文章目录
- 0.引言
- 1.CloudCompare界面设计配准(segment)按钮
- 2.欧式聚类分割(Euclidean_Seg)
- 3.基于区域生长的分割(Region_Seg)
0.引言
因笔者课题涉及点云处理,需要通过PCL进行点云数据一系列处理分析,查阅现有网络资料,对常用PCL点云分割进行代码实现,本文记录分割实现过程。
1.CloudCompare界面设计配准(segment)按钮
(1)设计.ui文件
①设计按钮
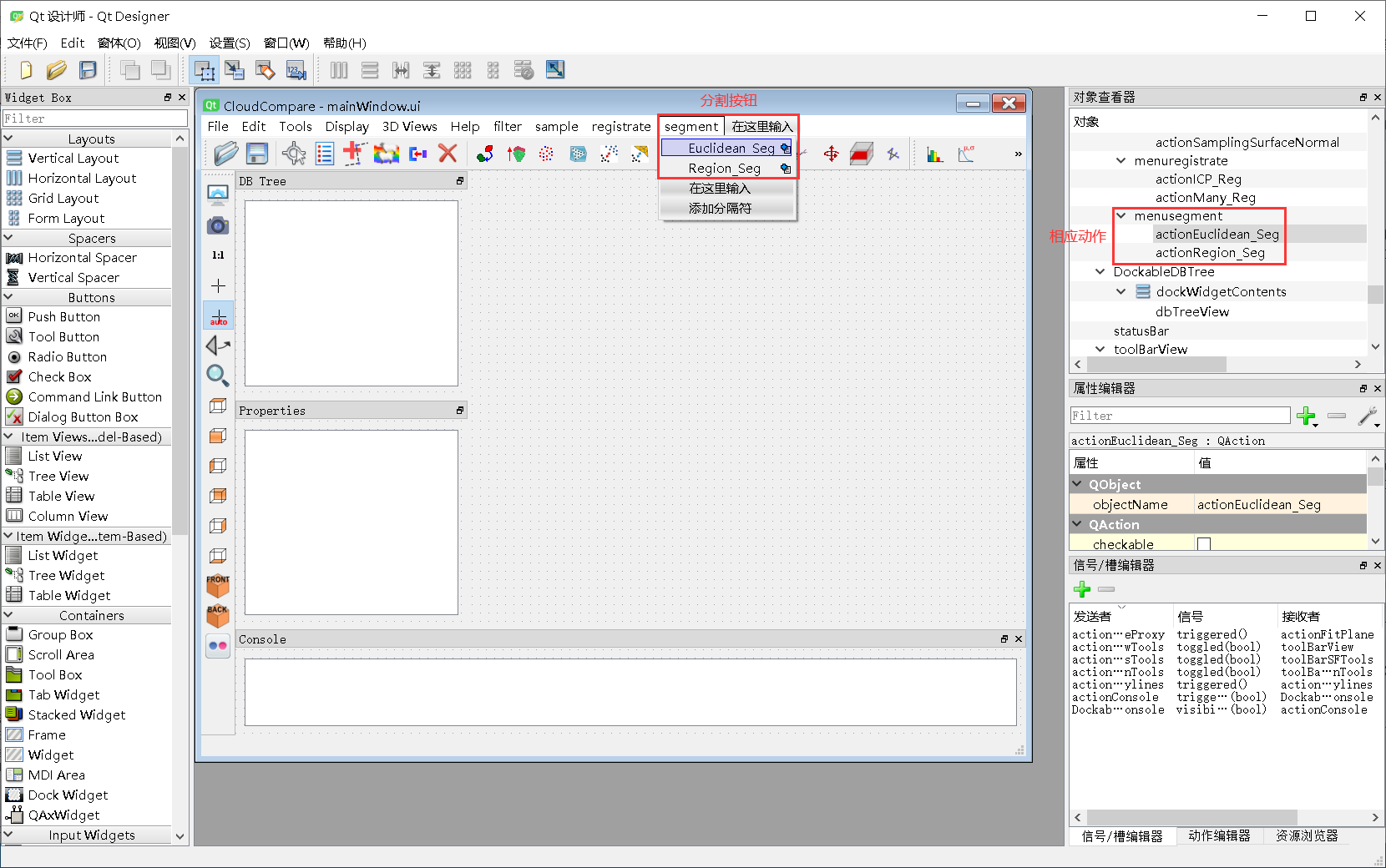
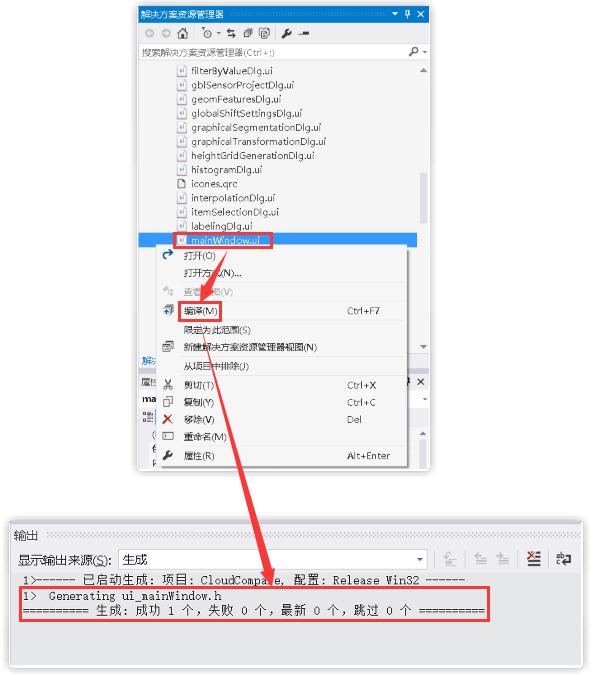
②编译.ui
(2)修改mainwindow.h文件
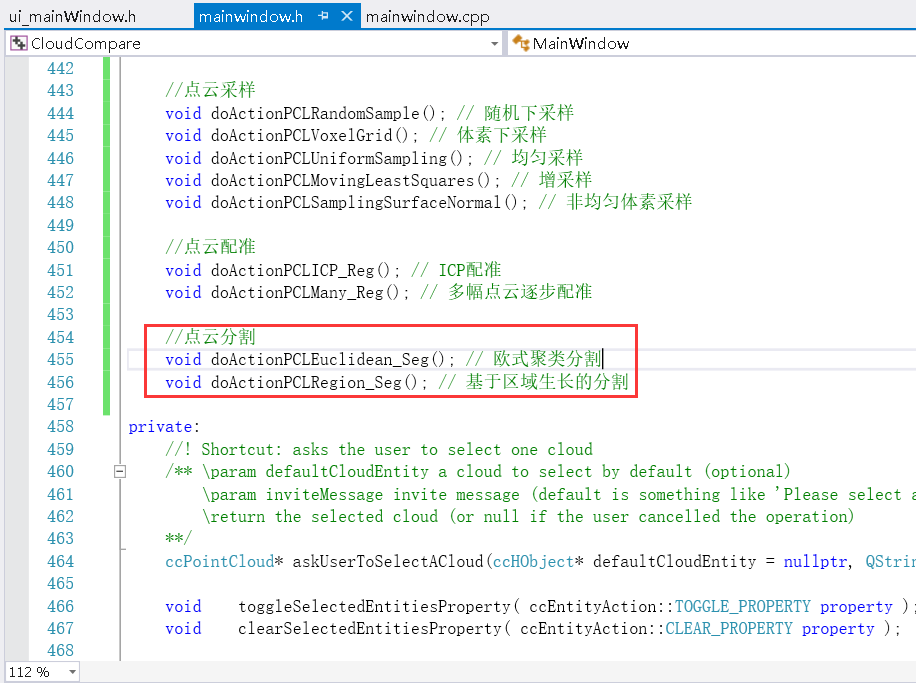
//点云分割
void doActionPCLEuclidean_Seg(); // 欧式聚类分割
void doActionPCLRegion_Seg(); // 基于区域生长的分割
(3)修改mainwindow.cpp文件
①添加头文件
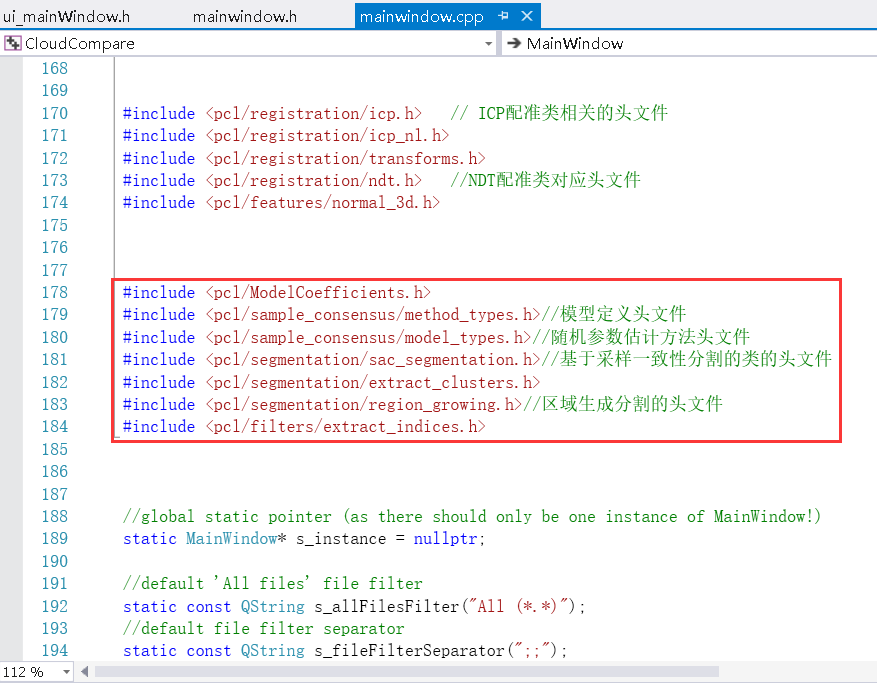
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>//模型定义头文件
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>//随机参数估计方法头文件
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>//基于采样一致性分割的类的头文件
#include <pcl/segmentation/extract_clusters.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/region_growing.h>//区域生成分割的头文件
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
②添加实现代码
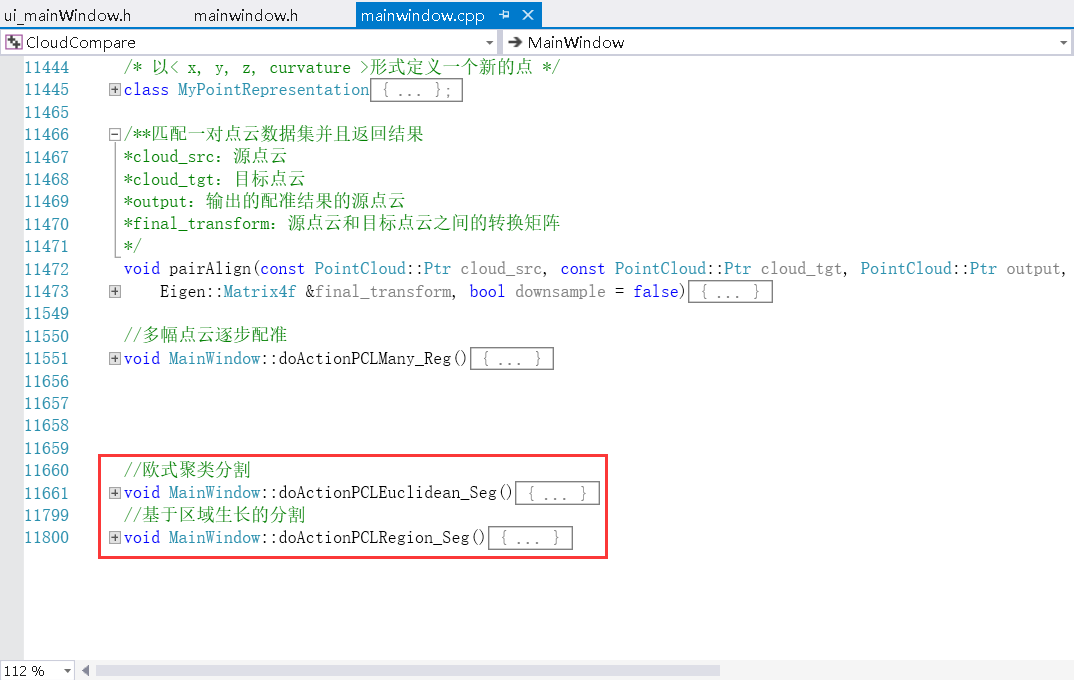
//欧式聚类分割
void MainWindow::doActionPCLEuclidean_Seg()
{
}
//基于区域生长的分割
void MainWindow::PCLRegion_Seg()
{
}
③添加信号槽函数
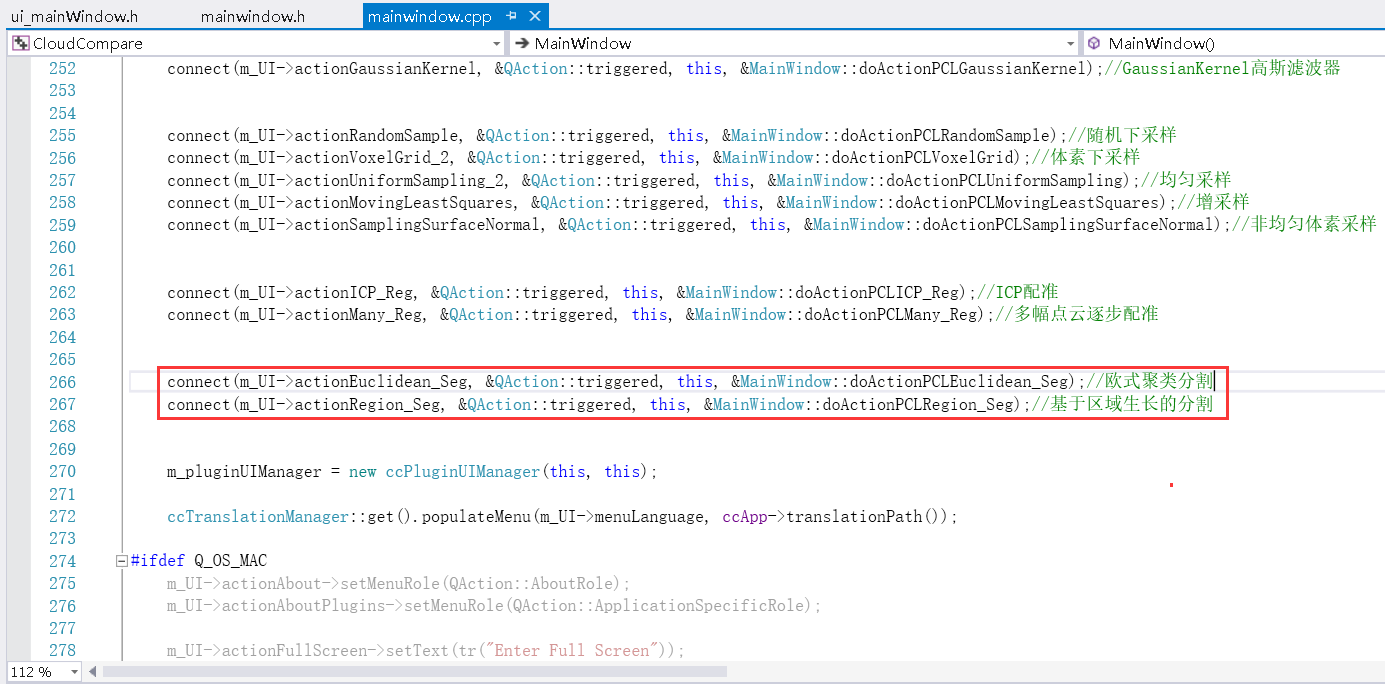
connect(m_UI->actionEuclidean_Seg, &QAction::triggered, this, &MainWindow::doActionPCLEuclidean_Seg);//欧式聚类分割
connect(m_UI->actionRegion_Seg, &QAction::triggered, this, &MainWindow::doActionPCLRegion_Seg);//基于区域生长的分割
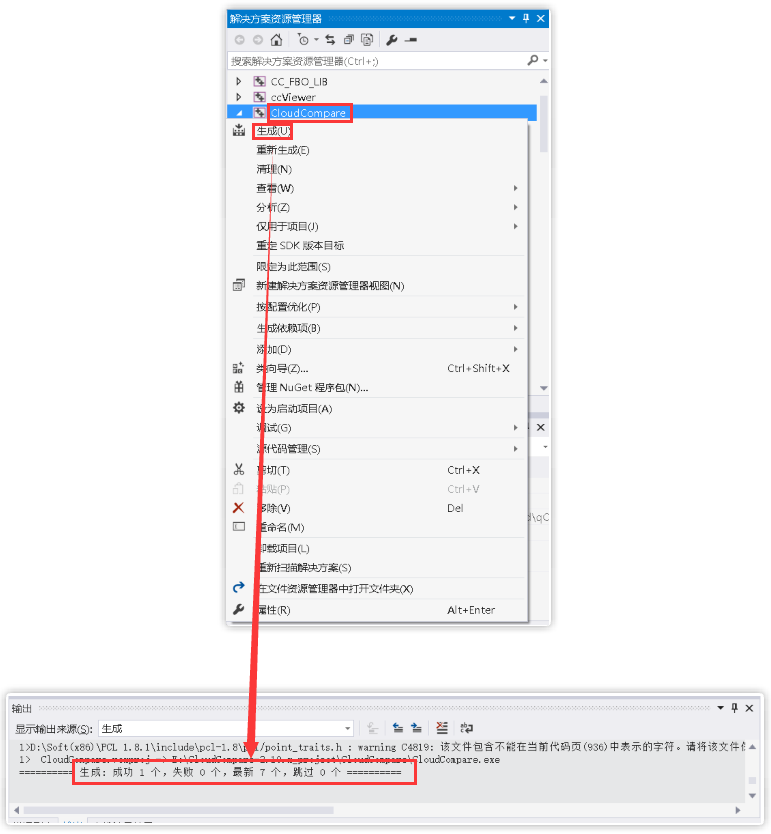
(4)生成
2.欧式聚类分割(Euclidean_Seg)
(1)实现代码
//欧式聚类分割
void MainWindow::doActionPCLEuclidean_Seg()
{
if (getSelectedEntities().size() != 1)
{
ccLog::Print(QStringLiteral("只能选择一个点云实体"));
return;
}
ccHObject* entity = getSelectedEntities()[0];
ccPointCloud* ccCloud = ccHObjectCaster::ToPointCloud(entity);
// ---------------------------读取数据到PCL----------------------------------
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
cloud->resize(ccCloud->size());
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr incloud(new pcl::PointCloud <pcl::PointNormal>());
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->size(); ++i)
{
const CCVector3* point = ccCloud->getPoint(i);
cloud->points[i].x = point->x;
cloud->points[i].y = point->y;
cloud->points[i].z = point->z;
pcl::PointNormal pt;
pt.x = point->x;
pt.y = point->y;
pt.z = point->z;
incloud->points.push_back(pt);
}
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> vg;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
vg.setInputCloud(cloud);
vg.setLeafSize(0.05f, 0.05f, 0.05f);
vg.filter(*cloud_filtered);
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;//实例化一个分割对象
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);//实例化一个索引
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);//实例化模型参数
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());//提取到的平面保存至cloud_plane
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_f(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());//提取到的平面保存至cloud_plane
//pcl::PCDWriter writer;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);//参数优化
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);//模型类型:平面
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);//参数估计方法
seg.setMaxIterations(100);//最大迭代次数
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.02);//设置内点到模型的距离允许最大值
//创建一个文件夹来放点云
ccHObject* CloudGroup = new ccHObject(QString("SegmentGroup"));
int i = 0, nr_points = (int)cloud_filtered->points.size();//计数变量i,记下提取的平面的个数
dispToConsole("cloud_filtered->points.size()1:" + QString::number(cloud_filtered->points.size()), ccMainAppInterface::STD_CONSOLE_MESSAGE);
while (cloud_filtered->points.size() > 0.3 * nr_points)
{
// Segment the largest planar component from the remaining cloud
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);//设置要分割的点云
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);//输出平面点的索引和参数
// Extract the planar inliers from the input cloud
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract;//实例化一个提取对象
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);//设置要提取的点云
extract.setIndices(inliers);//根据分割得到的平面的索引提取平面
extract.setNegative(false);//提取内点
// Write the planar inliers to disk
extract.filter(*cloud_plane);//保存提取到的平面
//std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
//存写指针的参数
cloud_plane->width = cloud_plane->points.size();
cloud_plane->height = 1;
cloud_plane->resize(cloud_plane->width);
cloud_plane->is_dense = false;
ccPointCloud* newPointCloud = new ccPointCloud(QString::number(i + 1) + ".1segment");
for (int i = 0; i < cloud_plane->size(); ++i)
{
double x = cloud_plane->points[i].x;
double y = cloud_plane->points[i].y;
double z = cloud_plane->points[i].z;
newPointCloud->addPoint(CCVector3(x, y, z));
}
newPointCloud->setRGBColor(ccColor::Rgba(255, 100, 100, 255));
newPointCloud->setRGBColor(ccColor::Rgba(rand() % 205 + 50, rand() % 155 + 100, rand() % 105 + 150, 255));
newPointCloud->showColors(true);
CloudGroup->addChild(newPointCloud);
//CloudGroup->getLastChild()->setEnabled(false);
addToDB(newPointCloud);
//计数变量加1
i++;
// Remove the planar inliers, extract the rest
extract.setNegative(true);//提取外点(除第一个平面之外的点)
extract.filter(*cloud_f);//保存除平面之外的剩余点
cloud_filtered = cloud_f;//将剩余点作为下一次分割、提取的平面的输入点云
}
// Creating the KdTree object for the search method of the extraction
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
tree->setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);//将无法提取平面的点云作为cloud_filtered
std::vector<pcl::PointIndices> cluster_indices;//保存每一种聚类,每一种聚类下还有具体的聚类的点
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction<pcl::PointXYZ> ec;//实例化一个欧式聚类提取对象
ec.setClusterTolerance(0.02); // 近邻搜索的搜索半径为2cm,重要参数
ec.setMinClusterSize(100);//设置一个聚类需要的最少点数目为100
ec.setMaxClusterSize(25000);//一个聚类最大点数目为25000
ec.setSearchMethod(tree);//设置点云的搜索机制
ec.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);//设置输入点云
ec.extract(cluster_indices);//将聚类结果保存至cluster_indices中
//迭代访问点云索引cluster_indices,直到分割出所有聚类,一个循环提取出一类点云
int j = 0;
for (std::vector<pcl::PointIndices>::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin(); it != cluster_indices.end(); ++it)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
//创建新的点云数据集cloud_cluster,直到分割出所有聚类
for (std::vector<int>::const_iterator pit = it->indices.begin(); pit != it->indices.end(); pit++)
cloud_cluster->points.push_back(cloud_filtered->points[*pit]); //*
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
ccPointCloud* newPointCloud = new ccPointCloud(QString::number(i + 1) + ".2segment");
for (int i = 0; i < cloud_cluster->size(); ++i)
{
double x = cloud_cluster->points[i].x;
double y = cloud_cluster->points[i].y;
double z = cloud_cluster->points[i].z;
newPointCloud->addPoint(CCVector3(x, y, z));
}
newPointCloud->setRGBColor(ccColor::Rgba(255, 255, 255, 255));
newPointCloud->showColors(true);
CloudGroup->addChild(newPointCloud);
CloudGroup->getLastChild()->setEnabled(false);
addToDB(newPointCloud);
j++;
}
m_ccRoot->addElement(CloudGroup);
}
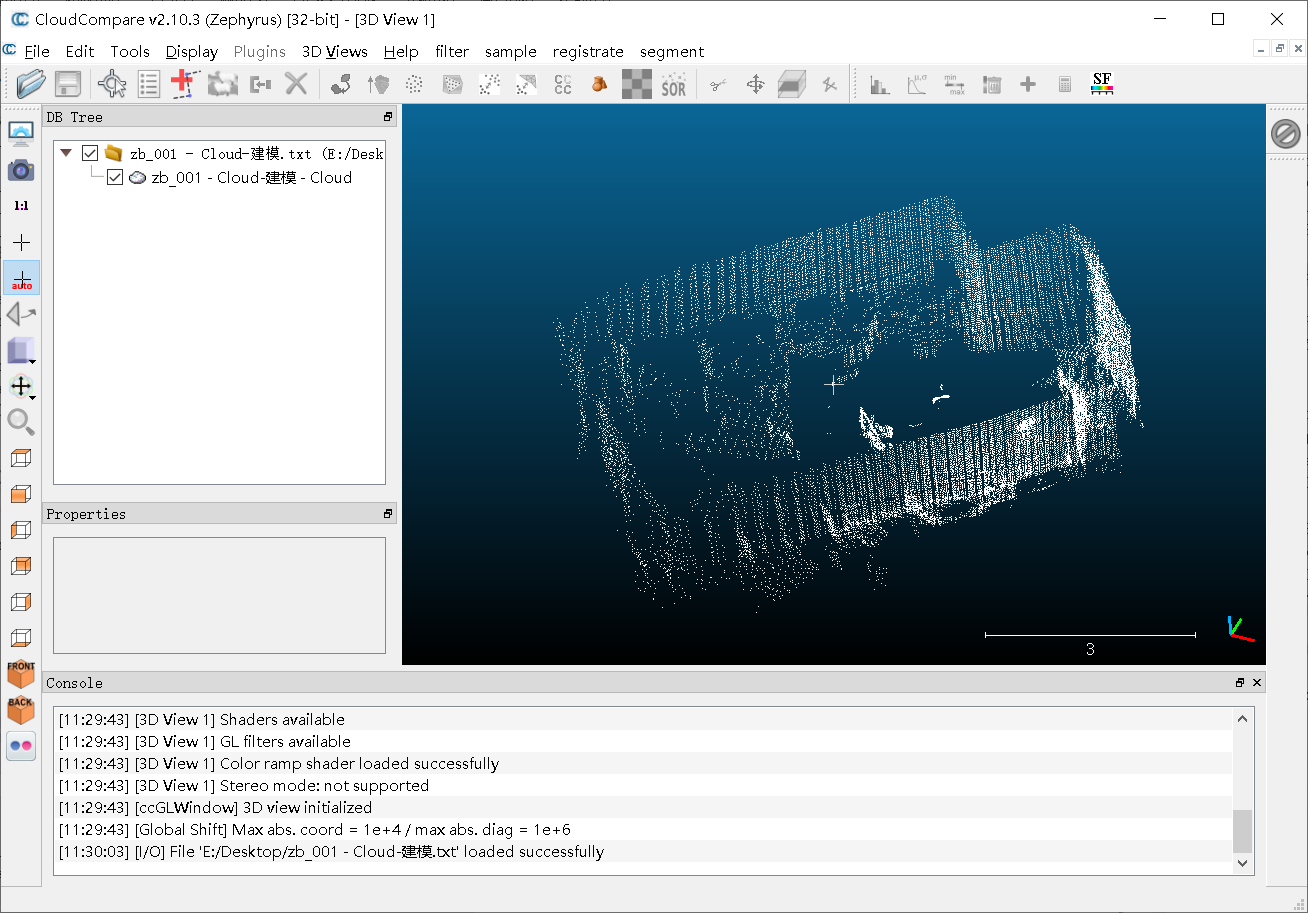
(2)分割结果
①分割前
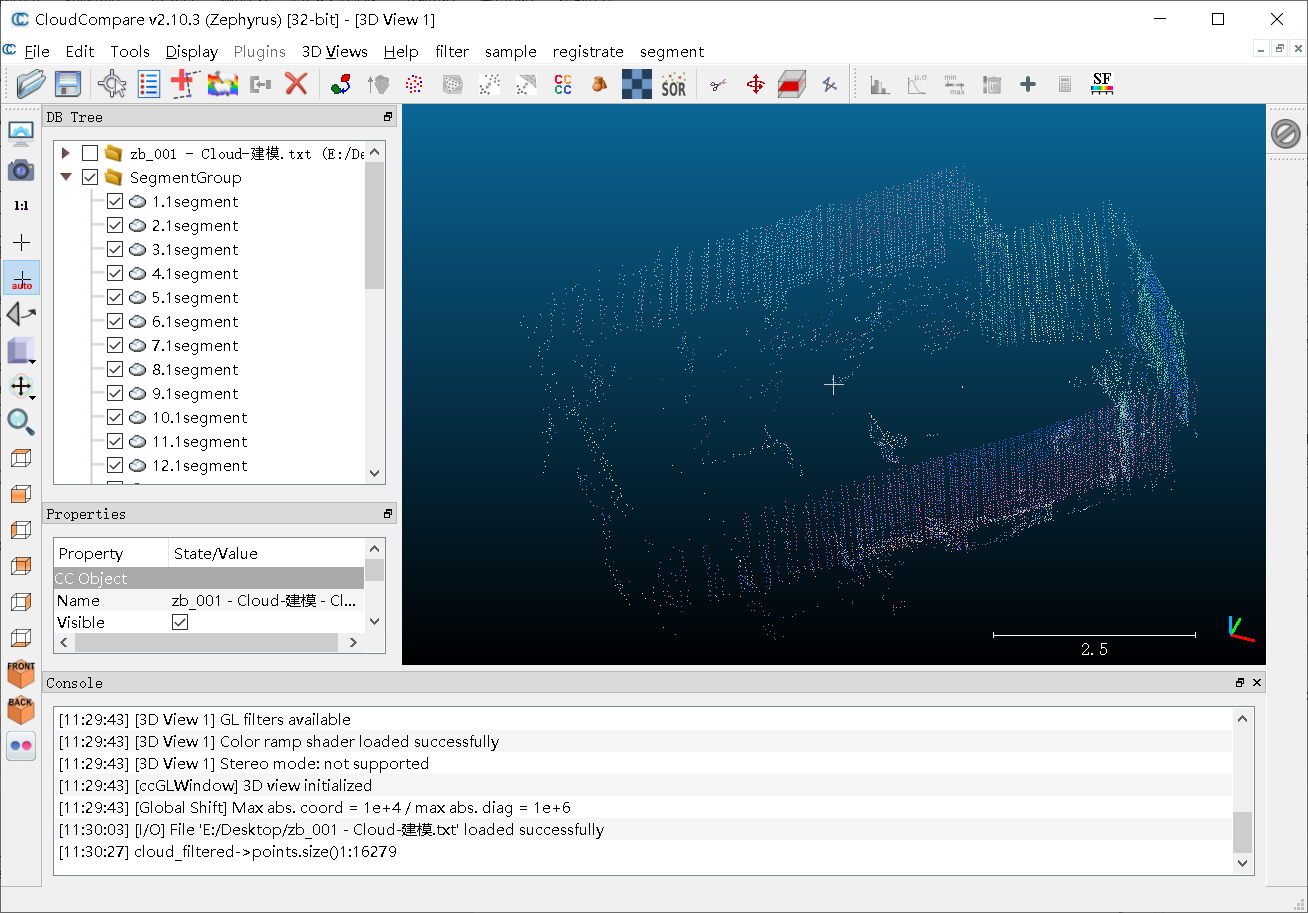
②分割后
3.基于区域生长的分割(Region_Seg)
(1)实现代码
//基于区域生长的分割
void MainWindow::doActionPCLRegion_Seg()
{
if (getSelectedEntities().size() != 1)
{
ccLog::Print(QStringLiteral("只能选择一个点云实体"));
return;
}
ccHObject* entity = getSelectedEntities()[0];
ccPointCloud* ccCloud = ccHObjectCaster::ToPointCloud(entity);
// ---------------------------读取数据到PCL----------------------------------
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
cloud->resize(ccCloud->size());
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr incloud(new pcl::PointCloud <pcl::PointNormal>());
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->size(); ++i)
{
const CCVector3* point = ccCloud->getPoint(i);
cloud->points[i].x = point->x;
cloud->points[i].y = point->y;
cloud->points[i].z = point->z;
pcl::PointNormal pt;
pt.x = point->x;
pt.y = point->y;
pt.z = point->z;
incloud->points.push_back(pt);
}
int KN_normal = 50; //设置默认输入参数
bool Bool_Cuting = false;//设置默认输入参数
float far_cuting = 10, near_cuting = 0, SmoothnessThreshold = 30.0, CurvatureThreshold = 0.05;//设置默认输入参数
pcl::search::Search<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree = boost::shared_ptr<pcl::search::Search<pcl::PointXYZ> >(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);//创建一个指向kd树搜索对象的共享指针
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud <pcl::Normal>);
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> normal_estimator;//创建法线估计对象
normal_estimator.setSearchMethod(tree);//设置搜索方法
normal_estimator.setInputCloud(cloud);//设置法线估计对象输入点集
normal_estimator.setKSearch(KN_normal);// 设置用于法向量估计的k近邻数目
normal_estimator.compute(*normals);//计算并输出法向量
// 区域生长算法的5个参数
pcl::RegionGrowing<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> reg;//创建区域生长分割对象
reg.setMinClusterSize(50);//设置一个聚类需要的最小点数
reg.setMaxClusterSize(1000000);//设置一个聚类需要的最大点数
reg.setSearchMethod(tree);//设置搜索方法
reg.setNumberOfNeighbours(30);//设置搜索的临近点数目
reg.setInputCloud(cloud);//设置输入点云
reg.setInputNormals(normals);//设置输入点云的法向量
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold(SmoothnessThreshold / 180.0 * M_PI);//设置平滑阈值
reg.setCurvatureThreshold(CurvatureThreshold);//设置曲率阈值
std::vector <pcl::PointIndices> clusters;//保存每一种聚类,每一种聚类下面还有具体的点
reg.extract(clusters);//获取聚类的结果,分割结果保存在点云索引的向量中。
//创建一个文件夹来放点云
ccHObject* CloudGroup = new ccHObject(QString("SegmentGroup"));
for (size_t i = 0; i < clusters.size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_seg1(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
for (std::vector<int>::const_iterator pit = clusters[i].indices.begin(); pit != clusters[i].indices.end(); pit++)//创建一个迭代器pit以访问第一个聚类的每一个点
{
cloud_seg1->points.push_back(cloud->points[*pit]);//迭代器pit类似于一个指针,将第一个聚类分割中的每一个点进行强制类型转换,并放置在points中
}
cloud_seg1->width = cloud_seg1->points.size();
cloud_seg1->height = 1;
cloud_seg1->is_dense = false;
ccPointCloud* newPointCloud = new ccPointCloud(QString::number(i + 1) + ".Region_Seg");
for (int i = 0; i < cloud_seg1->size(); ++i)
{
double x = cloud_seg1->points[i].x;
double y = cloud_seg1->points[i].y;
double z = cloud_seg1->points[i].z;
newPointCloud->addPoint(CCVector3(x, y, z));
}
//newPointCloud->setRGBColor(ccColor::Rgba(100, 255, 100, 255));
newPointCloud->setRGBColor(ccColor::Rgba(rand() % 105 + 150, rand() % 155 + 100, rand() % 205 + 50, 255));
newPointCloud->showColors(true);
CloudGroup->addChild(newPointCloud);
//CloudGroup->getLastChild()->setEnabled(false);
addToDB(newPointCloud);
}
m_ccRoot->addElement(CloudGroup);
}
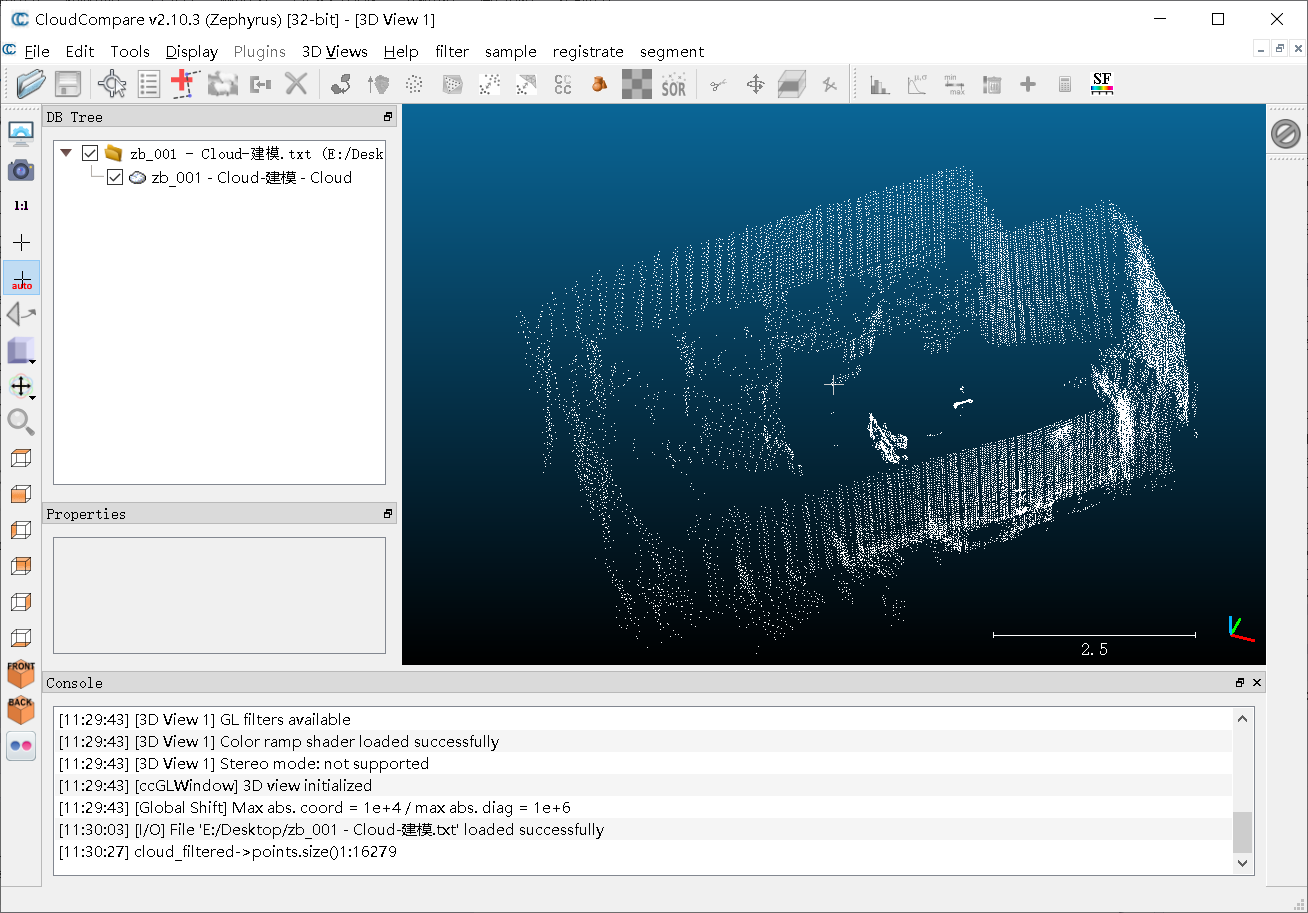
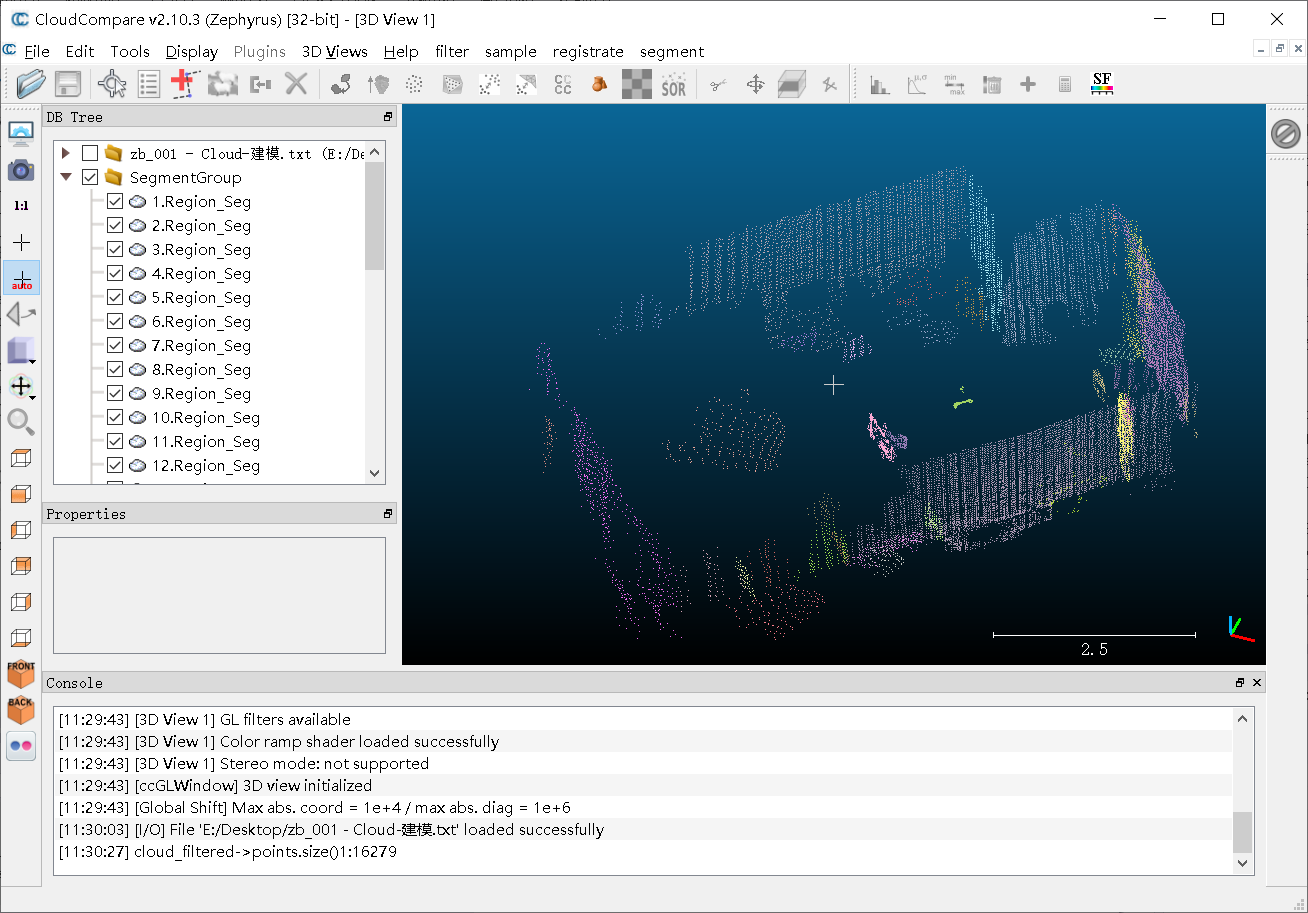
(2)分割结果
①分割前
②分割后
参考资料:
[1] 来吧!我在未来等你!. CloudCompare二次开发之如何配置PCL点云库?; 2023-05-15 [accessed 2023-05-17].
[2] Tech沉思录. PCL 【点云分割】; 2019-08-17 [accessed 2023-05-17].
[3] 步子小不扯淡. PCL: Segmentation模块之SACSegmentation点云分割; 2014-09-07 [accessed 2023-05-17].
[4] SOC罗三炮. PCL教程-点云分割之区域生长分割算法; 2023-01-08 [accessed 2023-05-17].
[5] 悠缘之空. PCL函数库摘要——点云分割; 2021-11-07 [accessed 2023-05-17].