深度学习框架Tensorflow2系列
注:大家觉得博客好的话,别忘了点赞收藏呀,本人每周都会更新关于人工智能和大数据相关的内容,内容多为原创,Python Java Scala SQL 代码,CV NLP 推荐系统等,Spark Flink Kafka Hbase Hive Flume等等~写的都是纯干货,各种顶会的论文解读,一起进步。
这个系列主要和大家分享深度学习框架Tensorflow2的各种api,从基础开始。
#博学谷IT学习技术支持#
文章目录
- 深度学习框架Tensorflow2系列
- 前言
- 一、时间序列预测任务实战
- 二、数据集介绍
- 三、实战代码
- 1.单特征构建序列数据
- 2.构建LSTM模型进行预测
- 3.用训练好的模型预测结果
- 总结
前言
通过时间序列预测任务实战案例,学习Tensorflow2中一些API
一、时间序列预测任务实战
数据集:气温数据,多种指标
任务目标:预测未来某一时间点的气温/未来某一时间片段的气温
二、数据集介绍
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import os
import pandas as pd
mpl.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8, 6)
mpl.rcParams['axes.grid'] = False
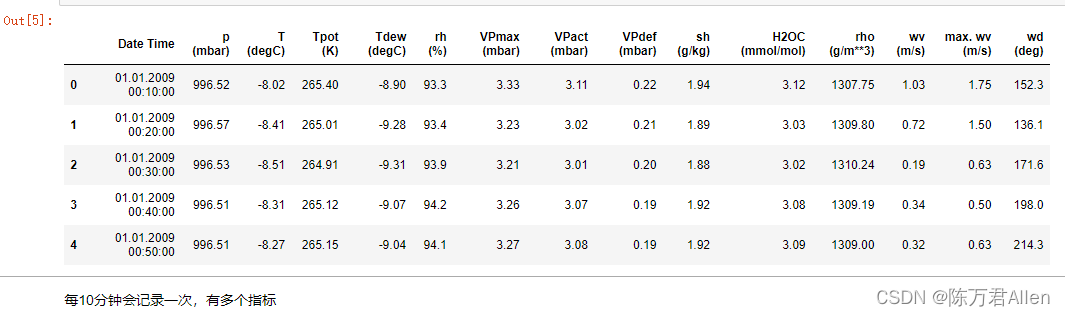
df = pd.read_csv('jena_climate_2009_2016.csv')
df.head()
三、实战代码
1.单特征构建序列数据
def univariate_data(dataset, start_index, end_index, history_size, target_size):
data = []
labels = []
start_index = start_index + history_size
if end_index is None:
end_index = len(dataset) - target_size
for i in range(start_index, end_index):
indices = range(i-history_size, i)
# Reshape data from (history_size,) to (history_size, 1)
data.append(np.reshape(dataset[indices], (history_size, 1)))
labels.append(dataset[i+target_size])
return np.array(data), np.array(labels)
TRAIN_SPLIT = 300000
tf.random.set_seed(13)
# 只选一个温度特征
uni_data = df['T (degC)']
uni_data.index = df['Date Time']
uni_data = uni_data.values
# 数据标准化
uni_train_mean = uni_data[:TRAIN_SPLIT].mean()
uni_train_std = uni_data[:TRAIN_SPLIT].std()
uni_data = (uni_data-uni_train_mean)/uni_train_std
univariate_past_history = 20
univariate_future_target = 0
x_train_uni, y_train_uni = univariate_data(uni_data, 0, TRAIN_SPLIT,
univariate_past_history,
univariate_future_target)
x_val_uni, y_val_uni = univariate_data(uni_data, TRAIN_SPLIT, None,
univariate_past_history,
univariate_future_target)
print ('Single window of past history')
print (x_train_uni[0])
print ('\n Target temperature to predict')
print (y_train_uni[0])
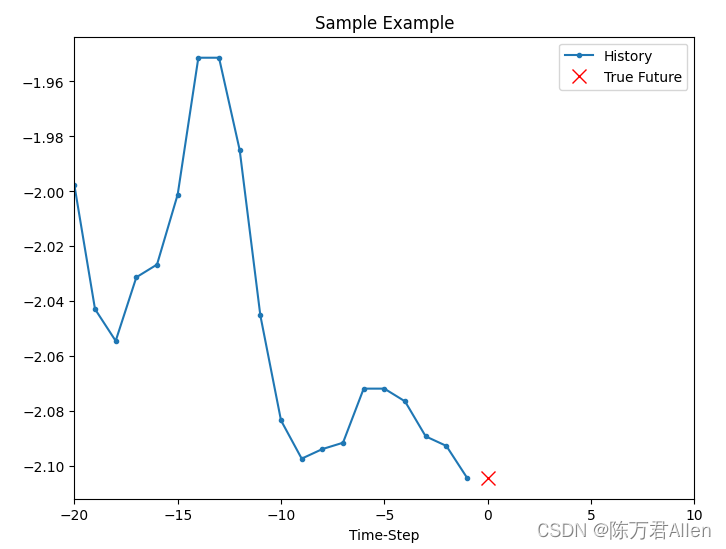
只用’T (degC)'的前20个数据,预测第21的值。

把数据画图展示一下
def create_time_steps(length):
time_steps = []
for i in range(-length, 0, 1):
time_steps.append(i)
return time_steps
def show_plot(plot_data, delta, title):
labels = ['History', 'True Future', 'Model Prediction']
marker = ['.-', 'rx', 'go']
time_steps = create_time_steps(plot_data[0].shape[0])
if delta:
future = delta
else:
future = 0
plt.title(title)
for i, x in enumerate(plot_data):
if i:
plt.plot(future, plot_data[i], marker[i], markersize=10,label=labels[i])
else:
plt.plot(time_steps, plot_data[i].flatten(), marker[i], label=labels[i])
plt.legend()
plt.xlim([time_steps[0], (future+5)*2])
plt.xlabel('Time-Step')
return plt
show_plot([x_train_uni[0], y_train_uni[0]], 0, 'Sample Example')
2.构建LSTM模型进行预测
BATCH_SIZE = 256
BUFFER_SIZE = 10000
train_univariate = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train_uni, y_train_uni))
train_univariate = train_univariate.cache().shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
val_univariate = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val_uni, y_val_uni))
val_univariate = val_univariate.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
simple_lstm_model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(8, input_shape=x_train_uni.shape[-2:]),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
simple_lstm_model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mae')
EPOCHS = 10
simple_lstm_model.fit(train_univariate, epochs=EPOCHS,
validation_data=val_univariate, validation_steps=50)
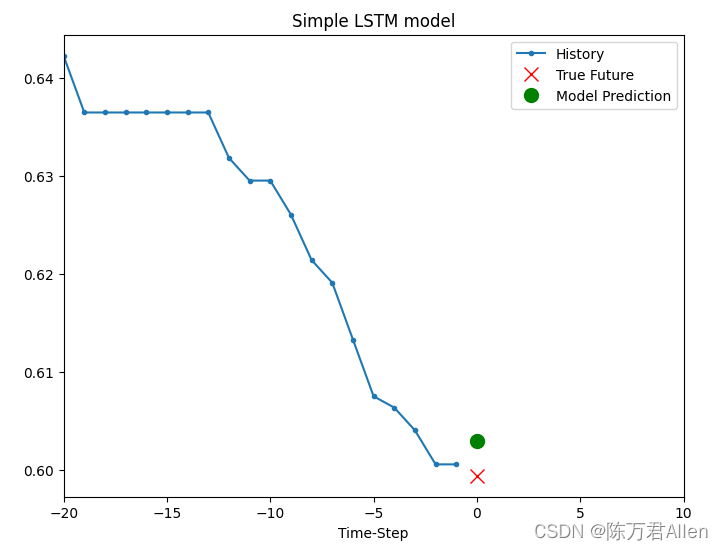
3.用训练好的模型预测结果
for x, y in val_univariate.take(1):
plot = show_plot([x[0].numpy(), y[0].numpy(),
simple_lstm_model.predict(x)[0]], 0, 'Simple LSTM model')
plot.show()
总结
通过时间序列预测任务实战案例,学习Tensorflow2中一些API