文章目录
- namespace
- access
- NSG(network security group )
- UDR (User-Defined Routing)
- Azure Firewall
namespace
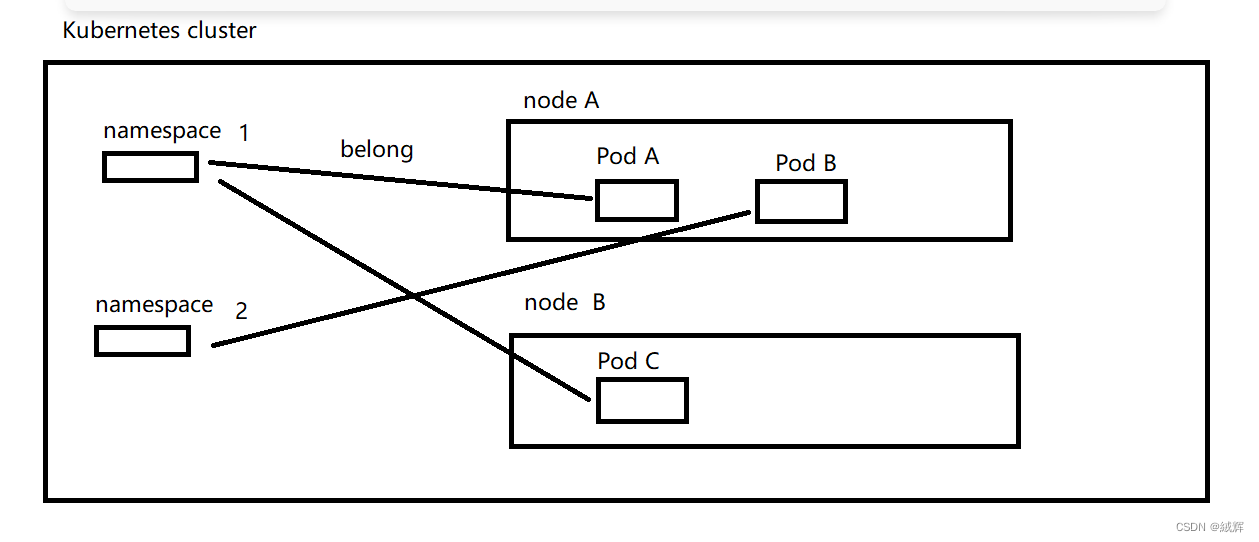
Namespaces are defined at the Kubernetes cluster level, so each namespace is unique throughout the cluster. In AKS, each namespace can contain Kubernetes resources on multiple nodes, and Kubernetes’ RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) mechanism can be used to control user or service principals’ access to resources in that namespace.
access
User can be assigned Kubernetes RBAC roles through the Azure portal to grant them access to specific services in the AKS.
Note that when assigning Kubernetes RBAC roles through the Azure portal, we can only grant built-in Kubernetes RBAC roles, not create custom RBAC roles. If we need to create custom RBAC roles, we can do so using the kubectl command line tool or the Kubernetes API.
NSG(network security group )
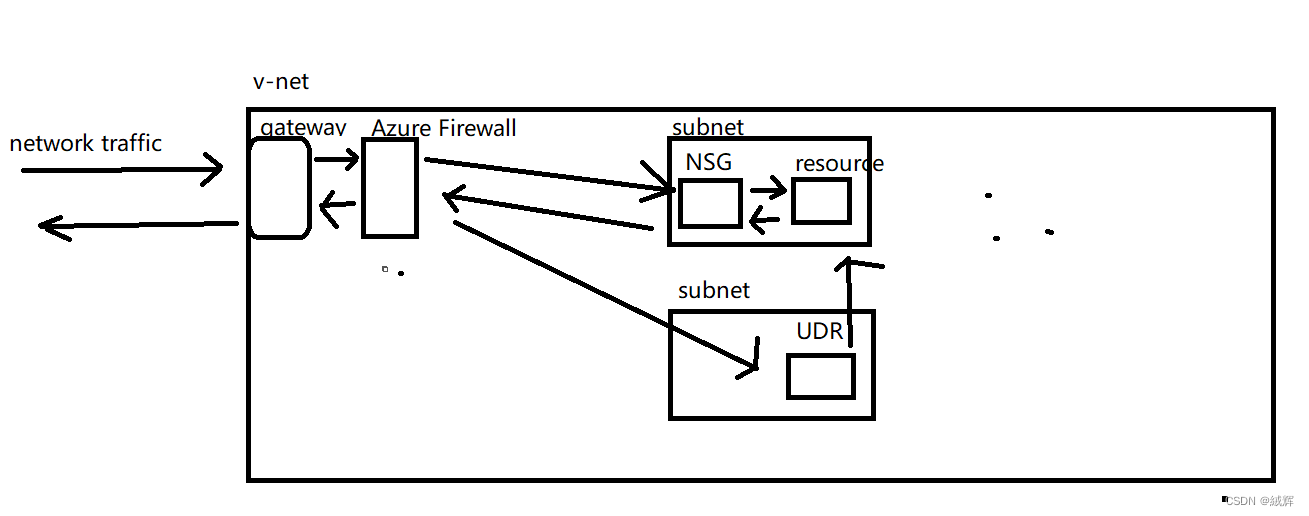
The NSG is an Azure resource that controls network traffic on a virtual network
First of all , before we learn this , we need to understand why the concept came into being.
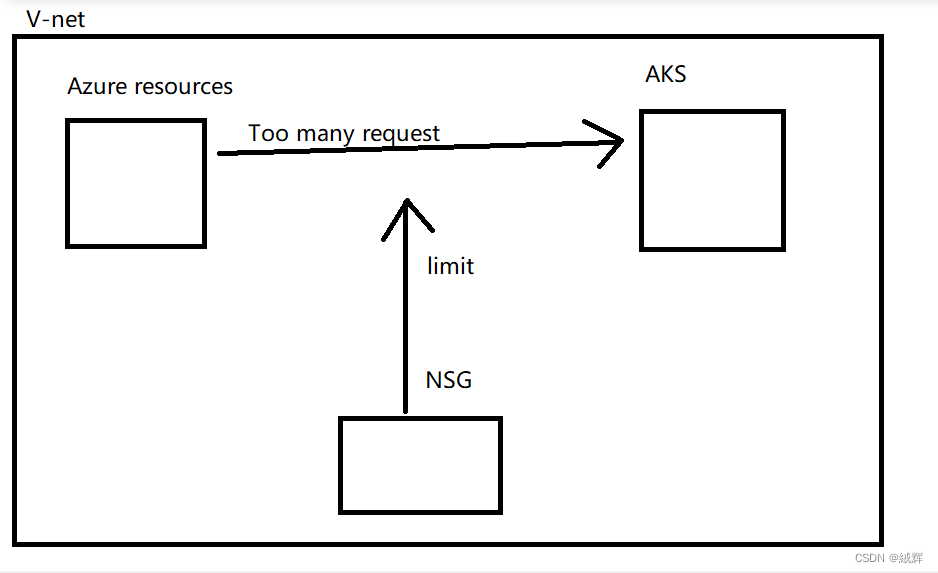
The emergence of NSG is to enhance the security of the virtual network in Azure. One of the main functions of NSG is to limit the access of other Azure resources to the Azure virtual machine. NSGS help you protect Azure resources and limit network traffic to improve network security and reliability。
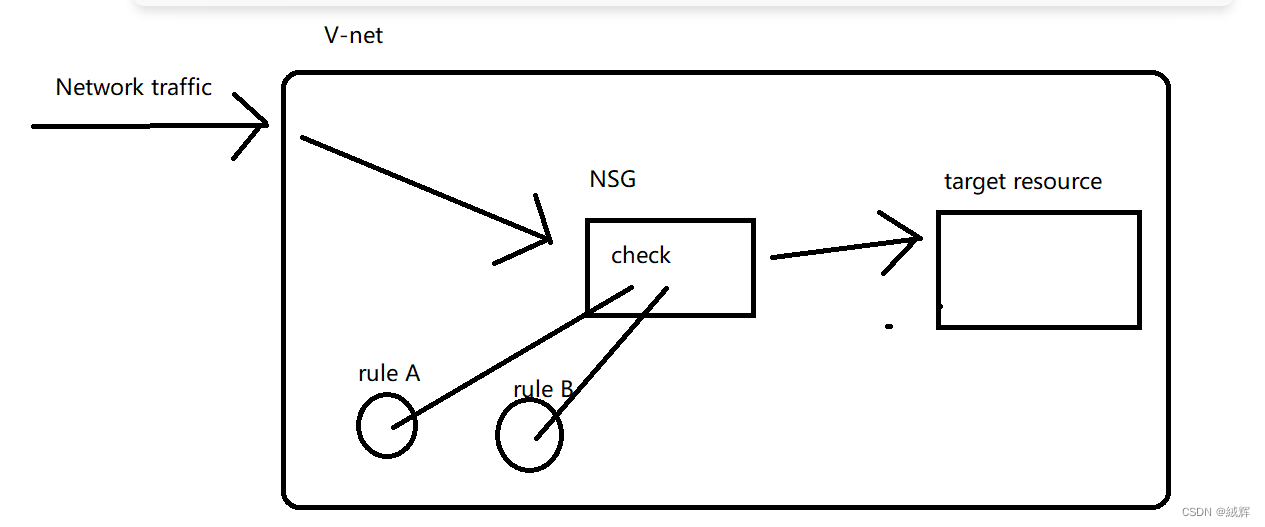
When network traffic enters a virtual network, the Azure system routes the traffic to corresponding resources based on information such as source IP address, destination IP address, protocol, and port. If traffic enters the resources associated with the NSG, the NSG matches the traffic and decides whether to allow the traffic to enter or leave the NSG based on the defined security rules.
Security rules of the NSG are in order. Rules with a higher priority override rules with a lower priority. When the traffic matches a rule, the NSG determines whether to allow or deny the traffic based on the rules. If the traffic does not comply with any rules, the NSG denies the traffic by default.
Note that NSG can operate at the subnet level or at the individual VM level. If you need to control traffic on a single VM, you can directly associate the NSG with the network interface of the VM.
UDR (User-Defined Routing)
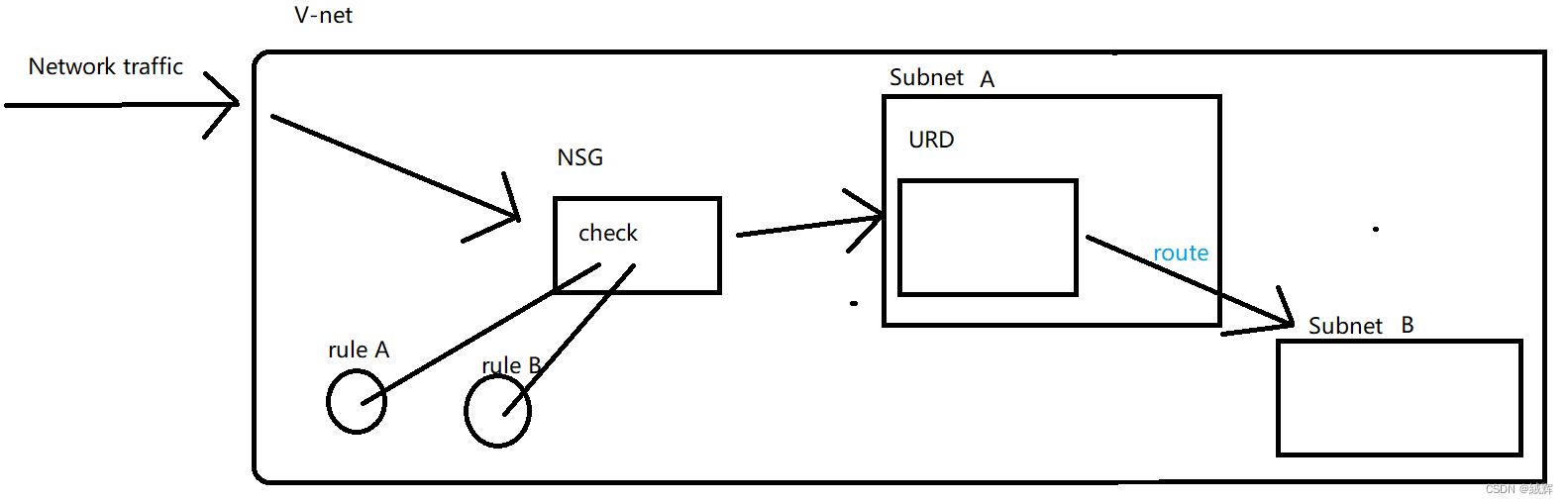
User-Defined Routing (UDR) is a function of user-defined routes on the Azure virtual network. It helps you flexibly manage network traffic.
Note that the UDR can only control the routes of traffic on the virtual network, but cannot control the routes of traffic on the public network. If you want to route public network traffic to a resource on the Azure virtual network, you need to use Load balancing services such as Azure Load Balancer or Azure Application Gateway.
After that , there are three things we have to know about UDR.
First thing is how to create a UDR
Create a UDR: First, you need to create a UDR and define routing rules. Routing rules can be matched and forwarded based on the destination IP address, source IP address, protocol, port, or next hop type. For example, you can define a routing rule to route traffic to a specific subnet or virtual network gateway.
Second thing is how to assign UDRs
Assign UDRs: After creating UDRs, you need to assign them to subnets or virtual nics. Assigning UDRs helps you control traffic routing within a virtual network. In Azure, you can assign UDRs through tools such as Azure Portal, Azure PowerShell, or Azure CLI.
Third thing is how to routed traffic
Routed traffic: After the UDR is created and allocated, the traffic within the virtual network is forwarded according to the routing rules defined in the UDR. For example, if you define A routing rule in the UDR to route traffic with destination IP address 10.0.0.0/16 to subnet A, traffic from within the virtual network with destination IP address 10.0.0.0/16 will be routed to subnet A.
Azure Firewall
The Azure Firewall functions as the front end of the virtual network. All traffic entering and leaving the virtual network must be checked and controlled by the Azure Firewall. When traffic enters or leaves the virtual network, it is routed to the public IP address of the Azure Firewall. The Azure Firewall checks whether the traffic complies with the rules and controls the traffic access and direction based on the rules.
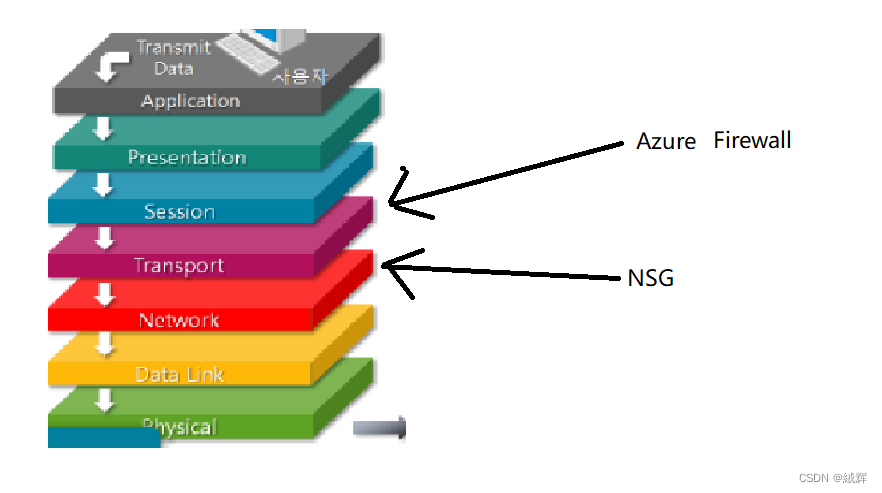
It should be noted that Azure Firewall and NSGS involve different levels of network security. Azure Firewall is located at the fourth layer (transport layer) of the OSI model, mainly because it is designed to protect network applications. NSG are located at the third layer of the OSI model (the network layer), mainly because they are designed to protect hosts and subnets in the network.
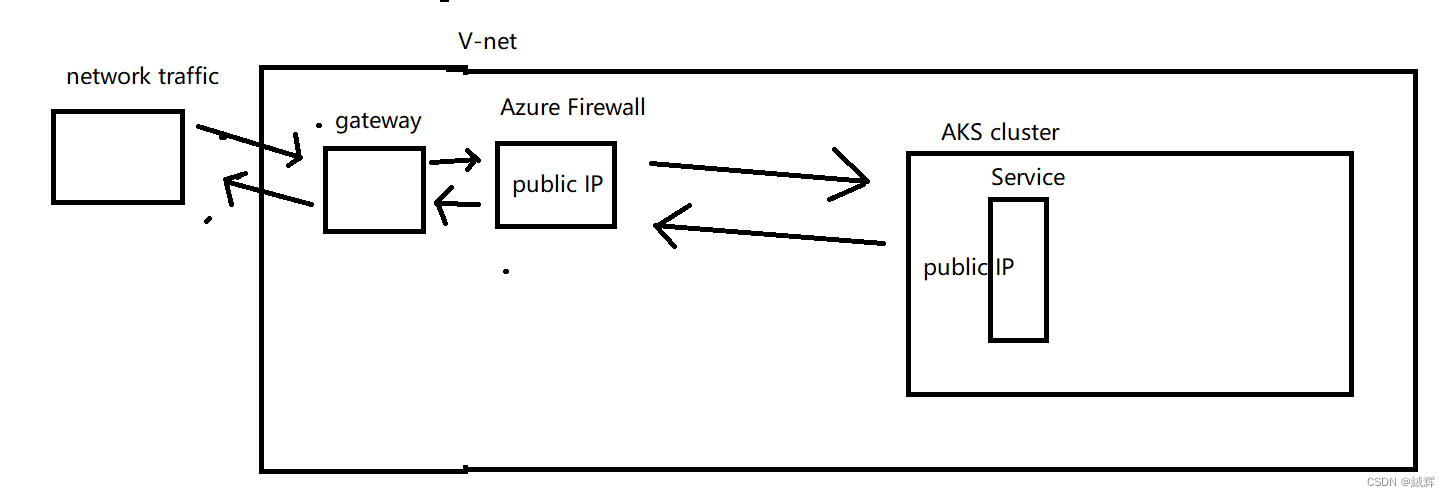
When you access a resource in the Azure virtual network from the Internet, such as a Service on AKS, you access the public IP address of the Azure Firewall. Azure Firewall will check if your request complies with the rules and control the access and direction of the request based on the rules. If the request complies with the rules, Azure Firewall will allow the request through and route it to the target resource. If the request does not conform to the rules, Azure Firewall blocks the request and logs the firewall for you to monitor and respond to.
To summary .