1 Steam流式思想概述
Stream和IO流(InputStream/OutputStream)没有任何关系,请暂时忘记对传统IO流的固有印象!
Stream流式思想类似于工厂车间的“生产流水线”,Stream流不是一种数据结构,不保存数据,而是对数据进行加工
处理。Stream可以看作是流水线上的一个工序。在流水线上,通过多个工序让一个原材料加工成一个商品。
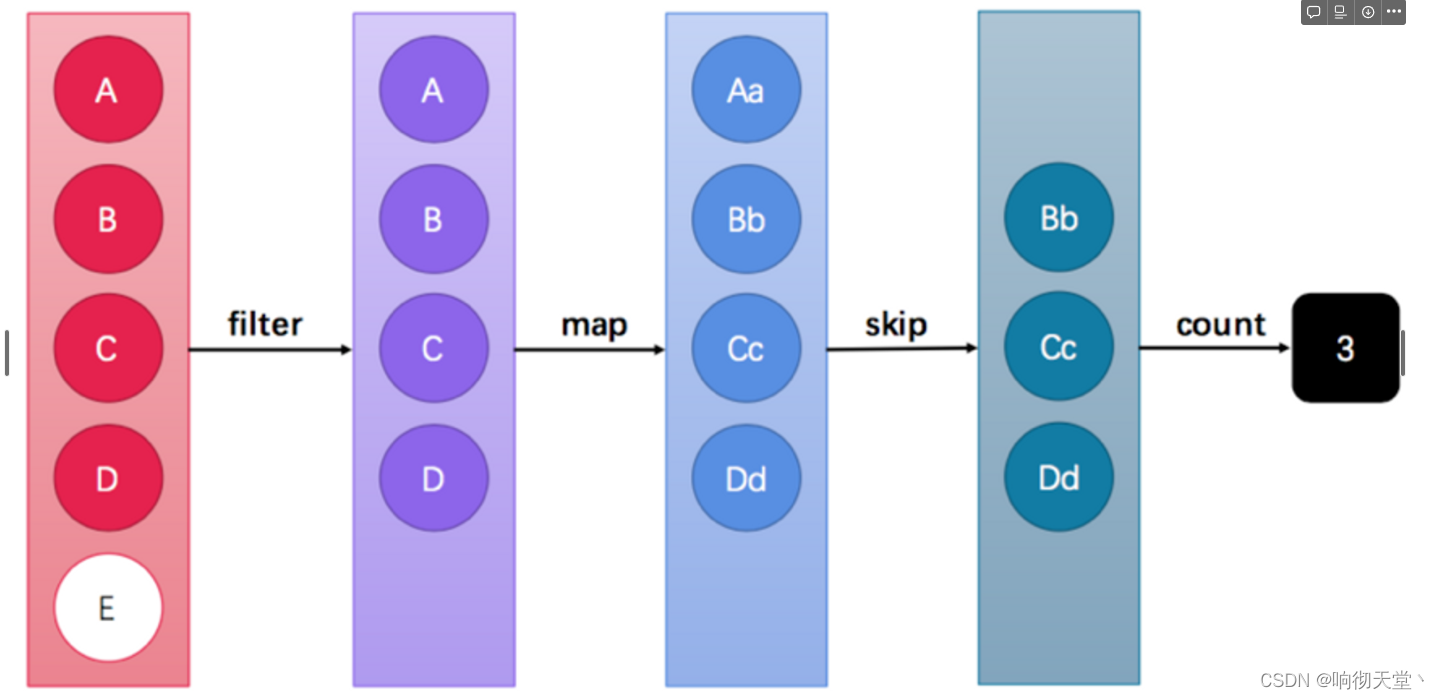
Stream API能让我们快速完成许多复杂的操作,如筛选、切片、映射、查找、去除重复,统计,匹配和归约。
2 Stream流的获取方式
首先,java.util.Collection 接口中加入了default方法 stream,也就是说Collection接口下的所有的实现都可以通过steam方法来获取Stream流。
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.stream();
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.stream();
Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.stream();
}
但是Map接口别没有实现Collection接口,那这时怎么办呢?这时我们可以根据Map获取对应的key value的集合。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Stream<String> stream = map.keySet().stream(); // key
Stream<Object> stream1 = map.values().stream(); // value
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Object>> stream2 = map.entrySet().stream(); // entry
}
3 Stream常用方法介绍
Stream常用方法
Stream流模型的操作很丰富,这里介绍一些常用的API。这些方法可以被分成两种:
| 方法名 | 方法作用 | 返回值类型 | 方法种类 |
|---|---|---|---|
| count | 统计个数 | long | 终结 |
| forEach | 逐一处理 | void | 终结 |
| filter | 过滤 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| limit | 取用前几个 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| skip | 跳过前几个 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| map | 映射 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| concat | 组合 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
终结方法:返回值类型不再是 Stream 类型的方法,不再支持链式调用。本小节中,终结方法包括 count 和 forEach 方法。
非终结方法:返回值类型仍然是 Stream 类型的方法,支持链式调用。除了终结方法外,其余方法均为非终结方法。
Stream注意事项(重要)
- Stream只能操作一次
- Stream方法返回的是新的流
- Stream不调用终结方法,中间的操作不会执行
3.1 forEach
遍历:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("Hello", "World");
words.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.2 count
Stream流中的count方法用来统计其中的元素个数的:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("Hello", "World");
//for each , count
System.out.println(words.stream().count());
}
3.3 filter
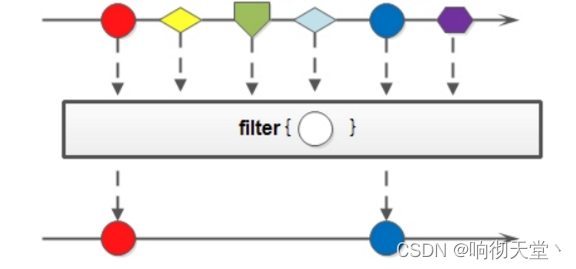
filter方法的作用是用来过滤数据的。返回符合条件的数据:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("hello", "world", "window", "good", "nice");
//for each , count
words.stream().filter(o->o.startsWith("w")).forEach(System.out::println);
}
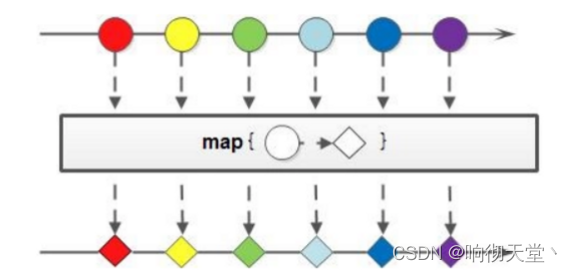
3.4 map
如果我们需要将流中的元素映射到另一个流中,可以使用map方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("hello", "world", "window", "good", "nice");
//for each , count
words.stream().map(String::length).forEach(System.out::println);
}
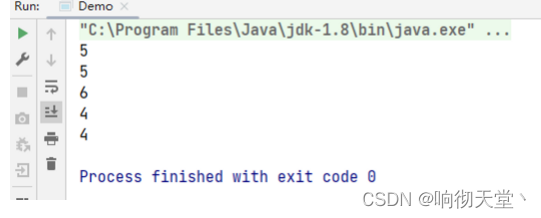
3.5 sorted
如果需要将数据排序,可以使用sorted方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("1", "22", "33", "20", "30");
//for each , count
words.stream().map(Integer::parseInt).sorted((n1, n2) -> n2 - n1).forEach(System.out::println);
}
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ujsDWZEh-1684739478779)(https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/secure.notion-static.com/1de44612-5ecf-445a-9365-7bcb0da5aed4/Untitled.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7c885b3d7d254994a730e7d3c3c676ba.png)
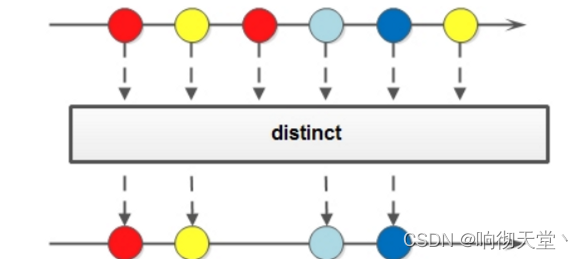
3.6 distinct
如果要去掉重复数据,可以使用distinct方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("1", "22", "22", "19", "33", "20", "30");
//for each , count
words.stream()
.distinct()
.map(Integer::parseInt)
.sorted((n1, n2) -> n2 - n1)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
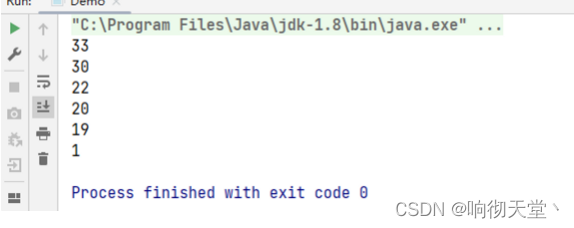
3.7 Max Min
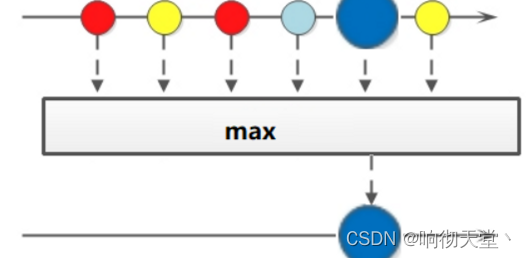
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("1", "22", "22", "19", "33", "20", "30");
//for each , count
Optional<Integer> max = words.stream().map(Integer::parseInt)
.max((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
System.out.println(max.get());
Optional<Integer> min = words.stream().map(Integer::parseInt)
.min((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
System.out.println(min.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> peoples = Arrays.asList(
new Person("r1", 12, 180),
new Person("r2", 13, 180),
new Person("r3", 14, 180)
);
Optional<Person> max = peoples.stream().max((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge());
System.out.println(max.get());
}
3.8 reduce

如果需要将所有数据归纳得到一个数据,可以使用reduce方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> peoples = Arrays.asList(
new Person("r1", 12, 180),
new Person("r2", 13, 180),
new Person("r3", 14, 180)
);
// 所有年龄
Integer reduce = peoples.stream().map(Person::getAge).reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println(reduce);
// 最大值
Integer maxAge = peoples.stream().map(Person::getAge).reduce(0, Integer::max);
System.out.println(maxAge);
}
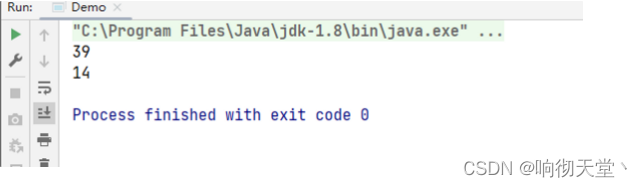
4 Stream结果收集
4.1 流中数据收集
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
// 收集到 Set集合中
Set<String> set = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(set);
}
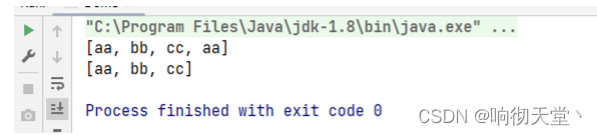
4.2 流中数据聚合计算
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取年龄的最大值
Optional<Person> maxAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).collect(Collectors.maxBy((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge() - p2.getAge()));
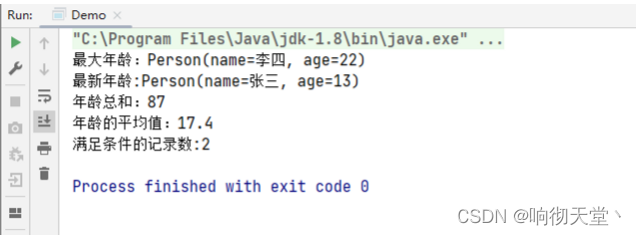
System.out.println("最大年龄:" + maxAge.get());
// 获取年龄的最小值
Optional<Person> minAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).collect(Collectors.minBy((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge() - p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("最新年龄:" + minAge.get());
// 求所有人的年龄之和
Integer sumAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
)
//.collect(Collectors.summingInt(s -> s.getAge()))
.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getAge))
;
System.out.println("年龄总和:" + sumAge);
// 年龄的平均值
Double avgAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println("年龄的平均值:" + avgAge);
// 统计数量
Long count = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).filter(p->p.getAge() > 18)
.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("满足条件的记录数:" + count);
}
4.3 对流中数据做分组操作
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性将数据分组
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> peoples = Arrays.asList(
new Person("r1", 12),
new Person("r2", 13),
new Person("r3", 14)
);
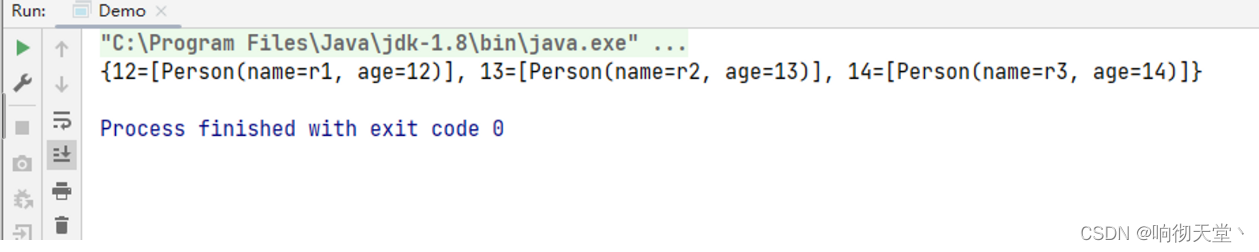
Map<Integer, List<Person>> collect = peoples.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getAge));
System.out.println(collect);
}