扫码关注下方公粽号,回复推文合集,获取400页单细胞学习资源!

本文共计1318字,阅读大约需要4分钟,目录如下:
- 方法简介
- 演示数据来源
- 代码演示
- 小结
- 代码参考
- 往期单细胞系统教程
单细胞自动注释细胞类型的软件和方法十分繁多,早在2021年便有文章《Automatic cell type identification methods for single-cell RNA sequencing》汇总比较了不同单细胞注释软件之间的优劣。
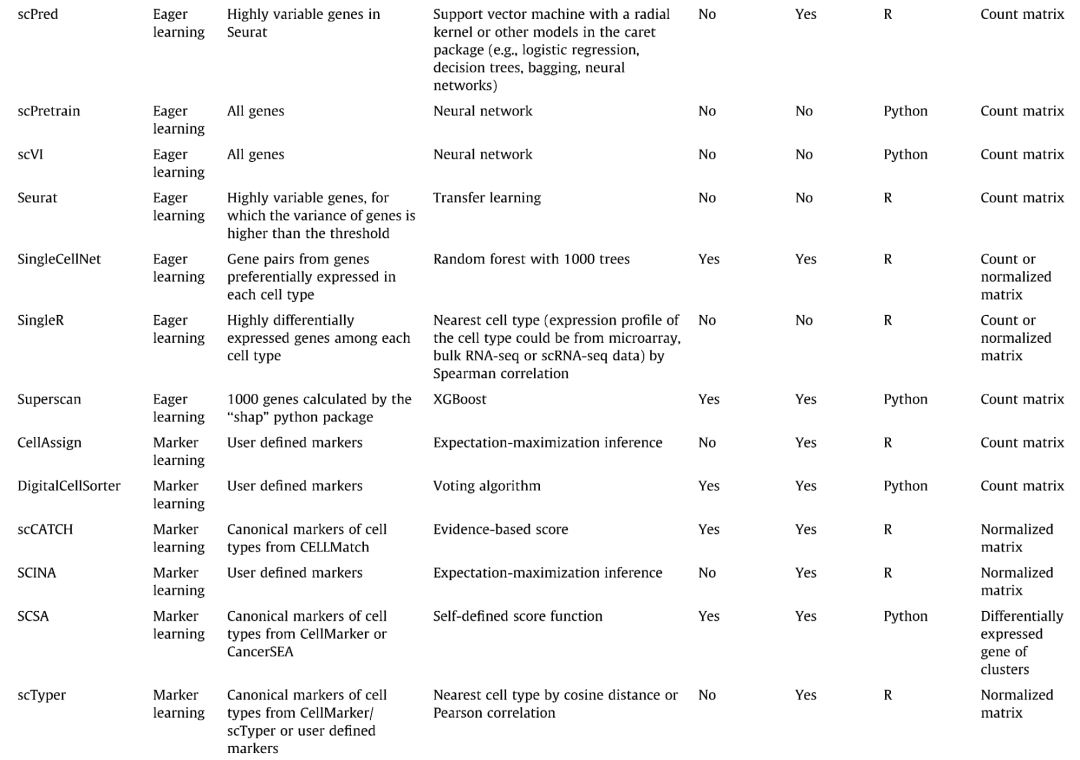
本次推文带来其中一种方法的演示,来自大家已经非常熟悉的Seurat包所自带的单细胞注释方法。
方法简介
该方法首次于2018年发表在Nature Biotechnology,题为《Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species》。作者首先通过典型关联分析(Canonical Correlation Analysis,CCA)的方法矫正不同样本间因为非生物因素造成的批次效应(考虑到文章发表较早,CCA容易出现过度矫正的可能及大样本合并的耗时太长等问题,在自己的数据进行实际操作时使用harmony或者其他方法合并亦可)来生成参考数据集。而后通过细胞类型标签对比及投射的方法获取验证数据集的单细胞类型及UMAP信息
简单解释一下就是准备好已知数据集去注释未知数据集,并且将未知数据集细胞的UMAP信息与已知数据集进行映射匹配,使得两组数据的同一种细胞类型在UMAP图中处于大概同一位置。
演示数据来源
本次为了方便大家获取数据,沿用原文作者使用的4例存储在R包SeuratData中的人类胰岛单细胞测序数据:CelSeq (GSE81076), CelSeq2 (GSE85241), Fluidigm C1 (GSE86469),和SMART-Seq2 (E-MTAB-5061)。
代码演示
###加载R包
library(Seurat)
library(SeuratData)
library(ggplot2)
library(cowplot)
library(patchwork)
###下载示例数据
InstallData("panc8")
###提取示例数据集
data("panc8")
pancreas.list <- SplitObject(panc8, split.by = "tech")
pancreas.list <- pancreas.list[c("celseq", "celseq2", "fluidigmc1", "smartseq2")]
###对list里的数据进行标准化并查找高变基因
for (i in 1:length(pancreas.list)) {
pancreas.list[[i]] <- NormalizeData(pancreas.list[[i]], verbose = FALSE)
pancreas.list[[i]] <- FindVariableFeatures(pancreas.list[[i]], selection.method = "vst", nfeatures = 2000,
verbose = FALSE)
}
###使用CCA的方法整合其中3例数据作为参考数据集
reference.list <- pancreas.list[c("celseq", "celseq2", "smartseq2")]
###识别锚点
pancreas.anchors <- FindIntegrationAnchors(object.list = reference.list, dims = 1:30)
###利用识别到的锚点对参考数据集进行整合消除批次效应
pancreas.integrated <- IntegrateData(anchorset = pancreas.anchors, dims = 1:30)
DefaultAssay(pancreas.integrated) <- "integrated"
###对参考数据集进行归一化,PCA及UMAP降维
pancreas.integrated <- ScaleData(pancreas.integrated, verbose = FALSE)
pancreas.integrated <- RunPCA(pancreas.integrated, npcs = 30, verbose = FALSE)
pancreas.integrated <- RunUMAP(pancreas.integrated, reduction = "pca", dims = 1:30, verbose = FALSE)
###查看参考数据集不同数据及不同细胞分布情况
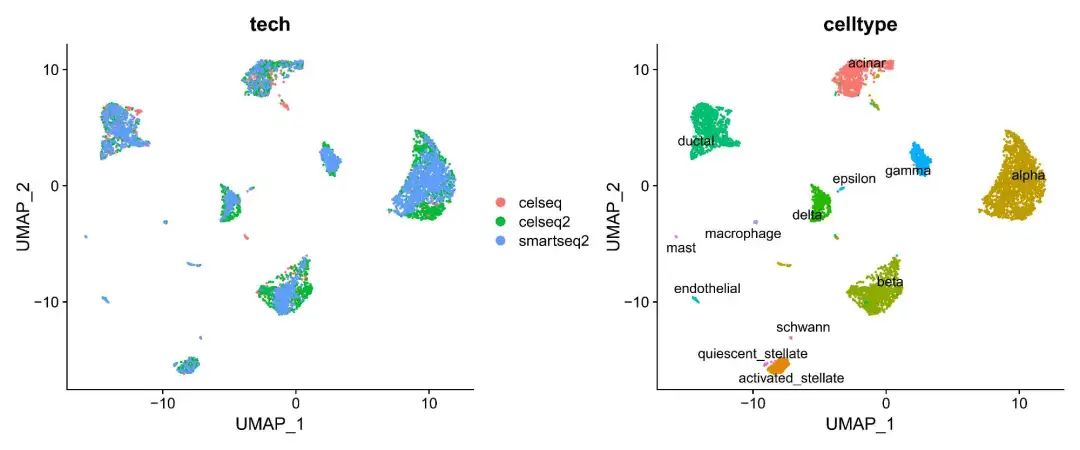
DimPlot(pancreas.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "tech") |
DimPlot(pancreas.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "celltype", label = TRUE, repel = TRUE) + NoLegend()
左图参考数据集经CCA合并后已基本消除不同测序方法的批次效应,右图不同细胞类型区分明显
###调用验证数据集
pancreas.query <- pancreas.list[["fluidigmc1"]]
###查找参考数据集及验证数据集之间的锚点
pancreas.anchors <- FindTransferAnchors(reference = pancreas.integrated, query = pancreas.query,dims = 1:30, reference.reduction = "pca")
###通过TransferData()函数预测验证数据集细胞类型
predictions <- TransferData(anchorset = pancreas.anchors, refdata = pancreas.integrated$celltype,dims = 1:30)
###添加预测细胞类型信息
pancreas.query <- AddMetaData(pancreas.query, metadata = predictions)
###验证预测细胞类型准确性
pancreas.query$prediction.match <- pancreas.query$predicted.id == pancreas.query$celltype
table(pancreas.query$prediction.match)
### FALSE TRUE
### 21 617
###超过96%的细胞预测准确
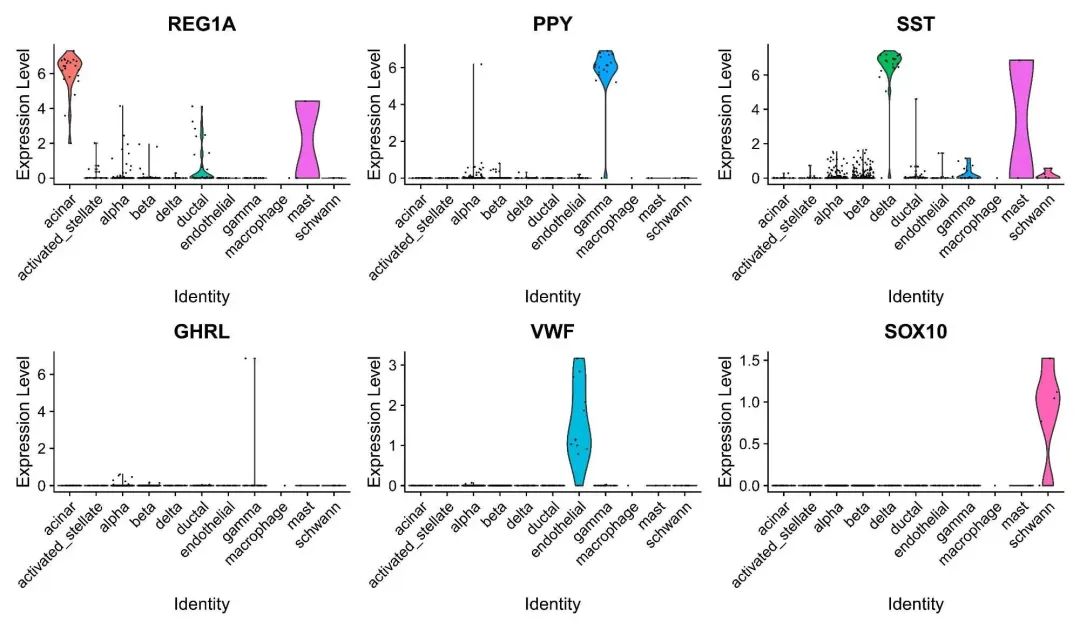
接下来作者又通过典型marker基因的方法对预测细胞类型的准确性进行判断
VlnPlot(pancreas.query, c("REG1A", "PPY", "SST", "GHRL", "VWF", "SOX10"), group.by = "predicted.id")
Seurat v4版本中,还添加了一项新的功能,就是可以通过MapQuery()函数统一参考数据集和验证数据集细胞的UMAP信息,大家看完图片展示就比较容易理解这一函数的作用了
###统一参考数据集和验证数据集UMAP信息
pancreas.integrated <- RunUMAP(pancreas.integrated, dims = 1:30, reduction = "pca", return.model = TRUE)
pancreas.query <- MapQuery(anchorset = pancreas.anchors, reference = pancreas.integrated, query = pancreas.query,refdata = list(celltype = "celltype"), reference.reduction = "pca", reduction.model = "umap")
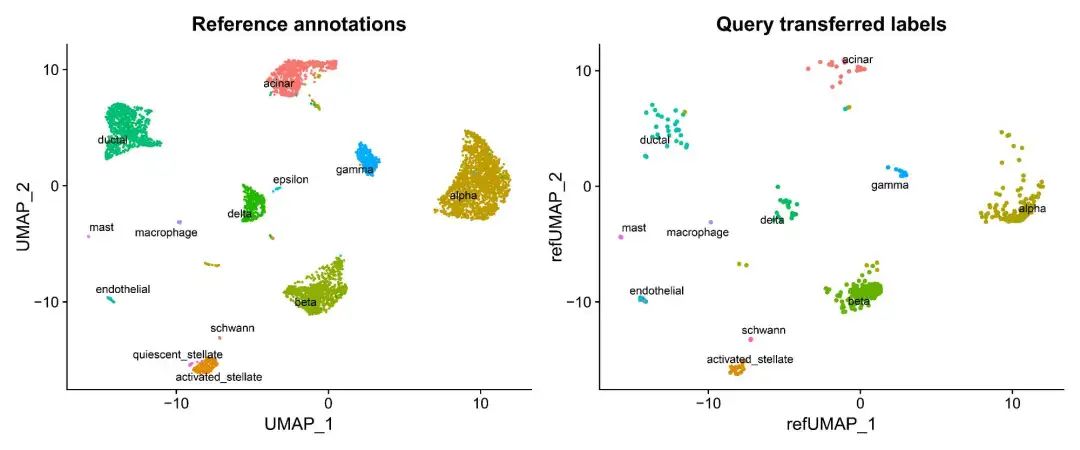
###绘制参考数据集及验证数据集UMAP图
DimPlot(pancreas.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "celltype", label = TRUE, label.size = 3, repel = TRUE) + NoLegend() + ggtitle("Reference annotations") | DimPlot(pancreas.query, reduction = "ref.umap", group.by = "predicted.celltype", label = TRUE, label.size = 3, repel = TRUE) + NoLegend() + ggtitle("Query transferred labels")
左右图分别为参考数据集和验证数据集UMAP图
小结
使用Seurat自带注释方法的人相对来说较少,不过还是可以作为一个参考,用合适的方法做出符合预期的结果,叙述好一个生物学故事才是单细胞数据分析与挖掘最为重要的地方,在小编看来单细胞的注释还是自动注释工具结合人工marker基因注释才能够对一些稀有细胞亚群进行较为准确的注释。
本次的分享到此结束,写作不易,如果觉得对您有所帮助,麻烦点个赞吧!感谢!
代码参考
代码参考:https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/integration_mapping.html
往期单细胞系统教程
单细胞分析实录(1): 认识Cell Hashing
单细胞分析实录(2): 使用Cell Ranger得到表达矩阵
单细胞分析实录(3): Cell Hashing数据拆分
单细胞分析实录(4): doublet检测
单细胞分析实录(5): Seurat标准流程
单细胞分析实录(6): 去除批次效应/整合数据
单细胞分析实录(7): 差异表达分析/细胞类型注释
推荐几个细胞注释网站
如何批量查询marker基因(对应的蛋白)会不会在膜上表达?
单细胞分析实录(8): 展示marker基因的4种图形(一)
单细胞分析实录(9): 展示marker基因的4种图形(二)
单细胞分析实录(10): 消除细胞周期的影响
单细胞分析实录(11): inferCNV的基本用法
单细胞分析实录(12): 如何推断肿瘤细胞
单细胞分析实录(13): inferCNV结合UPhyloplot2分析肿瘤进化
单细胞分析实录(14): 细胞类型注释的另一种思路 — CellID
单细胞分析实录(15): 基于monocle2的拟时序分析
单细胞分析实录(16): 非负矩阵分解(NMF)检测细胞异质性
单细胞分析实录(17): 非负矩阵分解(NMF)代码演示
单细胞分析实录(18): 基于CellPhoneDB的细胞通讯分析及可视化 (上篇)
单细胞分析实录(19): 基于CellPhoneDB的细胞通讯分析及可视化 (下篇)
一个对接CellPhoneDB的R包
【代码更新】单细胞分析实录(20): 将多个样本的CNV定位到染色体臂,并画热图
【代码更新】单细胞分析实录(21): 非负矩阵分解(NMF)的R代码实现,只需两步,啥图都有


![[电脑使用技巧]Windows 11安装安卓手机APP](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/17819950203441bfba9f50b4bbbd104a.png)