🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营中的学习记录博客 🍖 原作者:K同学啊|接辅导、项目定制
文章目录
一、Backbone模块代码 1.1 Conv模块 1.2 C3模块 Bottleneck模块 SPPF模块 二、数据集和相关参数设置 2.1 数据集操作 2.2 相关参数设置 2.3 定义Backbone网络 三、训练及结果可视化 3.1 训练及测试代码 3.2 训练循环代码 3.3 训练结果可视化
def autopad ( k, p= None ) :
"""
:param k: 卷积核的 kernel_size
:param p: 卷积的padding 一般是None
:return: 自动计算的需要pad值(0填充)
"""
if p is None :
p = k // 2 if isinstance ( k, int ) else [ x // 2 for x in k]
return p
class Conv ( nn. Module) :
def __init__ ( self, c1, c2, k= 1 , s= 1 , p= None , act= True , g= 1 ) :
"""
:param c1: 输入的channel值
:param c2: 输出的channel值
:param k: 卷积的kernel_size
:param s: 卷积的stride
:param p: 卷积的padding 一般是None
:param act: 激活函数类型 True就是SiLU(), False就是不使用激活函数
:param g: 卷积的groups数 =1就是普通的卷积 >1就是深度可分离卷积
"""
super ( Conv, self) . __init__( )
self. conv_1 = nn. Conv2d( c1, c2, k, s, autopad( k, p) , groups= g, bias= True )
self. bn = nn. BatchNorm2d( c2)
self. act = nn. SiLU( ) if act else nn. Identity( )
def forward ( self, x) :
return self. act( self. bn( self. conv_1( x) ) )
class C3 ( nn. Module) :
def __init__ ( self, c1, c2, n= 1 , shortcut= True , g= 1 , e= 0.5 ) :
"""
:param c1: 整个 C3 的输入channel
:param c2: 整个 C3 的输出channel
:param n: 有n个Bottleneck
:param shortcut: bool Bottleneck中是否有shortcut,默认True
:param g: C3中的3x3卷积类型 =1普通卷积 >1深度可分离卷积
:param e: expansion ratio
"""
super ( C3, self) . __init__( )
c_ = int ( c2 * e)
self. cv_1 = Conv( c1, c_, 1 , 1 )
self. cv_2 = Conv( c1, c_, 1 , 1 )
self. m = nn. Sequential( * [ Bottleneck( c_, c_, e= 1 , shortcut= True , g= 1 ) for _ in range ( n) ] )
self. cv_3 = Conv( 2 * c_, c2, 1 , 1 )
def forward ( self, x) :
return self. cv_3( torch. cat( ( self. m( self. cv_1( x) ) , self. cv_2( x) ) , dim= 1 ) )
class Bottleneck ( nn. Module) :
def __init__ ( self, c1, c2, e= 0.5 , shortcut= True , g= 1 ) :
"""
:param c1: 整个Bottleneck的输入channel
:param c2: 整个Bottleneck的输出channel
:param e: expansion ratio c2*e 就是第一个卷积的输出channel=第二个卷积的输入channel
:param shortcut: bool Bottleneck中是否有shortcut,默认True
:param g: Bottleneck中的3x3卷积类型 =1普通卷积 >1深度可分离卷积
"""
super ( Bottleneck, self) . __init__( )
c_ = int ( c2* e)
self. conv_1 = Conv( c1, c_, 1 , 1 )
self. conv_2 = Conv( c_, c2, 3 , 1 , g= g)
self. add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward ( self, x) :
return x + self. conv_2( self. conv_1( x) ) if self. add else self. conv_2( self. conv_1( x) )
class SPPF ( nn. Module) :
def __init__ ( self, c1, c2, k= 5 , e= 0.5 ) :
"""
:param c1: 输入通道
:param c2: 输出通道
:param k: 池化的卷积核
:param e: 用于控制中间的通道
"""
super ( SPPF, self) . __init__( )
c_ = int ( c2 * e)
self. conv1 = Conv( c1, c_, 1 , 1 )
self. pool_1 = nn. MaxPool2d( kernel_size= k, stride= 1 , padding= k // 2 )
self. pool_2 = nn. MaxPool2d( kernel_size= k, stride= 1 , padding= k // 2 )
self. pool_3 = nn. MaxPool2d( kernel_size= k, stride= 1 , padding= k // 2 )
self. conv2 = Conv( 4 * c_, c2, 1 , 1 )
def forward ( self, x) :
x_1 = self. conv1( x)
x_2 = self. pool_1( x_1)
x_3 = self. pool_2( x_2)
x_4 = self. pool_3( x_3)
return self. conv2( torch. cat( ( x_1, x_2, x_3, x_4) , dim= 1 ) )
import torch
from torch import nn
import datetime
import matplotlib. pyplot as plt
import copy
from torch. utils. data import DataLoader
import torchvision
from torchvision. transforms import ToTensor, transforms
total_dir = './weather_photos/'
transform = transforms. Compose( [
transforms. Resize( ( 224 , 224 ) ) ,
transforms. ToTensor( ) ,
transforms. Normalize( std= [ 0.5 , 0.5 , 0.5 ] , mean= [ 0.5 , 0.5 , 0.5 ] )
] )
total_data = torchvision. datasets. ImageFolder( total_dir, transform)
print ( total_data)
print ( total_data. class_to_idx)
idx_to_class = dict ( ( v, k) for k, v in total_data. class_to_idx. items( ) )
print ( idx_to_class)
train_size = int ( len ( total_data) * 0.8 )
test_size = int ( len ( total_data) ) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch. utils. data. random_split( total_data, [ train_size, test_size] )
train_dataloader = DataLoader( train_dataset, batch_size= 32 , shuffle= True )
test_dataloader = DataLoader( test_dataset, batch_size= 32 , shuffle= True )
device = 'cuda' if torch. cuda. is_available( ) else 'cpu'
model = YOLOv5_backbone( ) . to( device)
lr_rate = 1e - 4
optimizer = torch. optim. Adam( model. parameters( ) , lr= lr_rate)
loss_fn = nn. CrossEntropyLoss( )
def printlog ( info) :
nowtime = datetime. datetime. now( ) . strftime( '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S' )
print ( "\n" + "==========" * 8 + "%s" % nowtime)
print ( str ( info) + "\n" )
def adjust_learn_rate ( optimizer, epoch, lr_rate) :
lr = lr_rate* ( 0.9 ** ( epoch // 5 ) )
for p in optimizer. param_groups:
p[ 'lr' ] = lr
class YOLOv5_backbone ( nn. Module) :
def __init__ ( self) :
super ( YOLOv5_backbone, self) . __init__( )
self. c_1 = Conv( 3 , 64 , 3 , 2 , 2 )
self. c_2 = Conv( 64 , 128 , 3 , 2 )
self. c3_3 = C3( 128 , 128 , 1 )
self. c_4 = Conv( 128 , 256 , 3 , 2 )
self. c3_5 = C3( 256 , 256 , 1 )
self. c_6 = Conv( 256 , 512 , 3 , 2 )
self. c3_7 = C3( 512 , 512 , 1 )
self. c_8 = Conv( 512 , 1024 , 3 , 2 )
self. c3_9 = C3( 1024 , 1024 , 1 )
self. sppf = SPPF( 1024 , 1024 , 5 )
self. linear = nn. Sequential(
nn. Linear( 65536 , 1000 ) ,
nn. ReLU( ) ,
nn. Linear( 1000 , 4 )
)
def forward ( self, x) :
x = self. c_1( x)
x = self. c_2( x)
x = self. c3_3( x)
x = self. c_4( x)
x = self. c3_5( x)
x = self. c_6( x)
x = self. c3_7( x)
x = self. c_8( x)
x = self. c3_9( x)
x = self. sppf( x)
x = x. view( - 1 , 65536 )
x = self. linear( x)
return x
def train ( train_dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer) :
size = len ( train_dataloader. dataset)
num_of_batch = len ( train_dataloader)
train_correct, train_loss = 0.0 , 0.0
for x, y in train_dataloader:
x, y = x. to( device) , y. to( device)
pre = model( x)
loss = loss_fn( pre, y)
optimizer. zero_grad( )
loss. backward( )
optimizer. step( )
with torch. no_grad( ) :
train_correct += ( pre. argmax( 1 ) == y) . type ( torch. float ) . sum ( ) . item( )
train_loss += loss. item( )
train_correct /= size
train_loss /= num_of_batch
return train_correct, train_loss
def test ( test_dataloader, model, loss_fn) :
size = len ( test_dataloader. dataset)
num_of_batch = len ( test_dataloader)
test_correct, test_loss = 0.0 , 0.0
with torch. no_grad( ) :
for x, y in test_dataloader:
x, y = x. to( device) , y. to( device)
pre = model( x)
loss = loss_fn( pre, y)
test_loss += loss. item( )
test_correct += ( pre. argmax( 1 ) == y) . type ( torch. float ) . sum ( ) . item( )
test_correct /= size
test_loss /= num_of_batch
return test_correct, test_loss
epochs = 50
train_acc = [ ]
train_loss = [ ]
test_acc = [ ]
test_loss = [ ]
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range ( epochs) :
printlog( "Epoch {0} / {1}" . format ( epoch, epochs) )
model. train( )
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train( train_dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
adjust_learn_rate( optimizer, epoch, lr_rate)
model. eval ( )
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test( test_dataloader, model, loss_fn)
train_acc. append( epoch_train_acc)
train_loss. append( epoch_train_loss)
test_acc. append( epoch_test_acc)
test_loss. append( epoch_test_loss)
template = ( "train_acc:{:.5f}, train_loss:{:.5f}, test_acc:{:.5f}, test_loss:{:.5f}" )
print ( template. format ( epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss, epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss) )
print ( 'done' )
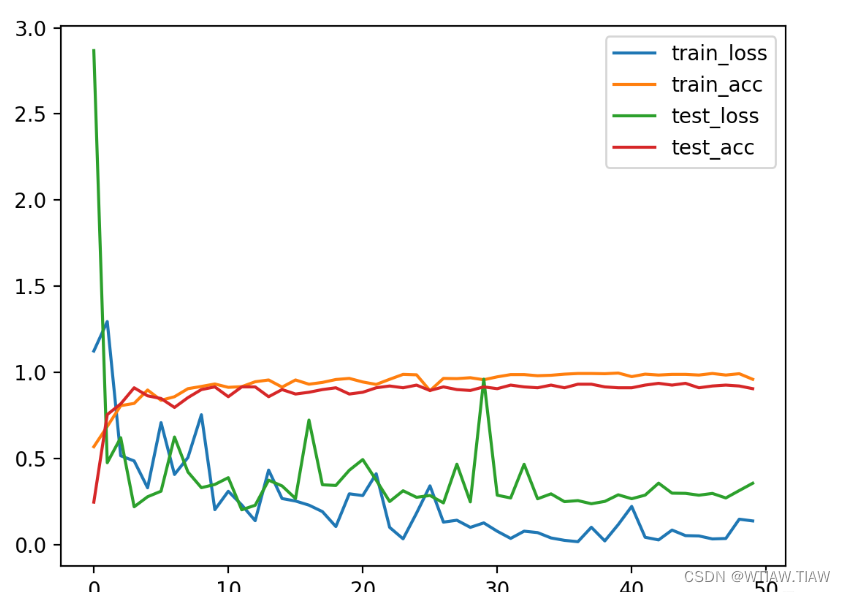
plt. plot( range ( epochs) , train_loss, label= 'train_loss' )
plt. plot( range ( epochs) , train_acc, label= 'train_acc' )
plt. plot( range ( epochs) , test_loss, label= 'test_loss' )
plt. plot( range ( epochs) , test_acc, label= 'test_acc' )
plt. legend( )
plt. show( )
print ( 'done' )