文章目录
- 1.前置知识
- 2.结构的改写与封装
- 2.1 map和set的结构框架
- 2.2 RBTreeNode结构的改写
- 2.3 RBTree结构改写(仿函数的引入)
- 3. 迭代器
- 3.1 RBTree的迭代器
- 3.2 map和set的迭代器封装
- 4. 插入的改写和operatorp[]的重载
- 4.1 insert的改写
- 4.2 map::operator[]重载的实现
- 4. 完整代码
- 4.1 RBTree的代码
- 4.2 map的代码
- 4.3 set的代码
- 4.4 测试代码
1.前置知识
在之前的文章中,我们模拟实现了红黑树的插入。STL种的map和set底层都是红黑树,所以今天我们要做的事情就是利用我们之前模拟实现的红黑树来简化的封装一个map和set
首先,我们把之前的红黑树代码中用于检测的部分剔除掉,下面是剔除之后的代码:
#include <iostream>
enum Color { RED, BLACK };
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
pair<K,V> _kv;
RBTreeNode* _left;
RBTreeNode* _right;
RBTreeNode* _parent;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K,V> kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_col(RED)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
if(_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_col = RED;
cur->_parent = parent;
if(parent->_kv.first > cur->_kv.first)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
while(parent && cur->_parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if(parent == grandfather->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
grandfather->_col = RED;
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if(parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if(parent->_right == cur)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur->_col = BLACK;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)//左单旋
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if(subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if(ppNode)
{
subR->_parent = ppNode;
if(ppNode->_left == parent)
{
ppNode->_left = subR;
}
else//paren
{
ppNode->_right = subR;
}
}
else
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
if(subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if(ppNode)
{
subL->_parent = ppNode;
if(ppNode->_left == parent)
ppNode->_left = subL;
else
ppNode->_right = subL;
}
else
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
我们要做的就是在此基础上改写部分代码,封装出map和set。
2.结构的改写与封装
现在直接让我们来封装肯定是一头雾水,所以首先我们来看一下STL源码是怎么实现的(这里参考的是SGI版本的stl3.0,与侯捷老师的STL源码剖析相对应)
这里简化一下源码,方便观看,去除掉一些不必要的东西
set的简化源码:

map的简化源码:

所以,map和set在底层上都是同一个红黑树,只是传入的第二个参数不同,set传入的第二个参数只是Key,而map传入的是一个<Key,value>键值对。
所以,这里对RBTree的模板做一下修改,变成template<class K, class T> class RBTree,这里的第二个参数类型就是分辨map和set的依据。
2.1 map和set的结构框架
所以对于map和set来说,其类的结构如下
//set传入Key和Key
template<class K>
class set
{
public:
//...
private:
RBTree<K,K> _t;
};
//map传入Key和pair
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
public:
//....
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>> _t;
};
那么这里出现一个问题:既然通过第二个参数就已经能够区分了,为什么还要传第一个参数?
✅对于insert来说,确实不需要第一个参数,插入的值是Key或者pair即可,但是对于find函数,通过传入的参数找到值得时候,找的是第一个参数Key而不是第二个参数,所以这里还是需要一个单独得Key存在的。
2.2 RBTreeNode结构的改写
由于在RBTree层,不知道要实现的是map还是set,所以这里使用T来代替节点内存放的数据,改写后的节点结构如下
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
T _data;//
RBTreeNode* _left;
RBTreeNode* _right;
RBTreeNode* _parent;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const T data)
:_data(data)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_col(RED)
{}
};
2.3 RBTree结构改写(仿函数的引入)
由于RBTreeNode结构的改写,RBTree也需要相应的改变,
template<class K, class T>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
}
但是这样的话会出现一个问题:怎么找到插入的位置?
在没有改写之前,可以采用kv.first的方式访问到Key,然后找到插入的位置和查找等。但是现在数据只有_data这一个东西,没办法确定传入的是pair还是Key,所以这里封装一个仿函数KeyOfT随着类型一起传入。所以改进后的RBTree结构和插入函数如下:
//最终的RBTree结构
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>//增加KeyOfT仿函数模板参数
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if(_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
KeyOfT kot;//实例化一个仿函数(函数对象),这个仿函数的功能是拿到Key
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
if(kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))//通过仿函数拿到Key
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))//通过仿函数拿到Key
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_col = RED;
cur->_parent = parent;
if(kot(parent->_data) > kot(cur->_data))//通过仿函数拿到Key
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
while(parent && cur->_parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if(parent == grandfather->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
grandfather->_col = RED;
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if(parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if(parent->_right == cur)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur->_col = BLACK;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
然后对于map和set,分别实现一个仿函数传入
//map
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
//set
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
这个时候,针对set和map,就可以通过KeyOfT实例化出不同的仿函数(函数对象),从而按照不同的方式获取到Value中的Key。
现在针对之前已有的代码的修改就已经差不多啦,下面就要开始增加一点东西了。
3. 迭代器
map和set的迭代器都是通过调用RBTree的迭代器来实现的,所以我们首先就要实现RBTree的迭代器
3.1 RBTree的迭代器
对于RBTree的迭代器,可以类比成list的迭代器的实现方式,由于原生指针不能很好的支持迭代器行为,所以需要实现一个迭代器类__RBTreeIteraotr。
和list的迭代器一样,这里为了支持const版本的迭代器,所以类模板有三个,如果对此有问题的话,可以去移步到【C++】list的模拟实现看详细的讲解。
所以迭代器类的框架如下
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*();
Ptr operator->();
Self& operator++();
Self& operator--();
Self operator++(int);
Self operator--(int);
bool operator==(const Self& s) const;
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const;
Node* _node;
};
这里实现的重点就是++和–的运算符重载
1. 迭代器++的逻辑:
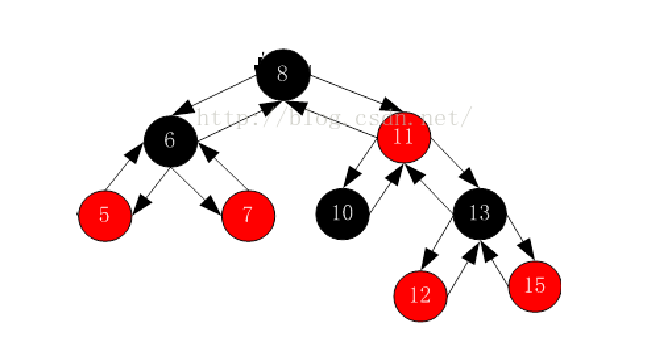
我们对照上面这个例子来说,如果要让迭代器按照中序的方式遍历这棵树的话,就是要走左子树-根-右子树的顺序,那么,对于任意一个节点,就把它当作一个子树的根节点来看,如果他的右子树不为空,就去访问它右子树的左子树,即右子树的最小节点,如果他的右子树为空,就表示此子树已经访问完毕,要找到下一个根节点,所以就要向上迭代,直到父节点是当前节点的右为止,然后访问父节点的父节点即可。代码如下:
Self& operator--()
{
if(_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while(max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
2. 迭代器- -的逻辑:
迭代器–和++的处理方式是类似的,只是把逻辑对称过来即可,所以代码如下
Self& operator--()
{
if(_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while(max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
所以迭代器类的实现就显而易见了:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;//重定义Node节点
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)//构造函数
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;//*的运算符重载,返回的是_data的值
}
Ptr operator->()//->的运算符重载,返回operator*的返回值的地址即可
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if(_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while(min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = _node->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if(_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while(max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置++和operator++()类似
{
Node* tmp = _node;
if(_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while(min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = _node->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return tmp;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--和operator--()类似
{
Node* tmp = _node;
if(_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while(max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
Node* _node;//成员变量
};
3. RBTree的迭代器封装
对于RBTree,其begin就是最左节点,end是最右节点的下一个位置,这里为了简化,就给成nullptr即可
所以,迭代器的封装如下:
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* left = _root;
while(left && left->_left)
{
left = left->_left;
}
return iterator(left);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
Node* left = _root;
while(left && left->_left)
{
left = left->_left;
}
return const_iterator(left);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
3.2 map和set的迭代器封装
1. map的迭代器封装
//这里对于没有实例化的类RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>中的iterator需要使用typename来告诉编译器这里的iterator是类型名,不是静态变量(静态变量的使用方式也是这样的)
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
2.set的迭代器封装
和map一样直接调用RBTree的迭代器即可。但是由于set的key是不允许修改的,所以这里不管是iterator还是const_iterator都可以直接使用RBTree中的const_iterator来重命名。
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
4. 插入的改写和operatorp[]的重载
4.1 insert的改写
之前的insert的返回值类型是bool,用于表示是否插入成功,但是STL库中的insert的返回值是一个pair类型,其中第一个成员变量是一个迭代器类型,指向插入的值得位置,第二个成员变量是bool类型,表示插入的位置,所以需要在RBTree层上改写一下insert的返回值
//RBTree
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if(_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);//构造一个pair返回
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
if(kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);//构造一个pair返回
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
cur->_col = RED;
cur->_parent = parent;
if(kot(parent->_data) > kot(cur->_data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
while(parent && cur->_parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if(parent == grandfather->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
grandfather->_col = RED;
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if(parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if(parent->_right == cur)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur->_col = BLACK;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);//构造一个pair返回
}
map层的改写:
//map
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
set层的改写:
//set
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
pair<typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(key);//底层红黑树的iterator是普通迭代器
return pair<iterator, bool>(ret.first, ret.second);//用普通迭代器构造const迭代器
}
4.2 map::operator[]重载的实现
在上面map的insert改写的基础上,就可以很方便的实现operator[]的重载
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));//调用insert
return ret.first->second;//ret的first是key对应的节点的迭代器,通过ret.first的second可以拿到对应的值second
}
4. 完整代码
4.1 RBTree的代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
enum Color{ RED, BLACK };
//这里使用T来封装
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
T _data;
RBTreeNode* _left;
RBTreeNode* _right;
RBTreeNode* _parent;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const T data)
:_data(data)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_col(RED)
{}
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
__RBTreeIterator(const iterator& s)
:_node(s._node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if(_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while(min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = _node->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if(_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while(max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Node* tmp = _node;
if(_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while(min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = _node->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return tmp;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Node* tmp = _node;
if(_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while(max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
Node* _node;
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* left = _root;
while(left && left->_left)
{
left = left->_left;
}
return iterator(left);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
Node* left = _root;
while(left && left->_left)
{
left = left->_left;
}
return const_iterator(left);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if(_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
//找到插入位置
while(cur)
{
if(kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
cur->_col = RED;
//连接上
cur->_parent = parent;
if(kot(parent->_data) > kot(cur->_data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
//判断颜色是否合法
while(parent && cur->_parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if(parent == grandfather->_left)//当parent是grandfather左节点
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//情况一:uncle存在且为红
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
grandfather->_col = RED;
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//出现下面的情况就说明树的结构出现问题,需要对结构进行调整(旋转)
else//uncle不存,或者在且为黑
{
//情况二:grandfather、parent、cur在一条直线上
if(parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
//情况二:grandfather、parent、cur在一条折线上
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//当parent是grandfather右节点
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//情况一:uncle存在且为红
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//uncle不存在,或者存在且为黑
{
//情况二:grandfather、parent、cur在一条直线上
if(parent->_right == cur)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
//情况二:grandfather、parent、cur在一条折线上
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur->_col = BLACK;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)//左单旋
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
//处理subRL的部分
parent->_right = subRL;
if(subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
//处理parent和subR之间的关系
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
//处理subR的parent
if(ppNode)//parent不是根节点的时候,需要处理parent的父亲节点
{
subR->_parent = ppNode;
if(ppNode->_left == parent)//parent是左节点
{
ppNode->_left = subR;
}
else//parent是右节点
{
ppNode->_right = subR;
}
}
else//parent是根节点的时候
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
if(subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if(ppNode)
{
subL->_parent = ppNode;
if(ppNode->_left == parent)
ppNode->_left = subL;
else
ppNode->_right = subL;
}
else
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
4.2 map的代码
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.hpp"
namespace zht
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
public:
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
};
4.3 set的代码
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.hpp"
namespace zht
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
public:
iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
pair<typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(key);
return pair<iterator, bool>(ret.first, ret.second);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
4.4 测试代码
#include <iostream>
#include "RBTree.h"
#include "map.h"
#include "set.h"
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void set_test1() {
int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };
thj::set<int> s;
for (auto e : a)
s.insert(e);
thj::set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end()) {
//*it = 10;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void map_test1() {
int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };
thj::map<int, int> m;
for (auto e : a)
m.insert(std::make_pair(e, e));
thj::map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end()) {
//it->first++;
it->second++;
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void map_test2() {
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "芒果", "西瓜", "苹果", "梨子", "西瓜","苹果", "香蕉", "西瓜", "香蕉" };
thj::map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : arr)
countMap[str]++;
for (auto& kv : countMap)
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void map_test3() {
srand((size_t)time(0));
thj::map<int, int> m;
int N = 1000;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
m.insert(make_pair(rand(), rand()));
}
auto it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end()) {
cout << it->first << endl;
++it;
}
}
int main() {
//set_test1();
//map_test1();
map_test2();
//map_test3();
return 0;
}
本节完