文章目录
- 代码示例
- 流程源码解析
- 开启全局事务
- 注册分支事务
- 一阶段提交
- 全局事务提交
- 分支事务二阶段提交
- 全局事务回滚
- 分支事务二阶段回滚
代码示例
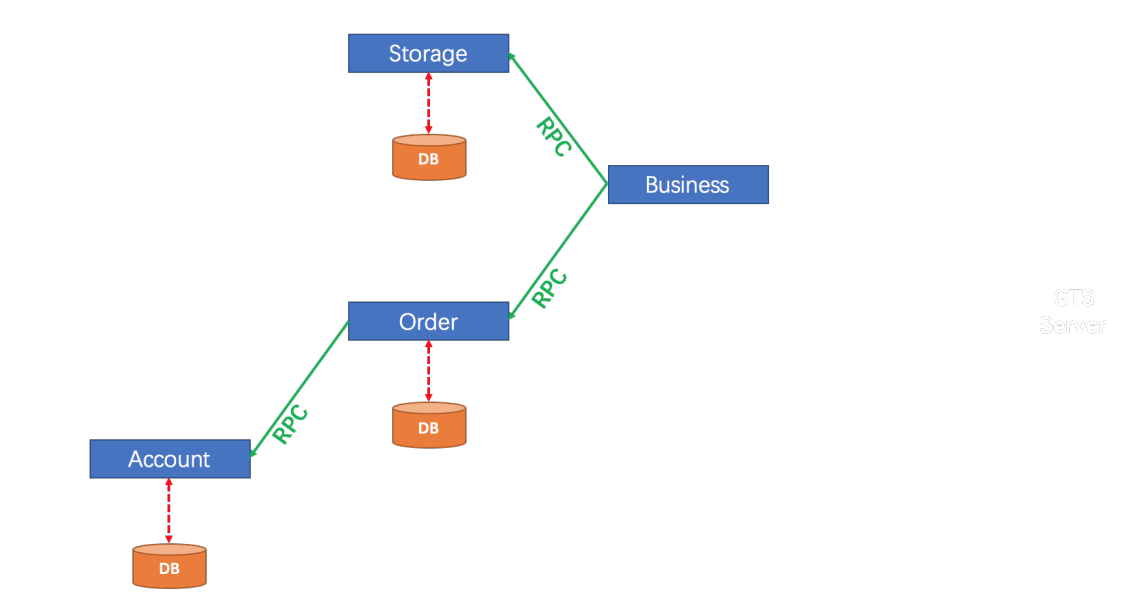
从一个微服务示例开始,案例采用Seata官方提供的Demo。
用户购买商品的业务逻辑。整个业务逻辑由3个微服务提供支持:
● 仓储服务:对给定的商品扣除仓储数量。
● 订单服务:根据采购需求创建订单。
● 帐户服务:从用户帐户中扣除余额。
架构图
订单服务
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void orderPay(String userId, Integer count, BigDecimal amount) {
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
log.info("===============全局事务xid:{}==============", xid);
log.info("===============创建订单================");
Order order = saveOrder(userId, count, amount);
log.info("===============账户扣减================");
accountService.payment(userId, amount);
orderMapper.update(order.getId(), OrderStatusEnum.PAY_SUCCESS.getCode());
log.info("===============订单完成================");
}
账户服务
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void payment(String userId, BigDecimal amount) {
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
log.info("============全局事务xid:{}=============", xid);
log.info("============执行付款接口===============");
int count = accountMapper.update(userId, amount);
if (count == 0) {
log.error("============余额不足,付款失败============");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
log.info("============付款成功==================");
}
仓储服务
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void deduct(String productId, int count) {
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
log.info("============全局事务xid:{}============", xid);
log.info("==========执行扣减库存接口===========");
int decrease = inventoryMapper.decrease(productId, count);
if (decrease == 0) {
log.error("============库存不足,扣减失败============");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
log.info("============库存扣减成功============");
}
主业务逻辑
public class BusinessServiceImpl implements BusinessService {
private StorageService storageService;
private OrderService orderService;
@GlobalTransactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void purchase(String userId, String productId, Integer count, BigDecimal amount) {
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
log.info("===============全局事务xid:{}==============", xid);
storageService.deduct(productId, count);
orderService.orderPay(userId, count, amount);
}
}
这里主要的就是在主业务方法上添加上全局事务注解@GlobalTransactional,代表从这里开始开启全局事务,该方法里的调用不管是本地调用还是远程调用,都在全局事务管辖范围内。
执行的流程如下:
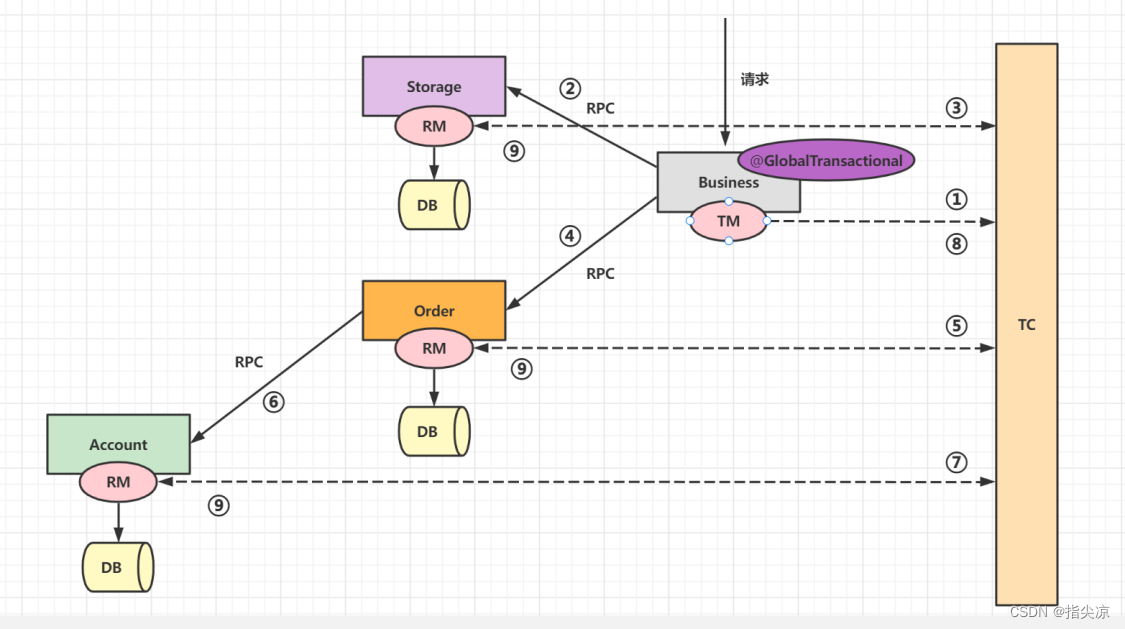
流程源码解析
上一篇说到,当调用被@GlobalTransactional或@GlobalLock注解修饰的方法时,会调到代理对象,而增强逻辑就在GlobalTransactionalInterceptor类的invoke方法里,所以就从这里开始解析。
GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
该类是全局事务拦截器,是开启,提交和回滚全局事务的入口。注意当前的角色是TM。
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
// 目标类
Class<?> targetClass =
methodInvocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(methodInvocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
// 目标方法
final Method method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// 获取 @GlobalTransactional 注解
final GlobalTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation =
getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalTransactional.class);
// 获取 @GlobalLock 注解
final GlobalLock globalLockAnnotation = getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalLock.class);
// 默认false
boolean localDisable = disable || (degradeCheck && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (!localDisable) {
// 处理 @GlobalTransactional
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null) {
return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, globalTransactionalAnnotation);
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
// 处理 @GlobalLock
return handleGlobalLock(methodInvocation, globalLockAnnotation);
}
}
}
// 调原始方法
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
当进来后会判断方法上是否有@GlobalTransactional 注解或@GlobalLock 注解,分别交由各自的方法进行处理,如果都没有,说明无需全局事务说全局锁,直接调用原始方法执行原业务逻辑即可。
该示例的主业务方法中存在@GlobalTransactional注解,所以这里进入handleGlobalTransaction方法处理全局事务。
Object handleGlobalTransaction(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation,
final GlobalTransactional globalTrxAnno) throws Throwable {
boolean succeed = true;
try {
// 使用全局事务执行业务逻辑的模板
return transactionalTemplate. execute(new TransactionalExecutor() {
/**
* 执行原方法
*/
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
public String name() {
String name = globalTrxAnno.name();
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(name)) {
return name;
}
return formatMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod());
}
/**
* 获取 @GlobalTransactional 注解的信息
*/
@Override
public TransactionInfo getTransactionInfo() {
// reset the value of timeout
int timeout = globalTrxAnno.timeoutMills();
if (timeout <= 0 || timeout == DEFAULT_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION_TIMEOUT) {
timeout = defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout;
}
TransactionInfo transactionInfo = new TransactionInfo();
transactionInfo.setTimeOut(timeout);
transactionInfo.setName(name());
transactionInfo.setPropagation(globalTrxAnno.propagation());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryInternal(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryInternal());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryTimes(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryTimes());
Set<RollbackRule> rollbackRules = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
transactionInfo.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return transactionInfo;
}
});
} catch (TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException e) {
// TM在处理全局事务时抛异常了
TransactionalExecutor.Code code = e.getCode();
switch (code) {
case RollbackDone:
throw e.getOriginalException();
case BeginFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onBeginFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case CommitFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onCommitFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case RollbackFailure:
failureHandler.onRollbackFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
case RollbackRetrying:
failureHandler.onRollbackRetrying(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
default:
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException(String.format("Unknown TransactionalExecutor.Code: %s", code));
}
} finally {
if (degradeCheck) {
EVENT_BUS.post(new DegradeCheckEvent(succeed));
}
}
}
这里调用事务模板来处理
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// 1. 获取 @GlobalTransactional 注解的信息
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
if (txInfo == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
}
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
// 从上下文中获取当前全局事务(即能获取到xid),如果不为空,则该事务的角色为“参与者”。
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
// 1.2 获取事务传播机制,默认是 REQUIRED
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
try {
switch (propagation) {
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED:
// 如果当前事务存在,则加入,否则创建一个新的事务
break;
case NEVER:
// 如果当前存在事务,抛异常
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// 1.3 If null, create new transaction with role 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher'.
// 如果当前全局事务为空,则创建一个全局事务,事务角色为“发起者”
if (tx == null) {
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// set current tx config to holder
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
// 如果事务角色是“发起者”,则发送开启全局事务的请求给TC,否则什么都不做
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// 执行自己原来的业务逻辑
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. 执行异常了,根据设置判断是否需要回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. 提交全局事务
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
triggerAfterCompletion();
cleanUp();
}
} finally {
// If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
}
}
}
这段代码看似很长,其实核心逻辑就以下几步:
1)获取或者创建一个全局事务;
2)begin全局事务;
3)执行业务逻辑;
4)异常rollback事务;
5)正常commit事务;
先获取 @GlobalTransactional 注解的信息,然后从上下文中判断是否已经处在全局事务中了,如果已经处在全局事务中的,则当前事务的角色为“参与者”,否则为“发起者”,代表要开启全局事务。然后根据是否存在全局事务和当前的事务传播机制执行不同的逻辑。默认传播机制是REQUIRED,表示如果当前事务存在,则加入,否则创建一个新的事务。
开启全局事务
这里由于全局事务还是为空的,所以需要创建一个新的全局事务对象,然后发送开启全局事务的请求给TC。
private void beginTransaction(TransactionInfo txInfo, GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
try {
// 钩子方法
triggerBeforeBegin();
// 开启全局事务,DefaultGlobalTransaction
tx.begin(txInfo.getTimeOut(), txInfo.getName());
// 钩子方法
triggerAfterBegin();
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe,
TransactionalExecutor.Code.BeginFailure);
}
}
调用默认的事务对象开启全局事务
@Override
public void begin(int timeout, String name) throws TransactionException {
// 开启全局事务的角色必须是“发起者”
if (role != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) {
assertXIDNotNull();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Begin(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
assertXIDNull();
String currentXid = RootContext.getXID();
// 事务id不为空,说明已经存在全局事务了,无法再开启一个新的
if (currentXid != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Global transaction already exists," +
" can't begin a new global transaction, currentXid = " + currentXid);
}
// 通过TransactionManager开启全局事务,并获取到xid
xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout);
// 事务状态是 Begin
status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
// 将xid绑定到全局上下文中,xid会通过全局上下文对象在各个微服务调用链上进行传播
RootContext.bind(xid);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
}
这里有个关键的点,开启全局事务的角色必须是“发起者” 。当主业务方法调用别的方法上也存在@GlobalTransactional 注解时,也会进入到这里,但是它的角色是“参与者”,因为上下文中存在XID,所以就不会继续往下执行去开启一个新的全局事务。
当要开启一个全局事务时,当前上下文中的XID必须为空。
之后通过TransactionManager开启全局事务,TransactionManager是定义全局事务跟操作全局事务的管理接口,接口实例是通过SPI方式加载的,默认是DefaultTransactionManager。获取到XID后绑定到全局上下文中,通过全局上下文对象在各个微服务调用链上进行传播。
DefaultTransactionManager
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
// 创建开启全局事务请求对象发送给TC,返回全局事务的ID
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
// 同步发送请求
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
// 从响应中获取到XID
return response.getXid();
}
private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {
// 通过TM Netty客户端实例发送请求
return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", toe);
}
}
创建一个GlobalBeginRequest请求,通过TM Netty客户端实例向TC发送开启全局事务的请求,至于netty是如何发送请求的就不是关注的重点了,没必要纠结这里。
Server端接收请求的入口统一都在AbstractNettyRemotingServer.ServerHandler类的channelRead方法
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (!(msg instanceof RpcMessage)) {
return;
}
processMessage(ctx, (RpcMessage) msg);
}
调用父类AbstractNettyRemoting的processMessage方法,该类有持有所有的处理器,收到请求后根据消息类型交给对应的Processor处理
protected final HashMap<Integer/*MessageType*/, Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService>> processorTable = new HashMap<>(32);
protected void processMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug(String.format("%s msgId:%s, body:%s", this, rpcMessage.getId(), rpcMessage.getBody()));
}
Object body = rpcMessage.getBody();
if (body instanceof MessageTypeAware) {
MessageTypeAware messageTypeAware = (MessageTypeAware) body;
// 根据消息类型编码TypeCode获取对应的执行器
final Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = this.processorTable.get((int) messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
if (pair != null) {
if (pair.getSecond() != null) {
try {
pair.getSecond().execute(() -> {
try {
// 获取处理器处理消息
pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
} catch (Throwable th) {
LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
} finally {
MDC.clear();
}
});
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
//...
}
} else {
//...
}
} else {
LOGGER.error("This message type [{}] has no processor.", messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
}
} else {
LOGGER.error("This rpcMessage body[{}] is not MessageTypeAware type.", body);
}
}
就是根据消息的不同类型交由不同的Processor处理,基本上不同的消息类型就会有不同的消息处理器,对应关系如下:
| 消息类型 | 用途 | MessageTypeAware | RemotingProcessor | 接收处理方 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYPE_GLOBAL_BEGIN = 1 | 全局事务开启 | GlobalBeginRequest | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_BEGIN_RESULT = 2 | 全局事务开启结果 | GlobalBeginResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_BRANCH_COMMIT = 3 | 分支事务提交 | BranchCommitRequest | RmBranchCommitProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_BRANCH_COMMIT_RESULT = 4 | 分支事务提交结果 | BranchCommitResponse | ServerOnResponseProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_BRANCH_ROLLBACK = 5 | 分支事务回滚 | BranchRollbackRequest | RmBranchRollbackProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_RESULT = 6 | 分支事务回滚结果 | BranchRollbackResponse | ServerOnResponseProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_COMMIT = 7 | 全局事务提交 | GlobalCommitRequest | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_COMMIT_RESULT = 8 | 全局事务提交结果 | GlobalCommitResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_ROLLBACK = 9 | 全局事务回滚 | GlobalRollbackRequest | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_ROLLBACK_RESULT = 10 | 全局事务回滚结果 | GlobalRollbackResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_BRANCH_REGISTER = 11 | 分支事务注册 | BranchRegisterRequest | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_BRANCH_REGISTER_RESULT = 12 | 分支事务注册结果 | BranchRegisterResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_BRANCH_STATUS_REPORT = 13 | 分支事务状态报告 | BranchReportRequest | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_BRANCH_STATUS_REPORT_RESULT = 14 | 分支事务状态报告结果 | BranchReportResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_STATUS = 15 | 获取全局事务状态 | GlobalStatusRequest | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_STATUS_RESULT = 16 | 获取全局事务状态结果 | GlobalStatusResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_REPORT = 17 | 全局事务报告 | GlobalReportRequest | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_REPORT_RESULT = 18 | 全局事务报告结果 | GlobalReportResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_LOCK_QUERY = 21 | 全局事务查询锁 | GlobalLockQueryRequest | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_GLOBAL_LOCK_QUERY_RESULT = 22 | 全局事务查询锁结果 | GlobalLockQueryResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_SEATA_MERGE = 59 | seata合并 | MergedWarpMessage | ServerOnRequestProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_SEATA_MERGE_RESULT = 60 | seata合并结果 | MergedResultMessage | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_REG_CLT = 101 | 注册TM | RegisterTMRequest | RegTmProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_REG_CLT_RESULT = 102 | 注册TM结果 | RegisterTMResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_REG_RM = 103 | 注册RM | RegisterRMRequest | RegRmProcessor | Server |
| TYPE_REG_RM_RESULT = 104 | 注册RM结果 | RegisterRMResponse | ClientOnResponseProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_RM_DELETE_UNDOLOG = 111 | RM删除undolog | UndoLogDeleteRequest | RmUndoLogProcessor | Client |
| TYPE_HEARTBEAT_MSG = 120 | 心跳 | HeartbeatMessage | ServerHeartbeatProcessor 和 ClientHeartbeatProcessor | Server 和 Client |
摘自——分布式事务解决方案–Seata源码解析
所以从以上表格可以看出全局事务开启的请求是由ServerOnRequestProcessor处理的,调用该处理器的process方法
@Override
public void process(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
// 判断是否是注册过的,只有注册过的rm,tm可以处理
if (ChannelManager.isRegistered(ctx.channel())) {
onRequestMessage(ctx, rpcMessage);
} else {
try {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("closeChannelHandlerContext channel:" + ctx.channel());
}
ctx.disconnect();
ctx.close();
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error(exx.getMessage());
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info(String.format("close a unhandled connection! [%s]", ctx.channel().toString()));
}
}
}
请求过来的TM必须是已经注册过的。
private void onRequestMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) {
//...
if (message instanceof MergedWarpMessage) {
//...
} else {
// the single send request message
final AbstractMessage msg = (AbstractMessage) message;
// 使用DefaultCoordinator处理请求
AbstractResultMessage result = transactionMessageHandler.onRequest(msg, rpcContext);
remotingServer.sendAsyncResponse(rpcMessage, ctx.channel(), result);
}
}
直接看最后的调用。还记得在Server启动注册ServerOnRequestProcessor处理器时传进来的处理程序类
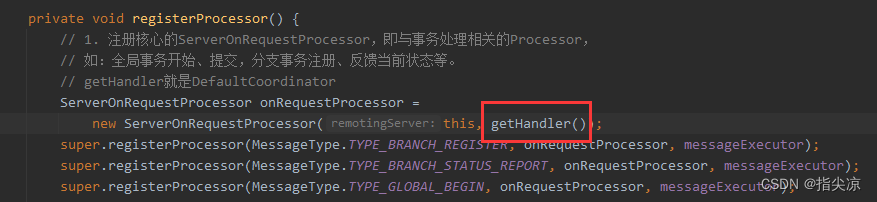
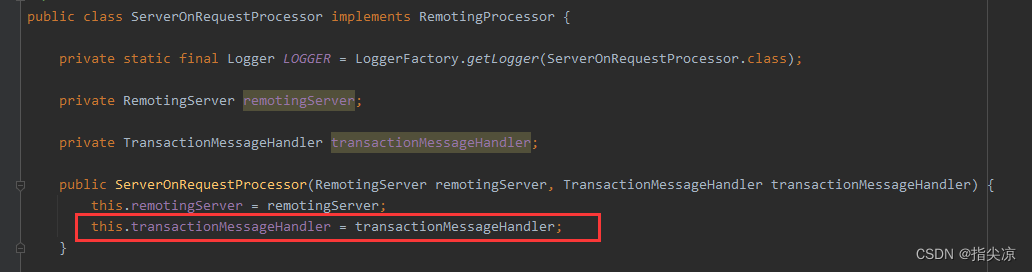
所以这里的transactionMessageHandler就是DefaultCoordinator。
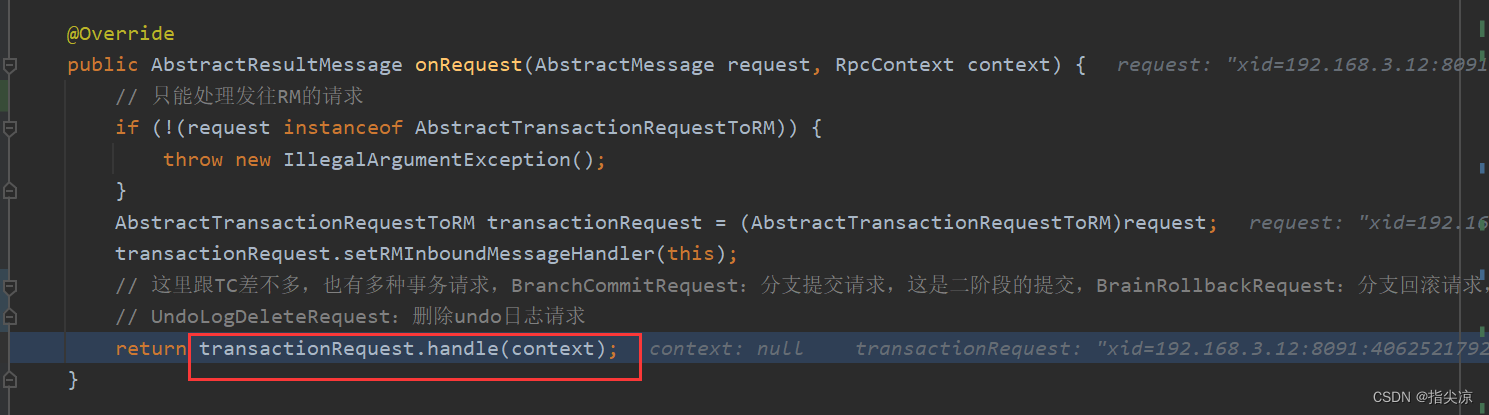
@Override
public AbstractResultMessage onRequest(AbstractMessage request, RpcContext context) {
// 请求必须是AbstractTransactionRequestToTC类型的,意思是由RM和TM发往TC的消息,因为这个类就是用来处理这些消息的
if (!(request instanceof AbstractTransactionRequestToTC)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
AbstractTransactionRequestToTC transactionRequest = (AbstractTransactionRequestToTC) request;
// 设置请求的处理器是当前对象,等下会重新回到该类
transactionRequest.setTCInboundHandler(this);
// 根据不同类型的请求调用不同request类的handle方法
return transactionRequest.handle(context);
}
这里会根据不同类型的请求调用不同request类的handle方法,因为AbstractTransactionRequestToTC有多个实现类,包括GlobalBeginRequest开启全局事务请求,BranchRegisterRequest注册分支事务请求,BranchReportRequest分支事务状态报告请求,GlobalLockQueryRequest全局锁请求,GlobalStatusRequest获取全局事务状态请求,GlobalRollbackRequest全局事务回滚请求,GlobalCommitRequest全局事务提交请求,GlobalReportRequest Saga 模式下,TM 上报全局事务状态请求。
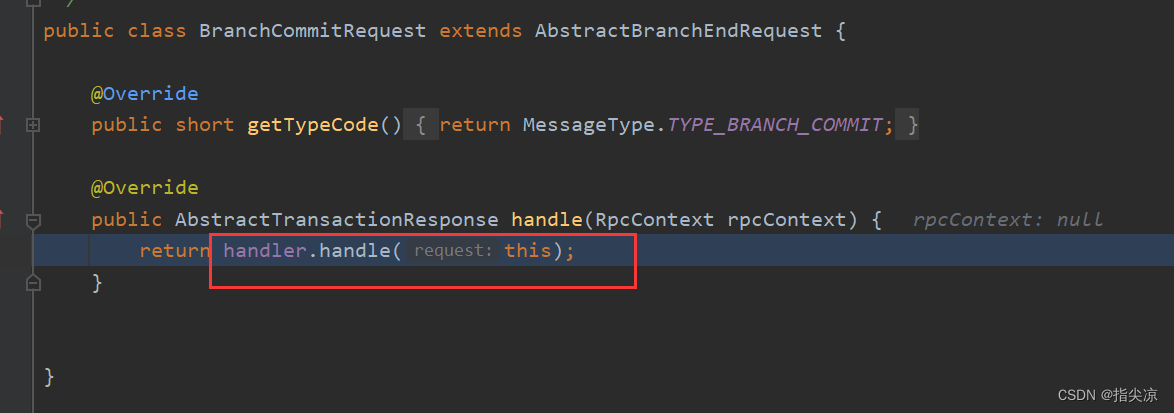
所以这里会调用到GlobalBeginRequest类的handle方法
@Override
public AbstractTransactionResponse handle(RpcContext rpcContext) {
return handler.handle(this, rpcContext);
}
上面不是设置了这个handler为DefaultCoordinator对象transactionRequest.setTCInboundHandler(this),所以重新调DefaultCoordinator的handle方法,由于DefaultCoordinator没有重写该方法,所以调到父类AbstractTCInboundHandler
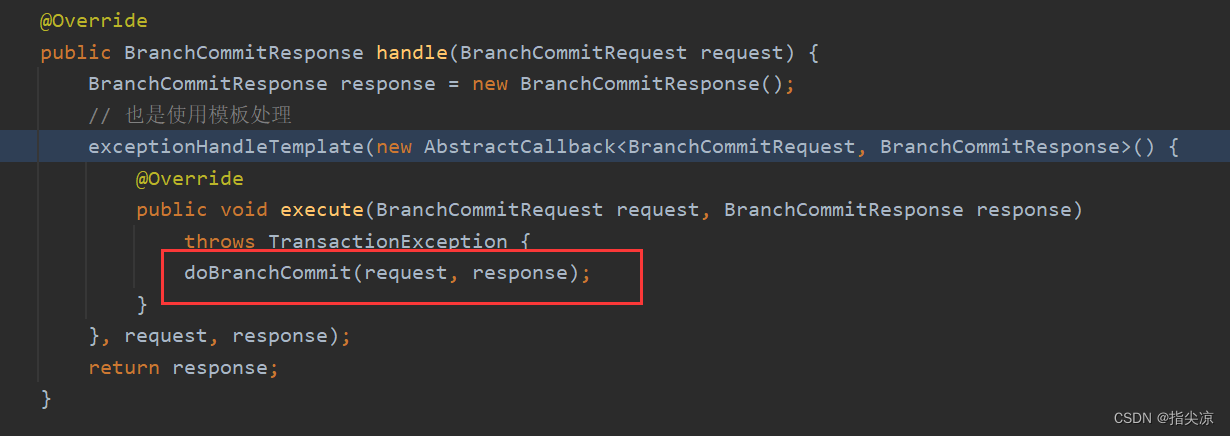
/**
* 处理开启全局事务的请求
*/
@Override
public GlobalBeginResponse handle(GlobalBeginRequest request, final RpcContext rpcContext) {
// 创建响应
GlobalBeginResponse response = new GlobalBeginResponse();
// 处理模板
exceptionHandleTemplate(new AbstractCallback<GlobalBeginRequest, GlobalBeginResponse>() {
@Override
public void execute(GlobalBeginRequest request, GlobalBeginResponse response) throws TransactionException {
try {
// 回到DefaultCoordinator中真正处理开启全局事务
doGlobalBegin(request, response, rpcContext);
} catch (StoreException e) {
throw new TransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedStore,
String.format("begin global request failed. xid=%s, msg=%s", response.getXid(), e.getMessage()),
e);
}
}
}, request, response);
return response;
}
调用doGlobalBegin方法真正开始处理开启全局事务
@Override
protected void doGlobalBegin(GlobalBeginRequest request, GlobalBeginResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext)
throws TransactionException {
// 委托给DefaultCore执委托给DefaultCore执行行,返回全局事务xid,并设置到响应中
response.setXid(core.begin(rpcContext.getApplicationId(), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
request.getTransactionName(), request.getTimeout()));
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction applicationId: {},transactionServiceGroup: {}, transactionName: {},timeout:{},xid:{}",
rpcContext.getApplicationId(), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup(), request.getTransactionName(), request.getTimeout(), response.getXid());
}
}
之后委托给DefaultCore执行
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
// 创建一个全局session,一个session就代表一个事务
GlobalSession session = GlobalSession.createGlobalSession(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, name,
timeout);
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, session.getXid());
// 添加session生命周期监听器,这里添加一个sessionManager作为监听器
session.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// 开启事务,即持久化事务,往数据库中插入一条全局事务记录
session.begin();
// 发布事务开启时间
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(session.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
session.getTransactionName(), applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, session.getBeginTime(), null, session.getStatus()));
// 返回全局事务xid
return session.getXid();
}
先创建一个全局Session,然后为给session添加一个生命周期监听器,其实就是事务持久化处理器,事务的持久化都是交由添加的监听器处理。seata提供了3种持久化方式,redis,file和database,对应的SessionManager分别是RedisSessionManager,FileSessionManager,DataBaseSessionManager。
持久化方式配置在file.conf文件中,一般都是推荐使用数据库方式,所以下面分析的都是通过数据库方式的。
然后调用GlobalSession的begin方法开启事务,即持久化事务,往数据库中插入一条全局事务记录。
@Override
public void begin() throws TransactionException {
// 全局事务状态刚开始都是Begin状态
this.status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
// 设置全局事务开启时间
this.beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 全局事务是活跃的
this.active = true;
for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
// 这里的监听器就是SessionManager,调用onBegin来持久化事务
lifecycleListener.onBegin(this);
}
}
这里的监听器就是上面说到的SessionManager,数据库方式就是DataBaseSessionManager
@Override
public void onBegin(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException {
// 持久化全局事务
addGlobalSession(globalSession);
}
@Override
public void addGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) throws TransactionException {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(taskName)) {
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addGlobalSession failed.");
}
} else {
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addGlobalSession failed.");
}
}
}
这里需要判断taskName是否为空。但是根据猜测开启全局事务应该传递LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD,但是还是需要验证下。
回到上面添加监听器的地方

监听器是从SessionHolder获取的,那就去到该方法
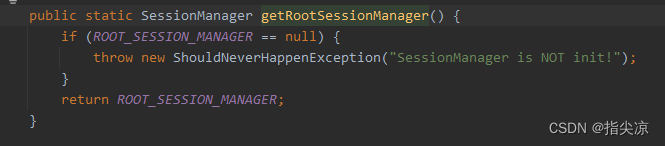
而ROOT_SESSION_MANAGER就是在SessionHolder初始化的时候通过SPI加载的
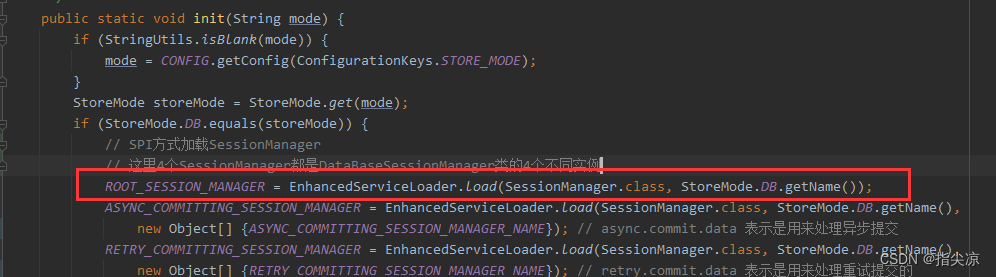
发现它并没有传递taskName参数,所以上面addGlobalSession方法里是进入第一个if里。
transactionStoreManager根据初始化方法可知是DataBaseTransactionStoreManager。
@Override
public boolean writeSession(LogOperation logOperation, SessionStorable session) {
// 根据操作类型处理
if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
// 往数据库添加全局事务的记录
return logStore.insertGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
// 更新全局事务记录
return logStore.updateGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.GLOBAL_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
// 删除全局事务记录
return logStore.deleteGlobalTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertGlobalTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD.equals(logOperation)) {
// 往数据库添加分支事务记录
return logStore.insertBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_UPDATE.equals(logOperation)) {
// 更新分支事务
return logStore.updateBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else if (LogOperation.BRANCH_REMOVE.equals(logOperation)) {
// 将数据库中的分支事务删除
return logStore.deleteBranchTransactionDO(SessionConverter.convertBranchTransactionDO(session));
} else {
throw new StoreException("Unknown LogOperation:" + logOperation.name());
}
}
开启全局事务本质就是往数据库中添加一条记录,所以这里将session转成跟数据库对应的实体类,然后调用insertGlobalTransactionDO方法插入,logStore从构造方法可知是LogStoreDataBaseDAO
@Override
public boolean insertGlobalTransactionDO(GlobalTransactionDO globalTransactionDO) {
// 生成SQL
String sql = LogStoreSqlsFactory.getLogStoreSqls(dbType).getInsertGlobalTransactionSQL(globalTable);
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 从数据源中获取一个连接
conn = logStoreDataSource.getConnection();
// 设置自动提交
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置参数
ps.setString(1, globalTransactionDO.getXid());
ps.setLong(2, globalTransactionDO.getTransactionId());
ps.setInt(3, globalTransactionDO.getStatus());
ps.setString(4, globalTransactionDO.getApplicationId());
ps.setString(5, globalTransactionDO.getTransactionServiceGroup());
String transactionName = globalTransactionDO.getTransactionName();
transactionName = transactionName.length() > transactionNameColumnSize ? transactionName.substring(0,
transactionNameColumnSize) : transactionName;
ps.setString(6, transactionName);
ps.setInt(7, globalTransactionDO.getTimeout());
ps.setLong(8, globalTransactionDO.getBeginTime());
ps.setString(9, globalTransactionDO.getApplicationData());
return ps.executeUpdate() > 0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new StoreException(e);
} finally {
IOUtil.close(ps, conn);
}
}
最终就是使用原生jdbc往global_table表插入一条全局事务的记录。这样就算是开启一个全局事务了,然后将XID响应回去。TM获取到XID后绑定到全局上下文中,通过全局上下文对象在各个微服务调用链上进行传播。
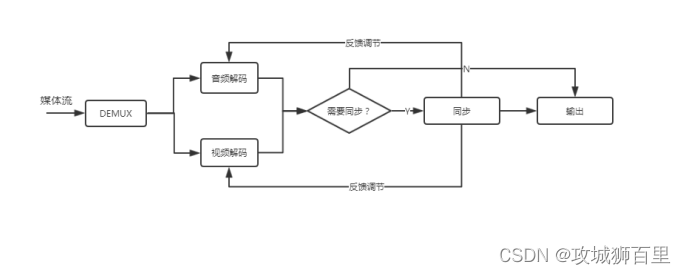
接着TM调用原方法,执行原业务逻辑,在上述示例中,就是执行主业务的purchase方法。方法里远程调用仓储服务deduct接口,即流程图中的第二步,这步会将XID一起带过去。
deduct方法并没有@GlobalTransactional或@GlobalLock注解,所以不会被GlobalTransactionalInterceptor拦截,直接执行方法就行。当执行到inventoryMapper.decrease(productId, count)时,该方法最终会通过数据源获取连接来操作数据库。
想想jdbc执行的流程
// 通过数据源获取连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
// 获得 声明
PrepareStatement pst = connection.prepareStatement();
// 执行SQL语句
pst.executeUpdate();
// 提交事务
connection.commit();
在Client启动那篇讲到,seata会对DataSource进行代理,调用DataSource接口方法时最终调会变成调代理数据源对象。dataSource 被DataSourceProxy代理,dataSource.getConnection 获得的对象是 ConnectionProxy 对象,connection.prepareStatement 获得的是 PreparedStatementProxy 对象。所以当inventoryMapper.decrease(productId, count)执行到上面流程时,就会被代理对象所取代。
先通过数据源获取连接,这时会进入AOP代理
/**
* 对DataSource进行增强,代理DataSource中的方法
*
* @author xingfudeshi@gmail.com
*/
public class SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, IntroductionInfo {
private final BranchType dataSourceProxyMode;
private final Class<? extends SeataDataSourceProxy> dataSourceProxyClazz;
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice(String dataSourceProxyMode) {
if (BranchType.AT.name().equalsIgnoreCase(dataSourceProxyMode)) {
this.dataSourceProxyMode = BranchType.AT;
this.dataSourceProxyClazz = DataSourceProxy.class;
} else if (BranchType.XA.name().equalsIgnoreCase(dataSourceProxyMode)) {
this.dataSourceProxyMode = BranchType.XA;
this.dataSourceProxyClazz = DataSourceProxyXA.class;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown dataSourceProxyMode: " + dataSourceProxyMode);
}
//Set the default branch type in the RootContext.
RootContext.setDefaultBranchType(this.dataSourceProxyMode);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 如果不是在@GlobalLock方法或事务模式跟当前的不匹配,则直接调用原方法
if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && dataSourceProxyMode != RootContext.getBranchType()) {
return invocation.proceed();
}
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
Object[] args = invocation.getArguments();
Method m = BeanUtils.findDeclaredMethod(dataSourceProxyClazz, method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes());
if (m != null && DataSource.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// 获取seata创建的代理数据源,调用代理数据源的方法
SeataDataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = DataSourceProxyHolder.get().putDataSource((DataSource) invocation.getThis(), dataSourceProxyMode);
return m.invoke(dataSourceProxy, args);
} else {
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
@Override
public Class<?>[] getInterfaces() {
return new Class[]{SeataProxy.class};
}
}
在这里面会获取seata对DataSource的代理,调用代理对象的同名方法getConnection,AT模式就是DataSourceProxy。所以调用getConnection方法获取连接变成调DataSourceProxy类的getConnection方法。
@Override
public ConnectionProxy getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection();
return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);
}
这里会返回Connection的代理对象ConnectionProxy。
然后connection.prepareStatement()就变成了ConnectionProxy类的prepareStatement()方法。
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = targetConnection.prepareStatement(sql, autoGeneratedKeys);
return new PreparedStatementProxy(this, preparedStatement, sql);
}
这里会返回PreparedStatement的代理对象PreparedStatementProxy。当执行executeUpdate()方法时就是执行PreparedStatementProxy类的方法
@Override
public int executeUpdate() throws SQLException {
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.executeUpdate());
}
执行SQL,但在真正执行SQL之前,会先解析SQL,相当于在statement.executeUpdate()的前后做了增强操作。
public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy,
StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
return execute(null, statementProxy, statementCallback, args);
}
public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers,
StatementProxy<S> statementProxy,
StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
// 如果不是处在全局事务中,则直接执行原来的SQL
if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && BranchType.AT != RootContext.getBranchType()) {
// Just work as original statement
return statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
}
// 数据库类型
String dbType = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().getDbType();
// 根据SQL类型和数据库类型获取对应的SQL识别器
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(
statementProxy.getTargetSQL(),
dbType);
}
Executor<T> executor;
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
// 如果是普通select查询,则使用该执行器
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
} else {
if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
// 根据SQL的类型,创建对应的执行器
switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
// insert执行器是通过SPI方式加载的,根据db类型从MySQLInsertExecutor,
// OracleInsertExecutor和PostgresqlInsertExecutor中选一个
case INSERT:
executor = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(InsertExecutor.class, dbType,
new Class[]{StatementProxy.class, StatementCallback.class, SQLRecognizer.class},
new Object[]{statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer});
break;
// update执行器
case UPDATE:
executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
// delete执行器
case DELETE:
executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
// select for update执行器
case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:
// 该执行器会申请本地锁和全局锁,用来避免脏读
executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
default:
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
break;
}
} else {
executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);
}
}
T rs;
try {
// 调用执行器的execute方法
rs = executor.execute(args);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {
// Turn other exception into SQLException
ex = new SQLException(ex);
}
throw (SQLException) ex;
}
return rs;
}
会判断是不是在全局事务下并且是不是AT模式,如果不是则直接执行原SQL,没做额外的事情。然后根据SQL类型和数据库类型获取对应的SQL识别器以及执行器,调用执行器的execute方法,这里就分析下UpdateExecutor
execute 方法的实现位于基类BaseTransactionalExecutor 中
@Override
public T execute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
// 先将全局事务id绑定到连接上下文中
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
if (xid != null) {
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().bind(xid);
}
// 处理@GlobalLock的
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().setGlobalLockRequire(RootContext.requireGlobalLock());
// 实现在AbstractDMLBaseExecutor
return doExecute(args);
}
@Override
public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
// 根据是否自动commit执行不同方法,但其实executeAutoCommitTrue也是先设为手动提交后再调用executeAutoCommitFalse方法
if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {
return executeAutoCommitTrue(args);
} else {
return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
}
}
从数据源中获取到的连接默认都是自动提交的,也就是走if里面的逻辑。如果在方法上加上@Transactional注解的话,Spring在处理@Transactional注解时会将连接设置为手动提交(在DataSourceTransactionManager的doBegin方法中),也就会走下面的else逻辑,这样commit的操作就不是由seata发起了,而是Spring(当然commit最终也是seata代理的)。但不论原先时自动的还是手动的,都会执行到executeAutoCommitFalse方法。看下如果是自动提交时,seata做了哪些处理。
protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
try {
// 设置为手动commit
connectionProxy.changeAutoCommit();
// 这里面会有一个无限循环,因为commit本地事务前,需要先拿到该记录的全局锁,
// 所以一旦锁冲突时,就会抛出异常,则需要一直循环等待别的全局事务释放该全局锁后才能提交自己的修改
return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
// 最终也是调用executeAutoCommitFalse方法
T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
// 如果本地事务执行成功,则 commit,提交本地事务
connectionProxy.commit();
return result;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}
首先还是会将事务设为手动commit,因为需要交由seata管理。然后会创建一个用于重试的类,执行它的execute方法,传进去一个匿名类,在它的外面包装一层重试逻辑,因为commit本地事务前,需要先拿到该记录的全局锁,一旦锁冲突时,就会抛出异常,则需要一直循环等待别的全局事务释放该全局锁后拿到该全局锁后才能提交自己的修改。所以自动提交和手动提交区别就在与多了一层锁冲突重试。
public <T> T execute(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
if (LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT) {
return doRetryOnLockConflict(callable);
} else {
return callable.call();
}
}
LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT默认是true,所以会执行doRetryOnLockConflict
protected <T> T doRetryOnLockConflict(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
LockRetryController lockRetryController = new LockRetryController();
while (true) {
try {
return callable.call();
} catch (LockConflictException lockConflict) {
// 如果是锁冲突异常,则会睡眠一小段后重试
onException(lockConflict);
lockRetryController.sleep(lockConflict);
} catch (Exception e) {
onException(e);
throw e;
}
}
}
最终还是调到executeAutoCommitFalse方法,然后调用代理对象的commit,提交本地事务。这里面有一个死循环,如果执行过程抛出了锁冲突异常,就会进行重试
public void sleep(Exception e) throws LockWaitTimeoutException {
if (--lockRetryTimes < 0) {
throw new LockWaitTimeoutException("Global lock wait timeout", e);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(lockRetryInternal);
} catch (InterruptedException ignore) {
}
}
当到达重试次数后抛出等待锁超时异常,结束循环。
接下来看executeAutoCommitFalse的执行逻辑,最终都是要执行该方法
protected T executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {
if (!JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType()) && isMultiPk()) {
throw new NotSupportYetException("multi pk only support mysql!");
}
// 生成前置镜像,就是执行SQL前数据长啥样,根据不同的SQL类型有不同实现
TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();
// 执行原业务逻辑的SQL,但还没提交
T result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
// 生成后置镜像,就是执行SQL后数据长啥样(如果是delete,则后置镜像就是空了)
TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);
// 根据前置镜像和后置镜像生成undolog,用于回滚(这里只是生成记录,还没执行)
prepareUndoLog(beforeImage, afterImage);
return result;
}
分为4个步骤:
1)生成前置镜像,因为需要将不同的 SQL 解析出相应的 SELECT 语句,查询操作前数据的快照,就是执行SQL前数据长啥样,根据不同的SQL类型有不同实现。当然insert就没有前置快照,因为还没有数据。看下update类型的UpdateExecutor
@Override
protected TableRecords beforeImage() throws SQLException {
ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList = new ArrayList<>();
// 查询表的元数据
TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta();
// 构建查询SQL
String selectSQL = buildBeforeImageSQL(tmeta, paramAppenderList);
// 执行查询SQL,返回相关记录
return buildTableRecords(tmeta, selectSQL, paramAppenderList);
}
private String buildBeforeImageSQL(TableMeta tableMeta, ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList) {
SQLUpdateRecognizer recognizer = (SQLUpdateRecognizer) sqlRecognizer;
List<String> updateColumns = recognizer.getUpdateColumns();
StringBuilder prefix = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
StringBuilder suffix = new StringBuilder(" FROM ").append(getFromTableInSQL());
String whereCondition = buildWhereCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(whereCondition)) {
suffix.append(WHERE).append(whereCondition);
}
String orderBy = recognizer.getOrderBy();
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(orderBy)) {
suffix.append(orderBy);
}
ParametersHolder parametersHolder = statementProxy instanceof ParametersHolder ? (ParametersHolder)statementProxy : null;
String limit = recognizer.getLimit(parametersHolder, paramAppenderList);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(limit)) {
suffix.append(limit);
}
// 会申请排它锁
suffix.append(" FOR UPDATE");
StringJoiner selectSQLJoin = new StringJoiner(", ", prefix.toString(), suffix.toString());
if (ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS) {
if (!containsPK(updateColumns)) {
selectSQLJoin.add(getColumnNamesInSQL(tableMeta.getEscapePkNameList(getDbType())));
}
for (String columnName : updateColumns) {
selectSQLJoin.add(columnName);
}
} else {
for (String columnName : tableMeta.getAllColumns().keySet()) {
selectSQLJoin.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(columnName, getDbType()));
}
}
return selectSQLJoin.toString();
}
如何构建查询SQL可以不用关注,但是可以看到在构建的过程在SQL语句的后面加上的“FOR UPDATE”,当使用“SELECT FOR UPDATE”时会去数据库申请查询的数据的行锁,也就是seata中说的申请本地锁,该锁在提交本地事务的时候自动释放。不止update有,delete时也会有该操作。如果行锁已经被占用了,在等待获取本地锁超时这里就抛异常了。如果是insert,前置镜像里面的记录就是空的。
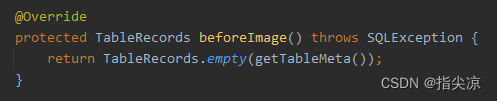
2)接着执行原业务逻辑的SQL,由于是手动提交的,所以这里还没提交。
3)然后构建后置镜像,就是执行SQL后数据长啥样,如果是delete,则后置镜像就是空的了,跟insert相反。
4)最后根据前置镜像和后置镜像生成一条undolog,用于回滚,这里只是生成记录,还没执行。
protected void prepareUndoLog(TableRecords beforeImage, TableRecords afterImage) throws SQLException {
// 如果前后镜像都是空的,则不生成undolog
if (beforeImage.getRows().isEmpty() && afterImage.getRows().isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 如果是更新操作,则前后镜像的行数要相同
if (SQLType.UPDATE == sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
if (beforeImage.getRows().size() != afterImage.getRows().size()) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("Before image size is not equaled to after image size, probably because you updated the primary keys.");
}
}
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
TableRecords lockKeyRecords = sqlRecognizer.getSQLType() == SQLType.DELETE ? beforeImage : afterImage;
// 构建全局锁对应的key
String lockKeys = buildLockKey(lockKeyRecords);
if (null != lockKeys) {
// 将key添加进上下文中
connectionProxy.appendLockKey(lockKeys);
// 构建undolog
SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog = buildUndoItem(beforeImage, afterImage);
// 将undolog添加到代理连接的上下文中,后面跟原业务sql一起提交
connectionProxy.appendUndoLog(sqlUndoLog);
}
}
还会顺便构建全局锁对应的key放在上下文中,key类似这样:t_user:pk1,pk2,表示改动了哪张表的哪几条记录,用于后面分支事务提交时申请全局锁。
执行完本地SQL就该去commit了,commit时也是通过代理对象ConnectionProxy。
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
try {
LOCK_RETRY_POLICY.execute(() -> {
// 执行事务提交
doCommit();
return null;
});
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
rollback();
}
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SQLException(e);
}
}
这里也包装了一层重试的策略,但是这里并不会重试
public <T> T execute(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
if (LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT) {
return callable.call();
} else {
return doRetryOnLockConflict(callable);
}
}
上面也说了LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT默认是true,所以会直接调到doCommit执行事务提交
private void doCommit() throws SQLException {
// 是否在全局事务中
if (context.inGlobalTransaction()) {
// 本地事务提交前需要先注册分支事务,拿到全局锁
processGlobalTransactionCommit();
} else if (context.isGlobalLockRequire()) {
// 针对 GlobalLock 的处理
processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks();
} else {
// 否则直接提交本地事务
targetConnection.commit();
}
}
这里会再判断是否在全局事务中或者需要全局锁,如果都没有则使用原始连接提交事务。
这里进入processGlobalTransactionCommit
private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
try {
// 注册分支事务
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
// 如果是锁冲突,则抛出锁冲突异常,使之可以进行循环重试
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
}
try {
// 分支注册成功,获取到了全局锁,则将undolog插入数据库,然后下面一起commit
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
// 将业务sql和undolog 一同提交,真正持久化数据库的地方
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 如果本地commit失败,则向TC报告本地事务提交失败,若报告失败,默认会重试5次
LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
report(false);
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
// 是否报告一阶段提交完成,默认为false
if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {
report(true);
}
// 重置上下文,解绑全局事务xid
context.reset();
}
首先在事务提交前,需要先注册下分支事务。
注册分支事务
private void register() throws TransactionException {
if (!context.hasUndoLog() || !context.hasLockKey()) {
return;
}
// 调用RM注册分支事务,获取到分支事务id,并获取全局锁
Long branchId = DefaultResourceManager.get().branchRegister(BranchType.AT, getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId(),
null, context.getXid(), null, context.buildLockKeys());
// 将分支事务id设置到上下文中
context.setBranchId(branchId);
}
这里通过RM向TC发送注册分支事务的请求,还会将全局锁key一起发送过去,申请全局锁。
Server端接收请求的前面一大段就跳过了,直接看DefaultCoordinator的doBranchRegister方法。
@Override
protected void doBranchRegister(BranchRegisterRequest request, BranchRegisterResponse response,
RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException {
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
// 委托给DefaultCore执行,返回分支事务id,并设置到响应中
response.setBranchId(
core.branchRegister(request.getBranchType(), request.getResourceId(), rpcContext.getClientId(),
request.getXid(), request.getApplicationData(), request.getLockKey()));
}
委托给DefaultCore
@Override
public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid,
String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
return getCore(branchType).branchRegister(branchType, resourceId, clientId, xid,
applicationData, lockKeys);
}
@Override
public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid,
String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
// 根据xid从数据库(存储介质)中查询GlobalSession,相当于全局事务,false表示不顺带查询分支事务
GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, false);
return SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
// 先检查全局事务状态,如果不是活跃的以及处于开始状态,则抛异常
globalSessionStatusCheck(globalSession);
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// 创建一个分支事务对象,BranchSession就代表一个分支事务
BranchSession branchSession = SessionHelper.newBranchByGlobal(globalSession, branchType, resourceId,
applicationData, lockKeys, clientId);
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_BRANCH_ID, String.valueOf(branchSession.getBranchId()));
// 尝试获取要修改记录的全局锁,获取不到时抛异常
branchSessionLock(globalSession, branchSession);
try {
// 持久化分支事务,并将分支事务添加进全局事务中
globalSession.addBranch(branchSession);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
branchSessionUnlock(branchSession);
throw new BranchTransactionException(FailedToAddBranch, String
.format("Failed to store branch xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),
branchSession.getBranchId()), ex);
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Register branch successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}, resourceId = {} ,lockKeys = {}",
globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId(), resourceId, lockKeys);
}
// 返回分支事务id
return branchSession.getBranchId();
});
}
创建一个分支事务对象后会尝试获取要操作的记录的全局锁,获取不到时抛异常,本质就是看看lock_table表中是否已经存在要操作记录主键相关的数据,如果有就说明已经被别的全局事务占用了,抛出异常,表示申请锁失败,否则就向lock_table表插入要操作记录主键相关的数据,表示获取到全局锁了。然后持久化分支事务。
public void addBranch(BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
// 持久化分支事务,初始状态是未知Unknown
lifecycleListener.onAddBranch(this, branchSession);
}
branchSession.setStatus(BranchStatus.Registered);
// 将分支事务添加进全局事务中
add(branchSession);
}
持久化分支事务本质上也是将分支事务对象插入到branch_table表,就不详细分析了,分支事务初始状态是Unknown。注册好后就将分支事务ID响应回去。
一阶段提交
回到RM注册分支事务的地方,如果在注册分支事务时申请全局锁失败,就会抛出锁冲突异常,就会在上面讲到的executeAutoCommitTrue方法里重试。
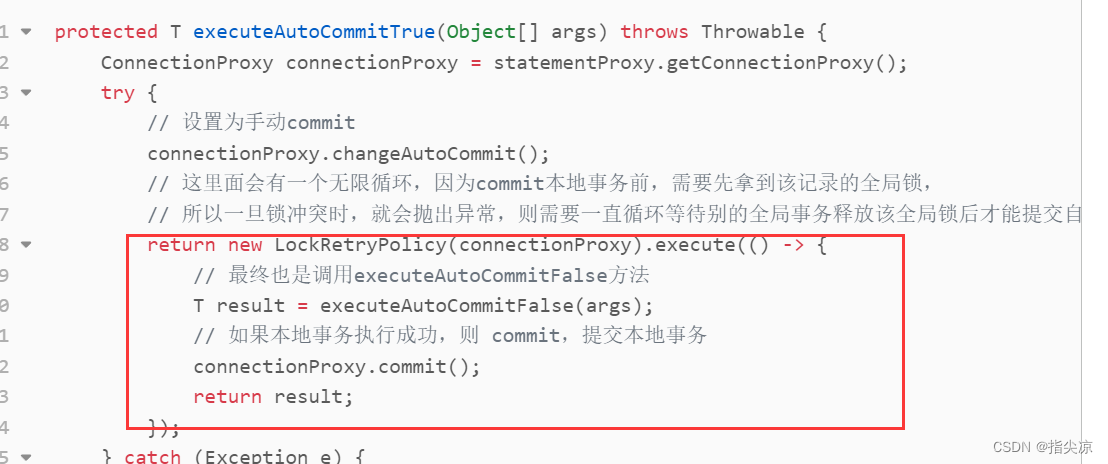
如果没有抛异常,则是分支事务注册成功以及申请到了全局锁,则将undolog回滚日志插入数据库undo_log表,下面使用原始connection提交,将undo log的SQL和原业务SQL真正持久化到数据库。业务数据和回滚日志记录在同一个本地事务中提交,释放本地锁和连接资源。这样一阶段就算执行成功了。
如果本地commit失败了,则会向TC报告本地事务提交失败,如果报告失败,则会重试5次。
默认情况下,一阶段执行成功不会向TC报告。
到这里,仓储服务就执行成功了,然后就是继续远程调用其它服务,执行流程跟上面的仓储服务一样,这里就假设订单服务和账户服务一阶段都执行成功了,接下来就该进入到二阶段全局提交的流程了。
全局事务提交
回到最上面TM全局事务执行模板TransactionalTemplate
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// 1. 获取 @GlobalTransactional 注解的信息
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
if (txInfo == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
}
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
// 从上下文中获取当前全局事务(即能获取到xid),如果不为空,则该事务的角色为“参与者”。
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
// 1.2 获取事务传播机制,默认是 REQUIRED
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
try {
switch (propagation) {
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED:
// 如果当前事务存在,则加入,否则创建一个新的事务
break;
case NEVER:
// 如果当前存在事务,抛异常
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// 1.3 If null, create new transaction with role 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher'.
// 如果当前全局事务为空,则创建一个全局事务,事务角色为“发起者”
if (tx == null) {
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// set current tx config to holder
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
// 如果事务角色是“发起者”,则发送开启全局事务的请求给TC,否则什么都不做
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// 执行自己原来的业务逻辑
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. 执行异常了,根据设置判断是否需要回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. 提交全局事务
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
triggerAfterCompletion();
cleanUp();
}
} finally {
// If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
}
}
}
当所有分支都正常执行完后,business.execute()该方法正常返回,没有抛异常则由TM发起全局事务的提交。
private void commitTransaction(GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
try {
triggerBeforeCommit();
// 全局事务提交
tx.commit();
triggerAfterCommit();
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
// 4.1 Failed to commit
throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe,
TransactionalExecutor.Code.CommitFailure);
}
}
@Override
public void commit() throws TransactionException {
// 如果是参与者,则不会提交,全局事务只会由发起者提交
if (role == GlobalTransactionRole.Participant) {
// Participant has no responsibility of committing
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Commit(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
assertXIDNotNull();
// 全局提交失败重试次数
int retry = COMMIT_RETRY_COUNT <= 0 ? DEFAULT_TM_COMMIT_RETRY_COUNT : COMMIT_RETRY_COUNT;
try {
while (retry > 0) {
try {
// 同步提交全局事务
status = transactionManager.commit(xid);
break;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to report global commit [{}],Retry Countdown: {}, reason: {}", this.getXid(), retry, ex.getMessage());
retry--;
if (retry == 0) {
throw new TransactionException("Failed to report global commit", ex);
}
}
}
} finally {
if (xid.equals(RootContext.getXID())) {
suspend();
}
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("[{}] commit status: {}", xid, status);
}
}
全局事务提交也会判断下是否是发起者,只有发起者才能发起全局事务提交。然后使用事务管理器提交全局事务,如果提交失败,默认会重试5次。
@Override
public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
GlobalCommitRequest globalCommit = new GlobalCommitRequest();
globalCommit.setXid(xid);
GlobalCommitResponse response = (GlobalCommitResponse) syncCall(globalCommit);
return response.getGlobalStatus();
}
构建全局事务提交请求,发起全局事务提交。
Server端看DefaultCoordinator的doGlobalCommit方法
@Override
protected void doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext)
throws TransactionException {
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
// 全局事务提交
response.setGlobalStatus(core.commit(request.getXid()));
}
委托给DefaultCore
@Override
public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
// 从数据库查询全局事务,同时把分支事务也一起查出来
GlobalSession globalSession = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(xid);
if (globalSession == null) {
return GlobalStatus.Finished;
}
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// just lock changeStatus
boolean shouldCommit = SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
// 关闭全局事务,让全局事务为非活跃状态,使之无法再注册分支事务,然后释放该全局事务的所有全局锁
globalSession.closeAndClean();
// 正常此时还是Begin状态
if (globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.Begin) {
// AT模式默认true,即默认是异步提交,下面shouldCommit中的逻辑不会执行
if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
// 异步提交
globalSession.asyncCommit();
return false;
} else {
globalSession.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.Committing);
return true;
}
}
return false;
});
if (shouldCommit) {
boolean success = doGlobalCommit(globalSession, false);
//If successful and all remaining branches can be committed asynchronously, do async commit.
if (success && globalSession.hasBranch() && globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
globalSession.asyncCommit();
return GlobalStatus.Committed;
} else {
return globalSession.getStatus();
}
} else {
// 如果状态是AsyncCommitting则响应Committed回去,因为二阶段提交是异步的,所以这里直接告诉已提交了
return globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.AsyncCommitting ? GlobalStatus.Committed : globalSession.getStatus();
}
}
首先根据XID从数据库中将全局事务查询出来,为了后面的分支事务的提交,也会同时将对应的分支事务也一起查出来。然后关闭全局事务,让全局事务为非活跃状态,使之无法再注册分支事务,然后释放该全局事务的所有全局锁,即根据全局事务的XID和分支事务id将lock_table中的记录删除。
然后调用全局事务对象的异步提交方法,其实就是将数据库里的全局事务状态从Begin更新为AsyncCommitting。而对RM发起的异步提交实际是由一个后台定时任务处理的。
public void asyncCommit() throws TransactionException {
this.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getAsyncCommittingSessionManager());
SessionHolder.getAsyncCommittingSessionManager().addGlobalSession(this);
// 全局事务状态更新为AsyncCommitting(数据库)
this.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.AsyncCommitting);
}
因为 AT 模式下一阶段已经完成数据落地,所以全局提交时服务端仅仅修改全局事务状态为 AsyncCommitting,并且已经不会发生回滚导致数据脏写或脏读,所以可以将全局锁都释放了。
最后就向TM响应全局事务已提交。
分支事务二阶段提交
在TC里会有一个定时任务(在Server启动的时候创建的),会对状态变更为AsyncCommitting的全局事务的分支事务分别发送事务提交请求。
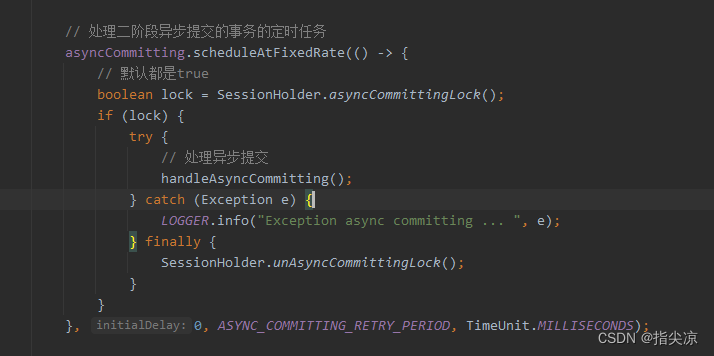
protected void handleAsyncCommitting() {
// 查询所有状态是AsyncCommitting的全局事务,就是分支事务的一阶段都执行完了,
// 本地事务都提交了,二阶段的全局事务也提交了,现在需要由TC向RM发起二阶段的分支异步提交请求
Collection<GlobalSession> asyncCommittingSessions = SessionHolder.getAsyncCommittingSessionManager()
.allSessions();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(asyncCommittingSessions)) {
return;
}
// 遍历处理
SessionHelper.forEach(asyncCommittingSessions, asyncCommittingSession -> {
try {
// 这里的asyncCommittingSession就是遍历的GlobalSession
// Instruction reordering in DefaultCore#asyncCommit may cause this situation
if (GlobalStatus.AsyncCommitting != asyncCommittingSession.getStatus()) {
//The function of this 'return' is 'continue'.
return;
}
asyncCommittingSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// 向RM发送异步提交请求
core.doGlobalCommit(asyncCommittingSession, true);
} catch (TransactionException ex) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to async committing [{}] {} {}", asyncCommittingSession.getXid(), ex.getCode(), ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean doGlobalCommit(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying) throws TransactionException {
boolean success = true;
// start committing event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(globalSession.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
globalSession.getTransactionName(), globalSession.getApplicationId(), globalSession.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
globalSession.getBeginTime(), null, globalSession.getStatus()));
// saga模式的处理
if (globalSession.isSaga()) {
success = getCore(BranchType.SAGA).doGlobalCommit(globalSession, retrying);
} else {
// 其他模式
// 遍历该全局事务下的分支事务
Boolean result = SessionHelper.forEach(globalSession.getSortedBranches(), branchSession -> {
// if not retrying, skip the canBeCommittedAsync branches
// 如果不能重试,则跳过异步提交的分支事务
if (!retrying && branchSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
return CONTINUE;
}
// 如果分支事务一阶段失败了,则移除该分支事务(都失败了为啥会到全局提交这里?)
BranchStatus currentStatus = branchSession.getStatus();
if (currentStatus == BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Failed) {
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
return CONTINUE;
}
try {
// 发送分支提交请求,RM收到分支提交请求后,把请求放入一个异步任务的队列中,
// 然后马上返回提交成功的结果到这里PhaseTwo_Committed
BranchStatus branchStatus = getCore(branchSession.getBranchType()).branchCommit(globalSession, branchSession);
switch (branchStatus) {
// 表示该分支事务二阶段异步提交成功
case PhaseTwo_Committed:
// 删除数据库中的分支事务记录以及移除GlobalSession持有的分支事务
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
return CONTINUE;
case PhaseTwo_CommitFailed_Unretryable:
if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
LOGGER.error(
"Committing branch transaction[{}], status: PhaseTwo_CommitFailed_Unretryable, please check the business log.", branchSession.getBranchId());
return CONTINUE;
} else {
SessionHelper.endCommitFailed(globalSession);
LOGGER.error("Committing global transaction[{}] finally failed, caused by branch transaction[{}] commit failed.", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
return false;
}
default:
if (!retrying) {
globalSession.queueToRetryCommit();
return false;
}
if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
LOGGER.error("Committing branch transaction[{}], status:{} and will retry later",
branchSession.getBranchId(), branchStatus);
return CONTINUE;
} else {
LOGGER.error(
"Committing global transaction[{}] failed, caused by branch transaction[{}] commit failed, will retry later.", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
return false;
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
StackTraceLogger.error(LOGGER, ex, "Committing branch transaction exception: {}",
new String[] {branchSession.toString()});
if (!retrying) {
globalSession.queueToRetryCommit();
throw new TransactionException(ex);
}
}
return CONTINUE;
});
// Return if the result is not null
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
//If has branch and not all remaining branches can be committed asynchronously,
//do print log and return false
if (globalSession.hasBranch() && !globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
LOGGER.info("Committing global transaction is NOT done, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
return false;
}
}
// 所有分支提交成功(分支可能还在异步操作)
if (success && globalSession.getBranchSessions().isEmpty()) {
// 全局事务结束,删除数据库中的全局事务记录
SessionHelper.endCommitted(globalSession);
// committed event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(globalSession.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
globalSession.getTransactionName(), globalSession.getApplicationId(), globalSession.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
globalSession.getBeginTime(), System.currentTimeMillis(), globalSession.getStatus()));
LOGGER.info("Committing global transaction is successfully done, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
}
return success;
}
当异步提交请求成功后,会删除数据库中的分支事务记录。当所有的分支事务异步提交请求都成功后,会删除数据库中的全局事务记录,此时RM可能还在进行异步删除undo log回滚日志的操作。
而RM处理TC发来的分支事务提交请求也是有一个专门的Processor。在Client初始化RM的时候,注册了几个Processor,其中就有一个叫RmBranchCommitProcessor,该Processor就是RM用来处理分支事务提交的,处理逻辑在process方法里


这里根据事务模式获取RM处理器处理,由于是AT模式,所以这里是RMHandlerAT
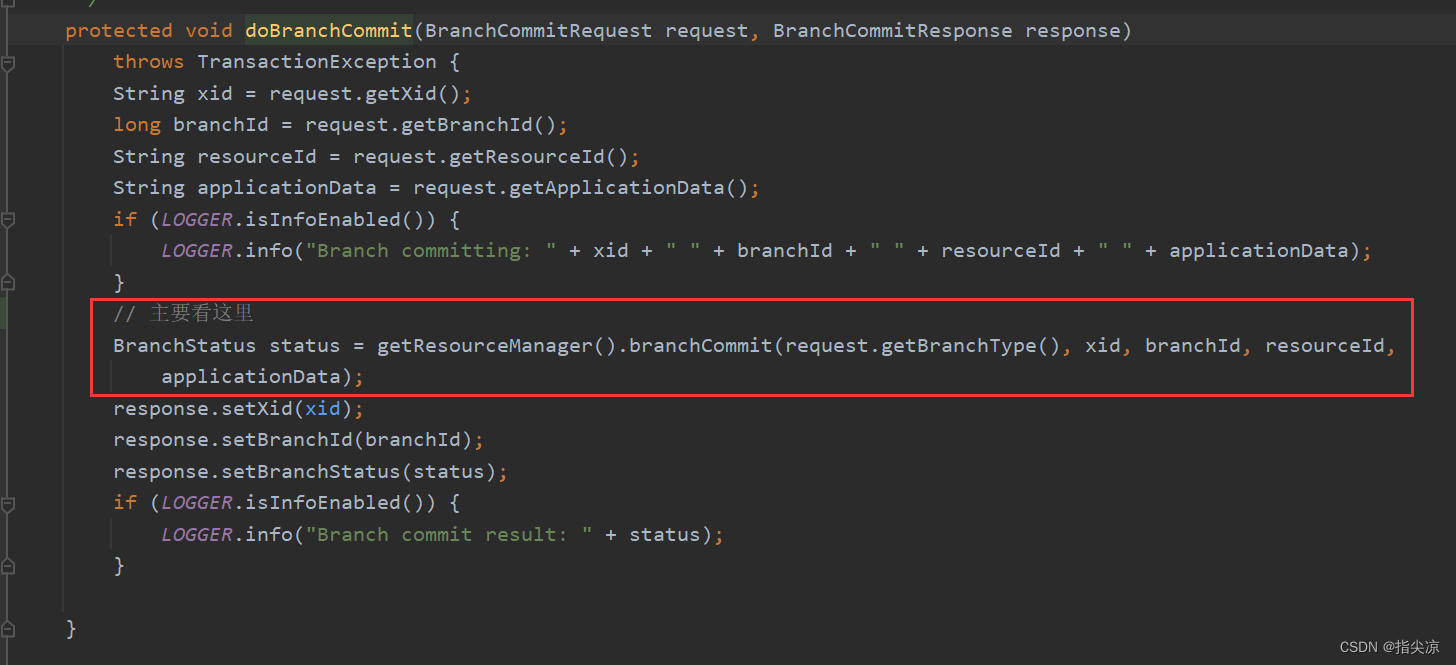
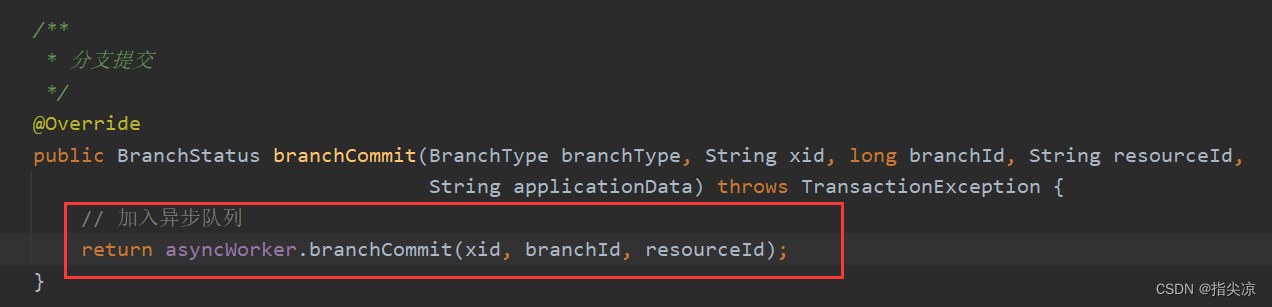
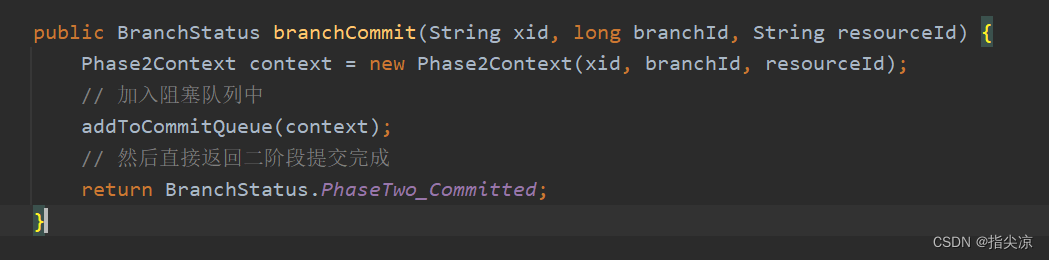
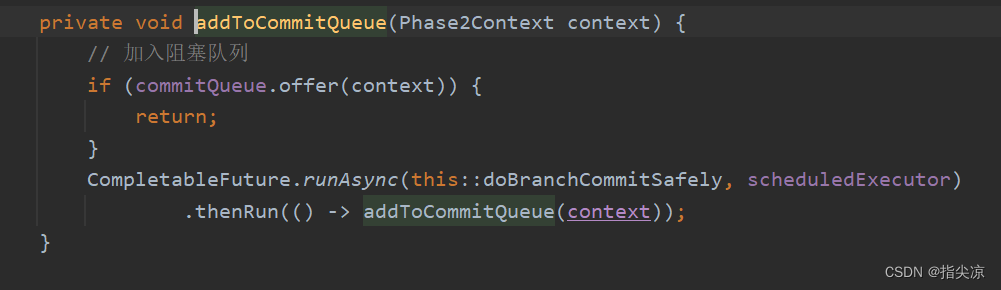
最后加入AsyncWorker类中的阻塞队列后就直接返回二阶段提交完成了,因为后续的删除undo log并不会对当前事务或其他事务有什么影响,所以可以异步操作。
在AsyncWorker类中有个定时任务,每隔1s从阻塞队列中取出数据,删除undo日志
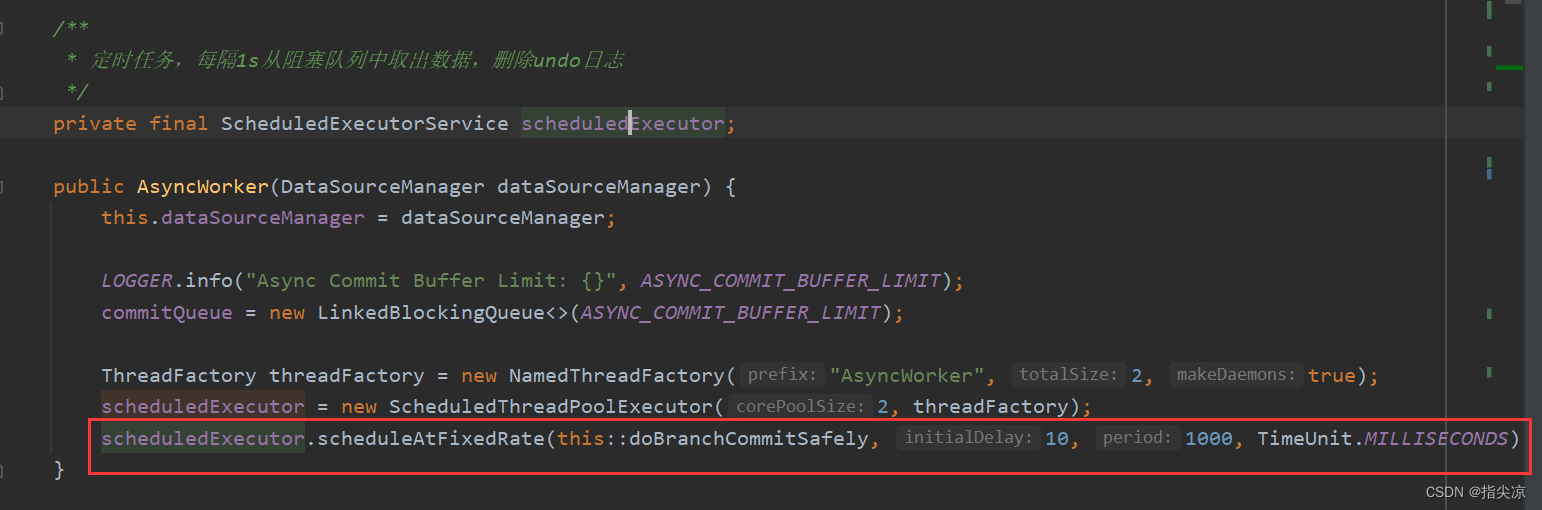
void doBranchCommitSafely() {
try {
doBranchCommit();
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.error("Exception occur when doing branch commit", e);
}
}
private void doBranchCommit() {
if (commitQueue.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// transfer all context currently received to this list
List<Phase2Context> allContexts = new LinkedList<>();
// 将commitQueue中的元素一次性全部移到allContexts中
commitQueue.drainTo(allContexts);
// 根据 resourceId 分组
Map<String, List<Phase2Context>> groupedContexts = groupedByResourceId(allContexts);
// 循环删除undo log
groupedContexts.forEach(this::dealWithGroupedContexts);
}
private void dealWithGroupedContexts(String resourceId, List<Phase2Context> contexts) {
DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = dataSourceManager.get(resourceId);
if (dataSourceProxy == null) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to find resource for {}", resourceId);
return;
}
Connection conn;
try {
conn = dataSourceProxy.getPlainConnection();
} catch (SQLException sqle) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to get connection for async committing on {}", resourceId, sqle);
return;
}
// 获取UndoLogManager
UndoLogManager undoLogManager = UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(dataSourceProxy.getDbType());
// split contexts into several lists, with each list contain no more element than limit size
// 1000个一组批量删除
List<List<Phase2Context>> splitByLimit = Lists.partition(contexts, UNDOLOG_DELETE_LIMIT_SIZE);
splitByLimit.forEach(partition -> deleteUndoLog(conn, undoLogManager, partition));
}
下面就不继续看了,只要知道这里删除了undo log回滚日志。
这样一个完整的正常成功的分布式事务就执行完了。
全局事务回滚
如果某一个分支执行失败了,TM就会进入全局事务回滚的逻辑。
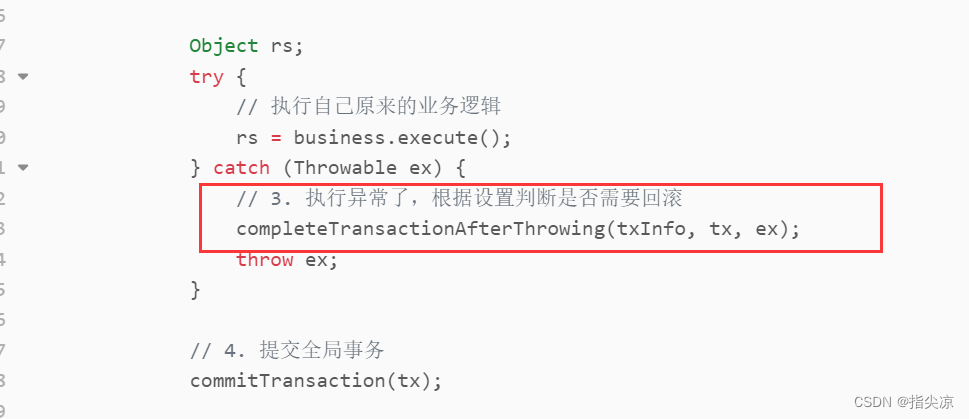
private void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(TransactionInfo txInfo, GlobalTransaction tx, Throwable originalException) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
// 判断是否是需要回滚的异常
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.rollbackOn(originalException)) {
try {
// 回滚
rollbackTransaction(tx, originalException);
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
// Failed to rollback
throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe,
TransactionalExecutor.Code.RollbackFailure, originalException);
}
} else {
// 不进行回滚,继续提交
commitTransaction(tx);
}
}
在回滚之前,需要判断抛出的异常是否在配置的回滚异常里面,如果不是的话,就不会回滚,还是继续全局提交。
private void rollbackTransaction(GlobalTransaction tx, Throwable originalException) throws TransactionException, TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
triggerBeforeRollback();
// 回滚
tx.rollback();
triggerAfterRollback();
// 3.1 Successfully rolled back
throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, GlobalStatus.RollbackRetrying.equals(tx.getLocalStatus())
? TransactionalExecutor.Code.RollbackRetrying : TransactionalExecutor.Code.RollbackDone, originalException);
}
/**
* 全局事务回滚
*/
@Override
public void rollback() throws TransactionException {
// 如果只是参与者,则不发起回滚
if (role == GlobalTransactionRole.Participant) {
// Participant has no responsibility of rollback
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Rollback(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
assertXIDNotNull();
// 回滚重试次数
int retry = ROLLBACK_RETRY_COUNT <= 0 ? DEFAULT_TM_ROLLBACK_RETRY_COUNT : ROLLBACK_RETRY_COUNT;
try {
while (retry > 0) {
try {
// 回滚
status = transactionManager.rollback(xid);
break;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to report global rollback [{}],Retry Countdown: {}, reason: {}", this.getXid(), retry, ex.getMessage());
retry--;
if (retry == 0) {
throw new TransactionException("Failed to report global rollback", ex);
}
}
}
} finally {
if (xid.equals(RootContext.getXID())) {
suspend();
}
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("[{}] rollback status: {}", xid, status);
}
}
跟全局提交一样,如果是参与者,就不发起全局回滚。
然后就是构建全局回滚的请求发给TC
/**
* 构建全局回滚请求,发起全局事务回滚
*/
@Override
public GlobalStatus rollback(String xid) throws TransactionException {
GlobalRollbackRequest globalRollback = new GlobalRollbackRequest();
globalRollback.setXid(xid);
GlobalRollbackResponse response = (GlobalRollbackResponse) syncCall(globalRollback);
return response.getGlobalStatus();
}
/**
* 全局事务回滚
*/
@Override
protected void doGlobalRollback(GlobalRollbackRequest request, GlobalRollbackResponse response,
RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException {
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
response.setGlobalStatus(core.rollback(request.getXid()));
}
@Override
public GlobalStatus rollback(String xid) throws TransactionException {
// 从数据库查询全局事务,同时把分支事务也一起查出来
GlobalSession globalSession = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(xid);
if (globalSession == null) {
return GlobalStatus.Finished;
}
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// just lock changeStatus
boolean shouldRollBack = SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
// 关闭全局事务,使事务状态为非活跃,这样别的分支事务就不会再注册上来
globalSession.close(); // Highlight: Firstly, close the session, then no more branch can be registered.
if (globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.Begin) {
// 更新数据库中的全局事务状态为Rollbacking
globalSession.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.Rollbacking);
return true;
}
// 如果是其他状态则不回滚
return false;
});
if (!shouldRollBack) {
return globalSession.getStatus();
}
// 开始回滚
doGlobalRollback(globalSession, false);
return globalSession.getStatus();
}
先关闭全局事务,这样其他的分支事务就不会再注册上来了。然后更新数据库中的全局事务状态为Rollbacking,表示在回滚中。调用doGlobalRollback方法执行真正回滚的逻辑。
@Override
public boolean doGlobalRollback(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying) throws TransactionException {
boolean success = true;
// start rollback event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(globalSession.getTransactionId(),
GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC, globalSession.getTransactionName(),
globalSession.getApplicationId(),
globalSession.getTransactionServiceGroup(), globalSession.getBeginTime(),
null, globalSession.getStatus()));
// saga模式
if (globalSession.isSaga()) {
success = getCore(BranchType.SAGA).doGlobalRollback(globalSession, retrying);
} else {
// 其他模式
// 遍历每个分支事务
Boolean result = SessionHelper.forEach(globalSession.getReverseSortedBranches(), branchSession -> {
BranchStatus currentBranchStatus = branchSession.getStatus();
// 如果一阶段是失败的,则直接删除分支事务即可
if (currentBranchStatus == BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Failed) {
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
return CONTINUE;
}
try {
// 向RM发送分支事务回滚的请求
BranchStatus branchStatus = branchRollback(globalSession, branchSession);
switch (branchStatus) {
case PhaseTwo_Rollbacked:
// 分支二阶段回滚成功,则释放该分支申请的全局锁,删除分支事务
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
LOGGER.info("Rollback branch transaction successfully, xid = {} branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
return CONTINUE;
case PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Unretryable:
// 分支二阶段回滚失败,并且是不能重试的,则结束全局回滚,需要人工处理了
SessionHelper.endRollbackFailed(globalSession);
LOGGER.info("Rollback branch transaction fail and stop retry, xid = {} branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
return false;
default:
LOGGER.info("Rollback branch transaction fail and will retry, xid = {} branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
if (!retrying) {
// 变更数据库中全局事务的状态为重试回滚中,然后会有一个后台定时任务拉取出可重试的全局事务进行回滚
globalSession.queueToRetryRollback();
}
return false;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
StackTraceLogger.error(LOGGER, ex,
"Rollback branch transaction exception, xid = {} branchId = {} exception = {}",
new String[] {globalSession.getXid(), String.valueOf(branchSession.getBranchId()), ex.getMessage()});
if (!retrying) {
// 变更数据库中全局事务的状态为重试回滚中,
// 然后会有一个后台定时任务拉取出可重试的全局事务进行回滚
globalSession.queueToRetryRollback();
}
throw new TransactionException(ex);
}
});
// result不为空,说明回滚出问题了
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
// In db mode, there is a problem of inconsistent data in multiple copies, resulting in new branch
// transaction registration when rolling back.
// 1. New branch transaction and rollback branch transaction have no data association
// 2. New branch transaction has data association with rollback branch transaction
// The second query can solve the first problem, and if it is the second problem, it may cause a rollback
// failure due to data changes.
GlobalSession globalSessionTwice = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(globalSession.getXid());
if (globalSessionTwice != null && globalSessionTwice.hasBranch()) {
LOGGER.info("Rollbacking global transaction is NOT done, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
return false;
}
}
if (success) {
// 更新数据库全局事务状态为Rollbacked,删除数据库中的全局事务记录
SessionHelper.endRollbacked(globalSession);
// rollbacked event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(globalSession.getTransactionId(),
GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC, globalSession.getTransactionName(),
globalSession.getApplicationId(),
globalSession.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
globalSession.getBeginTime(), System.currentTimeMillis(),
globalSession.getStatus()));
LOGGER.info("Rollback global transaction successfully, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
}
return success;
}
这里面会遍历全局事务下的每个分支,向RM同步发送分支事务回滚的请求。
如果响应回来的是二阶段回滚完成,则释放该分支申请的全局锁,删除数据库中的分支事务记录,这里释放全局锁跟提交时不一样,提交时是全部一次性释放,而这里是每个分支分别释放。
@Override
public void removeBranch(BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
// 释放全局锁,如果全局事务状态是Committing, CommitRetrying或AsyncCommitting,则不释放全局锁,
// 因为在DefaultCore.commit()方法中已经释放了
if (status != Committing && status != CommitRetrying && status != AsyncCommitting) {
if (!branchSession.unlock()) {
throw new TransactionException("Unlock branch lock failed, xid = " + this.xid + ", branchId = " + branchSession.getBranchId());
}
}
// 删除数据库中的分支事务记录
for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
lifecycleListener.onRemoveBranch(this, branchSession);
}
// 移除持有的分支事务
remove(branchSession);
}
等所有的分支事务都成功回滚后,就更新数据库全局事务状态为Rollbacked,删除数据库中的全局事务记录,这样分布式事务回滚就完成了。
public static void endRollbacked(GlobalSession globalSession) throws TransactionException {
GlobalStatus currentStatus = globalSession.getStatus();
// 全局事务是否超时,超时就将数据库中的状态更新为TimeoutRollbacked。否则更新为Rollbacked
if (isTimeoutGlobalStatus(currentStatus)) {
globalSession.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.TimeoutRollbacked);
} else {
globalSession.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.Rollbacked);
}
// 删除数据库中的全局事务记录
globalSession.end();
}
分支事务二阶段回滚
RM处理TC发来的分支事务回滚请求的Processor是RmBranchRollbackProcessor。
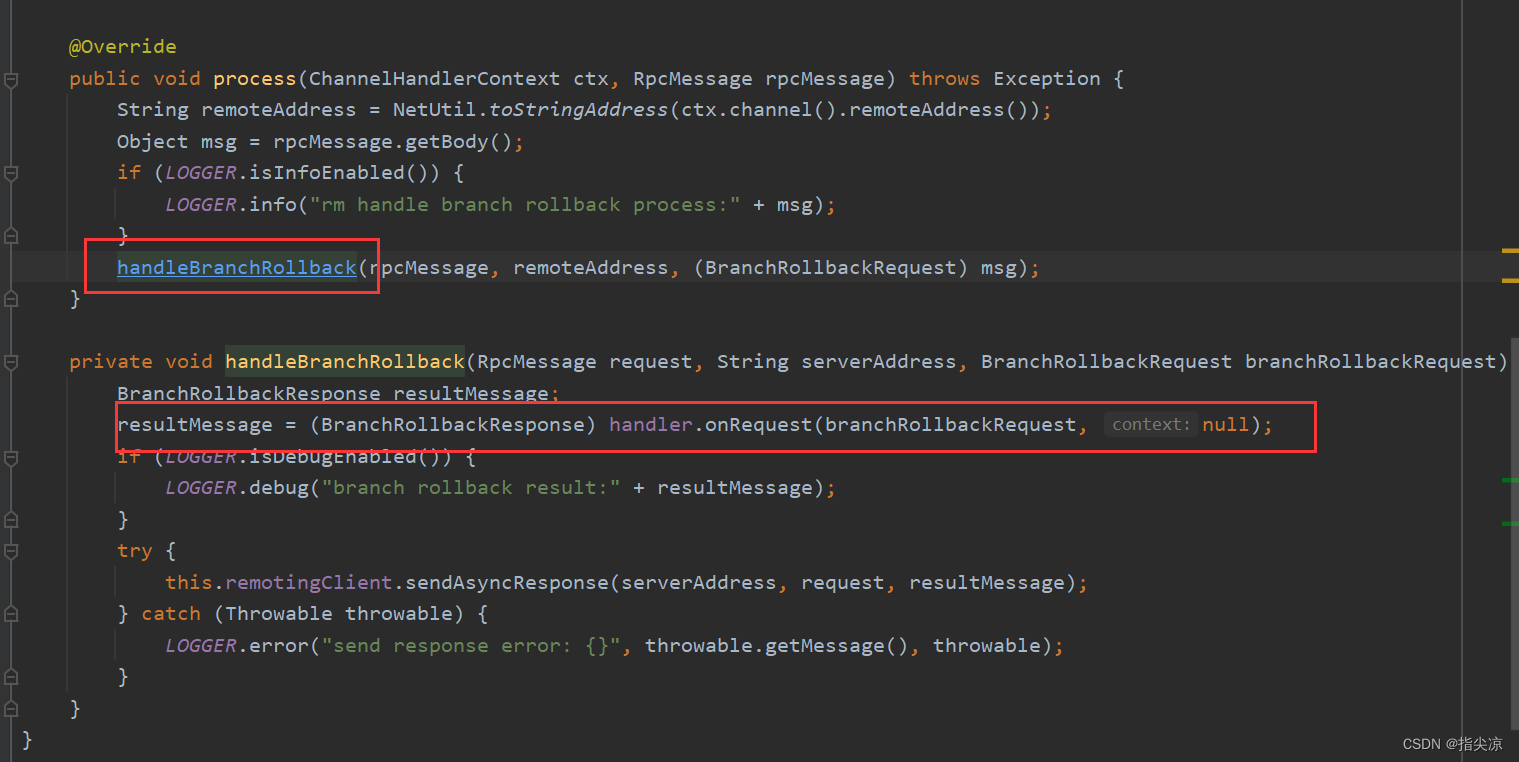

这里的事务请求是BrainRollbackRequest
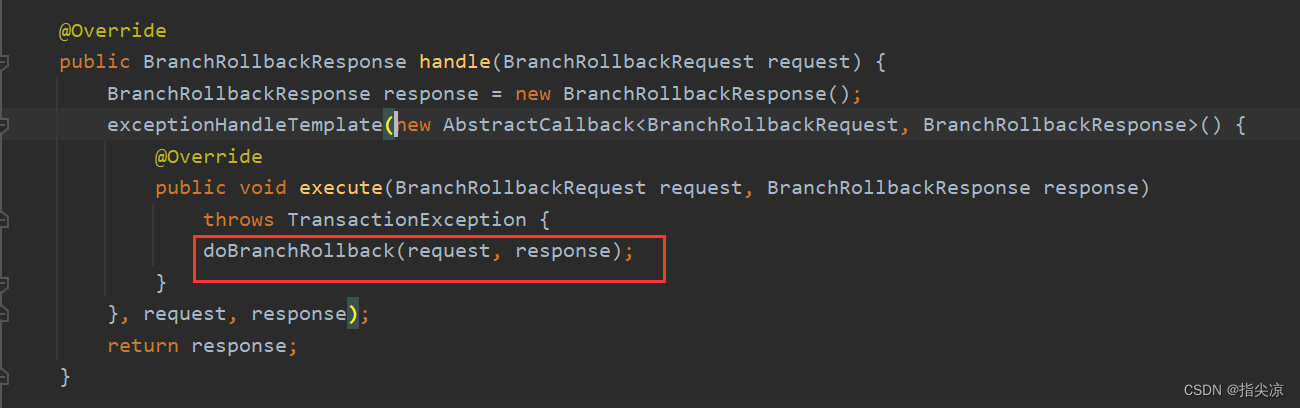

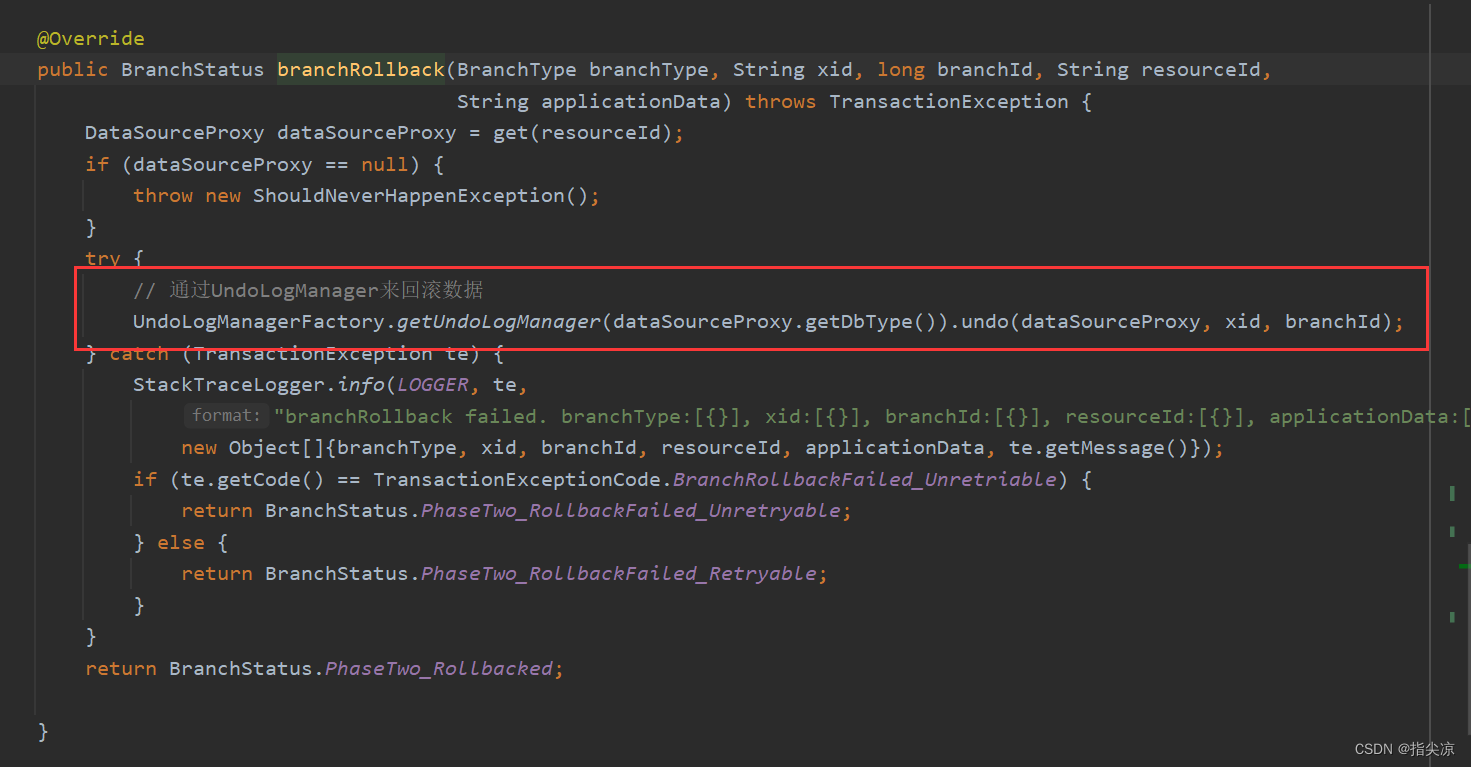
@Override
public void undo(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy, String xid, long branchId) throws TransactionException {
Connection conn = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
PreparedStatement selectPST = null;
boolean originalAutoCommit = true;
for (; ; ) {
try {
conn = dataSourceProxy.getPlainConnection();
// 设置手动提交,为了确保可以最后释放本地锁
if (originalAutoCommit = conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
}
// 将该分支事务的undo log查询出来,使用select for update方式,防止下面所说的多个线程同时回滚同一个分支事务
selectPST = conn.prepareStatement(SELECT_UNDO_LOG_SQL);
selectPST.setLong(1, branchId);
selectPST.setString(2, xid);
rs = selectPST.executeQuery();
// 解析undo log进行回滚
boolean exists = false;
while (rs.next()) {
// 代表当前事务分支存在undo log
exists = true;
// 判断undo log是否是正常状态,可否用于回滚。
// 因为服务端可能会重复发送多次回滚的请求,导致会有多个线程在处理同一个分支事务的回滚,
// 所以需要确保只有一个线程能回滚,上面的select for update方式已经确保了同一个分支事务这里不会有并发问题
int state = rs.getInt(ClientTableColumnsName.UNDO_LOG_LOG_STATUS);
if (!canUndo(state)) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, ignore {} undo_log", xid, branchId, state);
}
return;
}
String contextString = rs.getString(ClientTableColumnsName.UNDO_LOG_CONTEXT);
Map<String, String> context = parseContext(contextString);
byte[] rollbackInfo = getRollbackInfo(rs);
String serializer = context == null ? null : context.get(UndoLogConstants.SERIALIZER_KEY);
UndoLogParser parser = serializer == null ? UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance()
: UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance(serializer);
BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = parser.decode(rollbackInfo);
try {
// put serializer name to local
setCurrentSerializer(parser.getName());
List<SQLUndoLog> sqlUndoLogs = branchUndoLog.getSqlUndoLogs();
if (sqlUndoLogs.size() > 1) {
Collections.reverse(sqlUndoLogs);
}
for (SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog : sqlUndoLogs) {
TableMeta tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).getTableMeta(
conn, sqlUndoLog.getTableName(), dataSourceProxy.getResourceId());
sqlUndoLog.setTableMeta(tableMeta);
// 根据insert,update,delete获取不同类型undo执行器执行
AbstractUndoExecutor undoExecutor = UndoExecutorFactory.getUndoExecutor(
dataSourceProxy.getDbType(), sqlUndoLog);
undoExecutor.executeOn(conn);
}
} finally {
// remove serializer name
removeCurrentSerializer();
}
}
// 如果存在undo_log,说明该分支事务已经完成第一阶段,我们可以直接回滚清理undo_log,否则,说明该分支事务出现异常,
// 导致undo_log没有写入数据库。比如业务处理超时,全局事务是发起方回滚。为了保证数据的一致性,
// 我们可以插入一个带有 GlobalFinished 状态的 undo_log 来防止其他程序一阶段的本地事务被正确提交。
// 意思是rpc调用另一个服务超时时,TM发起全局回滚,这时候分支事务的代码可能是还在执行中,undo_log还没有写入,
// 该分支回滚返回成功(没有 undo_log),然后业务数据和分支事务的undo_log写入数据库,造成脏数据。
// See https://github.com/seata/seata/issues/489
if (exists) {
// 数据回滚完后删除undo log
deleteUndoLog(xid, branchId, conn);
conn.commit();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log deleted with {}", xid, branchId,
State.GlobalFinished.name());
}
} else {
// 插入一个带有 GlobalFinished 状态的 undo_log,来防止分支事务在全局事务回滚后插入 undo_log
insertUndoLogWithGlobalFinished(xid, branchId, UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance(), conn);
conn.commit();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log added with {}", xid, branchId,
State.GlobalFinished.name());
}
}
return;
} catch (SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException e) {
// 可能插入undo_log数据时违反唯一约束条件,已经有其他程序插入了,所以重新进入for循环回滚重试下
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log inserted, retry rollback", xid, branchId);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 回滚过程异常,释放本地锁,抛出回滚失败异常,状态是可重试,
// 由TC重新请求RM重试回滚。
// 其中一个情况就是回滚要先获取本地锁,但本地锁被其他全局事务占用了,
// 获取超时就抛出异常了,到这里,后续重试
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException rollbackEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close JDBC resource while undo ... ", rollbackEx);
}
}
// 抛出可重试的异常
throw new BranchTransactionException(BranchRollbackFailed_Retriable, String
.format("Branch session rollback failed and try again later xid = %s branchId = %s %s", xid,
branchId, e.getMessage()), e);
} finally {
//...
}
}
}
看主线逻辑根据insert,update,delete获取不同类型undo执行器执行
public void executeOn(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
// 判断是否需要校验数据,默认是需要的,校验数据是否可以回滚
if (IS_UNDO_DATA_VALIDATION_ENABLE && !dataValidationAndGoOn(conn)) {
return;
}
try {
// 构建回滚的SQL
String undoSQL = buildUndoSQL();
PreparedStatement undoPST = conn.prepareStatement(undoSQL);
TableRecords undoRows = getUndoRows();
for (Row undoRow : undoRows.getRows()) {
ArrayList<Field> undoValues = new ArrayList<>();
List<Field> pkValueList = getOrderedPkList(undoRows, undoRow, getDbType(conn));
for (Field field : undoRow.getFields()) {
if (field.getKeyType() != KeyType.PRIMARY_KEY) {
undoValues.add(field);
}
}
undoPrepare(undoPST, undoValues, pkValueList);
// 执行SQL回滚
undoPST.executeUpdate();
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (ex instanceof SQLException) {
throw (SQLException) ex;
} else {
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
}
}
protected boolean dataValidationAndGoOn(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
// 前置镜像
TableRecords beforeRecords = sqlUndoLog.getBeforeImage();
// 后置镜像
TableRecords afterRecords = sqlUndoLog.getAfterImage();
// 比较后置镜像和前置镜像的数据是否相同,如果相同则说明前后数据没变化,不需要再回滚了
Result<Boolean> beforeEqualsAfterResult = DataCompareUtils.isRecordsEquals(beforeRecords, afterRecords);
if (beforeEqualsAfterResult.getResult()) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Stop rollback because there is no data change " +
"between the before data snapshot and the after data snapshot.");
}
// no need continue undo.
return false;
}
// 校验脏数据
// select for update 查询当前的数据记录,这里会申请要回滚数据的本地锁
TableRecords currentRecords = queryCurrentRecords(conn);
// 比较当前的数据和后置镜像的数据
Result<Boolean> afterEqualsCurrentResult = DataCompareUtils.isRecordsEquals(afterRecords, currentRecords);
if (!afterEqualsCurrentResult.getResult()) {
// 如果当前数据库的数据和后置镜像的数据不一致,则再与前置镜像比较,
// 如果当前数据和前置镜像数据相同,说明当前数据与要回滚后的数据一样,就无需回滚了,不然就是发生了脏写,抛出异常
Result<Boolean> beforeEqualsCurrentResult = DataCompareUtils.isRecordsEquals(beforeRecords, currentRecords);
if (beforeEqualsCurrentResult.getResult()) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Stop rollback because there is no data change " +
"between the before data snapshot and the current data snapshot.");
}
// no need continue undo.
return false;
} else {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(afterEqualsCurrentResult.getErrMsg())) {
LOGGER.info(afterEqualsCurrentResult.getErrMsg(), afterEqualsCurrentResult.getErrMsgParams());
}
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("check dirty datas failed, old and new data are not equal," +
"tableName:[" + sqlUndoLog.getTableName() + "]," +
"oldRows:[" + JSON.toJSONString(afterRecords.getRows()) + "]," +
"newRows:[" + JSON.toJSONString(currentRecords.getRows()) + "].");
}
// 当前数据和前置镜像以及后置镜像都不一致,说明当前数据是脏数据,发生了脏写,无法回滚,抛异常,回滚失败。
// 如果都是在全局事务中,这里是不会发生脏写的,但如果一个不是seata管理的事务对记录进行了修改,就有可能发生脏写。
// 所以为了避免发生脏写,可以在方法上添加 @GlobalLock+@Transactional 来避免脏写
throw new SQLException("Has dirty records when undo.");
}
}
return true;
}
分支事务回滚说白了就是根据undo log回滚日志将数据恢复为原来的样子,回滚完后删除undo log,最后响应二阶段回滚完成。
总结下二阶段回滚流程:
1)TM捕获到异常后,向TC发送全局事务回滚的请求;
2)TC收到全局事务回滚的请求后,会向每个RM发送分支事务回滚的请求;
3)RM收到分支事务回滚的请求后,开启一个本地事务,一下操作都是在该本地事务内;
4)根据XID和分支ID查询对应的undo log;
5)数据校验,校验数据是否可以回滚:申请要回滚数据的本地锁,如果当前数据与前置镜像以及后置镜像都不同,说明发生了脏写,这时就需要人工处理了;
6)构建回滚的SQL,回滚数据,删除对应的undo log;
7)提交第3步中开启的本地事务,将回滚结果响应给TC,TC根据响应结果和重试机制判断是否需要重试。