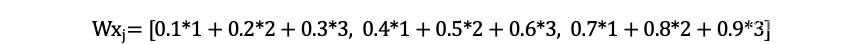C++回调函数理解
- 0.引言
- 1.回调函数的实现方式
- 2.普通函数以函数指针的形式进行实现
- 3.类成员函数以静态函数进行实现
- 4.类成员函数以非静态函数进行实现
- 5.std::funtion和std::bind的使用
- 6.c++回调的实现
- 7.应用实例
0.引言
看了一些介绍感觉太官方了,我的简单理解就是从模式设计思想出发,回调函数的目的就是为了将变化的模块抽离出来,延迟实现;固定的模块抽象出来设计好,“写死”。

- 参考博客1
- 参考博客2
1.回调函数的实现方式
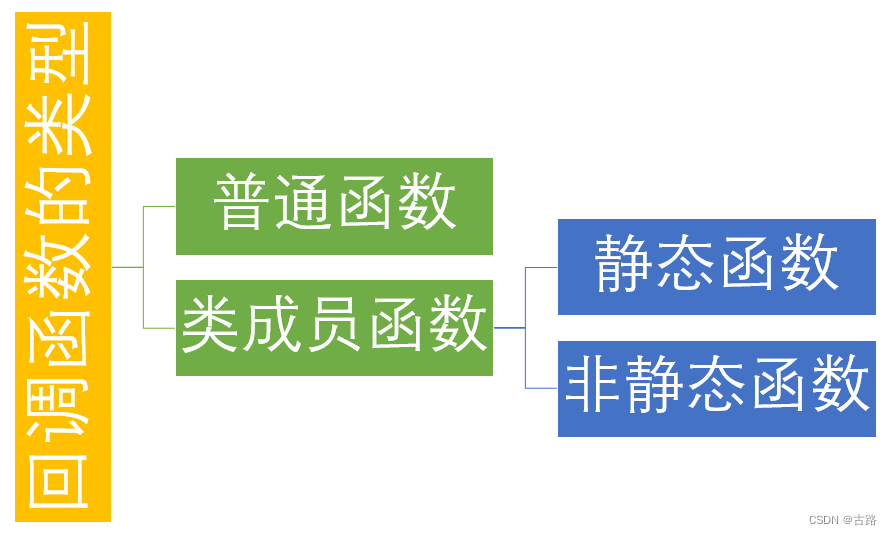
2.普通函数以函数指针的形式进行实现
#include <iostream>
// ===========不变的模块,写死================
// 回调函数类型
typedef void (*CallbackFunction)(int);
// 带回调函数参数的函数
void PerformOperation(int value, CallbackFunction callback) {
std::cout << "Performing operation with value: " << value << std::endl;
// 执行某些操作...
// 调用回调函数
callback(value * 2);
}
// =========变化的模块,放到客户端进行实现========
// 回调函数的实现
void Callback(int result) {
std::cout << "Callback received result: " << result << std::endl;
// 执行回调操作...
}
int main() {
int value = 5;
// 调用带回调函数参数的函数
PerformOperation(value, Callback);
return 0;
}
3.类成员函数以静态函数进行实现
#include <iostream>
// ===========不变的模块,写死================
// 定义回调函数类型
typedef void (*CallbackFunction)(int);
// 带回调函数参数的函数
void PerformOperation(int value, CallbackFunction callback) {
std::cout << "Performing operation with value: " << value << std::endl;
// 执行某些操作...
// 调用回调函数
callback(value * 2);
}
// =========变化的模块,放到客户端进行实现========
// 回调类
class CallbackClass {
public:
// 类的静态成员函数,当做全局函数使用
static void Callback(int result) {
std::cout << "Callback received result: " << result << std::endl;
// 执行回调操作...
}
};
int main() {
int value = 5;
// 创建回调类的对象
CallbackClass callbackObj;
// 将静态成员函数作为回调函数
CallbackFunction callback = CallbackClass::Callback;
// 调用带回调函数参数的函数
PerformOperation(value, callback);
return 0;
}
可以看出,以上两种方式没有什么本质的区别。
但这种实现有一个很明显的缺点:static 函数不能访问非static 成员变量或函数,会严重限制回调函数可以实现的功能。
4.类成员函数以非静态函数进行实现
- 实现1
#include <iostream>
// ===========不变的模块,写死================
// 定义回调函数类型
typedef void (*CallbackFunction)(int);
// 带回调函数参数的函数
void PerformOperation(int value, CallbackFunction callback) {
std::cout << "Performing operation with value: " << value << std::endl;
// 执行某些操作...
// 调用回调函数
callback(value * 2);
}
// =========变化的模块,放到客户端进行实现========
// 回调类
class CallbackClass {
public:
void Callback(int result) {
std::cout << "Callback received result: " << result << std::endl;
// 执行回调操作...
}
};
int main() {
int value = 5;
// 创建回调类的对象
CallbackClass callbackObj;
// 将非静态成员函数作为回调函数
CallbackFunction callback = [&](int result) {
callbackObj.Callback(result);
};
// 调用带回调函数参数的函数
PerformOperation(value, callback);
return 0;
}
- 实现2
#include <iostream>
// =========变化的模块,放到客户端进行实现========
class ProgramA {
public:
void FunA1() { printf("I'am ProgramA.FunA1() and be called..\n"); }
void FunA2() { printf("I'am ProgramA.FunA2() and be called..\n"); }
};
// ===========不变的模块,写死================
class ProgramB {
public:
void FunB1(void (ProgramA::*callback)(), void *context) {
printf("I'am ProgramB.FunB1() and be called..\n");
((ProgramA *)context->*callback)();
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
ProgramA PA;
PA.FunA1();
ProgramB PB;
PB.FunB1(&ProgramA::FunA2, &PA); // 此处都要加&
}
这种实现方式有很明显的缺点,不变的模块需要提前知道客户端的类型,显示不是很合理。
- 实现3
这里还有一种方法可以避免这样的问题,可以把非static的回调函数 包装为另一个static函数,这种方式也是一种应用比较广的方法。
#include <iostream>
// =========变化的模块,放到客户端进行实现========
class ProgramA {
public:
void FunA1() { printf("I'am ProgramA.FunA1() and be called..\n"); }
void FunA2() { printf("I'am ProgramA.FunA2() and be called..\n"); }
static void FunA2Wrapper(void *context) {
printf("I'am ProgramA.FunA2Wrapper() and be called..\n");
((ProgramA *)context)->FunA2(); // 此处调用的FunA2()是context的函数, 不是this->FunA2()
}
};
// ===========不变的模块,写死================
class ProgramB {
public:
void FunB2(void (*callback)(void *), void *context) {
printf("I'am ProgramB.FunB2() and be called..\n");
callback(context);
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
ProgramA PA;
PA.FunA1();
ProgramB PB;
PB.FunB2(ProgramA::FunA2Wrapper, &PA);
}
上面借助wrapper函数实现回调,虽然很灵活,但是还是不够优秀,比如:
- 1)多了一个不是太有实际用处的wrapper函数。
- 2)wrapper中还要对传入的指针进行强制转换。
- 3)FunB2调用时,不但要指定wrapper函数的地址,还要传入PA的地址。
5.std::funtion和std::bind的使用
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> // fucntion/bind
// =========变化的模块,放到客户端进行实现========
class ProgramA {
public:
void FunA1() { printf("I'am ProgramA.FunA1() and be called..\n"); }
void FunA2() { printf("I'am ProgramA.FunA2() and be called..\n"); }
static void FunA3() { printf("I'am ProgramA.FunA3() and be called..\n"); }
};
// ===========不变的模块,写死================
class ProgramB {
typedef std::function<void ()> CallbackFun;
public:
void FunB1(CallbackFun callback) {
printf("I'am ProgramB.FunB2() and be called..\n");
callback();
}
};
void normFun() { printf("I'am normFun() and be called..\n"); }
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
ProgramA PA;
PA.FunA1();
printf("\n");
ProgramB PB;
PB.FunB1(normFun);
printf("\n");
PB.FunB1(ProgramA::FunA3);
printf("\n");
PB.FunB1(std::bind(&ProgramA::FunA2, &PA));
}
std::funtion支持直接传入函数地址,或者通过std::bind指定。
简而言之,std::funtion是定义函数类型(输入、输出),std::bind是绑定特定的函数(具体的要调用的函数)。
6.c++回调的实现
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
// ===========不变的模块,写死================
class MyTest{
public:
MyTest() = default;
void doCalc(){
//干其他事,完了
// 执行回调
if(myCallBack!= nullptr){
myCallBack(1,2);
}
}
using callback_t = std::function<void(const int &a, const int &b)>;
// 注册回调
void setCallBackHandler(const callback_t &cb){
myCallBack = cb;
}
private:
// 定义回调
callback_t myCallBack;
};
// =========变化的模块,放到客户端进行实现========
// 回调函数
void handleCallBack(const int &a,const int &b){
std::cout << "this is from callback handleCallBack"<<std::endl;
}
int main(){
MyTest t;
// 回调函数
auto f= [](const int &a,const int &b){
std::cout << "this is from callback f"<<std::endl;
};
// 注册回调
// 写法一
t.setCallBackHandler(f);
// 写法二
t.setCallBackHandler([&f](auto &&a, auto &&b) {
f(std::forward<decltype(a)>(a), std::forward<decltype(b)>(b));
});
// 写法三
t.setCallBackHandler([](auto &&a, auto &&b) {
handleCallBack(std::forward<decltype(a)>(a), std::forward<decltype(b)>(b));
});
t.doCalc();
}
7.应用实例
- 摘抄自高博的代码。
(1)写死的模块
- io_utils.h
#include <fstream>
#include <functional>
#include <utility>
class TxtIO {
public:
TxtIO(const std::string &file_path) : fin(file_path) {}
/// 定义回调函数
using IMUProcessFuncType = std::function<void(const IMU &)>;
using OdomProcessFuncType = std::function<void(const Odom &)>;
using GNSSProcessFuncType = std::function<void(const GNSS &)>;
TxtIO &SetIMUProcessFunc(IMUProcessFuncType imu_proc) {
imu_proc_ = std::move(imu_proc);
return *this;
}
TxtIO &SetOdomProcessFunc(OdomProcessFuncType odom_proc) {
odom_proc_ = std::move(odom_proc);
return *this;
}
TxtIO &SetGNSSProcessFunc(GNSSProcessFuncType gnss_proc) {
gnss_proc_ = std::move(gnss_proc);
return *this;
}
// 遍历文件内容,调用回调函数
void Go();
private:
std::ifstream fin;
IMUProcessFuncType imu_proc_;
OdomProcessFuncType odom_proc_;
GNSSProcessFuncType gnss_proc_;
};
- io_utils.cc
#include "io_utils.h"
#include <glog/logging.h>
void TxtIO::Go() {
if (!fin) {
LOG(ERROR) << "未能找到文件";
return;
}
while (!fin.eof()) {
std::string line;
std::getline(fin, line);
if (line.empty()) {
continue;
}
if (line[0] == '#') {
// 以#开头的是注释
continue;
}
// load data from line
std::stringstream ss;
ss << line;
std::string data_type;
ss >> data_type;
if (data_type == "IMU" && imu_proc_) {
double time, gx, gy, gz, ax, ay, az;
ss >> time >> gx >> gy >> gz >> ax >> ay >> az;
// imu_proc_(IMU(time, Vec3d(gx, gy, gz) * math::kDEG2RAD, Vec3d(ax, ay, az)));
imu_proc_(IMU(time, Vec3d(gx, gy, gz), Vec3d(ax, ay, az)));
} else if (data_type == "ODOM" && odom_proc_) {
double time, wl, wr;
ss >> time >> wl >> wr;
odom_proc_(Odom(time, wl, wr));
} else if (data_type == "GNSS" && gnss_proc_) {
double time, lat, lon, alt, heading;
bool heading_valid;
ss >> time >> lat >> lon >> alt >> heading >> heading_valid;
gnss_proc_(GNSS(time, 4, Vec3d(lat, lon, alt), heading, heading_valid));
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "done.";
}
把读取文件的操作抽象出来写死,具体怎么处理留给回调函数(客户端)进行实现。
(2)变化的模块
/// 记录结果
auto save_result = [](std::ofstream& fout, double timestamp, const Sophus::SO3d& R, const Vec3d& v,
const Vec3d& p) {
auto save_vec3 = [](std::ofstream& fout, const Vec3d& v) { fout << v[0] << " " << v[1] << " " << v[2] << " "; };
auto save_quat = [](std::ofstream& fout, const Quatd& q) {
fout << q.w() << " " << q.x() << " " << q.y() << " " << q.z() << " ";
};
fout << std::setprecision(18) << timestamp << " " << std::setprecision(9);
save_vec3(fout, p);
save_quat(fout, R.unit_quaternion());
save_vec3(fout, v);
fout << std::endl;
};
std::ofstream fout("./data/ch3/state.txt");
io.SetIMUProcessFunc([&imu_integ, &save_result, &fout, &ui](const sad::IMU& imu) {
imu_integ.AddIMU(imu);
save_result(fout, imu.timestamp_, imu_integ.GetR(), imu_integ.GetV(), imu_integ.GetP());
if (ui) {
ui->UpdateNavState(imu_integ.GetNavState());
usleep(1e2);
}
}).Go();
可以,还是很实用。