前言
在上一篇的博客基于transformer的Seq2Seq机器翻译模型训练、预测教程讲述了怎么训练一个翻译的Seq2Seq模型,这篇博客则来说说怎么使用huggingface中训练好的模型来完成翻译的任务。
环境和模型说明
要想使用huggingface中的预训练模型,首先要安装transformers、torch和SentencePiece这几个库,使用如下命令即可
pip install transformers
pip install torch
pip install SentencePiece
huggingface中有很多nlp或者大的预训练好的语言模型,这次选用的是t5-small这个小一点的模型。
T5是一种编码器-解码器模型,在非常多的无监督和有监督任务上进行多任务训练,并将每个任务转换
为文本到文本格式。T5可以很好地处理各种任务,通过在每个任务对应的输入前加上不同的前缀,例
如:translate English to German: …,摘要:summarize: ….(注:这里是指输入的文本可以通过加入特
定前缀的方式指定是那种text-to-text任务,比如你想让T5做翻译任务,那么给他的输入就可以
是"translate English to German: What is your name?")。关于使用哪个前缀的更多信息,原论文的附
录D给出了所有的前缀。对于序列到序列的生成,建议使用generate()函数。这种方法负责通过cross-
attention层将编码输入到解码器,并自动回归生成解码器输出。T5使用相对标量嵌入。编码器输入填
充可以在左边和右边完成。
代码示例
from transformers import AutoModelWithLMHead, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelWithLMHead.from_pretrained("t5-small")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-small")
inputs = tokenizer.encode(
"translate English to German: Hugging Face is a technology company based in New York and Paris",
return_tensors="pt")
print(inputs)
outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_length=40, num_beams=4, early_stopping=True)
print(outputs[0])
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
运行上面的代码,会自动从huggingface的模型库中下载t5-small,同样,如果遇到自动下载失败,则可以手动下载模型,然后放置在相应的文件夹下,详情可以参考ReadTimeoutError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host=‘cdn-lfs.huggingface.co‘, port=443)这篇博客,里面有详细的教程。
运行上面的代码,就会输出Hugging Face is a technology company based in New York and Paris的德文翻译结果
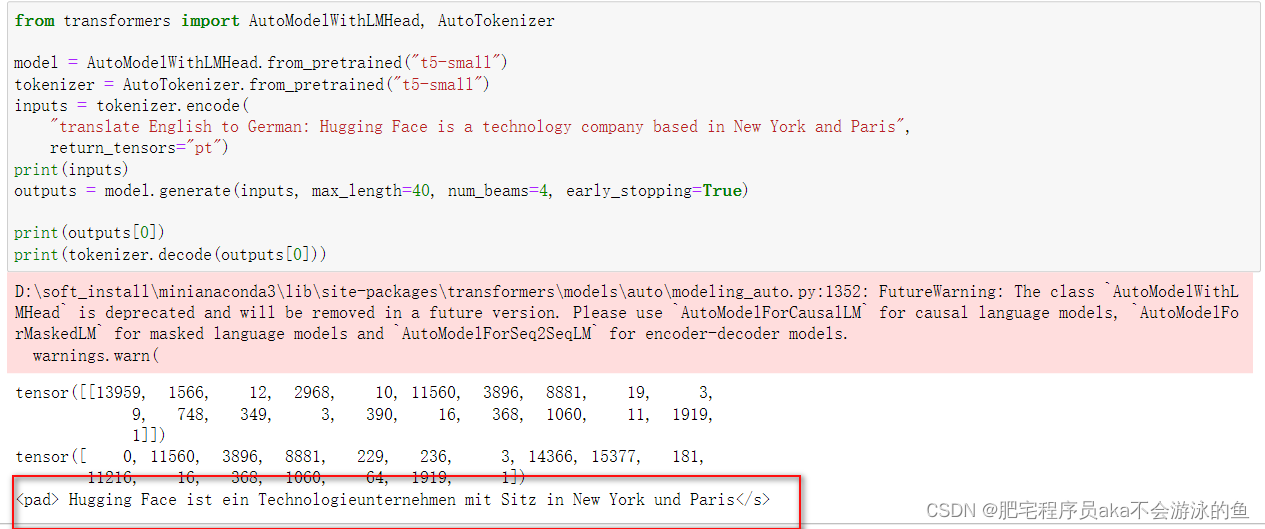
上面的是单条数据预测,可以使用batch数据预测:
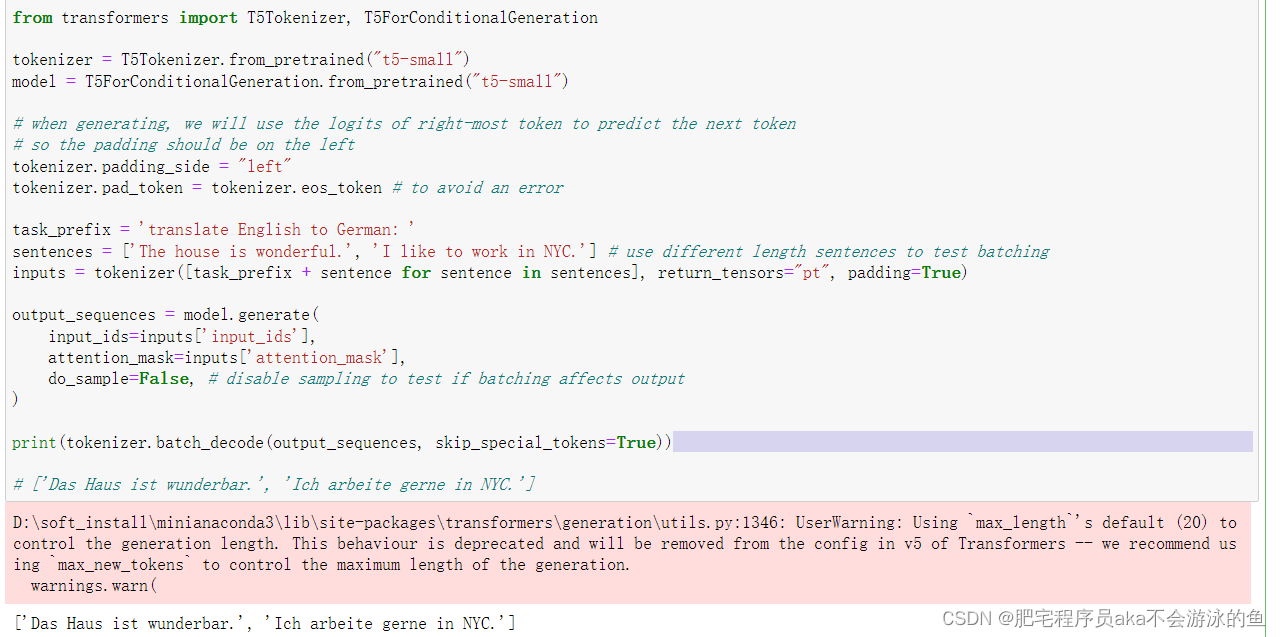
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-small")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("t5-small")
# when generating, we will use the logits of right-most token to predict the next token
# so the padding should be on the left
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token # to avoid an error
task_prefix = 'translate English to German: '
sentences = ['The house is wonderful.', 'I like to work in NYC.'] # use different length sentences to test batching
inputs = tokenizer([task_prefix + sentence for sentence in sentences], return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
output_sequences = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs['input_ids'],
attention_mask=inputs['attention_mask'],
do_sample=False, # disable sampling to test if batching affects output
)
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(output_sequences, skip_special_tokens=True))
模型输出结果为:
另外,如果你想要在这个预训练模型基础上做finetuning,训练自己的数据集,当然也可以按照下面的示例代码操作:
这是无监督的数据训练
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-small")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("t5-small")
input_ids = tokenizer('The <extra_id_0> walks in <extra_id_1> park', return_tensors='pt').input_ids
labels = tokenizer('<extra_id_0> cute dog <extra_id_1> the <extra_id_2>', return_tensors='pt').input_ids
# the forward function automatically creates the correct decoder_input_ids
loss = model(input_ids=input_ids, labels=labels).loss
这是有监督的数据训练
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-small")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("t5-small")
input_ids = tokenizer('translate English to German: The house is wonderful.', return_tensors='pt').input_ids
labels = tokenizer('Das Haus ist wunderbar.', return_tensors='pt').input_ids
# the forward function automatically creates the correct decoder_input_ids
loss = model(input_ids=input_ids, labels=labels).loss
总结一下,如果你的业务可以用这些通用的模型就可以cover住,或者你刚开始进入到机器翻译这个领域的研究,可以先玩一玩这些预训练模型,尝试看看效果如何。亦或者,你有一批小的数据集,也可也基于这个预训练模型做一些迁移学习来提升算法精度。上面的代码都可以给你一些参考