目录
A-Wireless Network
B-The Suspects
C - How Many Tables
D - How Many Answers Are Wrong
G - Supermarket
L - 小希的迷宫
M - Is It A Tree?
J - A Bug‘s Life
E - 食物链
A-Wireless Network
POJ - 2236

翻译:
东南亚发生了地震。ACM(亚洲合作医疗小组)已经与计算机建立了无线网络,但意外的余震袭击了,网络中的所有计算机都被破坏了。电脑被一台接一台地修理好了,网络渐渐又开始工作了。由于硬件的限制,每台计算机只能与距离不超过d米的计算机直接通信。但每一台计算机都可以被看作是其他两台计算机之间通信的中介,也就是说,如果计算机A和计算机B可以直接通信,或者有一台计算机C可以同时与计算机A和计算机B通信,那么计算机A和计算机B就可以通信。
在修复网络的过程中,工人们每时每刻都可以进行两种操作,一种是修复一台计算机,另一种是测试两台计算机是否可以通信。你的工作是回答所有的测试操作。
输入
第一行包含两个整数N和d (1 <= N <= 1001, 0 <= d <= 20000)。这里N是计算机数量,从1到N编号,D是两台计算机可以直接通信的最大距离。在接下来的N行中,每一行都包含两个整数xi, yi (0 <= xi, yi <= 10000),这是N台计算机的坐标。从第(N+1)行到输入的末尾,都是操作,逐个执行。每一行包含以下两种格式之一的操作:
1. “O p”(1 <= p <= N),表示修理计算机p。
2. "S p q" (1 <= p, q <= N),表示测试计算机p和q是否可以通信。
输入不超过300000行。
输出
对于每个测试操作,如果两台计算机可以通信,则打印“SUCCESS”,如果不能,则打印“FAIL”。
样例输入
4个1
0 1
0 2
0 3
0 4
1阿
O 2
O 4
s1 4
O 3
s1 4
样例输出
失败
成功
思路:经典的并查集板子题,查找合并,但是合并的时候,我们需要判断一下,是否修复,如果一个修复了一个没有修复是不能通信的,其他就没什么可以讲的了,暴力遍历+并查集板子,注意压缩路径,否则可能TLE?没有试过不压缩的。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
//inline __int128 read(){
// __int128 x = 0, f = 1;
// char ch = getchar();
// while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
// if(ch == '-')
// f = -1;
// ch = getchar();
// }
// while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
// x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
// ch = getchar();
// }
// return x * f;
//}
//inline void print(__int128 x){
// if(x < 0){
// putchar('-');
// x = -x;
// }
// if(x > 9)
// print(x / 10);
// putchar(x % 10 + '0');
//}
struct we{
int x,y;
}c[1005];
int n,d;
int a[1005];
int findd(int x){
if (a[x]==x) {
return x;
}
return a[x]=findd(a[x]);
}
void uuis(int x,int y){
int xx=findd(x);
int yy=findd(y);
if (xx!=yy) {
a[xx]=yy;
}
}
void ins(){
for (int i =1; i<=1005; i++) {
a[i]=i;
}
}
int bj[1005];
int w,ww;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
ins();
cin>>n>>d;
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
cin>>c[i].x>>c[i].y;
}
char ss;
while (cin>>ss) {
if (ss=='O') {
cin>>w;
bj[w]=1;
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
if (i==w||!bj[i]) {
continue;
}
ll jk=(c[i].x-c[w].x)*(c[i].x-c[w].x)+(c[i].y-c[w].y)*(c[i].y-c[w].y)-d*d;
if (jk<=0) {
uuis(i, w);
}
}
}
if (ss=='S') {
cin>>w>>ww;
if (findd(w)!=findd(ww)) {
printf("FAIL\n");
}
else{
printf("SUCCESS\n");
}
}
// for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
// printf("%d ",a[i]);
// }printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
——————————————————————————————————————————
B-The Suspects
POJ - 1611

翻译:
严重急性呼吸系统综合症(萨斯)是一种病因不明的非典型肺炎,于2003年3月中旬被确认为一种全球威胁。为了尽量减少传染给他人,最好的策略是将嫌疑人与他人隔离。
在不传播疾病的大学(NSYSU),有很多学生团体。同一个组的学生经常互相交流,一个学生可能加入好几个组。为了防止SARS的传播,学校收集了所有学生团体的成员名单,并在他们的标准操作程序(SOP)中制定了以下规则。
一旦组中的一个成员是可疑的,组中的所有成员都是可疑的。
然而,他们发现,当一名学生被认定为嫌疑人时,要识别出所有的嫌疑人并不容易。你的工作是编写一个程序找出所有的嫌疑犯。
输入
输入文件包含几个案例。每个测试用例都以一行中的两个整数n和m开始,其中n是学生的数量,m是小组的数量。你可以假设0 < n <= 30000和0 <= m <= 500。每个学生都用0到n−1之间的唯一整数编号,最初学生0在所有情况下都被认为是嫌疑人。这一行后面是m个组的成员列表,每个组一行。每一行都以一个整数k开头,k本身代表该组成员的数量。在成员数之后,有k个整数代表这个组的学生。一行中的所有整数至少用一个空格分隔。
n = 0, m = 0表示输入结束,不需要处理。
输出
对于每个案例,在一行中输出嫌疑犯的数量。
样例输入
100年4
2 1 2
5 10 13 11 12 14
2 0 1
2 99 2
200 2
1 5
5 1 2 3 4 5
1 0
0 0
样例输出
4
1
1
思路:板子题,直接合并,最后查询即可。
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
int a[30005],b[30000];
int find(int x){
if (a[x]==x) {
return x;
}
return a[x]=find(a[x]);
}
void uion(int x,int y){
int xx,yy;
xx=find(x);
yy=find(y);
if (xx!=yy) {
a[yy]=xx;
}return;
}
int main(){
int n,m;
while (~scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)) {
int rr=0;
if (n==0&&m==0) {
break;
}
for (int i =0; i<=n; i++) {
a[i]=i;
}
while (m--) {
int h;
scanf("%d",&h);
int w,q;
scanf("%d",&w);
for (int j=1; j<h; j++) {
scanf("%d",&q);
uion(w, q);
w=q;
}
}
for (int i =0; i<n; i++) {
if (find(i)==find(0)) {
rr++;
}
}
printf("%d\n",rr);
}
return 0;
}
———————————————————————————————————————————
C - How Many Tables
HDU - 1213

翻译:
今天是伊格那丢的生日。他邀请了很多朋友。现在该吃晚饭了。伊格那丢想知道他至少需要多少张桌子。你必须注意到,并不是所有的朋友都认识彼此,所有的朋友都不想和陌生人呆在一起。
这个问题的一个重要规则是如果我告诉你A认识B B认识C,这意味着A B C彼此认识,所以它们可以在一个表中。
例如:如果我告诉你A知道B, B知道C, D知道E,那么A, B, C可以留在一个表中,而D, E必须留在另一个表中。伊格那丢至少需要两张桌子。
输入
输入以整数T(1<=T<=25)开始,它表示测试用例的数量。然后是T测试用例。每个测试用例都以两个整数N和M(1<=N,M<=1000)开始。N为好友数,好友数从1到N,依次为M行。每一行包含两个整数A和B(A!=B),这意味着朋友A和朋友B认识彼此。两种情况之间将有一个空行。
输出
对于每个测试用例,只输出Ignatius至少需要多少个表。不要打印任何空白。
样例输入
2
5个3
1 2
2 3
4个5
5个1
2个5
样例输出
2
4
思路:板子题,合并,最后用map标记记录一下有几个不同的联通块即可。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<tuple>
#include<numeric>
#include<stack>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
int n,t;
inline __int128 read(){
__int128 x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
if(ch == '-')
f = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
inline void print(__int128 x){
if(x < 0){
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if(x > 9)
print(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
int a[1005];
void init(){
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
a[i]=i;
}
}
int fin(int x){
if (a[x]==x) {
return x;
}
return a[x]=fin(a[x]);
}
void uion(int x,int y){
int xx=fin(x),yy=fin(y);
if (xx!=yy) {
a[xx]=yy;
}
}
int m;
int w,ww;
void solv(){
map<int,int>q;
cin>>n>>m;
init();
for (int i =1; i<=m; i++) {
cin>>w>>ww;
uion(w, ww);
}
ll an=0;
// for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
// printf("%d %d ",a[i],fin(a[i]));
// }printf("\n");
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
int jk=fin(a[i]);
if (!q.count(jk)) {
an++;
q[jk]=1;
}
}printf("%lld\n",an);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
cin>>t;
while (t--) {
solv();
}
return 0;
}
———————————————————————————————————————————
D - How Many Answers Are Wrong
HDU - 3038
翻译:
TT和FF是…朋友。嗯…非常非常好的朋友-________-b
FF是一个坏男孩,他总是追求TT和他玩接下来的游戏。这是一个非常乏味的游戏。首先,TT应该写下一个整数序列-_-!!(无聊)。
然后,FF可以从中选择一个连续子序列(例如从第三个整数到第5个整数的子序列)。之后,FF会问TT他选择的子序列的和是多少。接下来,TT将回答FF的问题。然后,FF可以重做这个过程。最后,FF必须算出整个整数序列。
无聊~~无聊~~一个非常非常无聊的游戏!!TT根本不想和FF玩。为了惩罚FF,她经常故意告诉FF错误的答案。
这个坏孩子不是傻瓜。FF检测到一些答案不兼容。当然,这些矛盾使得计算顺序变得困难。
然而,TT是一个漂亮可爱的女孩。她不忍心对FF严厉。为了节省时间,她保证答案是正确的,如果没有逻辑错误的话。
更重要的是,如果FF发现一个答案是错误的,他会在判断下一个答案时忽略它。
但会有太多的问题,可怜的FF无法确定当前的答案是对还是错。所以他决定写一个程序来帮助他解决这个问题。节目将收到FF的一系列问题以及FF从TT收到的答案。这个节目的目的是找出有多少答案是错误的。只有忽略错误的答案,FF才能算出整个整数序列。可怜的FF没时间做这项工作。现在他在寻求你的帮助~(为什么要为自己找麻烦~~坏孩子)
输入
第1行:两个整数N和M (1 <= N <= 200000, 1 <= M <= 40000)。TT写了N个整数FF问了M个问题。
2号线. .M+1:第i+1行包含Ai、Bi、Si三个整数。TT回答FF Ai到Bi的和是Si。保证0 < Ai <= Bi <= N。
您可以假设子序列的任何和都适合32位整数。
输出
带有整数的一行表示有多少答案是错误的。
样例输入
10 5
1 10 100
7 10 28
1 3 32
4 6 41
6 6 1
样例输出
1
思路:
每次一个区间就会得到一个值,有多少答案是错误的,因为是l 到 r的总和,所以就是 a[r]-a[l-1],我们每次将其合并赋值,比如 1 3 3,我们将其合并赋值,ff[3]=3,a[3]=1, 1 5 3合并赋值就是,ff[5]=3,a[5]=1,可以直接得到3 5 是0,每次合并的时候看find是否相同,相同则判断值,不相同就是执行上边所说的操作。(保姆级题解~~)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
//#include<tuple>
#include<numeric>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
//inline __int128 read(){
// __int128 x = 0, f = 1;
// char ch = getchar();
// while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
// if(ch == '-')
// f = -1;
// ch = getchar();
// }
// while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
// x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
// ch = getchar();
// }
// return x * f;
//}
//inline void print(__int128 x){
// if(x < 0){
// putchar('-');
// x = -x;
// }
// if(x > 9)
// print(x / 10);
// putchar(x % 10 + '0');
//}
int n,m;
int a[200005];
ll ff[200005];
int fid(int x){
if (a[x]==x) {
return x;
}
int rm=fid(a[x]);
ff[x]+=ff[a[x]];
return a[x]=rm;
}
int q,w,e;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
while(cin>>n>>m){
for (int i =0; i<=n; i++) {
a[i]=i;
}
memset(ff, 0, sizeof ff);
ll na=0;
while (m--) {
cin>>q>>w>>e;
q=q-1;
int xx=fid(q),yy=fid(w);
if (xx!=yy) {
a[yy]=xx;
ff[yy]=ff[q]-ff[w]+e;
}
else{
if (ff[w]-ff[q]!=e) {
na++;
}
}
}
// for (int i =0; i<=n; i++) {
// printf("%d ",a[i]);
// }printf("\n");
// for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
// printf("%lld ",ff[i]);
// }printf("\n");
printf("%lld\n",na);}
//dddddd
return 0;
}
——————————————————————————————————————————
G - Supermarket
POJ - 1456
翻译:
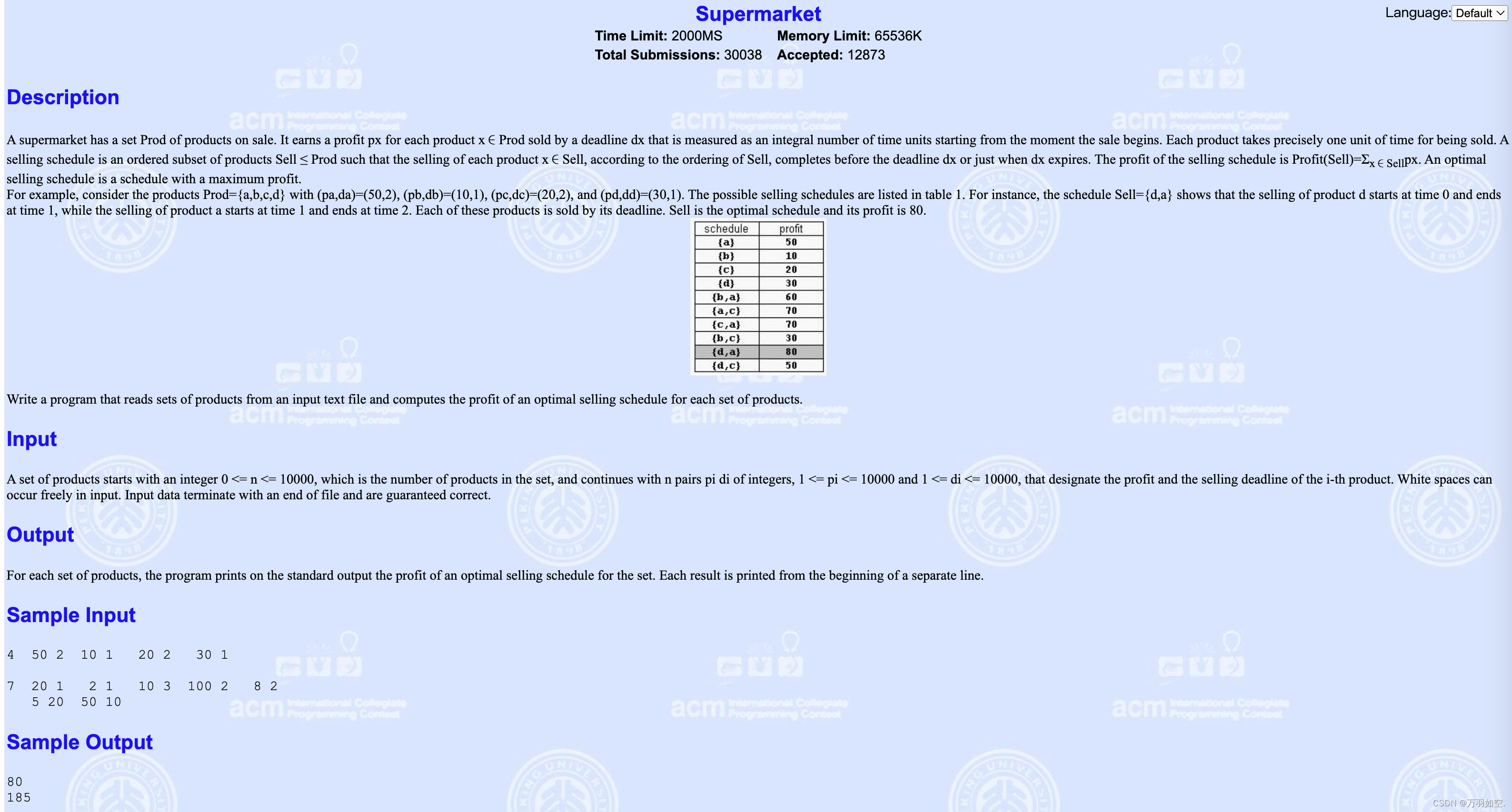
超级市场有一系列的商品在出售。每一件产品x∈Prod在截止日期dx之前售出,它获得的利润为px,该截止日期以从销售开始的时刻开始计算的时间单位的整数数来衡量。每件产品的销售只需要一个单位的时间。销售计划是Sell≤Prod的产品的有序子集,使每个产品x∈Sell的销售,根据Sell的排序,在截止日期dx之前或恰好在dx到期时完成。销售计划的利润为profit (Sell)=Σx∈Sellpx。最优销售时间表是利润最大的时间表。
例如,考虑产品刺激= {a, b, c, d} (pa, da) =(50, 2),(铅、db) = (10, 1), (pc, dc) =(20日2),和(pd, dd) =(30日1)。表1列出了可能的销售时间表。例如,时间表Sell={d,a}表明,产品d的销售从时间0开始,到时间1结束,而产品a的销售从时间1开始,到时间2结束。这些产品都在截止日期前售出。卖出是最优计划,利润是80。
编写一个程序,从输入文本文件中读取一组产品,并计算每组产品的最佳销售计划的利润。
输入
一个产品集合以整数0 <= n <= 10000开始,这是集合中的产品数量,然后是n对pi di的整数,1 <= pi <= 10000和1 <= di <= 10000,它们指定第i个产品的利润和销售截止日期。空白可以在输入中自由出现。输入数据以文件的结尾结束,并保证正确。
输出
对于每一组产品,程序在标准输出上打印该组产品的最优销售计划的利润。每个结果都从单独的行开始打印。
样例输入
4 50 2 10 1 20 2 30
7 20 1 2 1 10 3 100 2 8
5 20 50 10
样例输出
80
185
思路:在保质期前就可以出售,一天只能出售一个,最优的情况是在截止日期是出售,这样可以将前边多的日期留给别的商品,所以我们可以排个序,然后先卖价值大的,截止日期的前一天卖,这种情况是最优的,所以我们每次查询合并,如果前一天没有卖东西,我们就将其合并,卖了的话,就前边的区间就是别的值,继续向前延伸,到第0天就是卖不了,直接continue。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
//#include<tuple>
#include<numeric>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
//inline __int128 read(){
// __int128 x = 0, f = 1;
// char ch = getchar();
// while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
// if(ch == '-')
// f = -1;
// ch = getchar();
// }
// while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
// x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
// ch = getchar();
// }
// return x * f;
//}
//inline void print(__int128 x){
// if(x < 0){
// putchar('-');
// x = -x;
// }
// if(x > 9)
// print(x / 10);
// putchar(x % 10 + '0');
//}
int n;
struct we{
int x, y;
}c[10005];
bool cmp(we a,we b){
return a.x>b.x;
}
int a[10005];
ll na;
void init(){
for (int i=0; i<=10001; i++) {
a[i]=i;
}
}
int fid(int x){
if (a[x]==x) {
return a[x];
}
return a[x]=fid(a[x]);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
while (cin>>n) {
na=0;
init();
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
cin>>c[i].x>>c[i].y;
}
sort(c+1, c+1+n, cmp);
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
int xx=fid(c[i].y);
if (xx==0) {
continue;
}else{
a[xx]=fid(a[xx-1]);
na+=c[i].x;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",na);
}
return 0;
}
—————————————————————————————————————————
L - 小希的迷宫
HDU - 1272
思路:
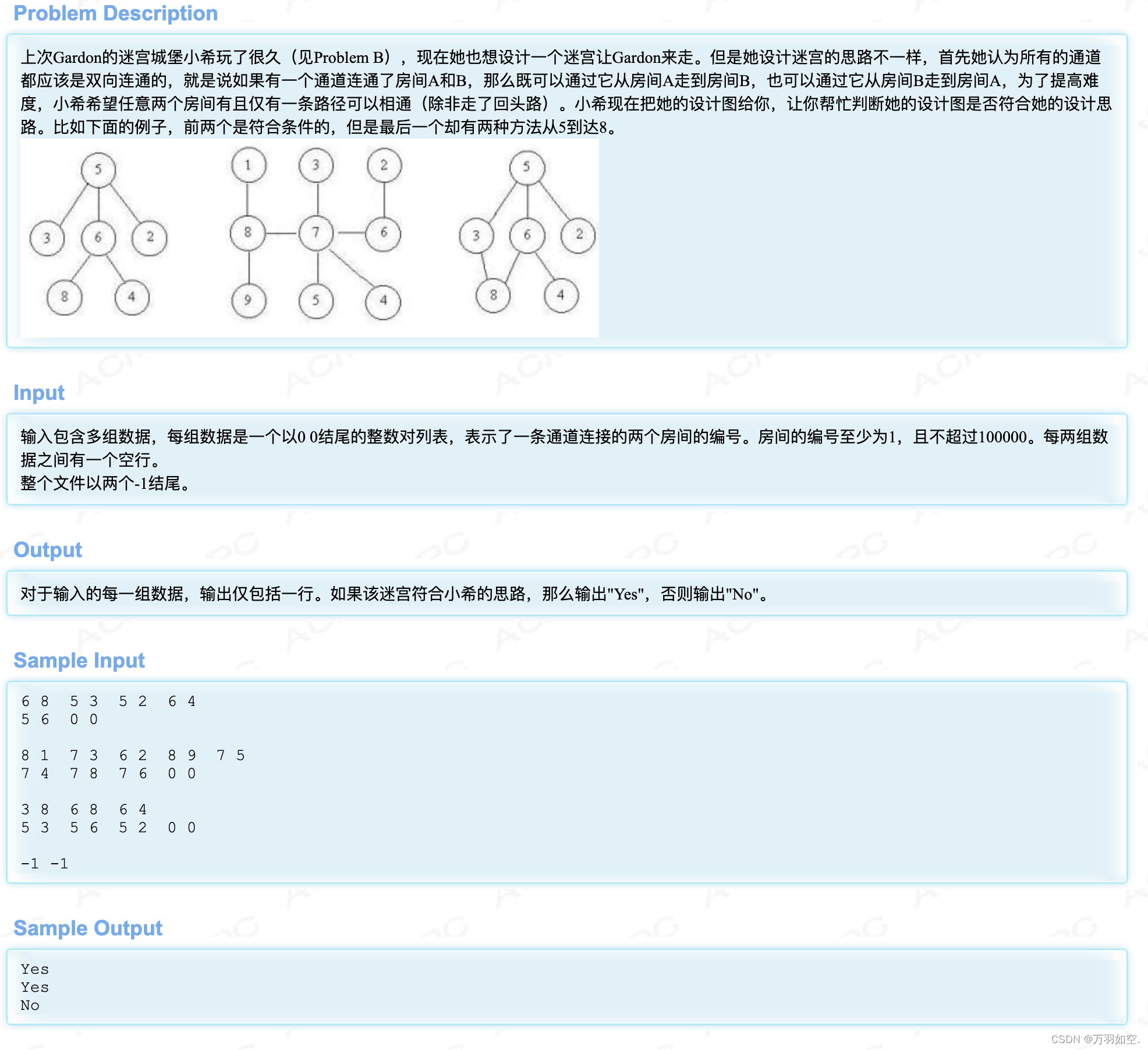
每个房间都要有路径能到达,但是不能具有两条路,很明显是一棵树。所以我们用并查集不断的去合并,如果在不断合并边的时候有相同的祖先,这就是出现了两条路径。同时也有可能出现两颗树的情况,这个时候它的路径都唯一,但是会有两个根结点,就是祖先,所以我们最后还需要遍历一下,标记判断。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
//#include<tuple>
#include<numeric>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
//inline __int128 read(){
// __int128 x = 0, f = 1;
// char ch = getchar();
// while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
// if(ch == '-')
// f = -1;
// ch = getchar();
// }
// while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
// x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
// ch = getchar();
// }
// return x * f;
//}
//inline void print(__int128 x){
// if(x < 0){
// putchar('-');
// x = -x;
// }
// if(x > 9)
// print(x / 10);
// putchar(x % 10 + '0');
//}
int n,m,xx;
int a[100005];
void init(){
for (int i=0; i<=100005; i++) {
a[i]=0;
}
}
int fid(int x){
if (a[x]==x) {
return a[x];
}
return a[x]=fid(a[x]);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
while (1) {
int bj=0;
init();
while (cin>>n>>m) {
if (n==-1&&m==-1) {
return 0;
}
if (n==0&&m==0) {
break;
}
if (a[n]==0) {
a[n]=n;
}
if (a[m]==0) {
a[m]=m;
}
int xx=fid(n);
int yy=fid(m);
if (xx==yy) {
bj=1;
}
else{
a[yy]=xx;
}
}
int su=0;
for (int i =1; i<=100005; i++) {
if (a[i]==i) {
su++;
}
}
// printf("su::%d\n",su);
if (su>1||bj) {
printf("No\n");
continue;
}
printf("Yes\n");
}
//d
return 0;
}
———————————————————————————————————————————
M - Is It A Tree?
POJ - 1308

翻译:
树是一种众所周知的数据结构,它要么是空的(null、void、nothing),要么是由满足以下属性的节点之间的有向边连接的一个或多个节点的集合。
只有一个节点,称为根节点,没有有向边指向它。
除了根节点,每个节点都只有一条边指向它。
从根结点到每个节点都有一个唯一的有向边序列。
例如,考虑下面的插图,其中节点用圆表示,边用带箭头的线表示。前两种是树,但最后一种不是。
在这道题中,我们将给出由有向边连接的节点集合的几种描述。对于其中的每一个,您要确定集合是否满足树的定义。
输入
输入将由一系列描述(测试用例)和一对负整数组成。每个测试用例将由一系列边描述和一对零组成。每个边描述将由一对整数组成;第一个整数标识了边开始的节点,第二个整数标识了边指向的节点。节点数将始终大于零。
输出
对于每个测试用例显示一行“用例k是树”或一行“用例k不是树”,其中k对应于测试用例编号(它们从1开始按顺序编号)。
样例输入
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0
1
样例输出
情形1是树。
情形2是树。
情形3不是树。
思路:题意和题目一样,判断是否成树,还是两个情况,到一个节点路径不唯一,然后可能不在一颗树,具有多个根节点,所以我们直接每次合并 到最后判断即可。
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
int a[100005],ans;
int find(int x){
if (a[x]==x) {
return x;
}
else
return a[x]=find(a[x]);
};
void uion(int x,int y){
int e=find(x);
int ee=find(y);
a[e]=ee;
};
bool vis[100005];
void ss(){
for (int i =0; i<100005; i++) {
a[i]=i;
vis[i]=false;
}
return;
};
int main(){
int n,m;
ss();
int bj=1;
int flag=0;
bool we=true;
while (~scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)) {
if (n==-1&&m==-1)
break;
if (n==0&&m==0) {
int jy=0;
for (int i =1; i<100005; i++) {
if (a[i]==i&&vis[i]) {
jy++;
}
}
if (jy>1||flag==1) {
printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",bj);
}
else
printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",bj);
bj++;
ss();
flag=0;
continue;
}
vis[n]=true;
vis[m]=true;
if (flag==1)
continue;
if (n==m)
flag=1;
int gx=find(n),gy=find(m);
if (gx==gy)
flag=1;
else
uion(n, m);
}
return 0;
}
——————————————————————————————————————————
J - A Bug‘s Life
POJ - 2492

翻译:
背景
霍珀教授正在研究一种稀有昆虫的性行为。他假设它们具有两种不同的性别,而且它们只与异性的昆虫相互作用。在他的实验中,单个昆虫及其相互作用很容易识别,因为它们的背上印有数字。
问题
给出一份昆虫相互作用的清单,判断这个实验是否支持他的假设,即两性之间没有同性恋的昆虫,或者它是否包含了一些可以推翻这一假设的昆虫相互作用。
输入
输入的第一行包含场景的数量。每个场景都以一行开始,用一个空格分隔出bug的数量(至少一个,最多2000个)和交互的数量(最多1000000个)。在下面几行中,每个交互都以两个不同的bug编号的形式给出,用一个空格分隔。从1开始依次编号。
输出
每个场景的输出都是包含“场景#i:”的一行,其中i是场景的编号,从1开始,后面的一行写着“没有发现可疑的虫子!”如果实验与他关于虫子性行为的假设一致,或者“发现可疑的虫子!”如果霍珀教授的假设绝对是错误的。
样例输入
2
3个3
1 2
2 3
1 3
4个2
1 2
3 4
样例输出
场景# 1:
发现可疑bug !
场景# 2:
没有发现可疑的bug !
提示
输入巨大,建议使用scanf。
思路:经典的带权并查集,如何判断可疑呢?同性的虫子会造成可疑,这里我们可以定义 雄性 权值为0.雌性权值为1,例如 a b,我们定义 a 0,b 1,那么接下来b c,c就一定是0,因为b是1,如果这时候又有 a c,那么两个权值相同,同性,就可以判断出可疑,所以我们可以让权值不断转移,每次+1,然后取余2,因为我们只需要 0 1的情况。如果两个的祖先相同,在一个共同的祖先下,权值相同就是同性,就是可疑。那么问题来了,如果在不同祖先的情况下呢,我们要怎么合并?
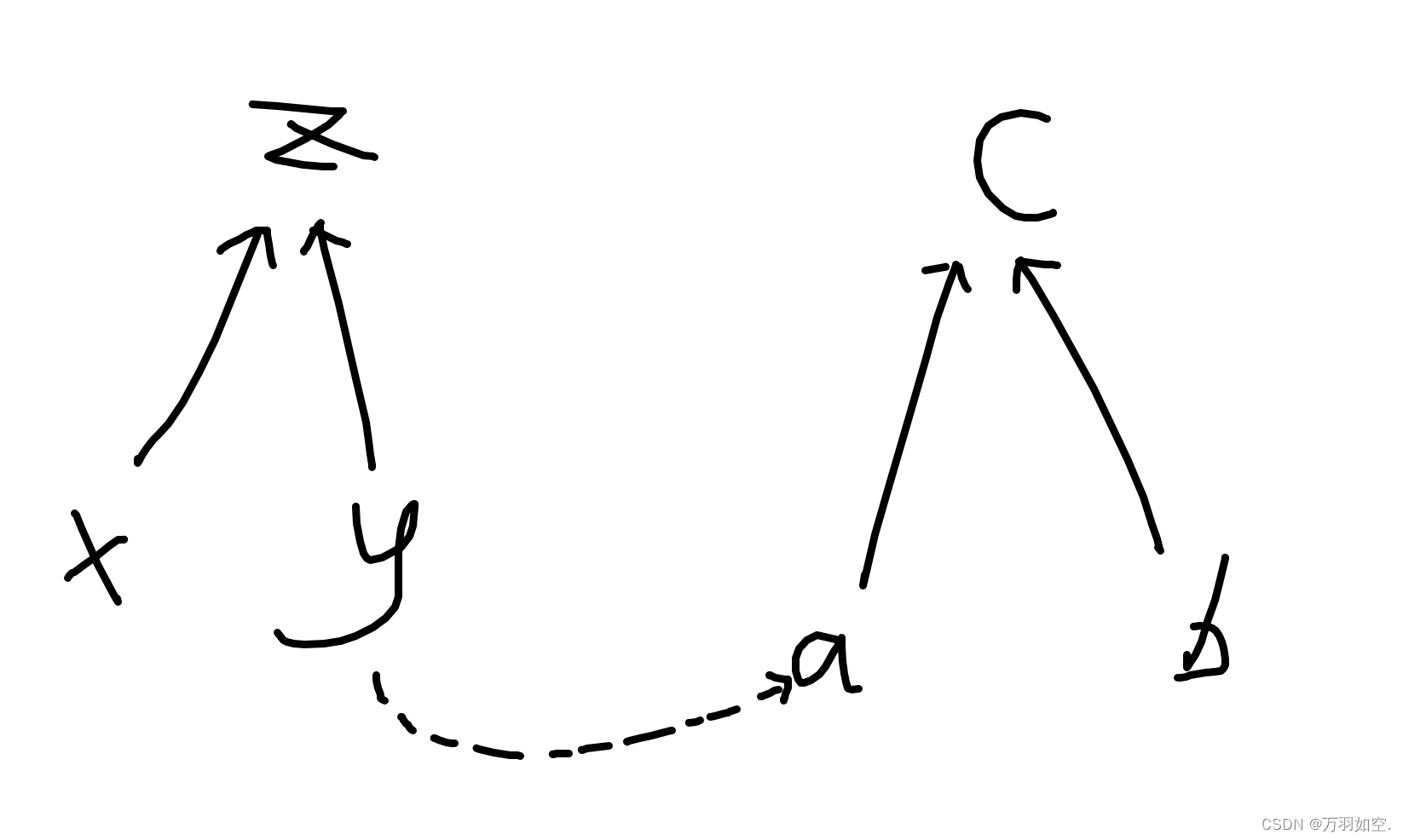
比如这种情况下合并 y a
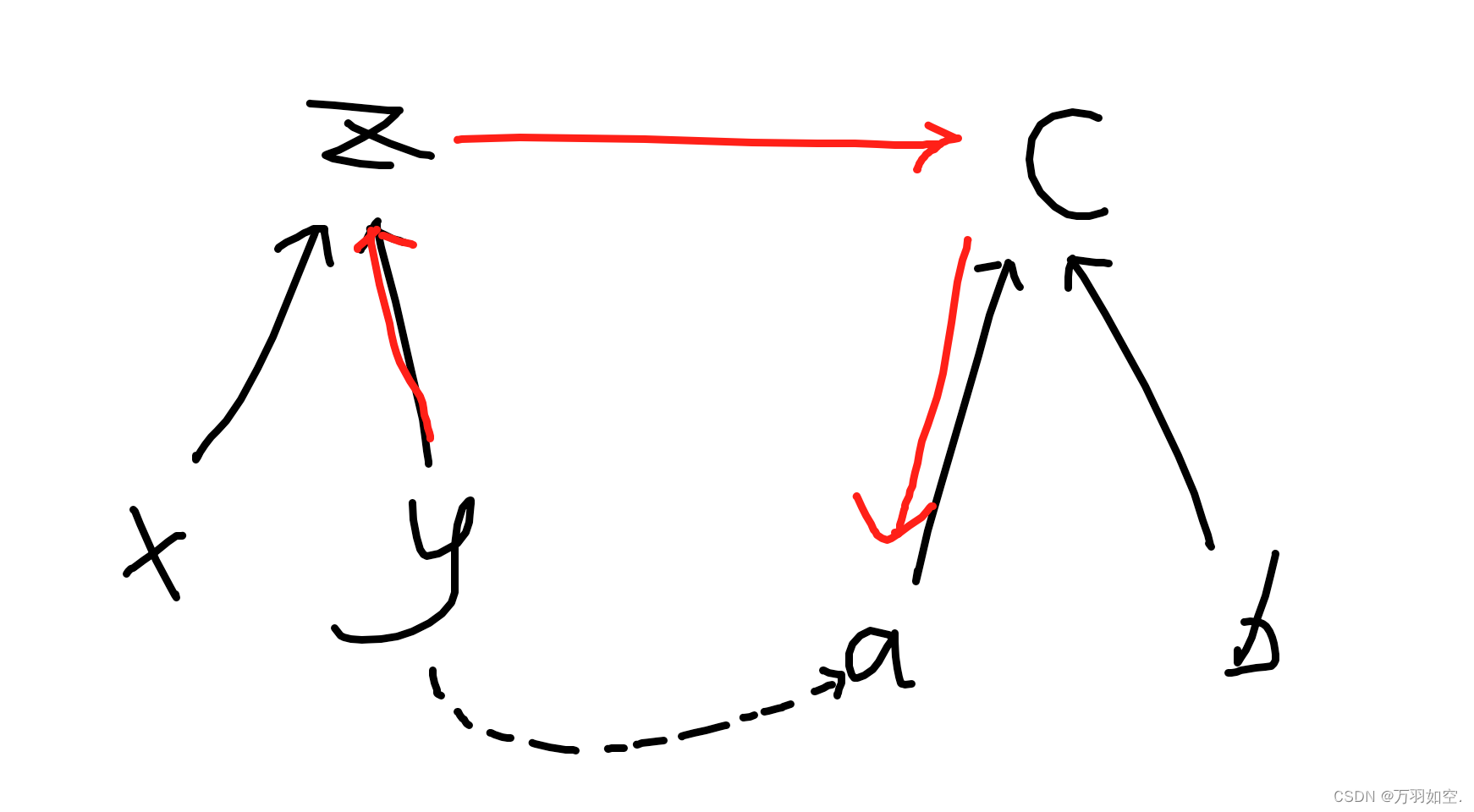
我们就可以写成这种形式,因为y a,我们可以把另一颗树的边反向过来。但因为有减法,所以我们需要+2再取余2,防止有负数产生,然后不同性,顺便权值加1,听上去可能不太懂,可以看代码,然后手动模拟一下。带权并查集,基本上都是这种写法。
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
int a[2001],qz[2001];
int m,k,bj=0;
int n,ans=0;
int find(int x){
if (x!=a[x]) {
int t=a[x];
a[x]=find(a[x]);
qz[x]=(qz[x]+qz[t])%2;
}
return a[x];
};
void uion(int x,int y){
int r=find(x);
int rr=find(y);
if (r==rr) {
if ((qz[x]+qz[y])%2==0) {
bj=1;
}
}
else{
a[r]=rr;
qz[r]=(qz[x]-qz[y]+1+2)%2;
}
return;
};
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
while (n--) {
ans++;
bj=0;
scanf("%d %d",&m,&k);
for (int i =1; i<=m; i++) {
a[i]=i;
qz[i]=0;
}
for (int i =0; i<k; i++) {
int q,w;
scanf("%d %d",&q,&w);
if (bj==1) {
continue;}
uion(q, w);
}
if (bj==1)
printf("Scenario #%d:\nSuspicious bugs found!\n\n",ans);
else
printf("Scenario #%d:\nNo suspicious bugs found!\n\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
———————————————————————————————————————————
E - 食物链
POJ - 1182

思路 :可以说是最经典的带权并查集的题目了,这里有三种可能 0 同类 1 吃 2被吃,和上一个题差不多,a b,b c,就可以得出c 吃a,所以我们判断同类可以看在一共同祖先下,权值是否相同,不同祖先,就是类似于上题的合并。判断捕食关系,也是类似,共同祖先判权值差1,不同则合并。具体细节在代码里面。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
//#include<tuple>
#include<numeric>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
//inline __int128 read(){
// __int128 x = 0, f = 1;
// char ch = getchar();
// while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
// if(ch == '-')
// f = -1;
// ch = getchar();
// }
// while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
// x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
// ch = getchar();
// }
// return x * f;
//}
//inline void print(__int128 x){
// if(x < 0){
// putchar('-');
// x = -x;
// }
// if(x > 9)
// print(x / 10);
// putchar(x % 10 + '0');
//}
int n ,k;
int a[50005],b[50005];
int fid(int x){
if (x!=a[x]) {
int nex=a[x];
a[x]=fid(a[x]);
b[x]=(b[x]+b[nex])%3;
}
return a[x];
}
int d,c,z;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
cin>>n>>k;
for ( int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
a[i]=i;
b[i]=0;
}
ll na=0;
for (int i =0; i<k; i++) {
cin>>d>>c>>z;
if (c>n||z>n) {
na++;continue;
}
if (c==z&&c==2) {
na++;continue;
}
int xx=fid(c);
int yy=fid(z);
if(d==1){
if (xx==yy&&b[c]!=b[z]) {
na++;
continue;
}
else if(xx!=yy){
a[xx]=yy;
b[xx]=(b[z]-b[c]+3)%3;
}
}
else if (d==2){
if (xx==yy) {
if ((b[c]-b[z]+3)%3!=1) {
na++;
}
}
else{
a[xx]=yy;
b[xx]=(b[z]-b[c]+4)%3;
}
}
}
printf("%lld\n",na);
return 0;
}
一些并查集的入门题目~~