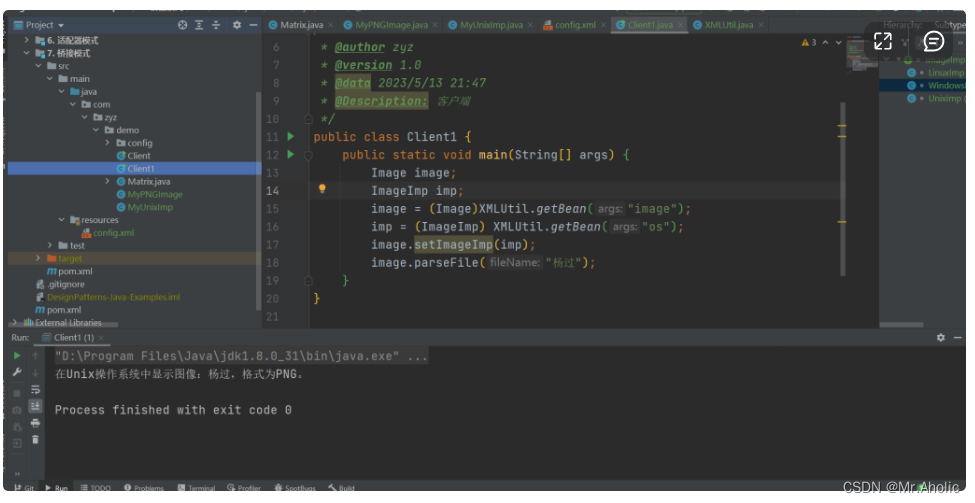
1题目
给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = "aab" 输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
示例 2:
输入:s = "a" 输出:[["a"]]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 16s仅由小写英文字母组成
2链接
题目链接:131. 分割回文串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
视频链接:带你学透回溯算法-分割回文串(对应力扣题目:131.分割回文串)| 回溯法精讲!_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
3解题思路
本题这涉及到两个关键问题:
- 切割问题,有不同的切割方式
- 判断回文
对于切割问题,可以抽象为一棵树形结构,如图:
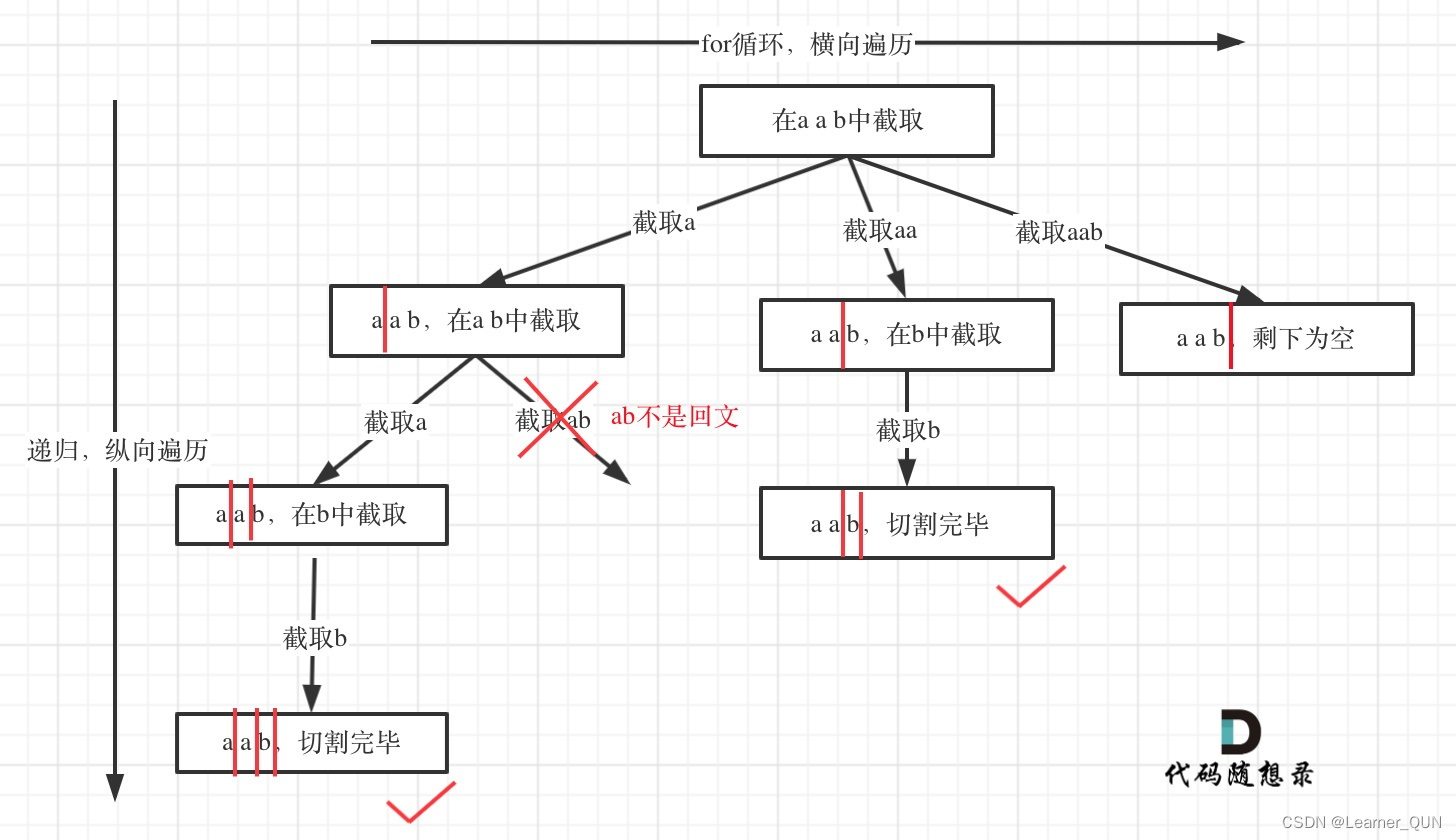
递归用来纵向遍历,for循环用来横向遍历,切割线(就是图中的红线)切割到字符串的结尾位置,说明找到了一个切割方法。
此时可以发现,切割问题的回溯搜索的过程和组合问题的回溯搜索的过程是差不多的。
回溯三部曲:
1、确定参数及返回值
全局变量数组path存放切割后回文的子串,二维数组result存放结果集。 (这两个参数可以放到函数参数里)
本题递归函数参数还需要startIndex,因为切割过的地方,不能重复切割,和组合问题也是保持一致的。
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> path; // 放已经回文的子串
void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {2、确定递归函数终止条件
从树形结构的图中可以看出:切割线切到了字符串最后面,说明找到了一种切割方法,此时就是本层递归的终止条件。
那么在代码里什么是切割线呢?
在处理组合问题的时候,递归参数需要传入startIndex,表示下一轮递归遍历的起始位置,这个startIndex就是切割线。
void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {
// 如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了
if (startIndex >= s.size()) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
}3、确定单层搜索逻辑
在for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++)循环中,我们 定义了起始位置startIndex,那么 [startIndex, i] 就是要截取的子串。
首先判断这个子串是不是回文,如果是回文,就加入在vector<string> path中,path用来记录切割过的回文子串。
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)) { // 是回文子串
// 获取[startIndex,i]在s中的子串
string str = s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1);
path.push_back(str);
} else { // 如果不是则直接跳过
continue;
}
backtracking(s, i + 1); // 寻找i+1为起始位置的子串
path.pop_back(); // 回溯过程,弹出本次已经填在的子串
}注意切割过的位置,不能重复切割,所以,backtracking(s, i + 1); 传入下一层的起始位置为i + 1
最后我们看一下回文子串要如何判断了,判断一个字符串是否是回文。
可以使用双指针法,一个指针从前向后,一个指针从后向前,如果前后指针所指向的元素是相等的,就是回文字符串了。
bool isPalindrome(const string& s, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s[i] != s[j]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}4代码
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> path; // 放已经回文的子串
void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {
// 如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了
if (startIndex >= s.size()) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)) { // 是回文子串
// 获取[startIndex,i]在s中的子串
string str = s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1);
path.push_back(str);
} else { // 不是回文,跳过
continue;
}
backtracking(s, i + 1); // 寻找i+1为起始位置的子串
path.pop_back(); // 回溯过程,弹出本次已经填在的子串
}
}
bool isPalindrome(const string& s, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s[i] != s[j]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
backtracking(s, 0);
return result;
}
};