一、认识前后端交互
1、前后端交互
- 前端向后端
发送请求, 索要数据- 因为前端没有办法
存储大量数据, 所以数据都存储在后端- 当前端需要数据时, 需要向后端
发送请求, 得到想要的数据
2、什么是ajax
- ajax全名async javascript and XML(
异步JavaScript和XML)- 是
前后台交互的能⼒,也就是我们客户端给服务端发送消息的⼯具,以及接受响应的⼯具- ajax
不是新的编程语言,而是一种使用现有标准的新方法。- AJAX 是与服务器交换数据并更新部分网页的艺术,
在不重新加载整个页面的情况下。- 是⼀个
默认异步执⾏机制的功能,AJAX分为同步(async = false)和异步(async = true)
3、简单实现一个ajax请求
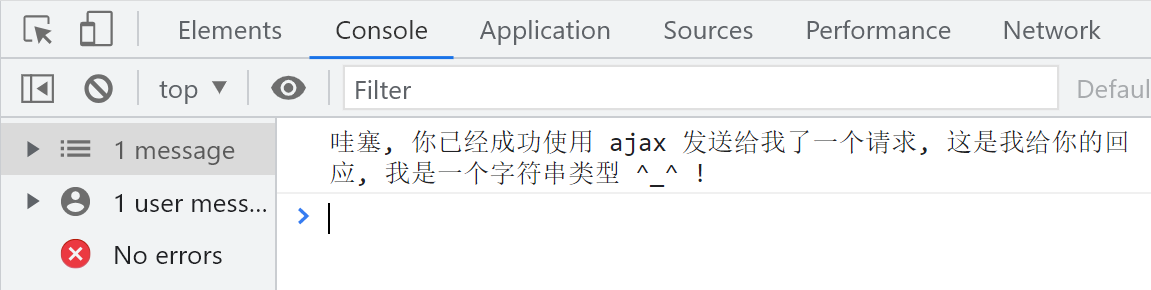
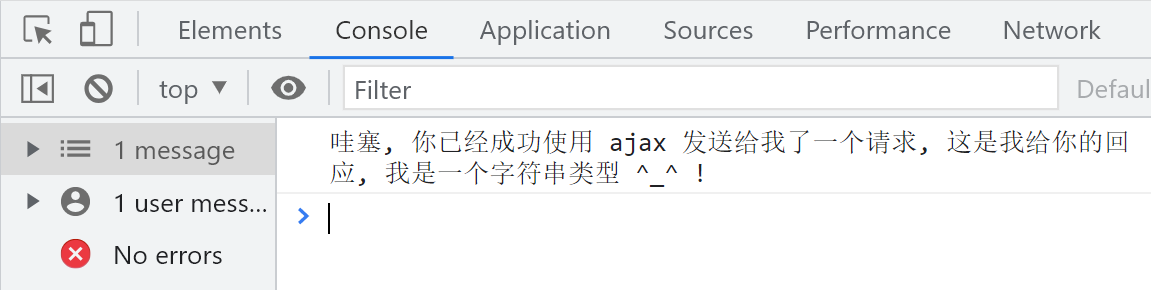
// 1. 创建ajax
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2. 向ajax配置数据
// xhr.open('参数一 ', '参数二', '参数三')
// 参数一:请求的方式, 看接口文档
// 参数二:请求的地址, 看接口文档
// 参数三:配置当前请求是否为异步, 默认是true也就是异步
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:8888/test/first', true);
// 3. 发送请求
xhr.send();
// 4. 接收响应
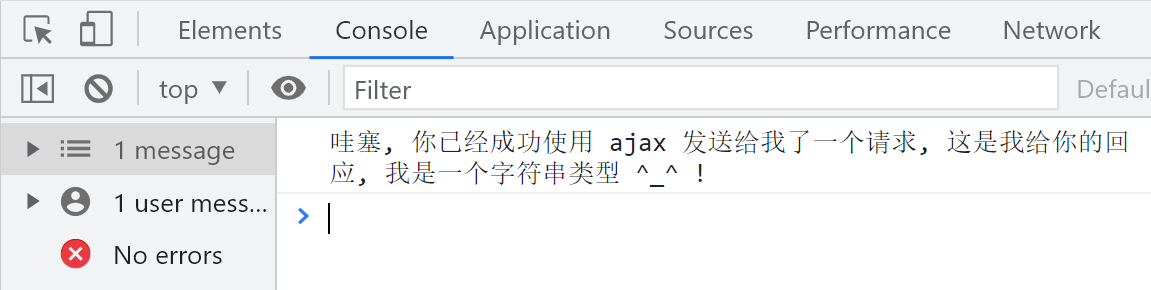
xhr.onload = function () {
console.log('接收到服务端的响应了');
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
二、ajax异步书写的问题
- 创建 ajax (
同步代码)- 配置信息 (
同步代码)- 发送请求 (
同步发送, 异步接收)- 接收到 服务端的响应 (
同步代码)
(一)异步代码的书写
1、 异步 (1 2 3 4)
- 创建
- 配置信息, 其中接收配置的是异步的
- 同步发送请求, 但是接收是异步(在接受前就会执行后续的同步代码)
- 配置接收到后的响应
- 接收到服务端的响应
// 1. 创建 ajax (同步代码)
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2. 配置信息 (同步代码)
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:8888/test/first', true)
// 3. 发送请求 (同步发送, 异步接收)
xhr.send()
// 4. 接收到 服务端的响应 (同步代码)
xhr.onload = function () {
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
2、异步(1 2 4 3)
- 创建
- 配置信息, 其中将接收配置为异步的
- 书写接收到服务器的相应的代码
- 发送请求
- 得到响应, 触发 onload 事件
// 1. 创建 ajax (同步代码)
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2. 配置信息 (同步代码)
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:8888/test/first', true)
// 4. 接收到 服务端的响应 (同步代码)
xhr.onload = function () {
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
// 3. 发送请求 (同步发送, 异步接收)
xhr.send()
- 异步代码按照 1 2 3 4,还是 1 2 4 3 都可以
(二)同步代码的书写
1、 同步 (1 2 3 4)
- 创建
- 配置信息 这里边将 接收 配置为 同步的
- 书写 接收到 服务端响应的 代码 onload
- 发送请求
- 得到服务端的响应
// 1. 创建 ajax (同步代码)
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2. 配置信息 (同步代码)
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:8888/test/first', false)
// 4. 接收到 服务端的响应 (同步代码)
xhr.onload = function () {
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
// 3. 发送请求 (同步发送, 异步接收)
xhr.send()
2、同步(1 2 4 3)
- 创建
- 配置信息, 第三个参数将 接收配置同步代码
- 发送请求 (同步发送, 同步接受)
- 接收会触发 onload
- 但是此时没有 onload 事件
- 配置 onload
- 但是此时服务端不会再有回馈,也就是说, onload 后续不会执行
// 1. 创建 ajax (同步代码)
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2. 配置信息 (同步代码)
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:8888/test/first', false)
// 3. 发送请求 (同步发送, 异步接收)
xhr.send()
// 4. 接收到 服务端的响应 (同步代码)
xhr.onload = function () {
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
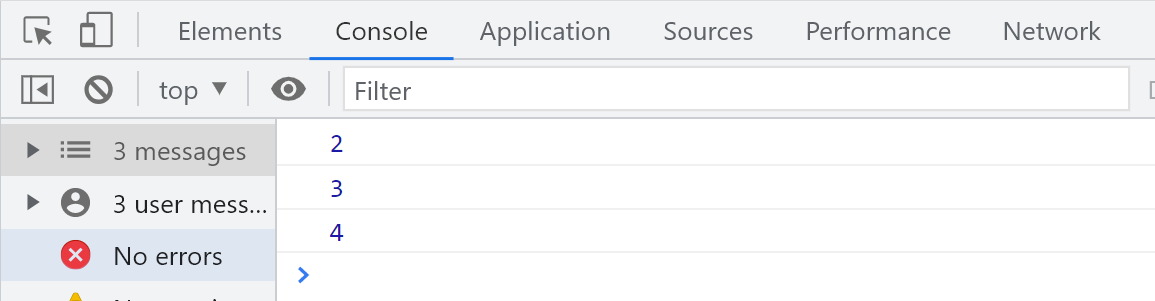
- 同步代码必须按照 1 2 4 3 的流程,按照1 2 4 3书写,返回来的是空
三、ajax的状态码
0: 表明ajax刚刚创建成功
1: 表明ajax刚刚配置成功
2: 表明ajax发送成功(还没接收到响应)
3: 表明服务端接收请求, 并反馈给我们一个响应, 此时浏览器正在解读响应的内容
4: 表明服务端接收请求,并返回一个响应, 且浏览器解读完成
// 1. 创建 ajax
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// console.log(xhr.readyState) // 打印0
// 2. 配置信息 (同步代码)
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:8888/test/first')
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
console.log(xhr.readyState)
}
// 3. 发送请求 (同步发送, 异步接收)
xhr.send()
// console.log(xhr.readyState) // 打印1
// 1. 创建 ajax
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2. 配置信息 (同步代码)
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:8888/test/first')
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
// console.log(xhr.readyState)
if (xhr.readyState === 2) {
// ajax 请求成功, 但还没有响应
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
if (xhr.readyState === 3) {
// 响应回来了, 但浏览器还在解读
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
// 响应回来了, 解读也完成
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
}
// 3. 发送请求 (同步发送, 异步接收)
xhr.send()
四、http(s) 传输协议(了解)
- http(s) 规定了请求只能由
前端发起,到后端- 再传输过程中, 如果我们有参数, 必须是字符串类型的
查询字符串
1. 建立连接
浏览器和服务端建立连接
2. 发送请求
- 前端的数据都是以
请求报文头的形式传递给后端浏览器帮我们完成
3. 返回响应
- 后端的数据都是响应报文头的形式传递给前端
- 响应状态码
4. 断开连接
- 浏览器和服务端断开连接
5、响应状态码
100~199 程序连接还在继续中
200~299 响应成功 (200)
300~399 连接重定向 (300 301 304)
400~499 代表客户端错误 (401 403 404) 一般这种都是前端出现问题, 如果确保自己没问题, 让后端检查
500~599 代表服务端错误 (500 501) 代表 后端出问题
五、ajax 请求方式的区别
(一)ajax 请求方式 (了解)
- 发get: 偏向
获取的意思- delete: 偏向获取的意思 (
删除)- post: 偏向于
提交的意思- put: 偏向于提交的意思(
修改)
常用的就只有get和post
(二)get和post的一个区别
1. 参数携带的位置
- get:将参数拼接到路径后, 参数和路径之间使用
问号分隔
- 'http://localhost:8888/test/first
?key=value&key2=value2- post:需要将参数请求体内书写
(xhr.send() 小括号内部书写)
2. 参数大小
- get:
2kb左右- post:
原则上没有限制, 服务端可以限制参数大小
3. 参数格式
- get:正常写一个 查询字符串 (
key=value&key2=value2)- post:再传参时, 需要再 请求头内设置
content-type
4. 安全性(相对安全)
- get:
明文传输, 相对不安全- post:
密文传输, 相对安全
六、测试请求
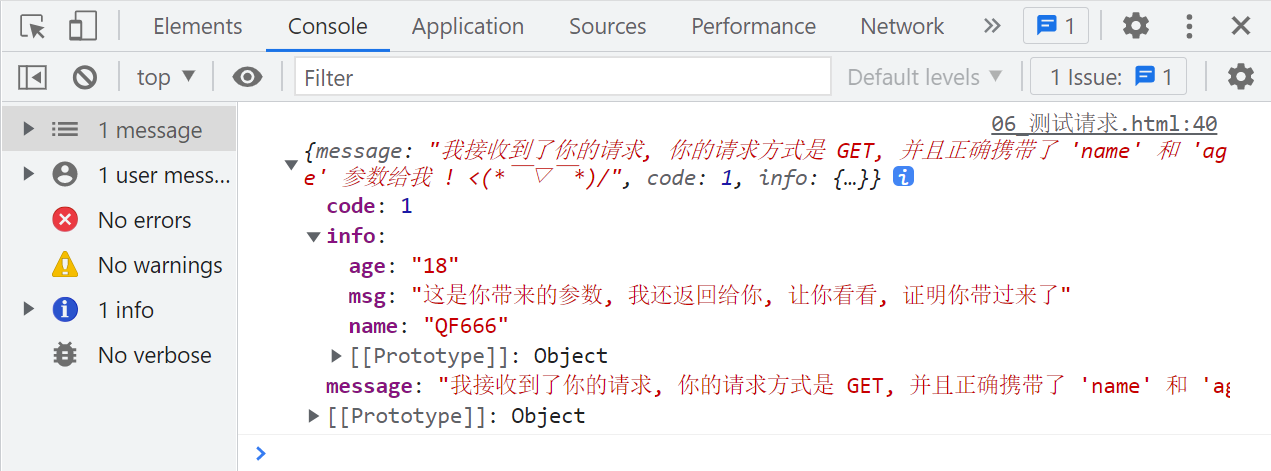
1、get参数的测试
let text1 = 'QF666'
let text2 = 18
// 1. 创建一个 ajax
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2. 配置 ajax 信息
xhr.open('GET', `http://localhost:8888/test/third?name=${text1}&age=${text2}`)
xhr.onload = function () {
const res = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText)
console.log(res)
}
xhr.send()
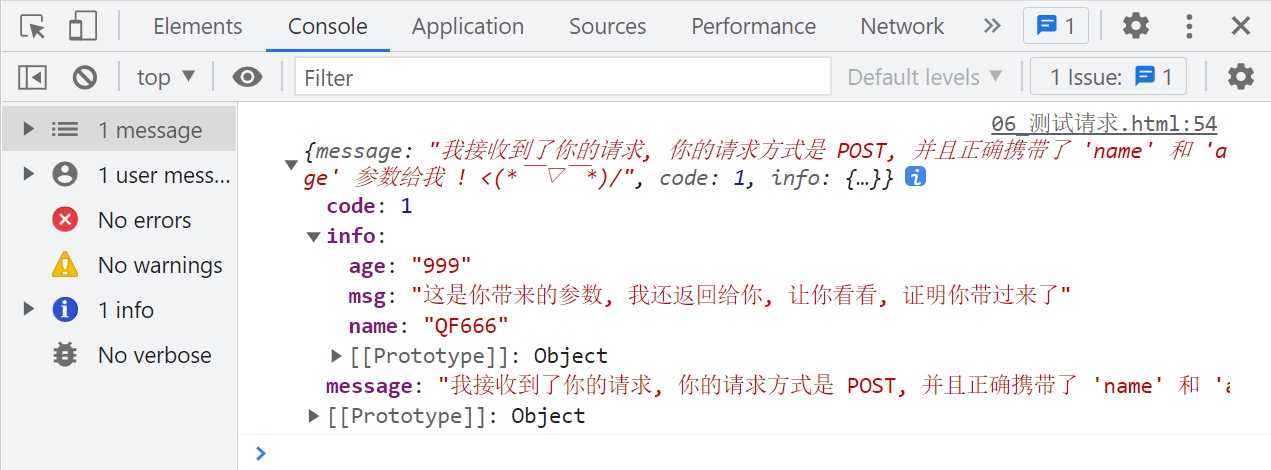
2、post参数的测试
- 如果是 post 请求, 传参时应该写在
send小括号内部, 还需要配置一下content-type- 查询字符串:
content-type配置application/x-www-form-urlencoded- JSON 字符串:
content-type配置为application/json
let text1 = 'QF666';
let text2 = 999;
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('POST', `http://localhost:8888/test/fourth`);
xhr.onload = function () {
const res = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText);
console.log(res);
}
xhr.setRequestHeader('content-type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
xhr.send(`name=${text1}&age=${text2}`);





![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot在线招聘网站](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b1e7567c34e74e0f91067c1a371a8c96.png)