10. Redis哨兵sentinel
- 是什么?
- 能干嘛
- 怎么玩(实战演示:)
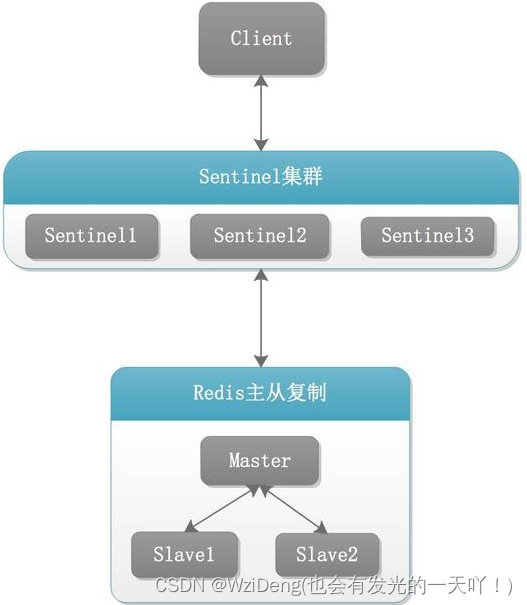
- Redis Sentinel架构,前提说明
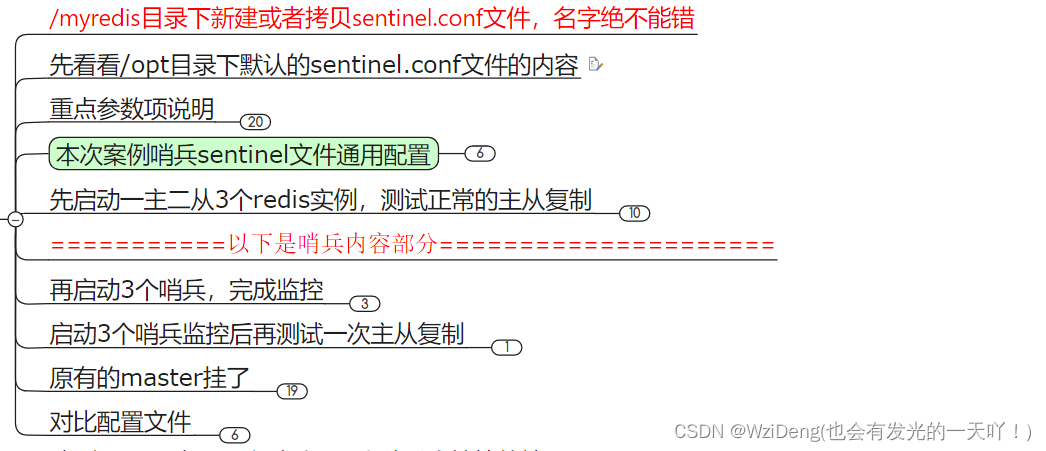
- 案例步骤,不服就干
- 重点参数项说明
- 其他
- 本次案例哨兵sentinel文件通用配置
- sentinel26379.conf
- sentinel26380.conf
- sentinel26381.conf
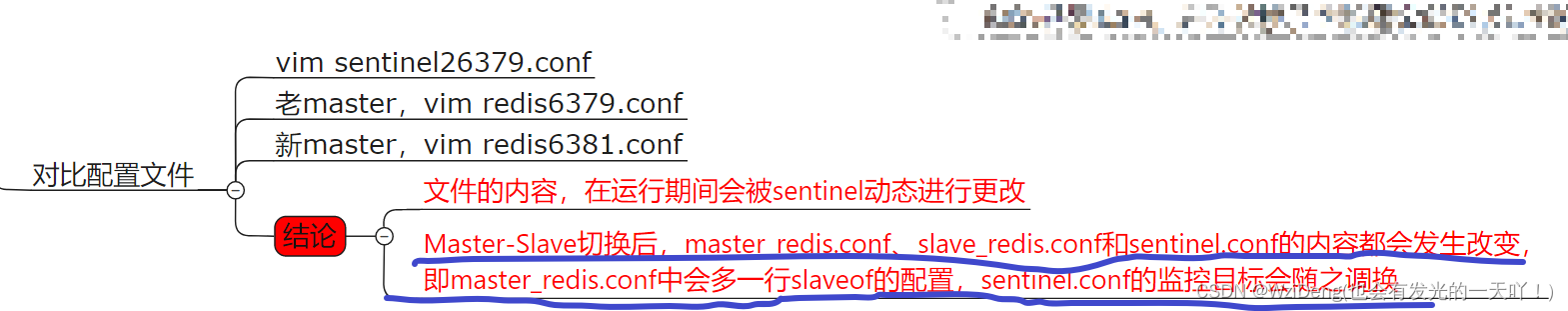
- 请看一眼sentinel26379.conf、sentinel26380.conf、sentinel26381.conf我们自己填写的内容
- master主机配置文件说明应
- 先启动一主二从3个redis实例,测试正常的主从复制
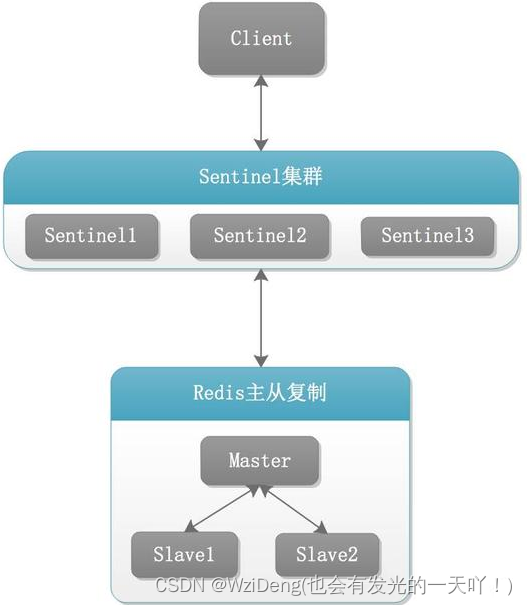
- 架构说明
- 以下是哨兵内容部分:
- 原有的master挂了
- 了解 Broken Pipe
- 哨兵运行流程和选举原理
- 运行流程,故障切换
- SDown主观下线(Subjectively Down)
- ODown客观下线(Objectively Down)
- 由兵王开始推动故障切换流程并选出一个新master
- 群臣俯首
- 小总结
- 哨兵使用建议
是什么?



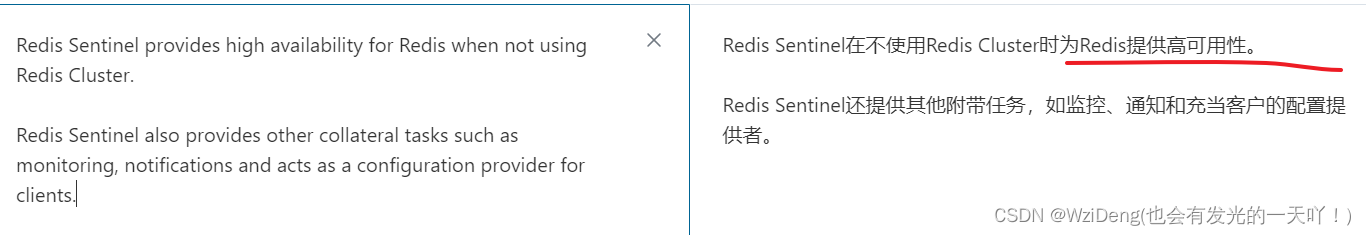
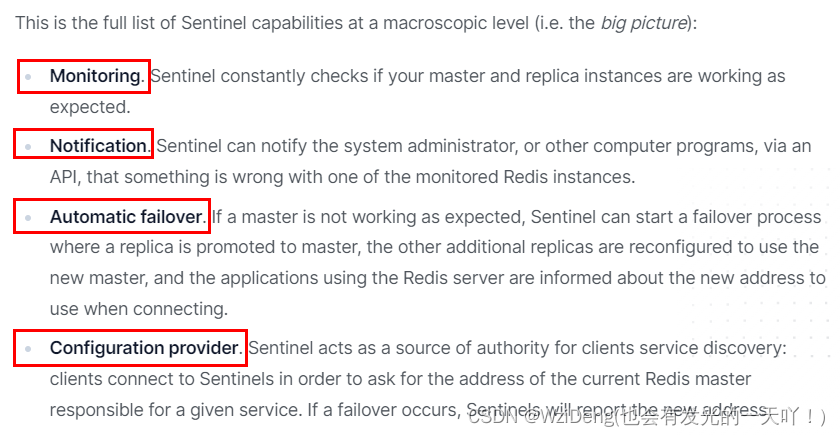
1.Redis Sentinel provides high availability for Redis when not using Redis Cluster.
2.Redis Sentinel also provides other collateral tasks such as monitoring, notifications and acts as a configuration provider for clients.
能干嘛


怎么玩(实战演示:)
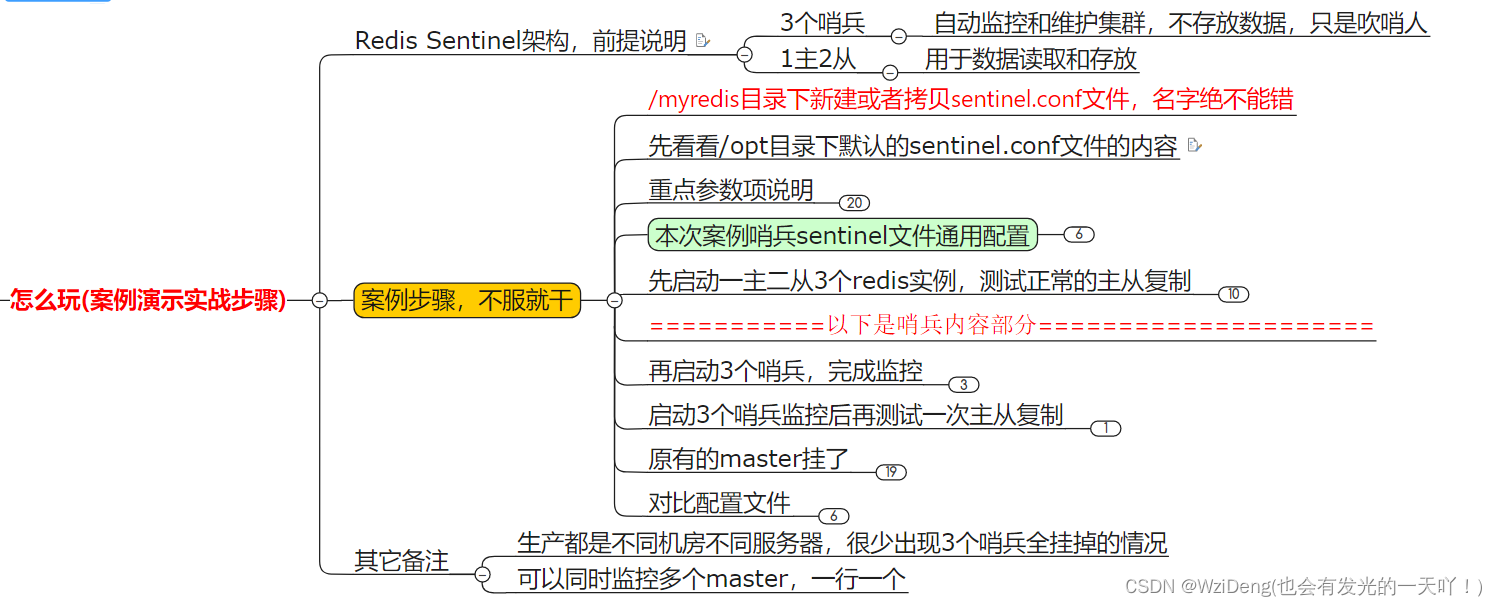
Redis Sentinel架构,前提说明

案例步骤,不服就干
1 # Example sentinel.conf
2
3 # By default protected mode is disabled in sentinel mode. Sentinel is reachable
4 # from interfaces different than localhost. Make sure the sentinel instance is
5 # protected from the outside world via firewalling or other means.
6 protected-mode no
7
8 # port <sentinel-port>
9 # The port that this sentinel instance will run on
10 port 26379
11
12 # By default Redis Sentinel does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it.
13 # Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid when
14 # daemonized.
15 daemonize no
16
17 # When running daemonized, Redis Sentinel writes a pid file in
18 # /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid by default. You can specify a custom pid file
19 # location here.
20 pidfile /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid
21
22 # Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force
23 # Sentinel to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard
24 # output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null
25 logfile ""
26
27 # sentinel announce-ip <ip>
28 # sentinel announce-port <port>
29 #
30 # The above two configuration directives are useful in environments where,
31 # because of NAT, Sentinel is reachable from outside via a non-local address.
32 #
33 # When announce-ip is provided, the Sentinel will claim the specified IP address
34 # in HELLO messages used to gossip its presence, instead of auto-detecting the
35 # local address as it usually does.
36 #
37 # Similarly when announce-port is provided and is valid and non-zero, Sentinel
38 # will announce the specified TCP port.
39 #
40 # The two options don't need to be used together, if only announce-ip is
41 # provided, the Sentinel will announce the specified IP and the server port
42 # as specified by the "port" option. If only announce-port is provided, the
43 # Sentinel will announce the auto-detected local IP and the specified port.
44 #
45 # Example:
46 #
47 # sentinel announce-ip 1.2.3.4
48
49 # dir <working-directory>
50 # Every long running process should have a well-defined working directory.
51 # For Redis Sentinel to chdir to /tmp at startup is the simplest thing
52 # for the process to don't interfere with administrative tasks such as
53 # unmounting filesystems.
54 dir /tmp
55
56 # sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum>
57 #
58 # Tells Sentinel to monitor this master, and to consider it in O_DOWN
59 # (Objectively Down) state only if at least <quorum> sentinels agree.
60 #
61 # Note that whatever is the ODOWN quorum, a Sentinel will require to
62 # be elected by the majority of the known Sentinels in order to
63 # start a failover, so no failover can be performed in minority.
64 #
65 # Replicas are auto-discovered, so you don't need to specify replicas in
66 # any way. Sentinel itself will rewrite this configuration file adding
67 # the replicas using additional configuration options.
68 # Also note that the configuration file is rewritten when a
69 # replica is promoted to master.
70 #
71 # Note: master name should not include special characters or spaces.
72 # The valid charset is A-z 0-9 and the three characters ".-_".
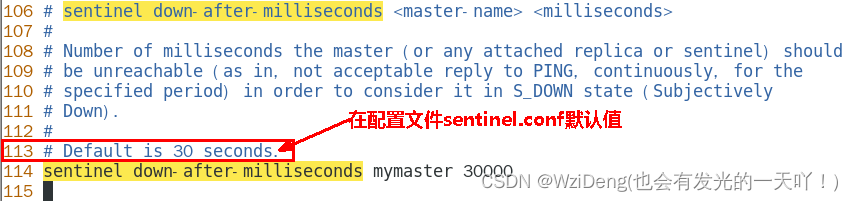
73 sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2
74
75 # sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>
76 #
77 # Set the password to use to authenticate with the master and replicas.
78 # Useful if there is a password set in the Redis instances to monitor.
79 #
80 # Note that the master password is also used for replicas, so it is not
81 # possible to set a different password in masters and replicas instances
82 # if you want to be able to monitor these instances with Sentinel.
83 #
84 # However you can have Redis instances without the authentication enabled
85 # mixed with Redis instances requiring the authentication (as long as the
86 # password set is the same for all the instances requiring the password) as
87 # the AUTH command will have no effect in Redis instances with authentication
88 # switched off.
89 #
90 # Example:
91 #
92 # sentinel auth-pass mymaster MySUPER--secret-0123passw0rd
93
94 # sentinel auth-user <master-name> <username>
95 #
96 # This is useful in order to authenticate to instances having ACL capabilities,
97 # that is, running Redis 6.0 or greater. When just auth-pass is provided the
98 # Sentinel instance will authenticate to Redis using the old "AUTH <pass>"
99 # method. When also an username is provided, it will use "AUTH <user> <pass>".
100 # In the Redis servers side, the ACL to provide just minimal access to
101 # Sentinel instances, should be configured along the following lines:
102 #
103 # user sentinel-user >somepassword +client +subscribe +publish \
104 # +ping +info +multi +slaveof +config +client +exec on
105
106 # sentinel down-after-milliseconds <master-name> <milliseconds>
107 #
108 # Number of milliseconds the master (or any attached replica or sentinel) should
109 # be unreachable (as in, not acceptable reply to PING, continuously, for the
110 # specified period) in order to consider it in S_DOWN state (Subjectively
111 # Down).
112 #
113 # Default is 30 seconds.
114 sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
115
116 # IMPORTANT NOTE: starting with Redis 6.2 ACL capability is supported for
117 # Sentinel mode, please refer to the Redis website https://redis.io/topics/acl
118 # for more details.
119
120 # Sentinel's ACL users are defined in the following format:
121 #
122 # user <username> ... acl rules ...
123 #
124 # For example:
125 #
126 # user worker +@admin +@connection ~* on >ffa9203c493aa99
127 #
128 # For more information about ACL configuration please refer to the Redis
129 # website at https://redis.io/topics/acl and redis server configuration
130 # template redis.conf.
131
132 # ACL LOG
133 #
134 # The ACL Log tracks failed commands and authentication events associated
135 # with ACLs. The ACL Log is useful to troubleshoot failed commands blocked
136 # by ACLs. The ACL Log is stored in memory. You can reclaim memory with
137 # ACL LOG RESET. Define the maximum entry length of the ACL Log below.
138 acllog-max-len 128
139
140 # Using an external ACL file
141 #
142 # Instead of configuring users here in this file, it is possible to use
143 # a stand-alone file just listing users. The two methods cannot be mixed:
144 # if you configure users here and at the same time you activate the external
145 # ACL file, the server will refuse to start.
146 #
147 # The format of the external ACL user file is exactly the same as the
148 # format that is used inside redis.conf to describe users.
149 #
150 # aclfile /etc/redis/sentinel-users.acl
151
152 # requirepass <password>
153 #
154 # You can configure Sentinel itself to require a password, however when doing
155 # so Sentinel will try to authenticate with the same password to all the
156 # other Sentinels. So you need to configure all your Sentinels in a given
157 # group with the same "requirepass" password. Check the following documentation
158 # for more info: https://redis.io/topics/sentinel
159 #
160 # IMPORTANT NOTE: starting with Redis 6.2 "requirepass" is a compatibility
161 # layer on top of the ACL system. The option effect will be just setting
162 # the password for the default user. Clients will still authenticate using
163 # AUTH <password> as usually, or more explicitly with AUTH default <password>
164 # if they follow the new protocol: both will work.
165 #
166 # New config files are advised to use separate authentication control for
167 # incoming connections (via ACL), and for outgoing connections (via
168 # sentinel-user and sentinel-pass)
169 #
170 # The requirepass is not compatible with aclfile option and the ACL LOAD
171 # command, these will cause requirepass to be ignored.
172
173 # sentinel sentinel-user <username>
174 #
175 # You can configure Sentinel to authenticate with other Sentinels with specific
176 # user name.
177
178 # sentinel sentinel-pass <password>
179 #
180 # The password for Sentinel to authenticate with other Sentinels. If sentinel-user
181 # is not configured, Sentinel will use 'default' user with sentinel-pass to authenticate.
182
183 # sentinel parallel-syncs <master-name> <numreplicas>
184 #
185 # How many replicas we can reconfigure to point to the new replica simultaneously
186 # during the failover. Use a low number if you use the replicas to serve query
187 # to avoid that all the replicas will be unreachable at about the same
188 # time while performing the synchronization with the master.
189 sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1
190
191 # sentinel failover-timeout <master-name> <milliseconds>
192 #
193 # Specifies the failover timeout in milliseconds. It is used in many ways:
194 #
195 # - The time needed to re-start a failover after a previous failover was
196 # already tried against the same master by a given Sentinel, is two
197 # times the failover timeout.
198 #
199 # - The time needed for a replica replicating to a wrong master according
200 # to a Sentinel current configuration, to be forced to replicate
201 # with the right master, is exactly the failover timeout (counting since
202 # the moment a Sentinel detected the misconfiguration).
203 #
204 # - The time needed to cancel a failover that is already in progress but
205 # did not produced any configuration change (SLAVEOF NO ONE yet not
206 # acknowledged by the promoted replica).
207 #
208 # - The maximum time a failover in progress waits for all the replicas to be
209 # reconfigured as replicas of the new master. However even after this time
210 # the replicas will be reconfigured by the Sentinels anyway, but not with
211 # the exact parallel-syncs progression as specified.
212 #
213 # Default is 3 minutes.
214 sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000
215
216 # SCRIPTS EXECUTION
217 #
218 # sentinel notification-script and sentinel reconfig-script are used in order
219 # to configure scripts that are called to notify the system administrator
220 # or to reconfigure clients after a failover. The scripts are executed
221 # with the following rules for error handling:
222 #
223 # If script exits with "1" the execution is retried later (up to a maximum
224 # number of times currently set to 10).
225 #
226 # If script exits with "2" (or an higher value) the script execution is
227 # not retried.
228 #
229 # If script terminates because it receives a signal the behavior is the same
230 # as exit code 1.
231 #
232 # A script has a maximum running time of 60 seconds. After this limit is
233 # reached the script is terminated with a SIGKILL and the execution retried.
234
235 # NOTIFICATION SCRIPT
236 #
237 # sentinel notification-script <master-name> <script-path>
238 #
239 # Call the specified notification script for any sentinel event that is
240 # generated in the WARNING level (for instance -sdown, -odown, and so forth).
241 # This script should notify the system administrator via email, SMS, or any
242 # other messaging system, that there is something wrong with the monitored
243 # Redis systems.
244 #
245 # The script is called with just two arguments: the first is the event type
246 # and the second the event description.
247 #
248 # The script must exist and be executable in order for sentinel to start if
249 # this option is provided.
250 #
251 # Example:
252 #
253 # sentinel notification-script mymaster /var/redis/notify.sh
254
255 # CLIENTS RECONFIGURATION SCRIPT
256 #
257 # sentinel client-reconfig-script <master-name> <script-path>
258 #
259 # When the master changed because of a failover a script can be called in
260 # order to perform application-specific tasks to notify the clients that the
261 # configuration has changed and the master is at a different address.
262 #
263 # The following arguments are passed to the script:
264 #
265 # <master-name> <role> <state> <from-ip> <from-port> <to-ip> <to-port>
266 #
267 # <state> is currently always "start"
268 # <role> is either "leader" or "observer"
269 #
270 # The arguments from-ip, from-port, to-ip, to-port are used to communicate
271 # the old address of the master and the new address of the elected replica
272 # (now a master).
273 #
274 # This script should be resistant to multiple invocations.
275 #
276 # Example:
277 #
278 # sentinel client-reconfig-script mymaster /var/redis/reconfig.sh
279
280 # SECURITY
281 #
282 # By default SENTINEL SET will not be able to change the notification-script
283 # and client-reconfig-script at runtime. This avoids a trivial security issue
284 # where clients can set the script to anything and trigger a failover in order
285 # to get the program executed.
286
287 sentinel deny-scripts-reconfig yes
288
289 # REDIS COMMANDS RENAMING (DEPRECATED)
290 #
291 # WARNING: avoid using this option if possible, instead use ACLs.
292 #
293 # Sometimes the Redis server has certain commands, that are needed for Sentinel
294 # to work correctly, renamed to unguessable strings. This is often the case
295 # of CONFIG and SLAVEOF in the context of providers that provide Redis as
296 # a service, and don't want the customers to reconfigure the instances outside
297 # of the administration console.
298 #
299 # In such case it is possible to tell Sentinel to use different command names
300 # instead of the normal ones. For example if the master "mymaster", and the
301 # associated replicas, have "CONFIG" all renamed to "GUESSME", I could use:
302 #
303 # SENTINEL rename-command mymaster CONFIG GUESSME
304 #
305 # After such configuration is set, every time Sentinel would use CONFIG it will
306 # use GUESSME instead. Note that there is no actual need to respect the command
307 # case, so writing "config guessme" is the same in the example above.
308 #
309 # SENTINEL SET can also be used in order to perform this configuration at runtime.
310 #
311 # In order to set a command back to its original name (undo the renaming), it
312 # is possible to just rename a command to itself:
313 #
314 # SENTINEL rename-command mymaster CONFIG CONFIG
315
316 # HOSTNAMES SUPPORT
317 #
318 # Normally Sentinel uses only IP addresses and requires SENTINEL MONITOR
319 # to specify an IP address. Also, it requires the Redis replica-announce-ip
320 # keyword to specify only IP addresses.
321 #
322 # You may enable hostnames support by enabling resolve-hostnames. Note
323 # that you must make sure your DNS is configured properly and that DNS
324 # resolution does not introduce very long delays.
325 #
326 SENTINEL resolve-hostnames no
327
328 # When resolve-hostnames is enabled, Sentinel still uses IP addresses
329 # when exposing instances to users, configuration files, etc. If you want
330 # to retain the hostnames when announced, enable announce-hostnames below.
331 #
332 SENTINEL announce-hostnames no
333
334 # When master_reboot_down_after_period is set to 0, Sentinel does not fail over
335 # when receiving a -LOADING response from a master. This was the only supported
336 # behavior before version 7.0.
337 #
338 # Otherwise, Sentinel will use this value as the time (in ms) it is willing to
339 # accept a -LOADING response after a master has been rebooted, before failing
340 # over.
341
342 SENTINEL master-reboot-down-after-period mymaster 0
重点参数项说明
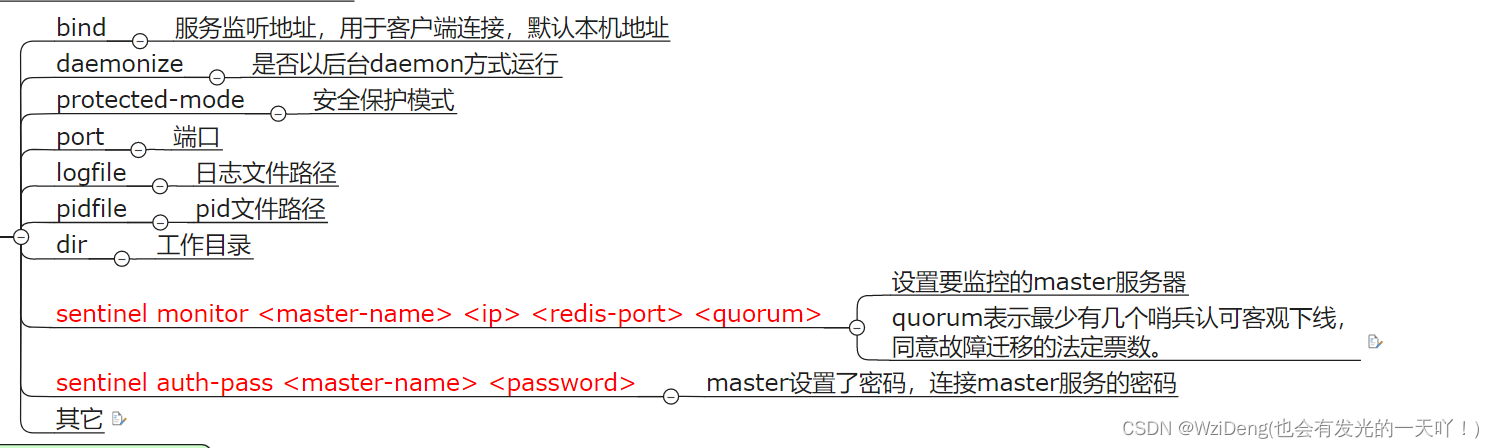
sentinel monitor < master-name> < ip> < redis-port> < quorum>


其他

本次案例哨兵sentinel文件通用配置

sentinel26379.conf
bind 0.0.0.0
daemonize yes
protected-mode no
port 26379
logfile "/myredis/sentinel26379.log"
pidfile /var/run/redis-sentinel26379.pid
dir /myredis
sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.111.169 6379 2
sentinel auth-pass mymaster 111111
sentinel26380.conf
bind 0.0.0.0
daemonize yes
protected-mode no
port 26380
logfile "/myredis/sentinel26380.log"
pidfile /var/run/redis-sentinel26380.pid
dir "/myredis"
sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.111.169 6379 2
sentinel auth-pass mymaster 111111
sentinel26381.conf
bind 0.0.0.0
daemonize yes
protected-mode no
port 26381
logfile "/myredis/sentinel26381.log"
pidfile /var/run/redis-sentinel26381.pid
dir "/myredis"
sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.111.169 6379 2
sentinel auth-pass mymaster 111111
请看一眼sentinel26379.conf、sentinel26380.conf、sentinel26381.conf我们自己填写的内容
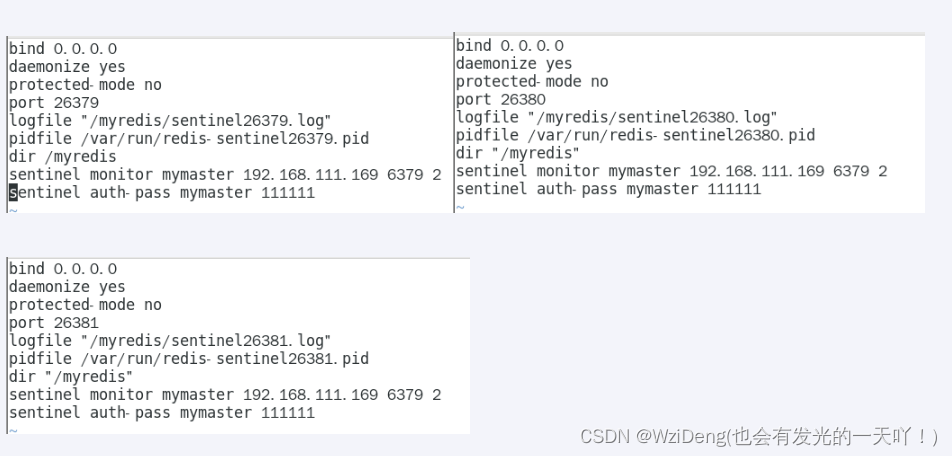
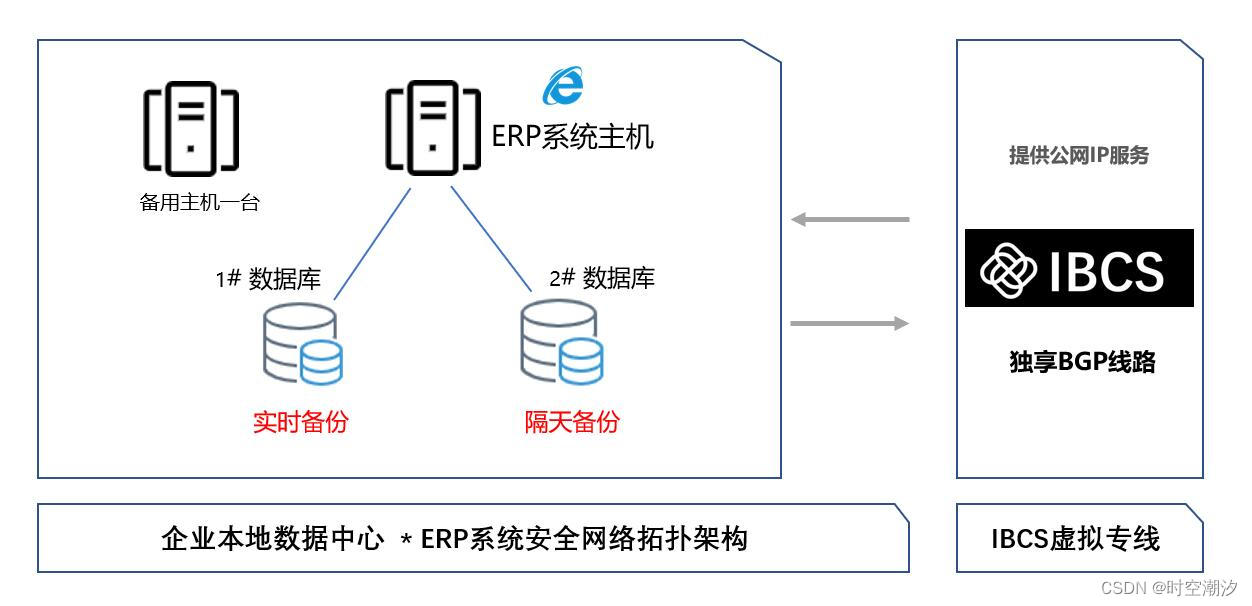
master主机配置文件说明应
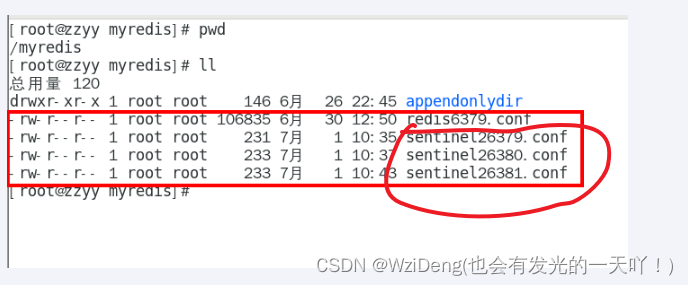
先启动一主二从3个redis实例,测试正常的主从复制
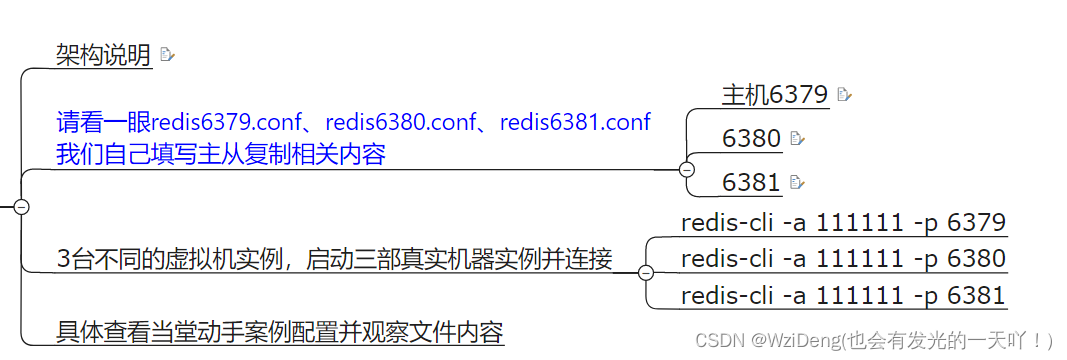
架构说明
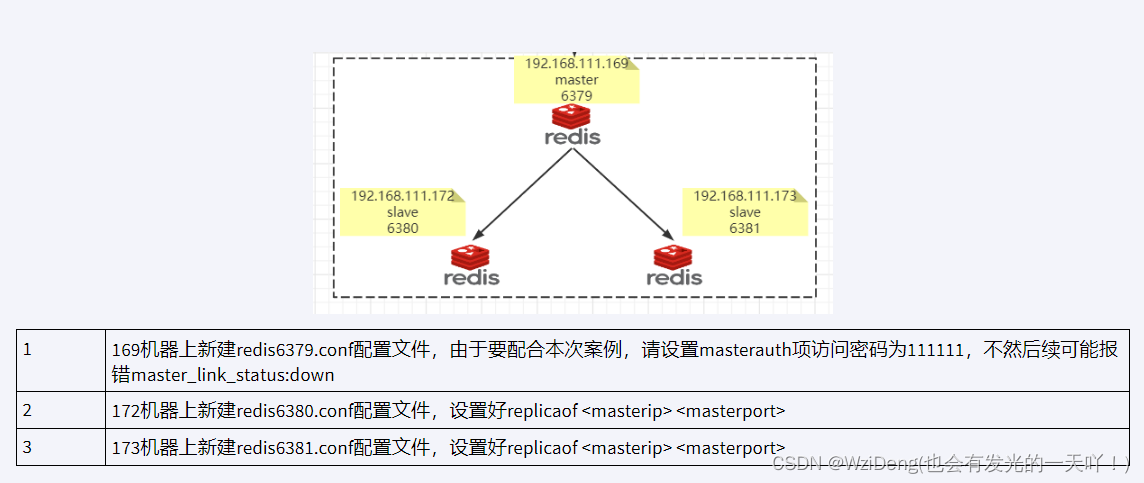
以下是哨兵内容部分:
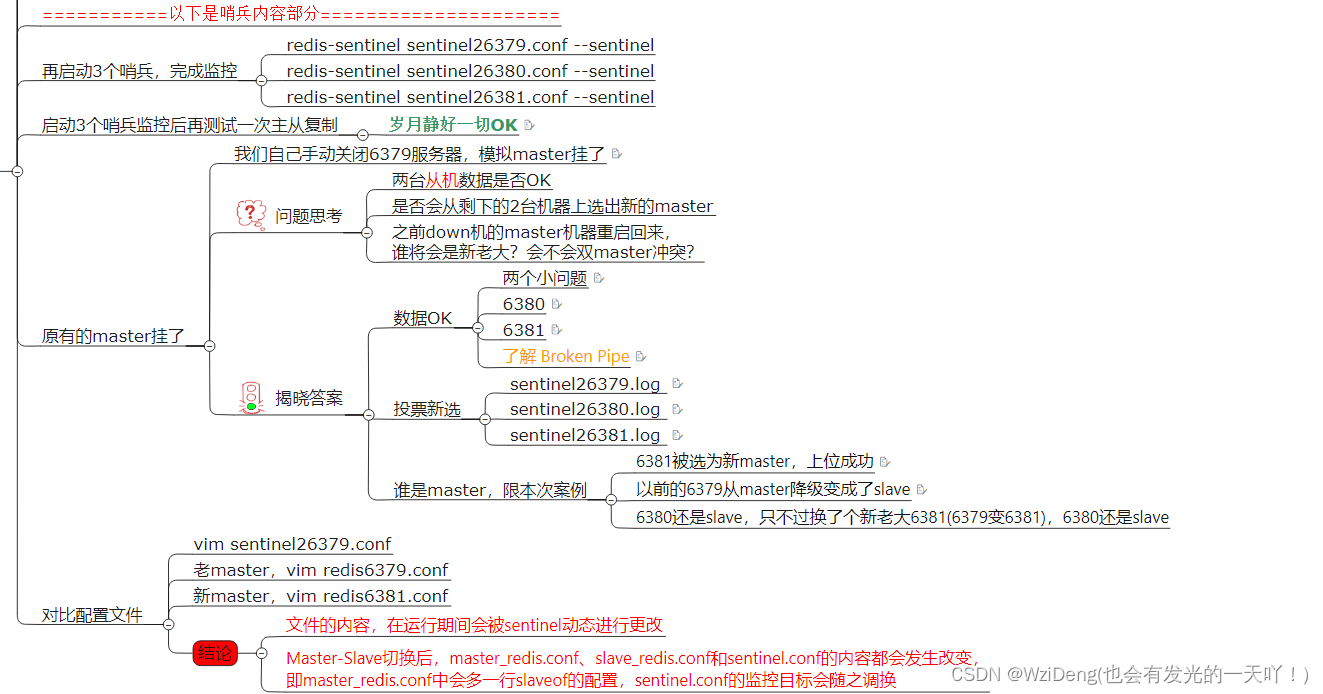
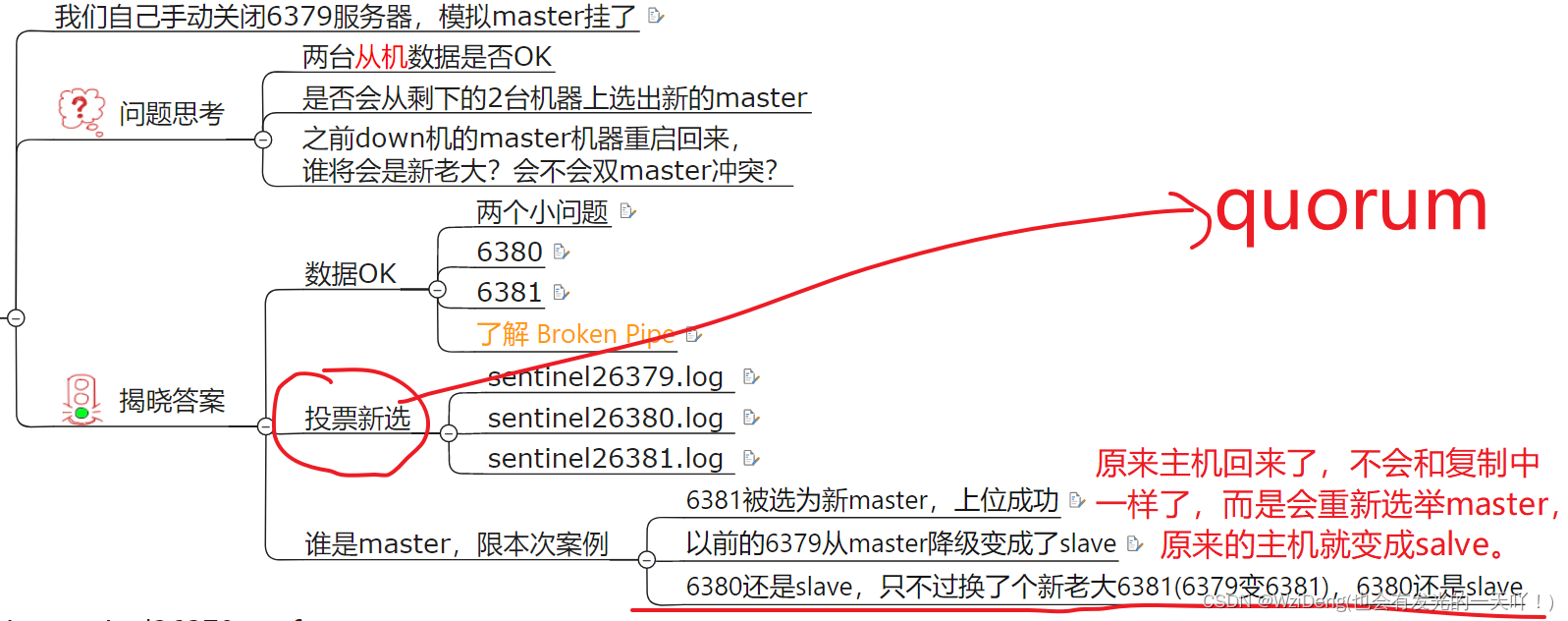
原有的master挂了
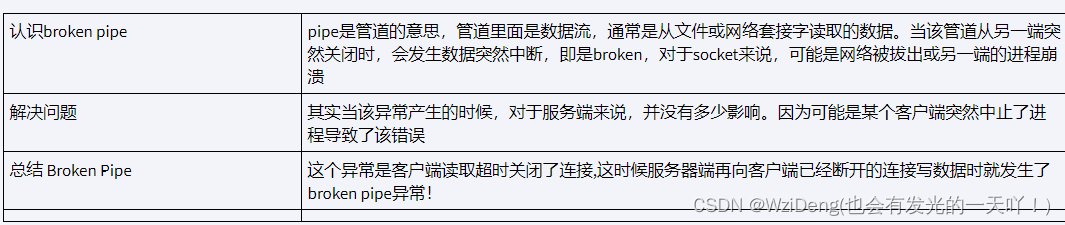
了解 Broken Pipe


哨兵运行流程和选举原理
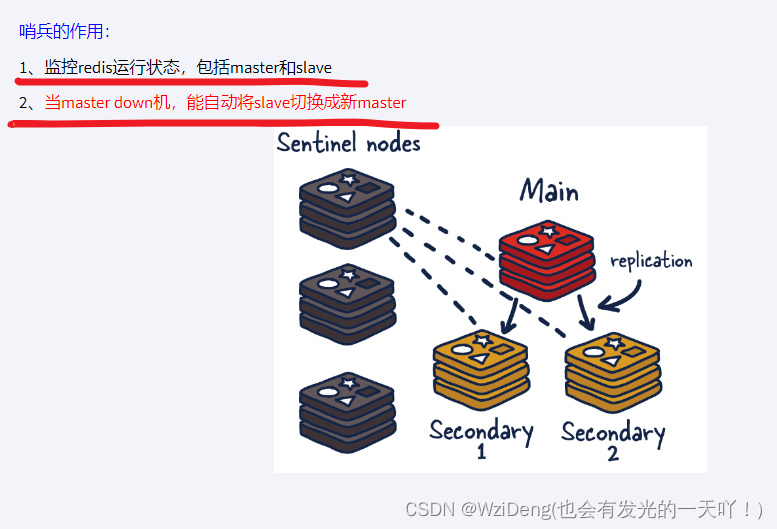
- 当一个主从配置中的master失效之后,sentinel可以选举出一个新的master。
- 用于自动接替原master的工作,主从配置中的其他redis服务器自动指向新的master同步数据。-般建议sentinel采取奇数台,防止某一台sentinel无法连接到master导致误切换。
运行流程,故障切换
三个哨兵监控一主二从,正常运行中
SDown主观下线(Subjectively Down)

所谓主观下线(Subjectively Down, 简称 SDOWN)指的是单个Sentinel实例对服务器做出的下线判断,即单个sentinel认为某个服务下线(有可能是接收不到订阅,之间的网络不通等等原因)。主观下线就是说如果服务器在[sentinel down-after-milliseconds]给定的毫秒数之内没有回应PING命令或者返回一个错误消息, 那么这个Sentinel会主观的(单方面的)认为这个master不可以用了,o(╥﹏╥)o
sentinel down-after-milliseconds
表示master被当前sentinel实例认定为失效的间隔时间,这个配置其实就是进行主观下线的一个依据。
master在多长时间内一直没有给Sentine返回有效信息,则认定该master主观下线。也就是说如果多久没联系上redis-servevr,认为这个redis-server进入到失效(SDOWN)状态。
ODown客观下线(Objectively Down)

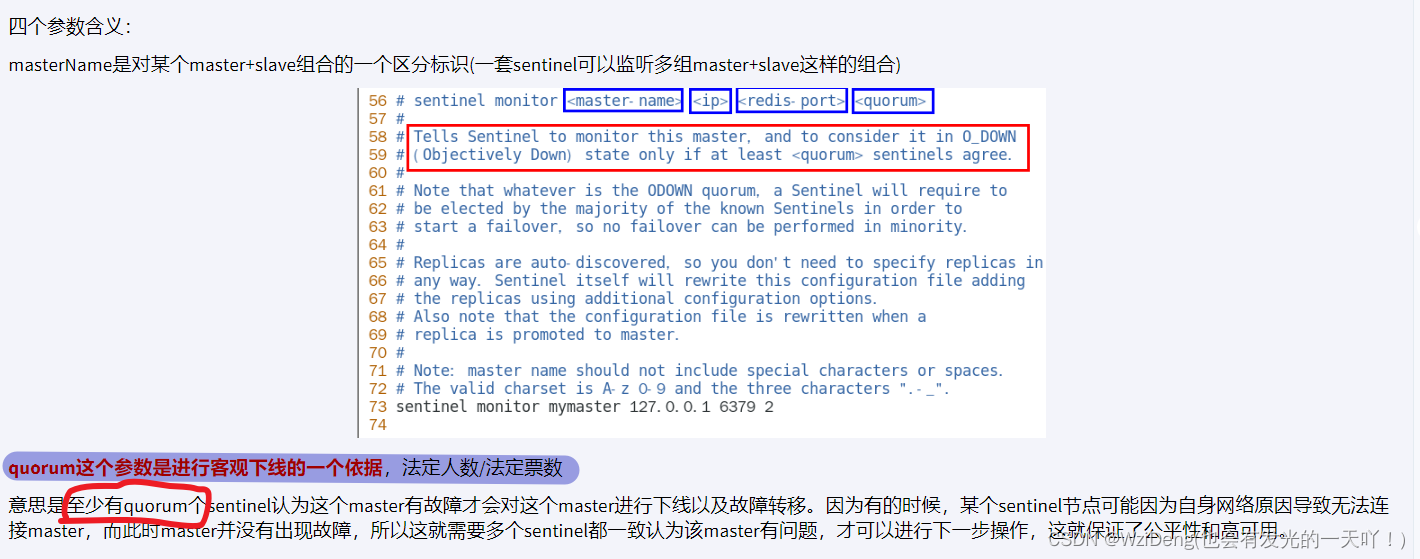

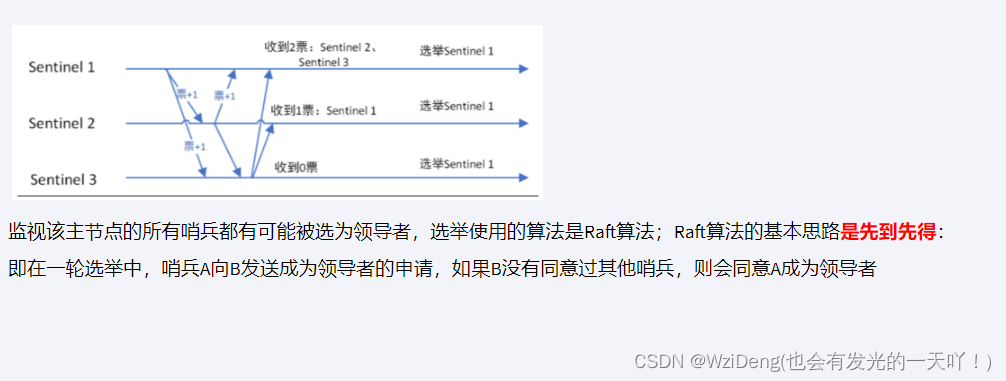
由兵王开始推动故障切换流程并选出一个新master

选出新master的规则,剩余slave节点健康前提下
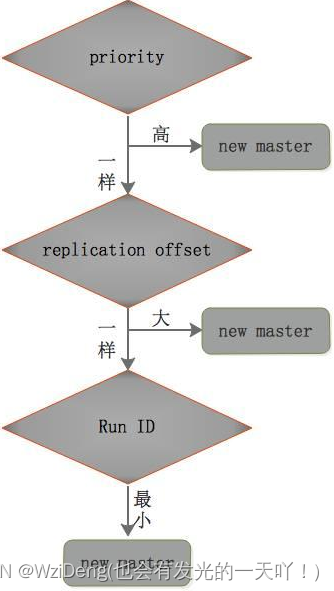

群臣俯首


小总结
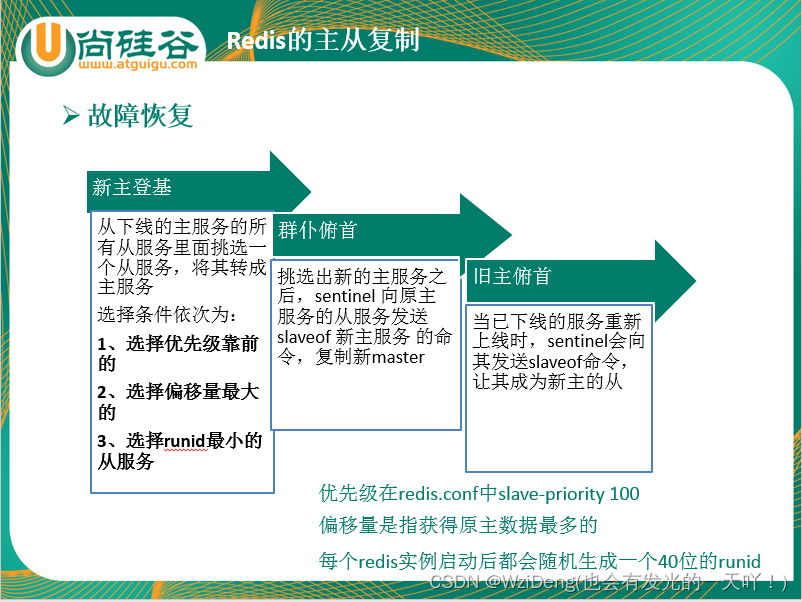
哨兵使用建议