作业要求
• Renderer.cpp 中的 Render():这里你需要为每个像素生成一条对应的光
线,然后调用函数 castRay() 来得到颜色,最后将颜色存储在帧缓冲区的相
应像素中。
• Triangle.hpp 中的 rayTriangleIntersect(): v0, v1, v2 是三角形的三个
顶点,orig 是光线的起点,dir 是光线单位化的方向向量。tnear, u, v 是你需
要使用我们课上推导的 Moller-Trumbore 算法来更新的参数。
具体实现
- Render()函数
这个函数的要求就是建立一条从相机到屏幕像素的一条光线,实现之前建议看下这篇文章,讲的很清晰,明白基本的原理实现起来就轻松许多。建立射线。
大致过程就是需要进行空间的变换,Raster space —> NDC space ----> Screen space —> Wordl space的变化。- Raster space光珊化空间,对应的坐标x = i + 0.5,y = j + 0.5
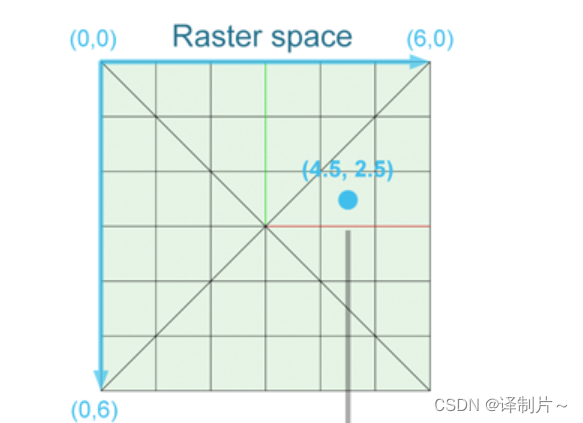
- NDC space:光栅化空间中的坐标分别除以屏幕的宽度和高度就得到了对应NDC空间的坐标,对应坐标x = (i + 0.5)/width,y = (j + 0.5)/height
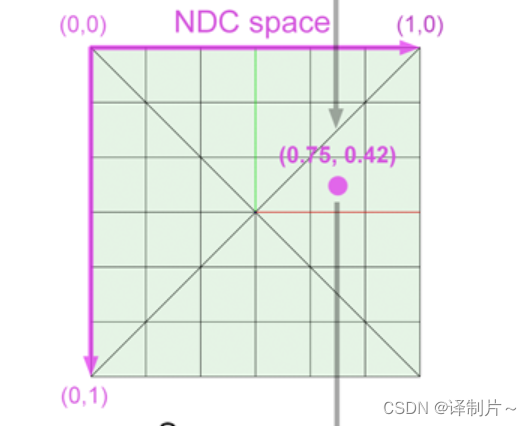
- Screen space:NDC空间得到的坐标经过如下变化就得到了屏幕空间的坐标
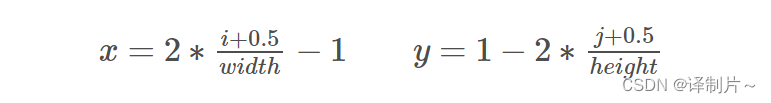
- Wordl space
屏幕空间下的公式是在宽高比为 1 并且物体本身也是分布在[-1,1]才适用。- 宽高比不为1的话就让 x 乘上宽高比(imageAspectRatio),y保持不变,此操作使 y 像素坐标(在屏幕空间中)保持不变,它仍在 [-1,1] 范围内,但 x 像素坐标现在在 [-imageAspectRatio, imageAspectRatio] 范围内。这样就能恢复成原始的比例。
- 物体本身不是在[-1,1]分布的话相当于进行了缩放,先来看物体分布在[-1,1]上的情况,如下图所示相机到屏幕空间的距离为1,而代码已给出的 Vector3f dir = Vector3f(x, y, -1) ,可以知道原本的图像屏幕距离X-Y平面为1,所以是否缩放取决于α角的大小。最后让x,y都乘上tan(α/2) 就可以得到世界空间下的坐标。
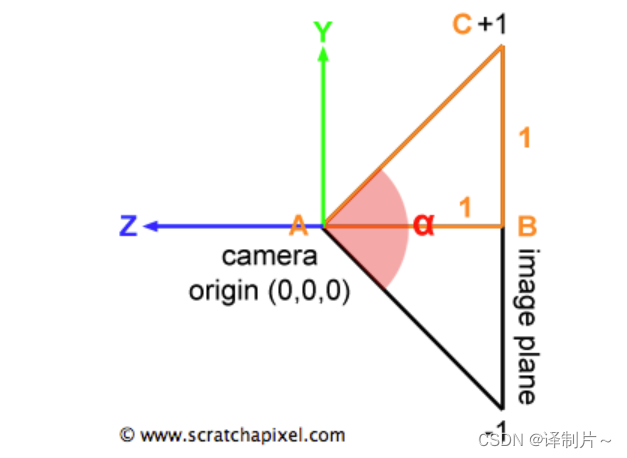
综上代码如下所示:
- Raster space光珊化空间,对应的坐标x = i + 0.5,y = j + 0.5
void Renderer::Render(const Scene& scene)
{
std::vector<Vector3f> framebuffer(scene.width * scene.height);
float scale = std::tan(deg2rad(scene.fov * 0.5f));
float imageAspectRatio = scene.width / (float)scene.height;
// Use this variable as the eye position to start your rays.
Vector3f eye_pos(0);
int m = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < scene.height; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < scene.width; ++i)
{
// generate primary ray direction
float x;
float y;
//转换成NDC空间
float PixelX = (i + 0.5)/scene.width;
float PixelY = (j + 0.5)/scene.height;
//转换成屏幕空间
x = (2 * PixelX - 1) * imageAspectRatio * scale;
y = (1 - 2 * PixelY) * scale;
// TODO: Find the x and y positions of the current pixel to get the direction
// vector that passes through it.
// Also, don't forget to multiply both of them with the variable *scale*, and
// x (horizontal) variable with the *imageAspectRatio*
Vector3f dir = normalize(Vector3f(x, y, -1)); // Don't forget to normalize this direction!
framebuffer[m++] = castRay(eye_pos, dir, scene, 0);
}
UpdateProgress(j / (float)scene.height);
}
// save framebuffer to file
FILE* fp = fopen("binary.ppm", "wb");
(void)fprintf(fp, "P6\n%d %d\n255\n", scene.width, scene.height);
for (auto i = 0; i < scene.height * scene.width; ++i) {
static unsigned char color[3];
color[0] = (char)(255 * clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].x));
color[1] = (char)(255 * clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].y));
color[2] = (char)(255 * clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].z));
fwrite(color, 1, 3, fp);
}
fclose(fp);
}
- rayTriangleIntersect()函数,这个是要根据上课时的公式来写就行
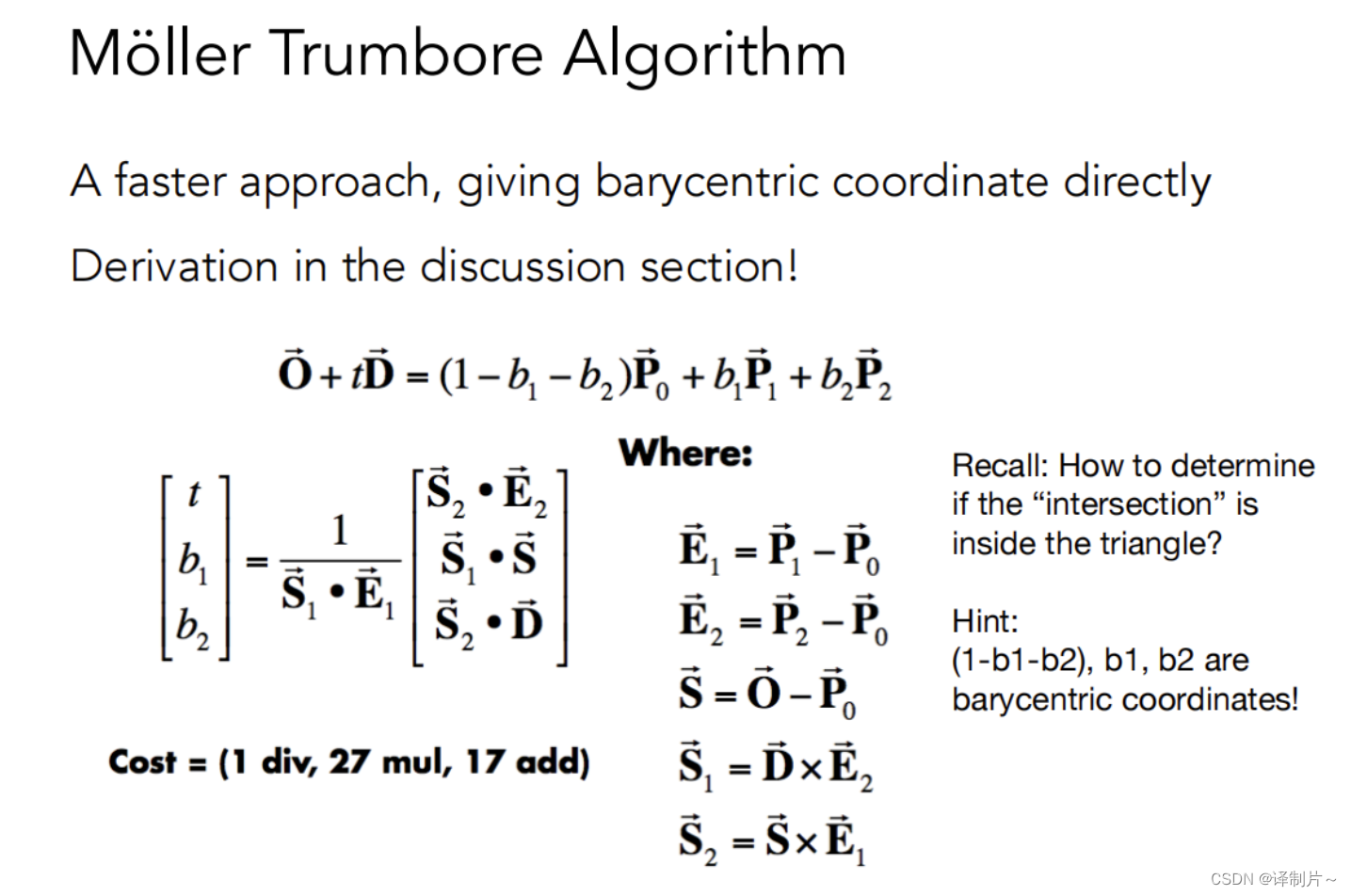
代码如下:
bool rayTriangleIntersect(const Vector3f& v0, const Vector3f& v1, const Vector3f& v2, const Vector3f& orig,
const Vector3f& dir, float& tnear, float& u, float& v)
{
// TODO: Implement this function that tests whether the triangle
// that's specified bt v0, v1 and v2 intersects with the ray (whose
// origin is *orig* and direction is *dir*)
// Also don't forget to update tnear, u and v.
Vector3f E1 = v1 - v0;
Vector3f E2 = v2 - v0;
Vector3f S = orig - v0;
Vector3f S1,S2;
S1 = crossProduct(dir,E2);
S2 = crossProduct(S,E1);
float num = dotProduct(S1,E1);
tnear = dotProduct(S2,E2) / num;
u = dotProduct(S1,S) / num;
v = dotProduct(S2,dir) / num;
if(tnear > 0 && u >= 0 && v >= 0 && (1-u-v) >= 0) //重心坐标非负表示在三角形内
return true;
else
return false;
}
最终结果
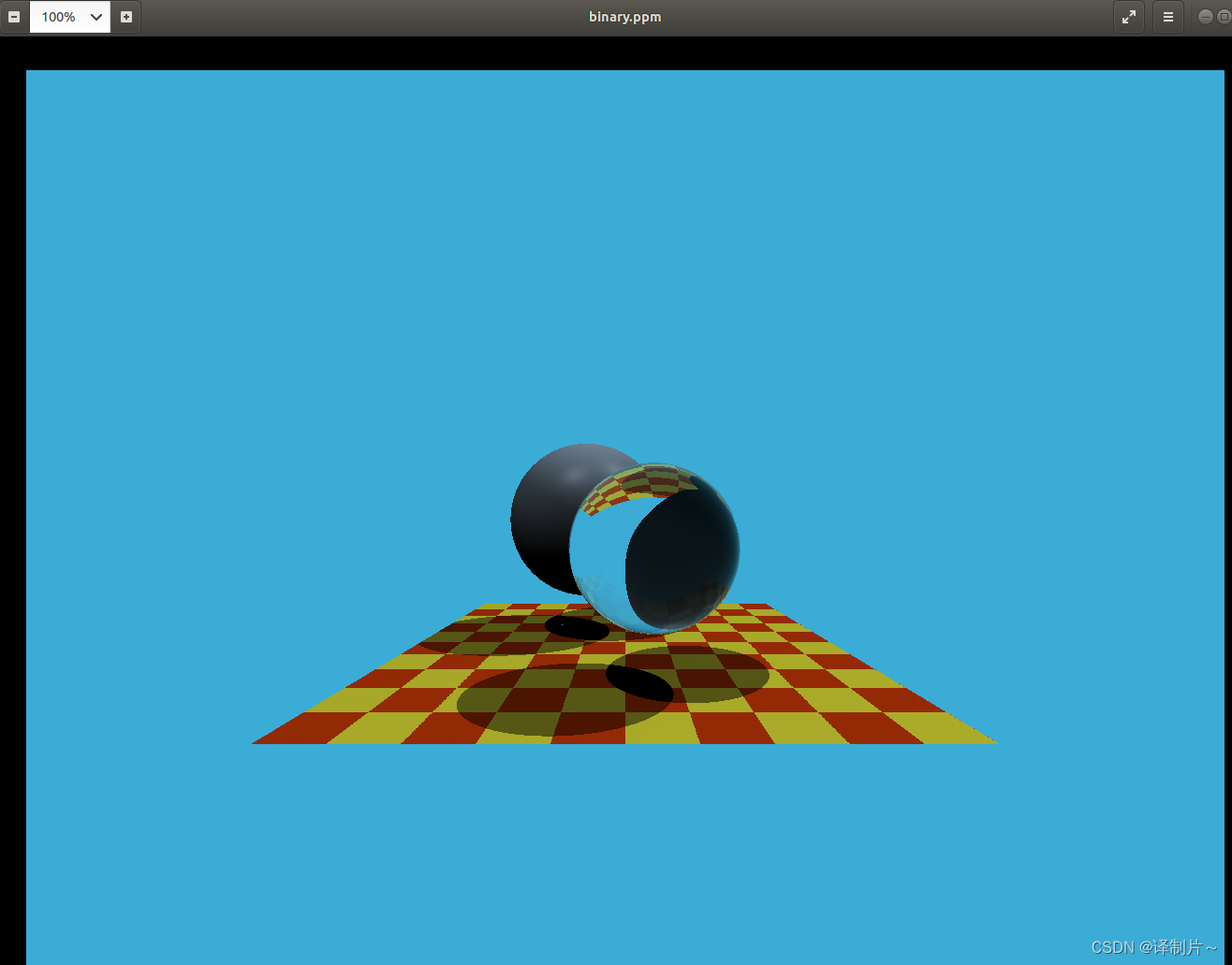
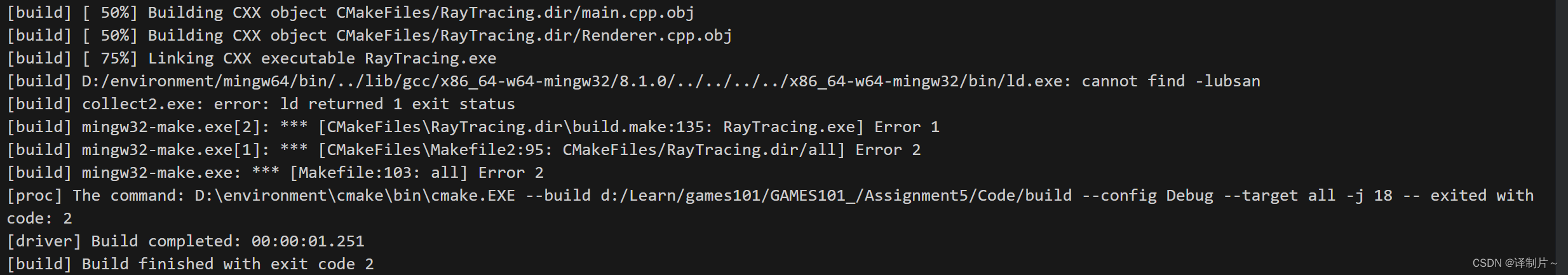
编译错误
如果你在自己电脑上运行发现如下错误说明你的mingw是64位的,而作业需要的是32位的环境,最后我有配置了个虚拟机的环境才运行出来。如果你有这个错误换个32位的环境就好了。





![【群智能算法改进】一种改进的沙丘猫群优化算法 改进沙丘猫群算法 改进SCSO[1]【Matlab代码#34】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e95879a529e04ce796e80c5913678e4d.png#pic_center)