一.简介
在SpringSecurity中实现会话并发控制,只需要配置一个会话数量就可以了,先介绍下如何配置会话并发控制,然后再。介绍下SpringSecurity 如何实现会话并发控制。
二.创建项目
如何创建一个SpringSecurity项目,前面文章已经有说明了,这里就不重复写了。
三.代码实现
3.1设置只有一个会话
SecurityConfig 类,代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
.sessionManagement()
.maximumSessions(1);
return http.build();
}
}
登陆一个客户端
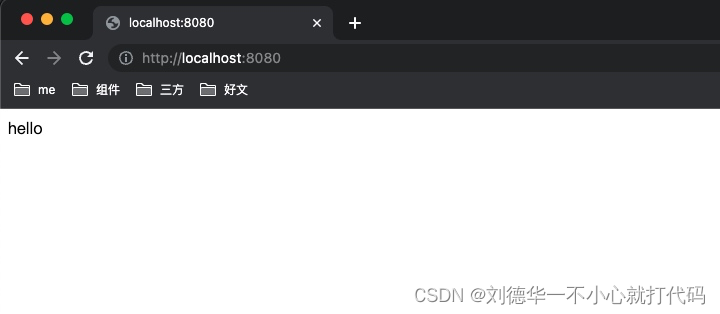
登陆第二个客户端
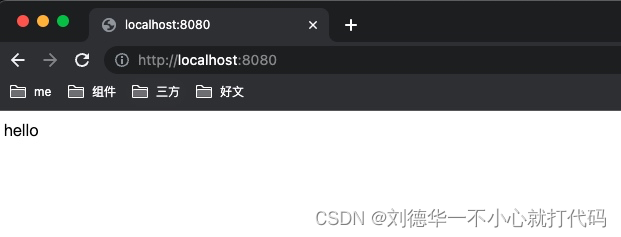
刷新第一个客户端
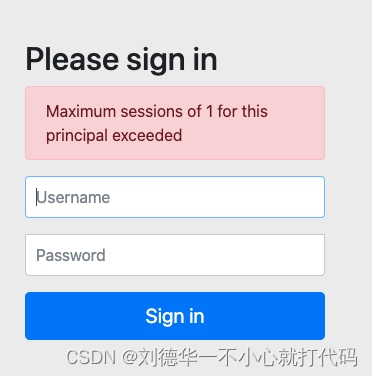
这时候发现已经被挤掉了。
目前默认策略是:后来的会把前面的给挤掉,现在我们通过配置,禁止第二个客户端登陆
3.2禁止第二个客户端登陆
SecurityConfig 类,代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
.sessionManagement()
.maximumSessions(1)
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true);
return http.build();
}
}
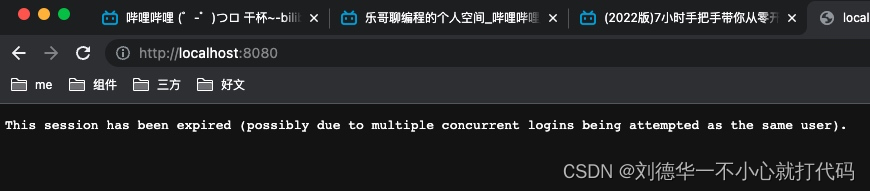
登陆第一个客户端
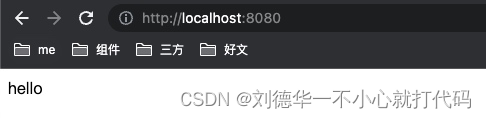
登陆第二个客户端
四.实现原理分析
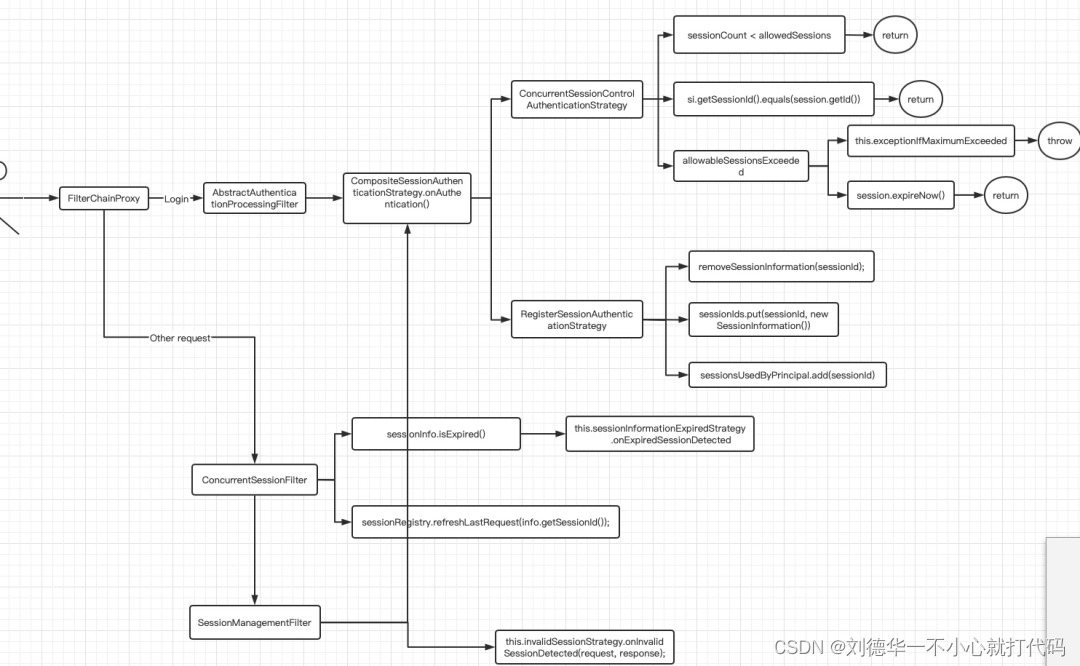
session默认的过滤器是SessionManagementConfigurer
4.1SessionManagementConfigurer
点击.sessionManagement()进去,找到SessionManagementConfigurer,点进去看下主要是看init和configure方法。
4.1.1 init()方法
- 创建SecurityContextRepository
- 初始化 SessionAuthenticationStrategy,并添加到容器
ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy
defaultSessionAuthenticationStrategy
RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategy
setMaximumSessions
setExceptionIfMaximumExceeded = maxSessionsPreventsLogin
CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy
InvalidSessionStrategy
4.1.2 configure()方法
- 初始化 SessionManagementFilter
- 添加sessionManagementFilter 到http链中
- isConcurrentSessionControlEnabled &&添加ConcurrentSessionFilter 到http链中
- !this.enableSessionUrlRewriting && 添加 DisableEncodeUrlFilter
- SessionCreationPolicy.ALWAYS && 添加 ForceEagerSessionCreationFilter
4.2CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy
CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy是一个代理策略,它里面会包含很多SessionAuthenticationStrategy,主要有ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy和RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategy。
4.3RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategy
处理并发登录人数的数量,代码如下:
public void onAuthentication(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
this.sessionRegistry.registerNewSession(request.getSession().getId(), authentication.getPrincipal());
}
这里直接调用this.sessionRegistry.registerNewSession方法,代码如下:
public void registerNewSession(String sessionId, Object principal) {
Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract");
Assert.notNull(principal, "Principal required as per interface contract");
if (getSessionInformation(sessionId) != null) {
removeSessionInformation(sessionId);
}
this.sessionIds.put(sessionId, new SessionInformation(principal, sessionId, new Date()));
this.principals.compute(principal, (key, sessionsUsedByPrincipal) -> {
if (sessionsUsedByPrincipal == null) {
sessionsUsedByPrincipal = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
}
sessionsUsedByPrincipal.add(sessionId);
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Sessions used by '%s' : %s", principal, sessionsUsedByPrincipal));
return sessionsUsedByPrincipal;
});
}
- 根据sessionId查找session,如果有,则移除
- 创建新的SessionInformation,维护到sessionIds中
- 维护sessionId到principals中
4.4ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy
onAuthentication方法代码如下:
public void onAuthentication(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
int allowedSessions = getMaximumSessionsForThisUser(authentication);
if (allowedSessions == -1) {
// We permit unlimited logins
return;
}
List<SessionInformation> sessions = this.sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(authentication.getPrincipal(), false);
int sessionCount = sessions.size();
if (sessionCount < allowedSessions) {
// They haven't got too many login sessions running at present
return;
}
if (sessionCount == allowedSessions) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
// Only permit it though if this request is associated with one of the
// already registered sessions
for (SessionInformation si : sessions) {
if (si.getSessionId().equals(session.getId())) {
return;
}
}
}
// If the session is null, a new one will be created by the parent class,
// exceeding the allowed number
}
allowableSessionsExceeded(sessions, allowedSessions, this.sessionRegistry);
}
- 获取当前用户允许同时在线的数量,如果 == -1(没有限制)则跳过并发校验
- 获取当前用户的所有在线session数量,如果小于限制数量则返回
- 如果等于限制数量,则判断当前的sessionId是否已经在集合中,如果在,则返回
- 否则走allowableSessionsExceeded 校验
allowableSessionsExceeded方法代码如下:
protected void allowableSessionsExceeded(List<SessionInformation> sessions, int allowableSessions,
SessionRegistry registry) throws SessionAuthenticationException {
if (this.exceptionIfMaximumExceeded || (sessions == null)) {
throw new SessionAuthenticationException(
this.messages.getMessage("ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy.exceededAllowed",
new Object[] { allowableSessions }, "Maximum sessions of {0} for this principal exceeded"));
}
// Determine least recently used sessions, and mark them for invalidation
sessions.sort(Comparator.comparing(SessionInformation::getLastRequest));
int maximumSessionsExceededBy = sessions.size() - allowableSessions + 1;
List<SessionInformation> sessionsToBeExpired = sessions.subList(0, maximumSessionsExceededBy);
for (SessionInformation session : sessionsToBeExpired) {
session.expireNow();
}
}
- 如果配置了 maxSessionsPreventsLogin,则直接抛出异常,禁止新用户登录,否则往下走
- 将当前用户的所有session按照最后访问时间排序
- 获取最大允许同时在线的数量,然后在集合中 top n,其余的全部设置过期
- expireNow();
this.expired = true;
4.5SessionManagementFilter
代码如下:
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (!this.securityContextRepository.containsContext(request)) {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null && !this.trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication)) {
// The user has been authenticated during the current request, so call the
// session strategy
try {
this.sessionAuthenticationStrategy.onAuthentication(authentication, request, response);
}
catch (SessionAuthenticationException ex) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
this.failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, ex);
return;
} this.securityContextRepository.saveContext(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), request, response);
}
else {
if (request.getRequestedSessionId() != null && !request.isRequestedSessionIdValid()) {
if (this.invalidSessionStrategy != null) {
this.invalidSessionStrategy.onInvalidSessionDetected(request, response);
return;
}
}
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
- 如果securityContextRepository 有Context信息
- 如果抛出异常,则进行异常处理,并清楚context信息
获取authentication
如果authentication 不为空,则调用sessionAuthenticationStrategy.onAuthentication
如果为空,则调用invalidSessionStrategy的onInvalidSessionDetected方法
4.6ConcurrentSessionFilter
ConcurrentSessionFilter类,代码如下:
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
SessionInformation info = this.sessionRegistry.getSessionInformation(session.getId());
if (info != null) {
if (info.isExpired()) {
// Expired - abort processing
this.logger.debug(LogMessage
.of(() -> "Requested session ID " + request.getRequestedSessionId() + " has expired."));
doLogout(request, response);
this.sessionInformationExpiredStrategy
.onExpiredSessionDetected(new SessionInformationExpiredEvent(info, request, response));
return;
}
// Non-expired - update last request date/time
this.sessionRegistry.refreshLastRequest(info.getSessionId());
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
4.7AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
这个过滤器也会调用sessionStrategy.onAuthentication,进行session维护,代码如下:
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
Authentication authenticationResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authenticationResult, request, response);
}
整体流程图,截图如下: