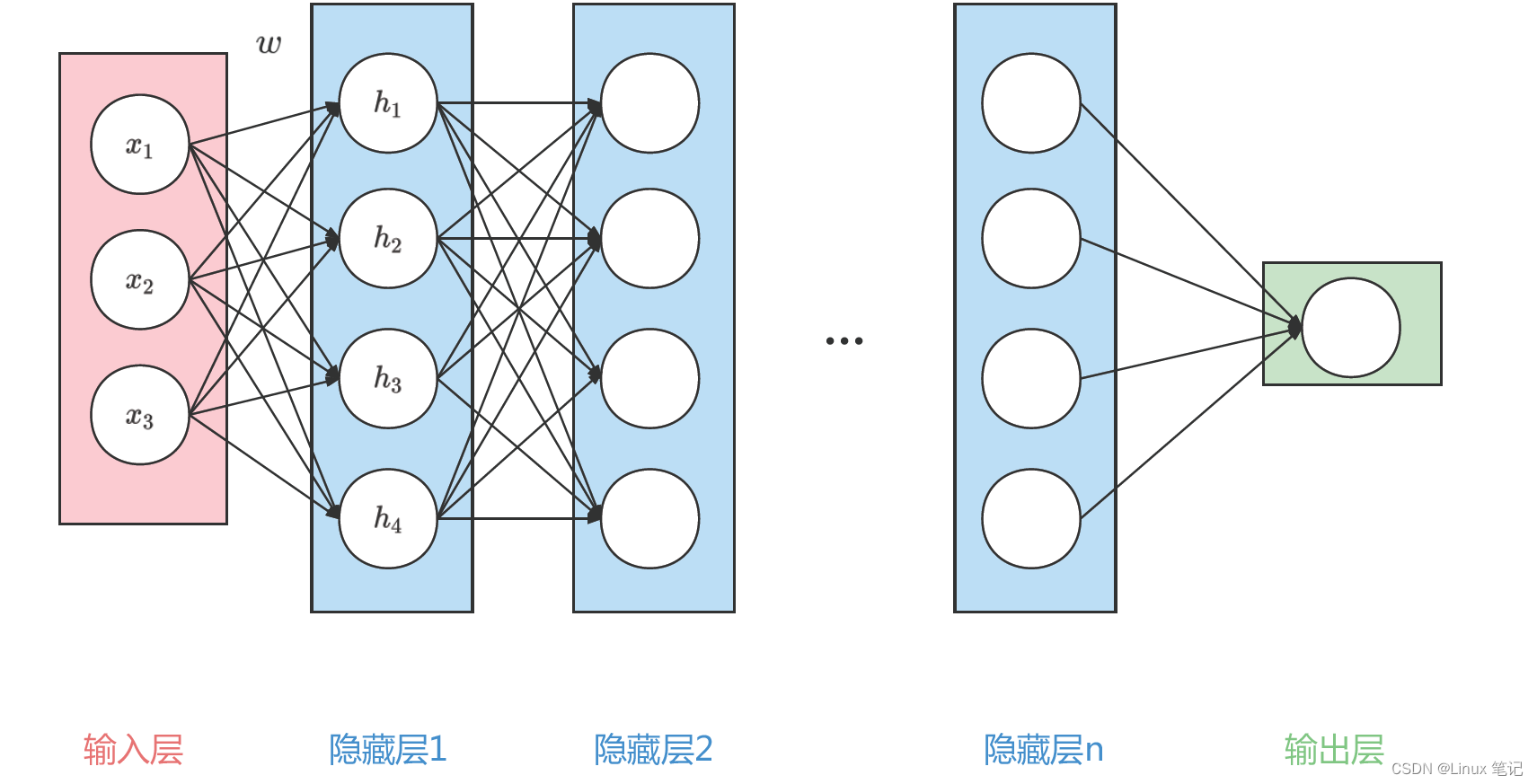
如上图所示LSTM神经元存在两个状态向量:h(t)和c(t)(可将h(t)视为短期状态,c(t)视为长期状态) 首先,将当前输入向量x(t)和先前的短期状态h(t-1)馈入四个不同的全连接层(FC)。它们都有不同的目的:
主要层是输出g(t)的层:它通常的作用是分析当前输入x(t)和先前(短期)状态 h(t-1),得到本时间步的信息。
遗忘门(由f(t)控制):控制长期状态的哪些部分应当被删除。
输入门(由i(t)控制):控制应将g(t)的哪些部分添加到长期状态。
输出门(由o(t)控制):控制应在此时间步长读取长期状态的哪些部分并输出 到h(t)和y(t)。
如图1,LSTM神经元运用了三个sigmoid激活函数和一个tanh激活函数,
Tanh 作用在于帮助调节流经网络的值,使得数值始终限制在 -1 和 1 之间。
Sigmoid 激活函数与 tanh 函数类似,不同之处在于 sigmoid 是把值压缩到0~1 这样的设置有助于更新或忘记信息,可将其理解为比例(任何数乘以 0 都得 0,这部分信息就会剔除掉;同样的,任何数乘以 1 都得到它本身,这部分信息就会完美地保存下来)因记忆能力有限,记住重要的,忘记不重要的。
例子:以输入门为例,首先输入x(t)和先前(短期)状态 h(t-1),得到本时间步的信息向量g(t) = (g1(t),g2(t),g3(t)……gn(t))(其中n个神经元的个数,g1(t)取值范围为(-1,1)),然后与向量i(t)=(i1(t),i2(t),i3(t)……in(t))(ii(t)取值范围为(0,1))对应元素相乘,得到向量(g1(t)*i1(t), g2(t)*i2(t)……gn(t)*in(t)),即本时间步有用信息,然后把他加上长期记忆c(t-1)中进行保存。
LSM关键的思想是网络可以学习长期状态下存储的内容、丢弃的内容以及从中读取的内容。当长期状态c(t-1)从左到右遍历网络时,可以看到它首先经过一个遗 忘门,丢掉了一些记忆,然后通过加法操作添加了一些新的记忆(由输入门选择的记忆)。结果c(t)直接送出来,无须任何进一步的转换。因此,在每个时间步长中,都会 丢掉一些记忆,并添加一些记忆。此外,在加法运算之后,长期状态被复制并通过tanh函数传输,然后结果被输出门滤波。这将产生短期状态h(t)(等于该时间步长的单元输出 y(t))。
原理:
本文使用LSTM生成古诗,那么RNN是怎么用作我们的文本生成呢?话不多说,其实用RNN来生成的思想很简单, 就是将前一个字进行词嵌入,后一个字作为标签,将这个组合输入到RNN的网络里面等待训练拟合之后,再用一个引导词,训练出它的预测结果,再用其预测结果,来训练下一个词,循环往复,从而实现RNN生成文本的效果.
main.py
import numpy as np
import collections
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.optim as optim
import rnn
start_token = 'G'
end_token = 'E'
batch_size = 64
def process_poems1(file_name):
"""
:param file_name:
:return: poems_vector have two dimmention ,first is the poem, the second is the word_index
e.g. [[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10],[9,6,3,8,5,2,7,4,1]]
"""
poems = []
i = 1
with open(file_name, "r", encoding='utf-8', ) as f:
for line in f.readlines():
try:
i = i+1
title, content = line.strip().split(':')
# content = content.replace(' ', '').replace(',','').replace('。','')
content = content.replace(' ', '')
if '_' in content or '(' in content or '(' in content or '《' in content or '[' in content or \
start_token in content or end_token in content:
continue
if len(content) < 5 or len(content) > 80:
continue
content = start_token + content + end_token
poems.append(content)
except ValueError as e:
print(line)
print(i)
print("error")
pass
# 按诗的字数排序
poems = sorted(poems, key=lambda line: len(line))
# print(poems)
# 统计每个字出现次数
all_words = []
j = 0
for poem in poems:
all_words += [word for word in poem] # 数据连接
counter = collections.Counter(all_words) # 统计词和词频。
count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1]) # d.items() 以列表的形式返回可遍历的元组数组 逆序排序
words, _ = zip(*count_pairs) # zip(*) 可理解为解压,返回二维矩阵式
words = words[:len(words)] + (' ',) #(‘ ’,) 为一个元素的元祖
word_int_map = dict(zip(words, range(len(words))))
poems_vector = [list(map(word_int_map.get, poem)) for poem in poems] # 第一位为一个函数,后一位为一个迭代器
return poems_vector, word_int_map, words # 诗句的向量表示,单词映射表,单词表
def process_poems2(file_name):
"""
:param file_name:
:return: poems_vector have tow dimmention ,first is the poem, the second is the word_index
e.g. [[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10],[9,6,3,8,5,2,7,4,1]]
"""
poems = []
with open(file_name, "r", encoding='utf-8', ) as f:
# content = ''
for line in f.readlines():
try:
line = line.strip()
if line:
content = line.replace(' '' ', '').replace(',','').replace('。','')
if '_' in content or '(' in content or '(' in content or '《' in content or '[' in content or \
start_token in content or end_token in content:
continue
if len(content) < 5 or len(content) > 80:
continue
# print(content)
content = start_token + content + end_token
poems.append(content)
# content = ''
except ValueError as e:
# print("error")
pass
# 按诗的字数排序
poems = sorted(poems, key=lambda line: len(line))
# print(poems)
# 统计每个字出现次数
all_words = []
for poem in poems:
all_words += [word for word in poem]
counter = collections.Counter(all_words) # 统计词和词频。
count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1]) # 排序
words, _ = zip(*count_pairs)
words = words[:len(words)] + (' ',)
word_int_map = dict(zip(words, range(len(words))))
poems_vector = [list(map(word_int_map.get, poem)) for poem in poems]
return poems_vector, word_int_map, words
def generate_batch(batch_size, poems_vec, word_to_int):
#生成训练数据
n_chunk = len(poems_vec) // batch_size #34813/100 = 348 古诗的向量表示
x_batches = []
y_batches = []
for i in range(n_chunk):
start_index = i * batch_size
end_index = start_index + batch_size
x_data = poems_vec[start_index:end_index]
y_data = []
for row in x_data:
y = row[1:]
y.append(row[-1])
y_data.append(y)
"""
x_data y_data
[6,2,4,6,9] [2,4,6,9,9] 文本生成,所以用后面一位数据做label
[1,4,2,8,5] [4,2,8,5,5]
"""
# print(x_data[0])
# print(y_data[0])
# exit(0)
x_batches.append(x_data)
y_batches.append(y_data)
return x_batches, y_batches
def run_training():
# 处理数据集
# poems_vector, word_to_int, vocabularies = process_poems2('./tangshi.txt')
poems_vector, word_to_int, vocabularies = process_poems1('./poems.txt')
# 生成batch
print("finish loadding data")
BATCH_SIZE = 100
torch.manual_seed(5)
word_embedding = rnn.word_embedding( vocab_length= len(word_to_int) + 1 , embedding_dim= 100) #6123 x 100
#print(word_embedding.shape)
rnn_model = rnn.RNN_model(batch_sz = BATCH_SIZE,vocab_len = len(word_to_int) + 1 ,word_embedding = word_embedding ,embedding_dim= 100, lstm_hidden_dim=128)
# optimizer = optim.Adam(rnn_model.parameters(), lr= 0.001)
optimizer=optim.RMSprop(rnn_model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
loss_fun = torch.nn.NLLLoss()
# rnn_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./poem_generator_rnn')) # if you have already trained your model you can load it by this line.
for epoch in range(3):
batches_inputs, batches_outputs = generate_batch(BATCH_SIZE, poems_vector, word_to_int) #生成训练数据 由batch组成的数组 348
n_chunk = len(batches_inputs)
for batch in range(n_chunk):
batch_x = batches_inputs[batch]
batch_y = batches_outputs[batch] # (batch , time_step)
loss = 0
for index in range(BATCH_SIZE): #batch_size = 100
x = np.array(batch_x[index], dtype = np.int64)
y = np.array(batch_y[index], dtype = np.int64)
x = Variable(torch.from_numpy(np.expand_dims(x,axis=1))) #将数组转换成张量 np.expand_dims扩展数据的形状 x.sahpe = 7x1,
y = Variable(torch.from_numpy(y ))
pre = rnn_model(x) # 7 x 6125
loss += loss_fun(pre , y)
if index == 0:
_, pre = torch.max(pre, dim=1)# pre为张量,tolist转换成列表
print('prediction', pre.data.tolist()) # the following three line can print the output and the prediction
print('b_y ', y.data.tolist()) # And you need to take a screenshot and then past is to your homework paper.
print('*' * 30)
loss = loss / BATCH_SIZE
print("epoch ",epoch,'batch number',batch,"loss is: ", loss.data.tolist())
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm(rnn_model.parameters(), 1) # 梯度裁剪 可以预防梯度爆炸,参数的平方和
optimizer.step() #训练参数
if batch % 20 ==0:
torch.save(rnn_model.state_dict(), './poem_generator_rnn')
print("finish save model")
def to_word(predict, vocabs): # 预测的结果转化成汉字
sample = np.argmax(predict)
if sample >= len(vocabs):
sample = len(vocabs) - 1
return vocabs[sample]
def pretty_print_poem(poem): # 令打印的结果更工整
shige=[]
for w in poem:
if w == start_token or w == end_token:
break
shige.append(w)
poem_sentences = poem.split('。')
for s in poem_sentences:
if s != '' and len(s) > 2:
# print(s + '。')
print(s + '。')
def gen_poem(begin_word):
# poems_vector, word_int_map, vocabularies = process_poems2('./tangshi.txt') # use the other dataset to train the network
poems_vector, word_int_map, vocabularies = process_poems1('./poems.txt')
word_embedding = rnn.word_embedding(vocab_length=len(word_int_map) + 1, embedding_dim=100)
rnn_model = rnn.RNN_model(batch_sz=64, vocab_len=len(word_int_map) + 1, word_embedding=word_embedding,
embedding_dim=100, lstm_hidden_dim=128)
rnn_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./poem_generator_rnn'))
# 指定开始的字
poem = begin_word
word = begin_word
while word != end_token:
input = np.array([word_int_map[w] for w in poem],dtype= np.int64)
input = Variable(torch.from_numpy(input))
output = rnn_model(input, is_test=True)
word = to_word(output.data.tolist(), vocabularies)
poem += word
if len(poem) > 30:
break
return poem
#run_training() # 如果不是训练阶段 ,请注销这一行 。 网络训练时间很长。
pretty_print_poem(gen_poem("日"))
pretty_print_poem(gen_poem("红"))
pretty_print_poem(gen_poem("山"))
pretty_print_poem(gen_poem("夜"))
pretty_print_poem(gen_poem("湖"))
pretty_print_poem(gen_poem("湖"))
pretty_print_poem(gen_poem("湖"))
pretty_print_poem(gen_poem("君"))rnn.py
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
def weights_init(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__ # obtain the class name
if classname.find('Linear') != -1:
weight_shape = list(m.weight.data.size()) #6123 x 128
fan_in = weight_shape[1]
fan_out = weight_shape[0]
w_bound = np.sqrt(6. / (fan_in + fan_out))
m.weight.data.uniform_(-w_bound, w_bound)
m.bias.data.fill_(0)
print("inital linear weight ")
class word_embedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,vocab_length , embedding_dim):
super(word_embedding, self).__init__()
w_embeding_random_intial = np.random.uniform(-1,1,size=(vocab_length ,embedding_dim)) #生成服从均匀分布的随机数
self.word_embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_length,embedding_dim) #创建一个embedding层
self.word_embedding.weight.data.copy_(torch.from_numpy(w_embeding_random_intial))
def forward(self,input_sentence):
"""
:param input_sentence: a tensor ,contain several word index.
:return: a tensor ,contain word embedding tensor
"""
sen_embed = self.word_embedding(input_sentence)
return sen_embed
class RNN_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, batch_sz ,vocab_len ,word_embedding,embedding_dim, lstm_hidden_dim):
super(RNN_model,self).__init__()
self.word_embedding_lookup = word_embedding
self.batch_size = batch_sz
self.vocab_length = vocab_len
self.word_embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.lstm_dim = lstm_hidden_dim
#########################################
# here you need to define the "self.rnn_lstm" the input size is "embedding_dim" and the output size is "lstm_hidden_dim"
# the lstm should have two layers, and the input and output tensors are provided as (batch, seq, feature)
# ???
self.rnn_lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=embedding_dim,hidden_size=lstm_hidden_dim, num_layers=2,batch_first=True)
##########################################
self.fc = nn.Linear(lstm_hidden_dim, vocab_len )
self.apply(weights_init) # call the weights initial function.
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax() # the activation function.
# self.tanh = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self,sentence,is_test = False):
batch_input = self.word_embedding_lookup(sentence).view(1,-1,self.word_embedding_dim) # sentence=[7,1] [7x1x100] batch_input=[1,7,100])
# print(batch_input.size()) # print the size of the input
################################################
# here you need to put the "batch_input" input the self.lstm which is defined before.
# the hidden output should be named as output, the initial hidden state and cell state set to zero.
# ???
#print(batch_input.shape)
output,_ = self.rnn_lstm(batch_input) # 1x7x128
################################################
out = output.contiguous().view(-1,self.lstm_dim) #1x128
#print(out.shape)
out = F.relu(self.fc(out))
out = self.softmax(out)
if is_test:
prediction = out[ -1, : ].view(1,-1) #[1,6125]
#prediction = torch.max(out,0)
output = prediction
else:
output = out
# print(out)
return output