如果你在做一件事情之前就过分放大它的困难,这就会逐渐降低自己去做它的动机和动力,还没开始你就已经削弱了自己的行动能力,在气势上就已经输了。
不要害怕困难,勇敢的去面对问题,解决问题,你就会在气势上更盛。
1、什么事务
(1)事务是数据库操作最基本单元,逻辑上一组操作,要么都成功,如果有一个失败所有操作都失败
(2)典型场景:银行转账
- lucy 转账100元 给mary
- lucy少100,mary多100
2、事务四个特性(ACID)
(1)原子性
(2)一致性
(3)隔离性
(4)持久性
事务操作 事务操作
1、事务添加到JavaEE三层结构里面Service层(业务逻辑层)
2、在Spring进行事务管理操作
(1)有两种方式:编程式事务管理和声明式事务管理(使用)
3、声明式事务管理
(1)基于注解方式(使用)
(2)基于xml配置文件方式
4、在Spring进行声明式事务管理,底层使用AOP原理
5、Spring事务管理API
(1)提供一个接口,代表事务管理器,这个接口针对不同的框架提供不同的实现类
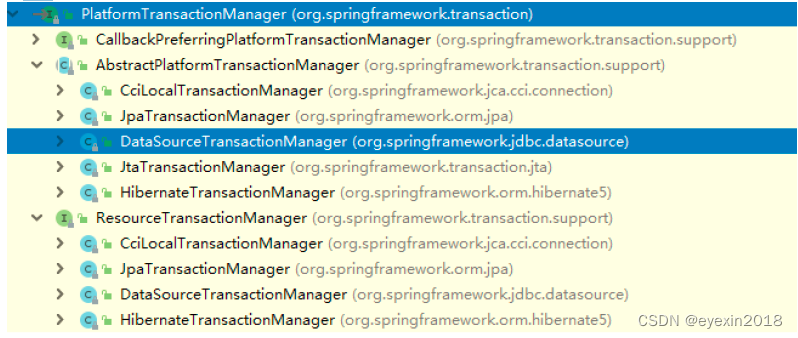
基于注解
1、在spring配置文件配置事务管理器
<!--创建事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!--注入数据源--> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean>
2、在spring配置文件,开启事务注解
(1)在spring配置文件引入名称空间
tx <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
(2)开启事务注解
<!--开启事务注解--> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
3、在service类上面(或者service类里面方法上面)添加事务注解
(1)@Transactional,这个注解添加到类上面,也可以添加方法上面
(2)如果把这个注解添加类上面,这个类里面所有的方法都添加事务
(3)如果把这个注解添加方法上面,为这个方法添加事务
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
参数理解
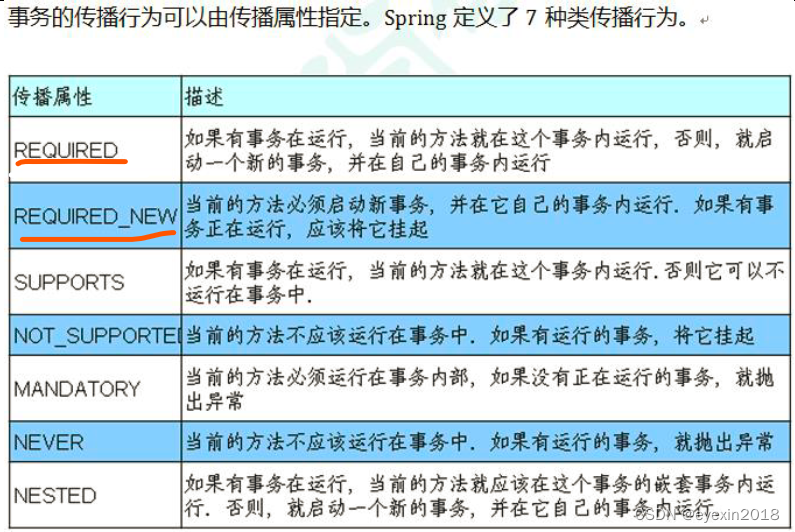
其中前两个划线的最重要
required

required_new

supports