OpenVINO 2022.3实战四:POT API 实现 YOLOv5 模型 INT8 量化
将预训练的 YOLOv5m Pytorch 模型转换为 OpenVINO™ FP32 Intermediate Representation (IR) 模型。下一步,通过 OpenVINO™ Post-Training Optimization Tool (POT) API 来定义客制化DataLoader和Metric,从而复用 YOLOv5 客制化的前后处理(letterbox,Non-maximum Suppression)及精度计算等模块。采用 “DefaultQuantization” 的量化算法,定义和运行量化流水线对FP32模型进行 INT8 量化。
1 准备需要量化的模型
下载yolov5代码 ultralytics/yolov5
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include torchscript onnx openvino
导出模型为 yolov5s_openvino_model
2 定义数据加载
继承来自 openvino.tools.pot.api 的 DataLoader类, 创建 YOLOv5DataLoader Class:定义数据和annotation加载和预处理;
class YOLOv5DataLoader(DataLoader):
""" Inherit from DataLoader function and implement for YOLOv5.
"""
def __init__(self, config):
if not isinstance(config, Dict):
config = Dict(config)
super().__init__(config)
self._data_source = config.data_source
self._imgsz = config.imgsz
self._batch_size = 1
self._stride = 32
self._single_cls = config.single_cls
self._pad = 0.5
self._rect = False
self._workers = 1
self._data_loader = self._init_dataloader()
self._data_iter = iter(self._data_loader)
def __len__(self):
return len(self._data_loader.dataset)
def _init_dataloader(self):
dataloader = create_dataloader(self._data_source['val'], imgsz=self._imgsz, batch_size=self._batch_size, stride=self._stride,
single_cls=self._single_cls, pad=self._pad, rect=self._rect, workers=self._workers)[0]
return dataloader
def __getitem__(self, item):
try:
batch_data = next(self._data_iter)
except StopIteration:
self._data_iter = iter(self._data_loader)
batch_data = next(self._data_iter)
im, target, path, shape = batch_data
im = im.float()
im /= 255
nb, _, height, width = im.shape
img = im.cpu().detach().numpy()
target = target.cpu().detach().numpy()
annotation = dict()
annotation['image_path'] = path
annotation['target'] = target
annotation['batch_size'] = nb
annotation['shape'] = shape
annotation['width'] = width
annotation['height'] = height
annotation['img'] = img
return (item, annotation), img
3 精度验证功能
继承来自 openvino.tools.pot.api 的 Metric 类, 创建 COCOMetric Class:定义模型后处理及精度计算方法;
class COCOMetric(Metric):
""" Inherit from DataLoader function and implement for YOLOv5.
"""
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self._metric_dict = {"AP@0.5": [], "AP@0.5:0.95": []}
self._names = (*self._metric_dict,)
self._stats = []
self._last_stats = []
self._conf_thres = config.conf_thres
self._iou_thres = config.iou_thres
self._single_cls = config.single_cls
self._nc = config.nc
self._class_names = {idx:name for idx,name in enumerate(config.names)}
self._device = config.device
@property
def value(self):
""" Returns metric value for the last model output.
Both use AP@0.5 and AP@0.5:0.95
"""
mp, mr, map50, map = self._process_stats(self._last_stats)
return {self._names[0]: [map50], self._names[1]: [map]}
@property
def avg_value(self):
""" Returns metric value for all model outputs.
Both use AP@0.5 and AP@0.5:0.95
"""
mp, mr, map50, map = self._process_stats(self._stats)
return {self._names[0]: map50, self._names[1]: map}
def _process_stats(self, stats):
mp, mr, map50, map = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
stats = [np.concatenate(x, 0) for x in zip(*stats)]
if len(stats) and stats[0].any():
tp, fp, p, r, f1, ap, ap_class = ap_per_class(*stats, plot=False, save_dir=None, names=self._class_names)
ap50, ap = ap[:, 0], ap.mean(1)
mp, mr, map50, map = p.mean(), r.mean(), ap50.mean(), ap.mean()
np.bincount(stats[3].astype(np.int64), minlength=self._nc)
else:
torch.zeros(1)
return mp, mr, map50, map
def update(self, output, target):
""" Calculates and updates metric value
Contains postprocessing part from Ultralytics YOLOv5 project
:param output: model output
:param target: annotations
"""
annotation = target[0]["target"]
width = target[0]["width"]
height = target[0]["height"]
shapes = target[0]["shape"]
paths = target[0]["image_path"]
im = target[0]["img"]
iouv = torch.linspace(0.5, 0.95, 10).to(self._device) # iou vector for mAP@0.5:0.95
niou = iouv.numel()
seen = 0
stats = []
# NMS
annotation = torch.Tensor(annotation)
annotation[:, 2:] *= torch.Tensor([width, height, width, height]).to(self._device) # to pixels
lb = []
out = output[0]
out = torch.Tensor(out).to(self._device)
out = non_max_suppression(out, self._conf_thres, self._iou_thres, labels=lb,
multi_label=True, agnostic=self._single_cls)
# Metrics
for si, pred in enumerate(out):
labels = annotation[annotation[:, 0] == si, 1:]
nl = len(labels)
tcls = labels[:, 0].tolist() if nl else [] # target class
_, shape = Path(paths[si]), shapes[si][0]
seen += 1
if len(pred) == 0:
if nl:
stats.append((torch.zeros(0, niou, dtype=torch.bool), torch.Tensor(), torch.Tensor(), tcls))
continue
# Predictions
if self._single_cls:
pred[:, 5] = 0
predn = pred.clone()
scale_coords(im[si].shape[1:], predn[:, :4], shape, shapes[si][1]) # native-space pred
# Evaluate
if nl:
tbox = xywh2xyxy(labels[:, 1:5]) # target boxes
scale_coords(im[si].shape[1:], tbox, shape, shapes[si][1]) # native-space labels
labelsn = torch.cat((labels[:, 0:1], tbox), 1) # native-space labels
correct = process_batch(predn, labelsn, iouv)
else:
correct = torch.zeros(pred.shape[0], niou, dtype=torch.bool)
stats.append((correct.cpu(), pred[:, 4].cpu(), pred[:, 5].cpu(), tcls))
self._stats.append((correct.cpu(), pred[:, 4].cpu(), pred[:, 5].cpu(), tcls))
self._last_stats = stats
def reset(self):
""" Resets metric """
self._metric_dict = {"AP@0.5": [], "AP@0.5:0.95": []}
self._last_stats = []
self._stats = []
def get_attributes(self):
"""
Returns a dictionary of metric attributes {metric_name: {attribute_name: value}}.
Required attributes: 'direction': 'higher-better' or 'higher-worse'
'type': metric type
"""
return {self._names[0]: {'direction': 'higher-better',
'type': 'AP@0.5'},
self._names[1]: {'direction': 'higher-better',
'type': 'AP@0.5:0.95'}}
4 运行优化流程
设置量化算法及相关参数,定义并运行量化流水线。
def get_config():
""" Set the configuration of the model, engine,
dataset, metric and quantization algorithm.
"""
config = dict()
data_yaml = check_yaml("./data/coco128.yaml")
data = check_dataset(data_yaml)
model_config = Dict({
"model_name": "yolov5s",
"model": "./weights/yolov5s_openvino_model/yolov5s.xml",
"weights": "./weights/yolov5s_openvino_model/yolov5s.bin"
})
engine_config = Dict({
"device": "CPU",
"stat_requests_number": 8,
"eval_requests_number": 8
})
dataset_config = Dict({
"data_source": data,
"imgsz": 640,
"single_cls": True,
})
metric_config = Dict({
"conf_thres": 0.001,
"iou_thres": 0.65,
"single_cls": True,
"nc": 1, # if opt.single_cls else int(data['nc']),
"names": data["names"],
"device": "cpu"
})
algorithms = [
{
"name": "DefaultQuantization", # or AccuracyAware
"params": {
"target_device": "CPU",
"preset": "mixed",
"stat_subset_size": 300
}
}
]
config["model"] = model_config
config["engine"] = engine_config
config["dataset"] = dataset_config
config["metric"] = metric_config
config["algorithms"] = algorithms
return config
""" Download dataset and set config
"""
print("Run the POT. This will take few minutes...")
config = get_config()
init_logger(level='INFO')
save_dir = Path("./weights/yolov5s_openvino_model/")
save_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir
# Step 1: Load the model.
model = load_model(config["model"])
# Step 2: Initialize the data loader.
data_loader = YOLOv5DataLoader(config["dataset"])
# Step 3 (Optional. Required for AccuracyAwareQuantization): Initialize the metric.
metric = COCOMetric(config["metric"])
# Step 4: Initialize the engine for metric calculation and statistics collection.
engine = IEEngine(config=config["engine"], data_loader=data_loader, metric=metric)
# Step 5: Create a pipeline of compression algorithms.
pipeline = create_pipeline(config["algorithms"], engine)
metric_results = None
# Step 6: Execute the pipeline to calculate Min-Max value
compressed_model = pipeline.run(model)
# Step 7 (Optional): Compress model weights to quantized precision
# in order to reduce the size of final .bin file.
compress_model_weights(compressed_model)
# Step 8: Save the compressed model to the desired path.
optimized_save_dir = Path(save_dir).joinpath("optimized")
save_model(compressed_model, Path(Path.cwd()).joinpath(optimized_save_dir), config["model"]["model_name"])
5 比较原始模型和量化模型的准确性
FP32:
# Step 9 (Optional): Evaluate the compressed model. Print the results.
metric_results_i8 = pipeline.evaluate(compressed_model)
print("Quantized INT8 model metric_results: {}".format(metric_results_i8))
输出:
FP32 model metric_results: {'AP@0.5': 0.7051576693437555, 'AP@0.5:0.95': 0.44624265930493545}
INT8:
# Step 9 (Optional): Evaluate the compressed model. Print the results.
metric_results_i8 = pipeline.evaluate(compressed_model)
print("Quantized INT8 model metric_results: {}".format(metric_results_i8))
输出:
Quantized INT8 model metric_results: {'AP@0.5': 0.6924341121617621, 'AP@0.5:0.95': 0.43698028961534857}
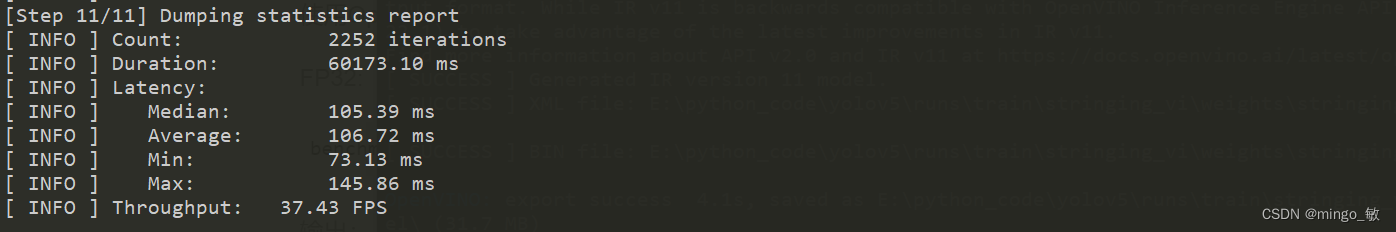
6 比较原始模型和量化模型的性能
使用OpenVINO中的Benchmark Tool(推理性能测量工具)测量FP32和INT8模型的推理性能
FP32:
benchmark_app -m .\weights\yolov5s_openvino_model\yolov5s.xml -d CPU -api async
输出:
INT8:
benchmark_app -m .\weights\yolov5s_openvino_model\optimized\yolov5s.xml -d CPU -api async
输出: