Apollo与SpringBoot整合原理深度剖析
- Spring环境上下文模块
- @Value注解如何完成属性注入
- application.yml等配置文件加载时机
- 监听环境上下文prepared事件
- Loader加载配置文件
- Apollo与SpringBoot整合原理
- @Value注解的热更新原理
Spring环境上下文模块
- Spring Envionment设计如下:
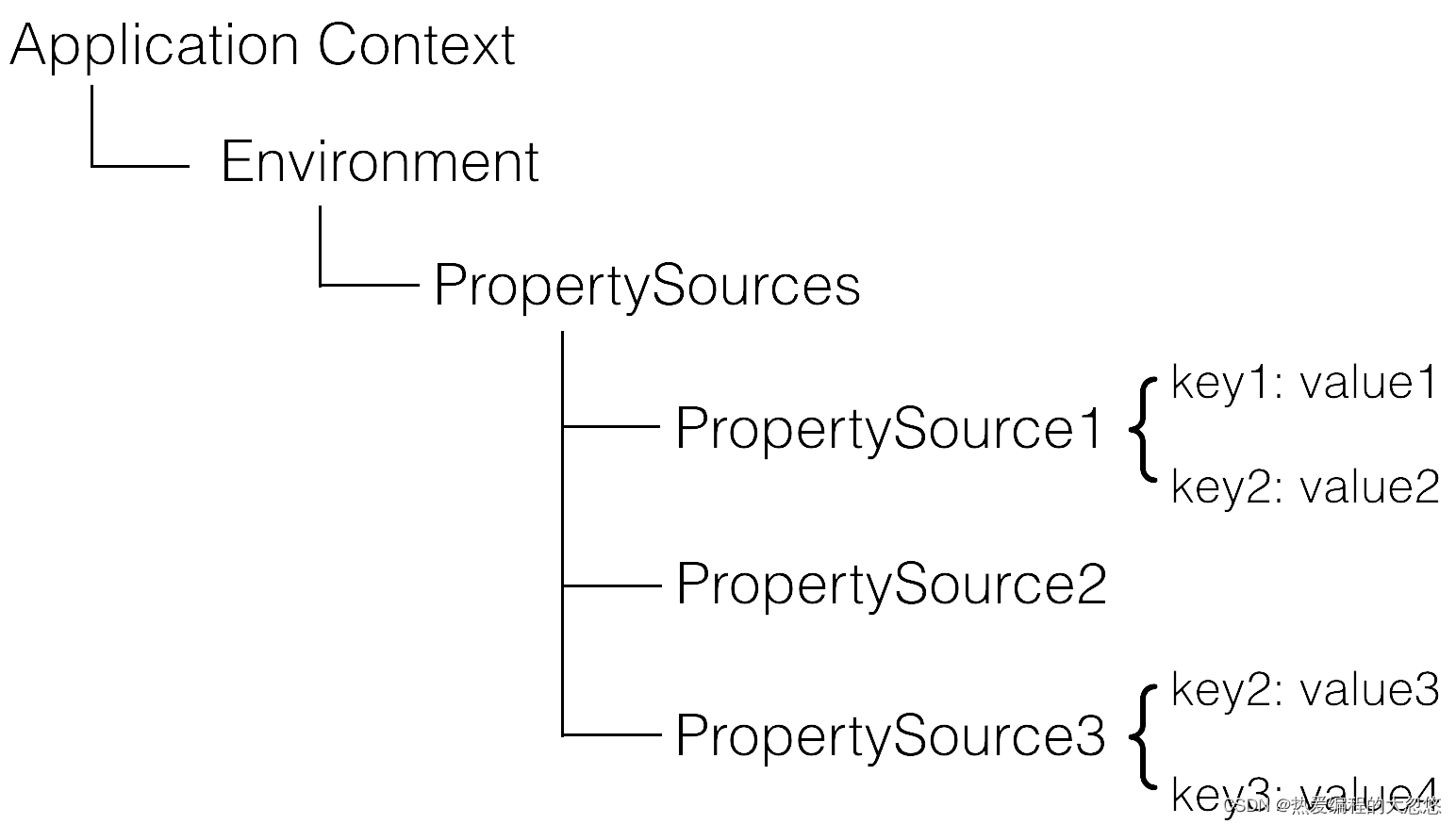
- 需要注意的是,PropertySource之间是有优先级顺序的,如果有一个Key在多个property source中都存在,那么在前面的property source优先。
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {
//Spring中并不是直接用一个List<PropertySource>管理多个属性源,而是用一个MutablePropertySources进行管理
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources(this.logger);
...
}
//MutablePropertySources中本质还是使用一个List集合进行管理---组合模式的体现
public class MutablePropertySources implements PropertySources {
//一个写时复制集合,考虑到了线程安全性,同时兼顾了性能,因为对于PropertySource而言,读大于写,一般属性源在Spring应用程序启动完毕后,基本就确定不动了
private final List<PropertySource<?>> propertySourceList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
...
}
- Spring中的Environment模块组织结构如下所示:
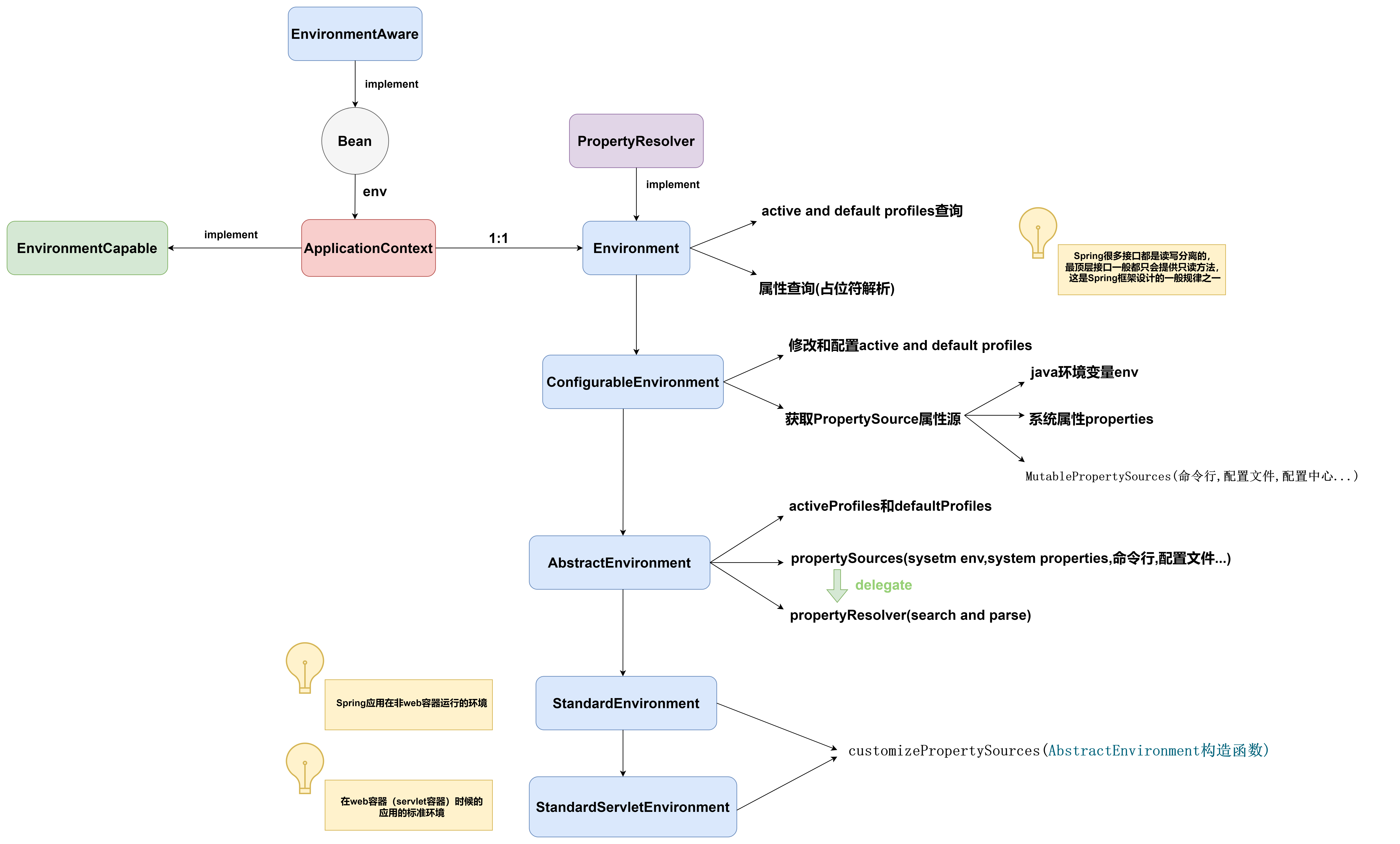
- ApplicationContext继承EnvironmentCapable接口,表明具备管理和对外暴露环境上下文对象的能力
- 普通的Spring Bean可以通过继承EnvironmentAware,在依赖注入阶段,从容器中获取并注入环境上下文实例对象
- PropertyResolver接口对外暴露获取解析过后的属性的相关方法 --> 只负责解析
${}占位符 , 不负责解析EL表达式#{}占位符 - Environment接口继承了PropertyResolver接口,从而具备了获取解析过后的属性的能力,并且自身对外暴露获取激活配置文件和默认配置文件方法
这里Environment根据配置文件中设置的spring.active.active属性来管理当前激活的Profile(配置文件)
- ConfigurableEnvironment接口主要对外暴露修改激活的Profile和默认Profile的方法,同时还对外暴露出MutablePropertySources属性源,SystemProperties属性源和SystemEnvironment属性源,用户获取后可以进行修改
Spring很多接口都是读写分离的,最顶层接口一般都只会提供只读方法,Configurablexxx接口中提供写方法,这是Spring框架设计的一般规律之一
- AbstractEnvironment对顶层读写接口功能进行具体落地实现,同时也作为抽象基础类将属性源管理和profile管理全部实现,但是具体是标准环境上下文,Web环境上下文还是响应式Web环境上下文,给出不同实现类区分即可
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {
//管理激活配置文件的容器
private final Set<String> activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<>();
//管理默认配置文件的容器
private final Set<String> defaultProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(getReservedDefaultProfiles());
//MutablePropertySources负责管理多个属性源---组合模式体现
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources(this.logger);
//负责${}占位符属性解析
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =
new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
public AbstractEnvironment() {
//留给子类扩展其他属性源的钩子方法
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
}
...
}
- Environment返回的是解析后的属性,因此所有的getProperty的系列方法,实际都是由propertyResolver负责完成。
- propertyResolver负责search and parse
- search是根据key遍历属性源集合找到第一个存在该key的propertySource并返回value
- parse是对找到的value进行${}占位符解析,最终返回的是parse过后的value
- StandardEnvironment代表标准环境上下文,可以在非Web和Web环境下使用
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
//StandardEnvironment只干了一件事,通过钩子接口customizePropertySources向属性源集合添加系统属性源和系统上下文属性源
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
}
Java环境变量(Env)和系统属性(Property)区别介绍
- StandardServletEnvironment代表Servlet作为Web容器环境下的上下文
public class StandardServletEnvironment extends StandardEnvironment implements ConfigurableWebEnvironment {
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletContextInitParams";
public static final String SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletConfigInitParams";
public static final String JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "jndiProperties";
//StandardServletEnvironment同样是通过钩子接口,向属性源集合中添加上面三个属性源
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
//此处的Stub意思为桩,表示模拟属性源--在initPropertySources方法中会对Stub属性源进行实际替换操作
//之所以这里采用Stud模拟属性源,因为环境上下文模块初始化早于Servlet容器初始化和启动
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
//调用父类钩子方法,添加系统属性源和系统上下文属性源
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
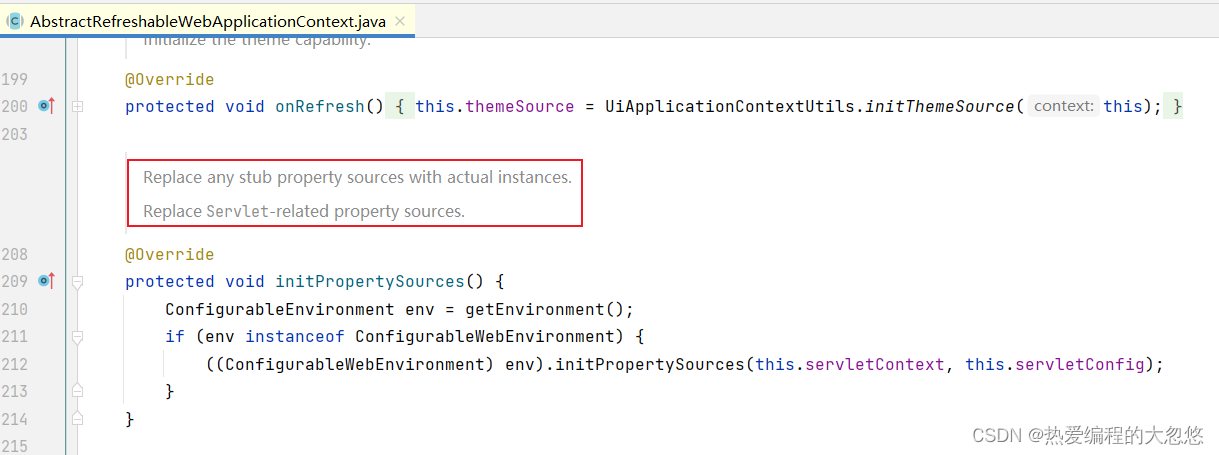
//initPropertySources方法来源于ConfigurableWebEnvironment接口,当Servlet容器启动时,调用此方法完成上面两个stub属性源的替换
//initPropertySources回调接口何时被调用,大家可以追踪一下SpringBoot环境下Servlet容器初始化过程
@Override
public void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig){
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}
}
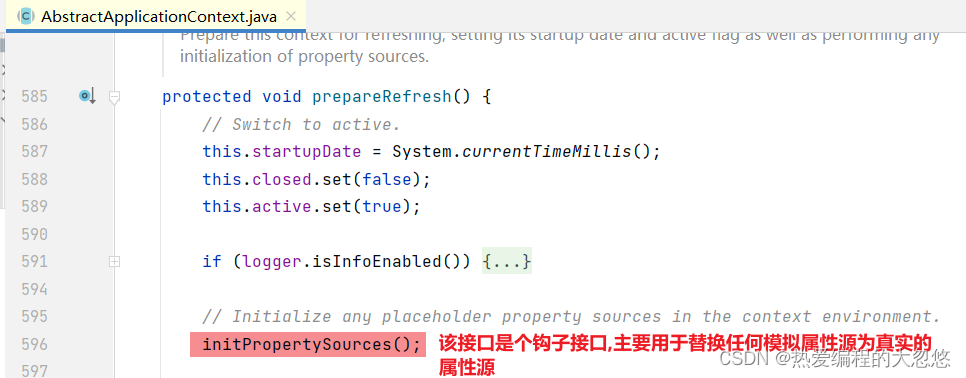
- initServletPropertySources方法完成模拟属性源替换工作
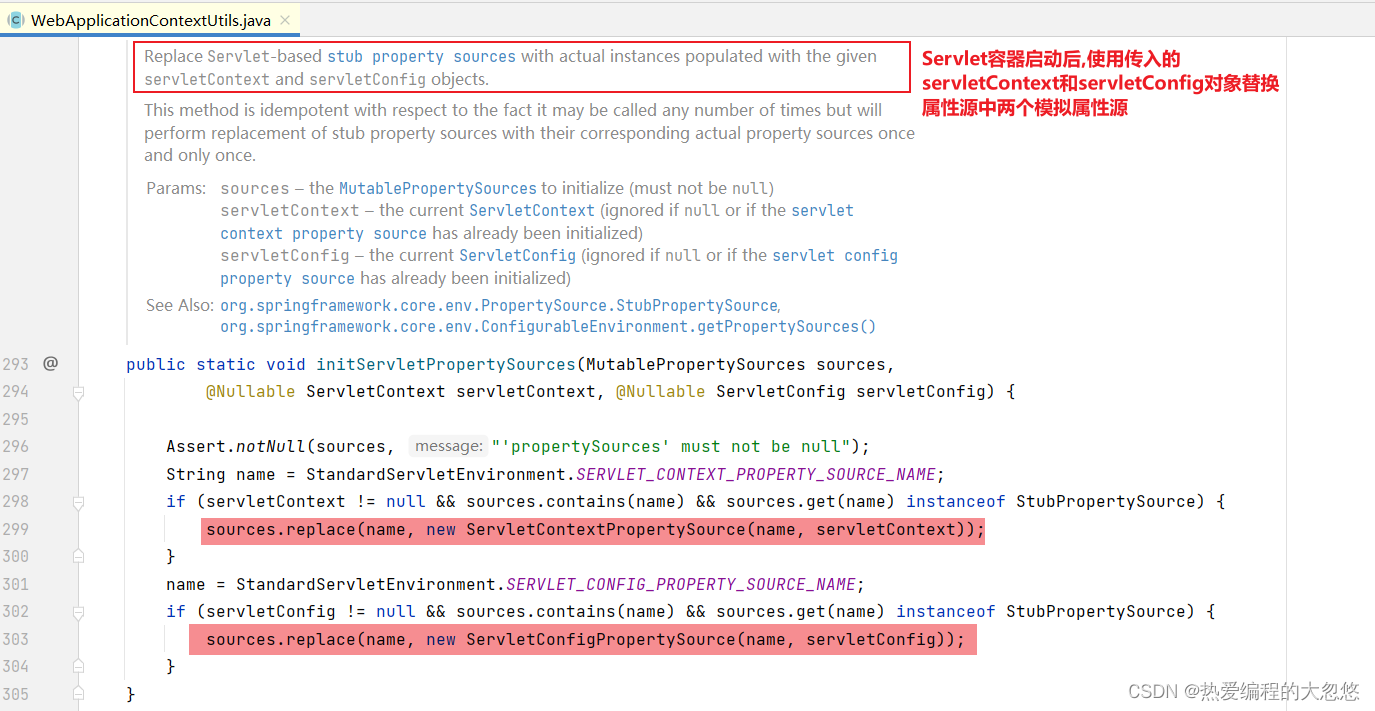
- initPropertySources调用链
@Value注解如何完成属性注入
- 回顾一下Bean的生命周期

- 依赖注入阶段是如何完成属性注入的呢 ?
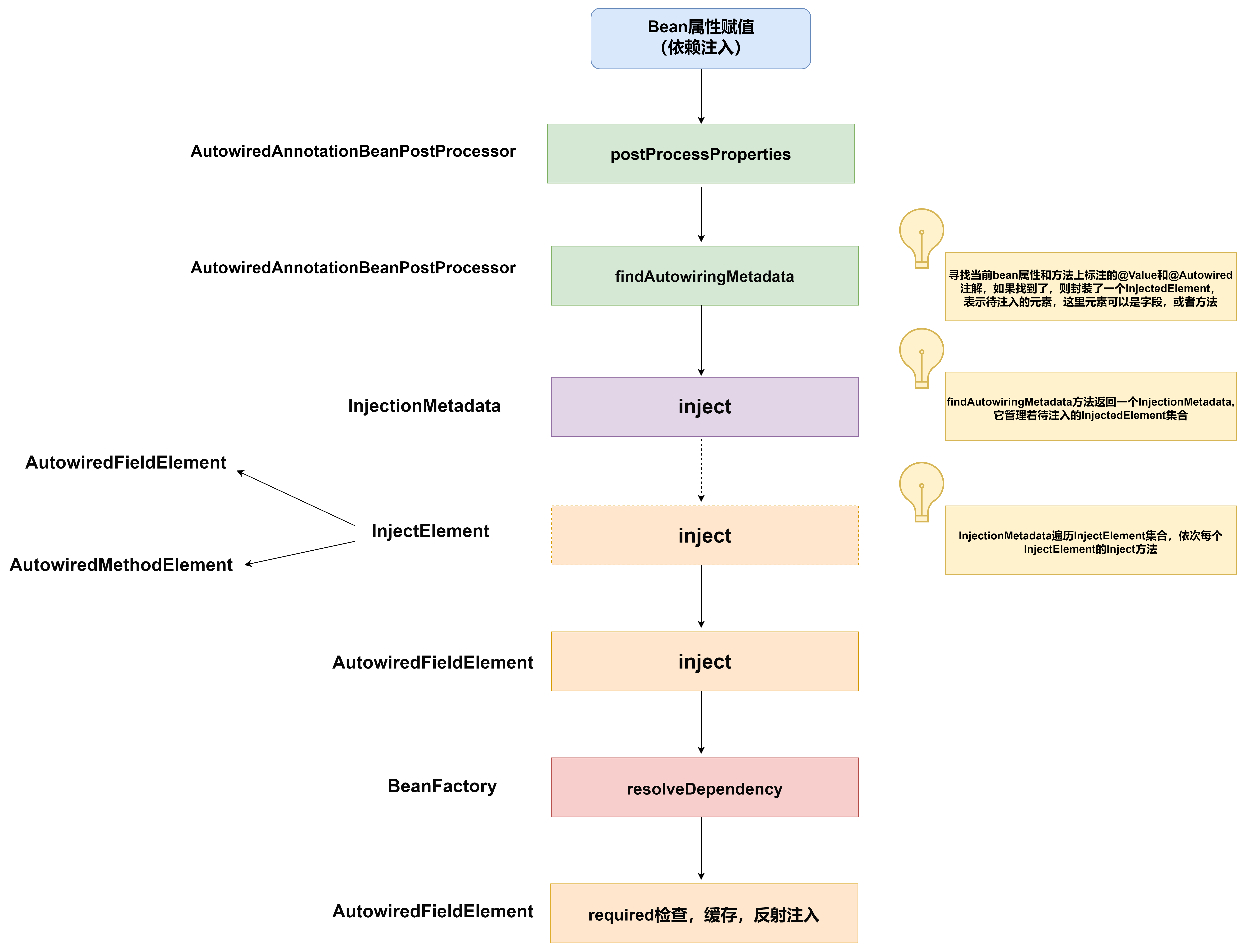
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessPropertyValues方法负责处理由注解形式指定的依赖注入点集合
需要依赖注入的点指定方式在Spring中有两种方式,一种是配置文件方式,一种是注解形式。
- 配置文件方式指定的依赖注入点集合在populateBean方法中,由BeanWrapper利用setter方法完成依赖注入
- 注解方式指定的依赖注入点集合在populateBean方法中,由SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的postProcessPropertyValues方法进行处理,默认通过反射方式完成依赖注入
- 如果配置文件和注解指定的依赖注入点集合中存在重叠的注入点,虽然注解指定的依赖注入点先被处理,但是postProcessPropertyValues方法中会判断当前注入点是否已经在配置文件中指定,如果指定了,那么跳过处理。
public class AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter
implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered, BeanFactoryAware {
private final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> autowiredAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
private String requiredParameterName = "required";
private boolean requiredParameterValue = true;
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private final Map<String, InjectionMetadata> injectionMetadataCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
//当前Bean后置处理器负责处理Autowired,Value,Inject注解
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
try {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));
logger.info("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
}
}
//处理注解指定的依赖注入
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeanCreationException{
//寻找当前bean属性和方法上所有标注了相关注解的地方,如果找到了,则封装为一个InjectedElement对象实例
//表示待注入元素,这里待注入元素可以是字段,或者方法
//InjectionMetadata内部管理从当前bean上找到的所有InjectedElement
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
//进行注解标注的依赖注入---遍历InjectionMetadata内部管理的InjectedElement集合
//依次调用每个InjectedElement的inject方法
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
...
//
return pvs;
}
...
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs){
// InjectionMetadata会被缓存起来--key为beanName
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
//双重锁机制,确保单例
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
//为当前bean构建InjectionMetadata
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历当前类上所有属性,寻找到存在相关注解的属性
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
//排除静态属性的注入
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
//从注解中取出required属性--表明是否必须注入成功
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
//封装为AutowiredFieldElement后返回
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
//遍历当前bean所有方法,寻找存在相关注解的方法,并且方法不是静态的,封装为AutowiredMethodElement后返回
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
...
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
...
return;
}
...
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
//注入依赖注入一并处理当前父类上标注的相关依赖注入点
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
//创建一个InjectionMetadata返回,InjectionMetadata管理当前bean中所有依赖注入点
return new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements);
}
}
- InjectionMetadata的inject方法负责完成实际的基于注解搜集到依赖注入点的依赖注入
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
...
//遍历所有InjectedElement,调用其inject方法完成依赖注入
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
...
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
依赖注入点InjectedElement分为两种实现类: AutowiredFieldElement和AutowiredMethodElement,此处只看AutowiredMethodElement的inject方法实现
- AutowiredMethodElement的inject方法进行方法级别的依赖注入之前,会调用checkPropertySkipping方法检查是否和配置文件中指定的依赖注入点重叠,如果是,则跳过处理。
private class AutowiredFieldElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
private final boolean required;
private volatile boolean cached = false;
@Nullable
private volatile Object cachedFieldValue;
...
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
...
//构建依赖描述符
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
...
//类型转换器
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
//调用beanFactory的resolveDependency方法,根据依赖描述符完成依赖查找
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
...
//反射注入
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
}
- resolveDependency作为依赖查找核心,怎么查找的?
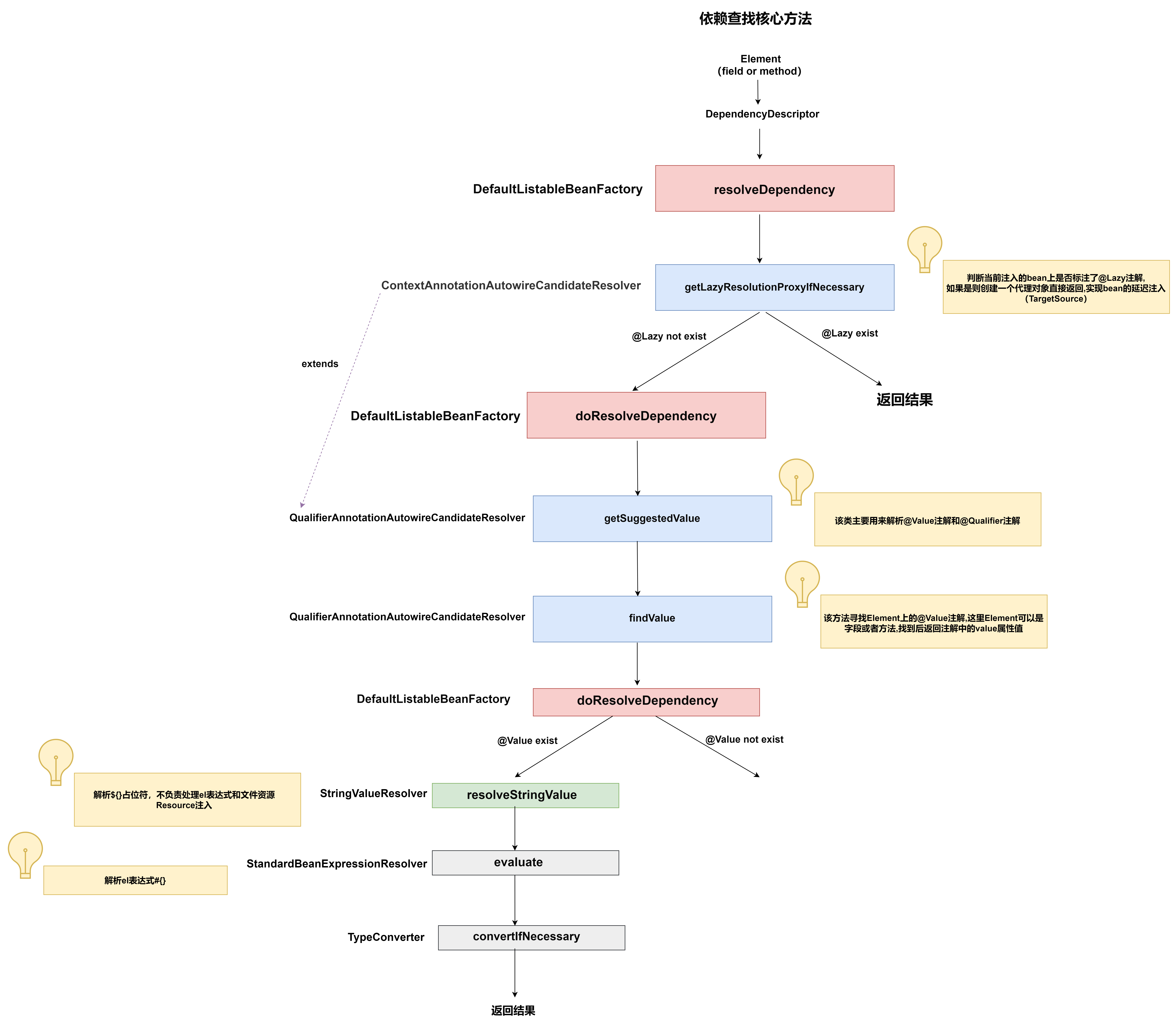
- DefaultListableBeanFactory的resolveDependency方法作为IOC容器进行依赖查找的核心方法
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
//初始化方法参数名解析器
descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());
...
//如果当前依赖注入点上存在@Lazy注解,则创建一个代理对象返回,为的是实现依赖延迟注入---这块逻辑很简单,不展开,自己看源码
Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
//正常情况下进入依赖查找逻辑
if (result == null) {
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
return result;
}
}
- doResolveDependency方法中真正负责依赖查找工作,依赖查找要么根据value注解中的属性值进行解析,把解析后的结果作为依赖查找结果返回。要么就是@Autowired属性注入–> 也就是我们平常认为的依赖查找应该干的事情。
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
//描述符解析过了,直接返回--相当于缓存
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
//获取要查找的bean类型---当然这里可能是bean类型(@Autowired注解),也可能需要查找的是String字符串(@Value注解)
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
//当前依赖注入点上是否存在@Value注解--如果存在返回注解中value属性值,否则返回null
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
//如果value不为null,说明当前依赖查找需要解析value注解中的value属性值,然后返回作为依赖查找结果
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
//解析${}占位符
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ? getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
//解析EL表达式
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
//获取类型转换器
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
//@Value注解可以标注在Resource资源对象上,因为value字符串经过${}占位符解析和EL表达式解析后
//可能得到的是一个资源路径或者url字符串表示形式,可以使用类型转换器将字符串形式表示的资源路径转换为
//实际的资源类型对象
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
//下面是@Autowired等注解的依赖查找过程,非本文重点,这里不进行讲解
...
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}
EL表达式的解析部分本文也不展开讲解
- resolveEmbeddedValue方法解析${}占位符
public String resolveEmbeddedValue(@Nullable String value) {
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
String result = value;
for (StringValueResolver resolver : this.embeddedValueResolvers) {
result = resolver.resolveStringValue(result);
if (result == null) {
return null;
}
}
return result;
}
AbstractBeanFactory的embeddedValueResolvers集合中StringValueResolver 的注册时机是什么呢?
- StringValueResolver的注册时机(有两处,另一处---->PropertyResourceConfigurer#processProperties–>PropertyResourceConfigurer#postProcessBeanFactory)
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
...
// 若没有指定EmbeddedValueResolver
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
//创建一个匿名内部类的实现,核心交给环境上下文对象完成
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() {
@Override
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) {
return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal);
}
});
}
...
}
}
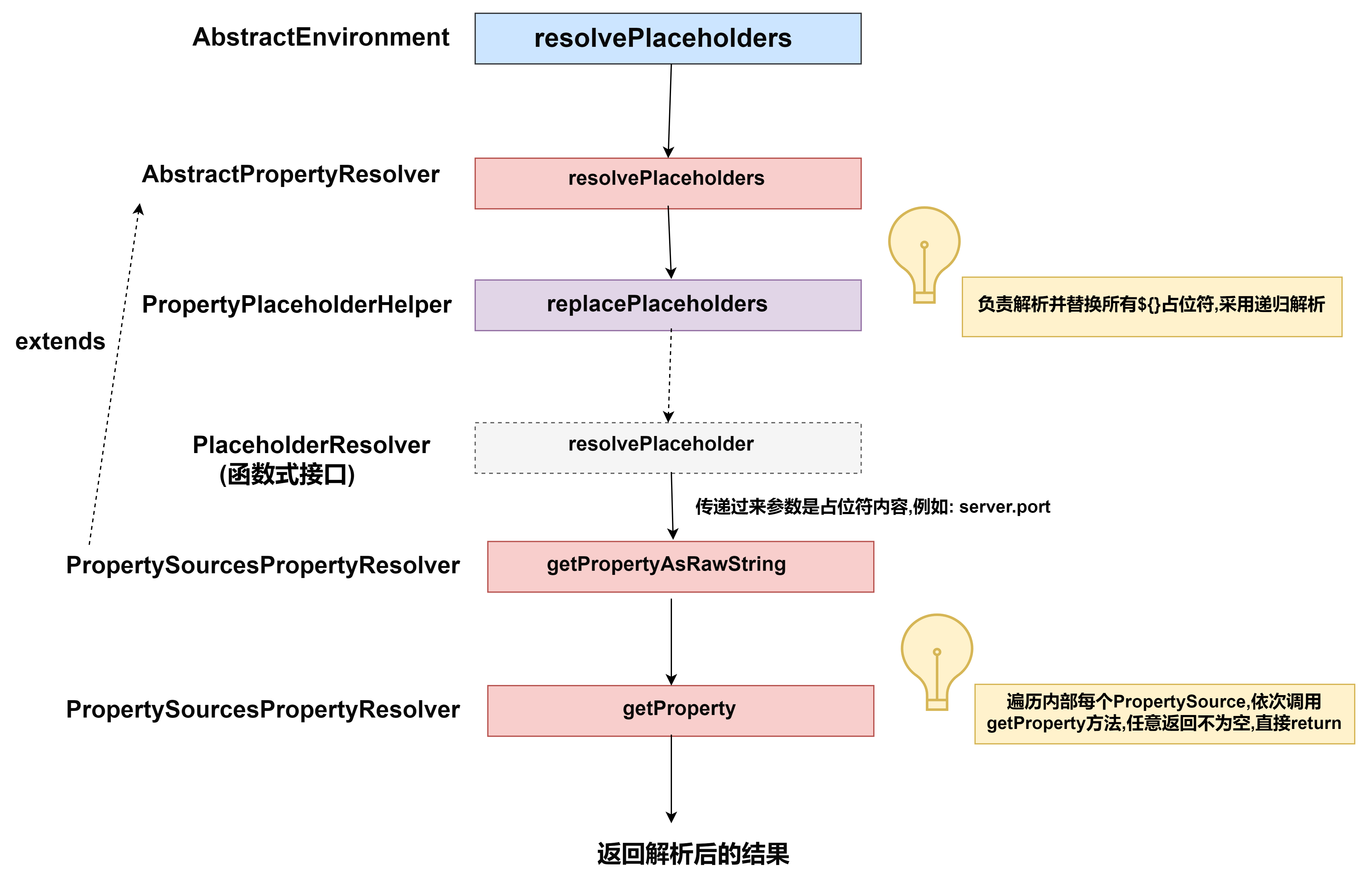
- AbstractEnvironment的resolvePlaceholders方法实现最终是交给PropertySourcesPropertyResolver完成的
- AbstractPropertyResolver抽象类中给出resolvePlaceholders方法实现
@Override
public String resolvePlaceholders(String text) {
//这里的strict表示是否忽略无法被解析的${}占位符,如果不忽略,则会抛出异常
if (this.nonStrictHelper == null) {
this.nonStrictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(true);
}
// 真正进行占位符解析
return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.nonStrictHelper);
}
private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) {
//借助PropertyPlaceholderHelper完成占位符解析
return helper.replacePlaceholders(text, this::getPropertyAsRawString);
}
//子类实现根据PropertyPlaceholderHelper取出${server.port}占位符中的server.port
//去属性源集合中根据取出的server.port作为key,进行查找
protected abstract String getPropertyAsRawString(String key);
- 占位符核心解析逻辑在PropertyPlaceholderHelper的parseStringValue方法中
//传入的是value注解中的value属性值,如: ${server.port}
public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) {
Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null");
return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet<>());
}
protected String parseStringValue(
String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value);
//定位 ${ 出现的位置
int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
while (startIndex != -1) {
//定位 } 出现的位置
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
//截取${server.post}占位符之间的值--> server.port
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
//拿到传入的占位符解析器
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
...
// 递归解析${}占位符,因为可能会存在${${config.key}.value}的情况
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// 调用传入的占位符解析器的resolvePlaceholder方法解析占位符
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
//valueSeparator默认为":",表示默认值
//如果val值为null,那么尝试查找默认值
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
//如: ${server.port:8079}---如果存在默认值设置,那么将默认值作为结果
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
//如果解析结果不为null
if (propVal != null) {
//考虑到根据${dhy.name}中的dhy.name查找属性源得到的值可能是${xpy.name}这种形式
//因此需要继续递归解析
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
...
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
//ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders为false的情况下,抛出解析失败异常
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in value \"" + value + "\"");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
}
return result.toString();
}
- PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver提供的resolvePlaceholder方法,根据PropertyPlaceholderHelper取出${server.port}占位符中的server.port,去属性源集合中根据取出的server.port作为key,进行查找
protected String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholder) {
if (this.sources != null) {
//挨个遍历每个属性源,哪个先找到,就直接返回---这里引出了配置优先级问题
for (PropertySource<?> source : this.sources) {
Object value = source.getProperty(placeholder);
if (value != null) {
return String.valueOf(value);
}
}
}
return null;
}
application.yml等配置文件加载时机
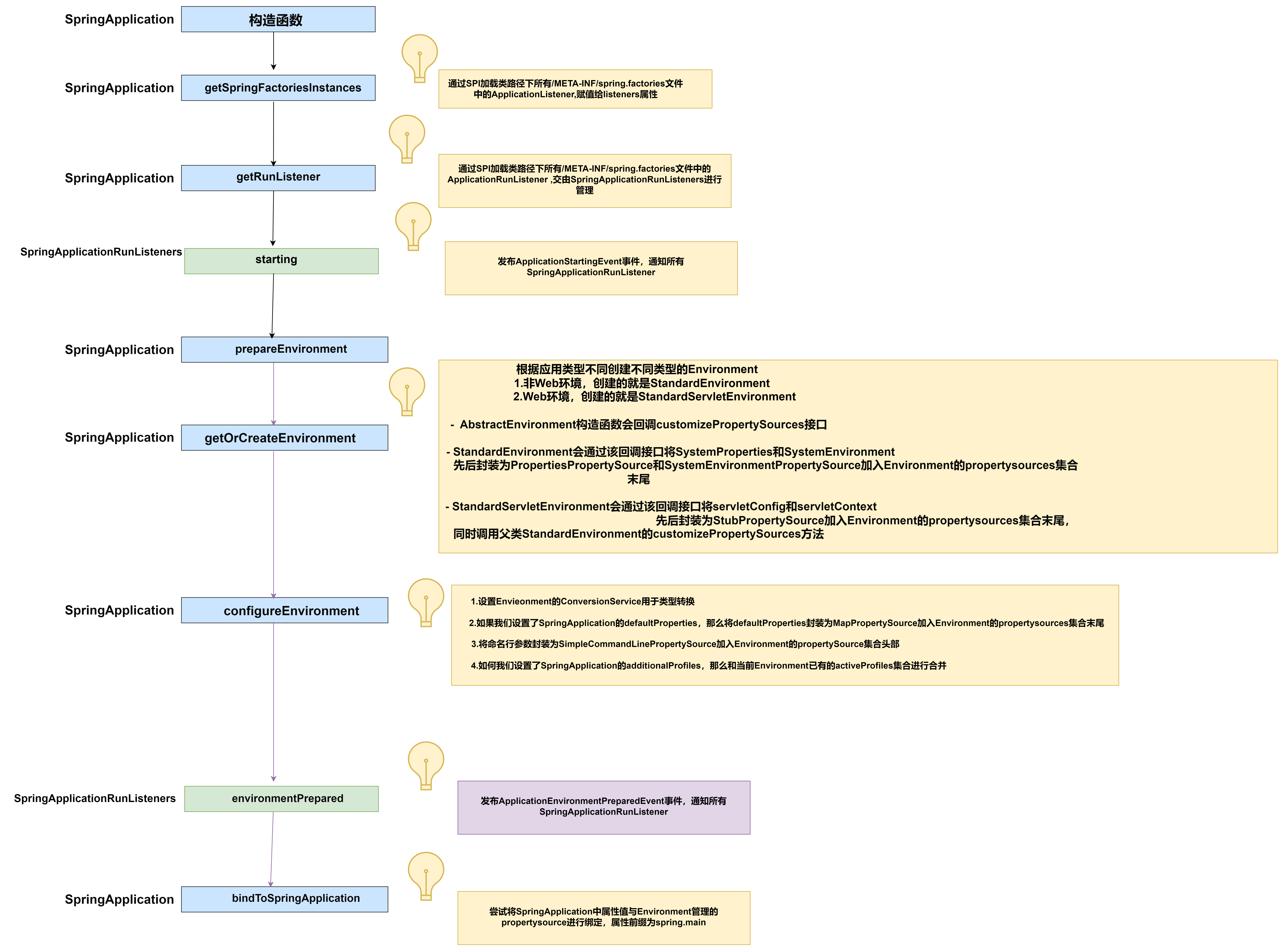
- SpringApplication的构造函数中通过SPI完成ApplicationContextInitializer和ApplicationListener实现类的加载
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
- 这里重点关注通过SPI加载得到的,专门负责加载配置文件的监听器
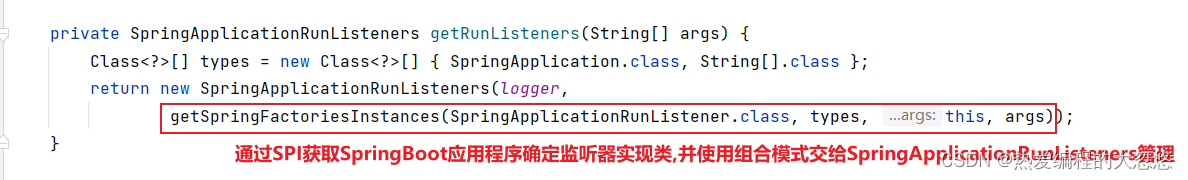
- SpringApplication的Run方法启动SpringBoot应用程序—这里只关注和配置文件加载相关的监听器部分
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
..
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
...
//SPI加载SpringApplicationRunListener实现类,然后交给SpringApplicationRunListeners管理---组合模式
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
...
return context;
}
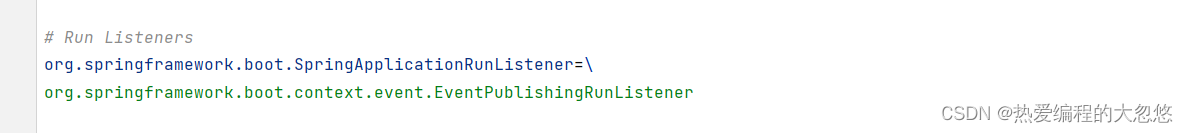
- 默认情况下,可以通过SPI机制获取到: 负责发布SpringBoot应用程序生命周期事件的监听器
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
//事件派发器
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
//从SpringApplication拿到通过SPI加载得到的ApplicationListener集合
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
SpringApplicationRunListeners,EventPublishingRunListener和ApplicationListener三者关系如下:

我们继续回到SpringBoot run启动方法中来;
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
..
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
...
//SPI加载SpringApplicationRunListener实现类,然后交给SpringApplicationRunListeners管理---组合模式
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//发布SpringBoot应用程序启动事件
listeners.starting();
try {
//封装命令行参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//环境上下文准备--配置类加载的地方
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
...
context = createApplicationContext();
...
//这里我们需要关注一点: 此处会调用经过SPI加载得到的ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
...
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
...
listeners.running(context);
return context;
}
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//主要干的事情: 封装命令行参数为propertySource,加入环境上下文管理的属性源集合中
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//发布环境上下文准备好的事件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
...
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
//根据当前应用程序类型的不同,创建不同的环境上下文实现类
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
//封装命令行参数为propertySource,加入环境上下文管理的属性源集合中
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
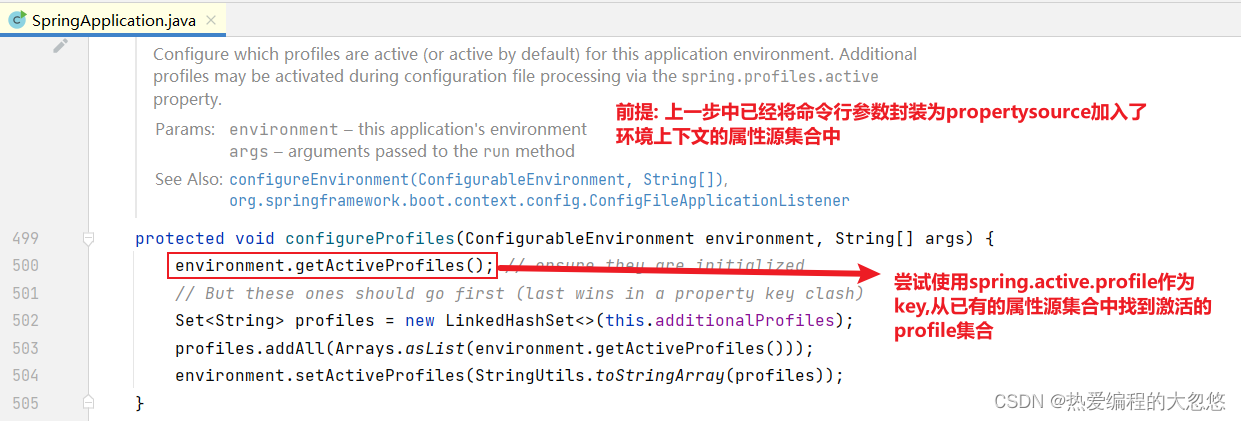
// 从已有的属性源集合中更新激活profile的配置
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
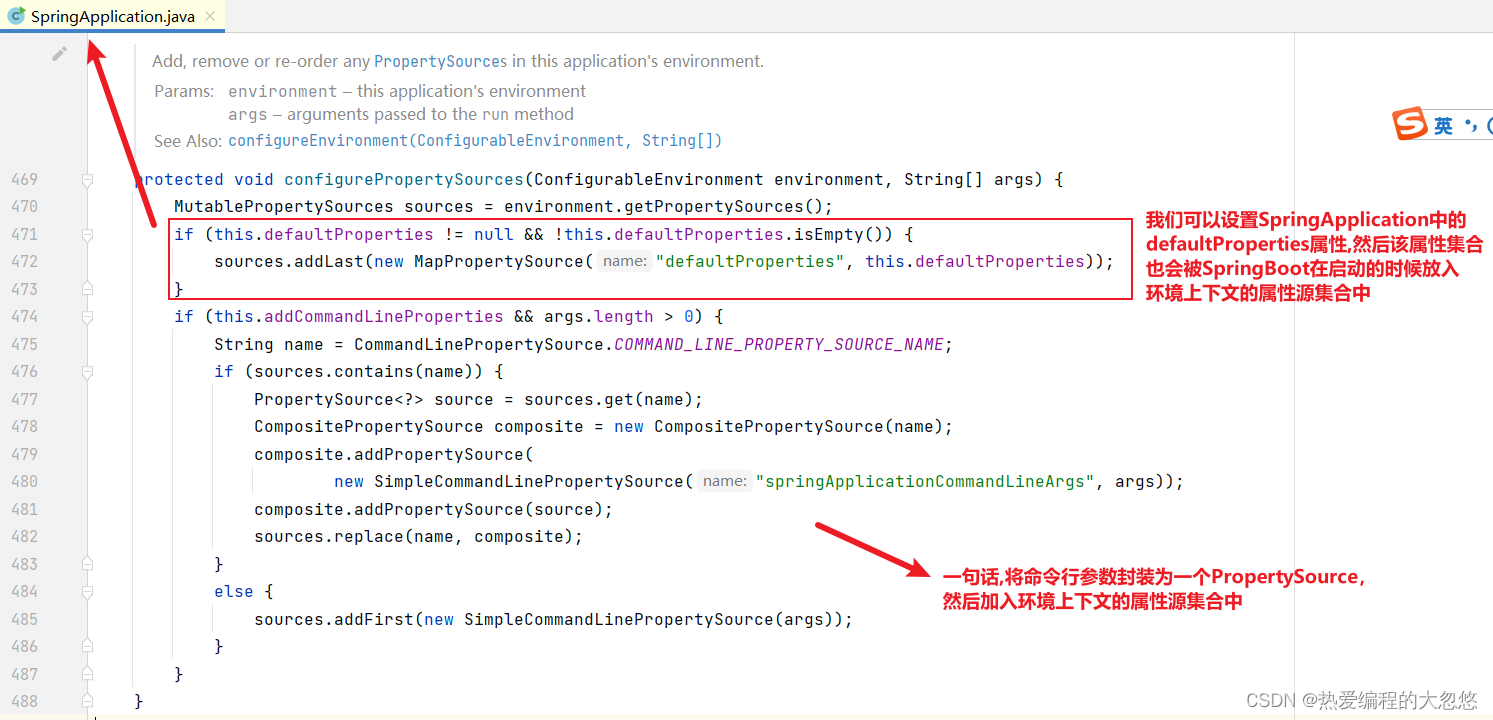
监听环境上下文prepared事件
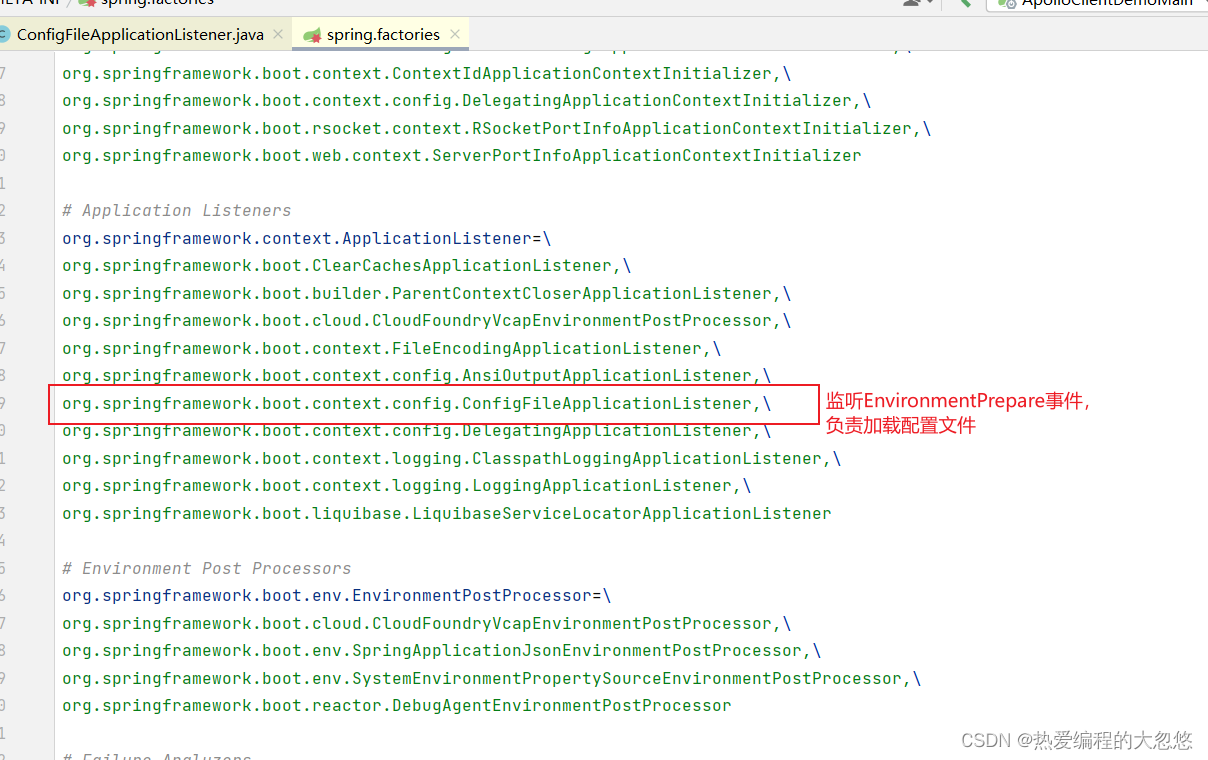
- ConfigFileApplicationListener是如何加载配置文件的呢?
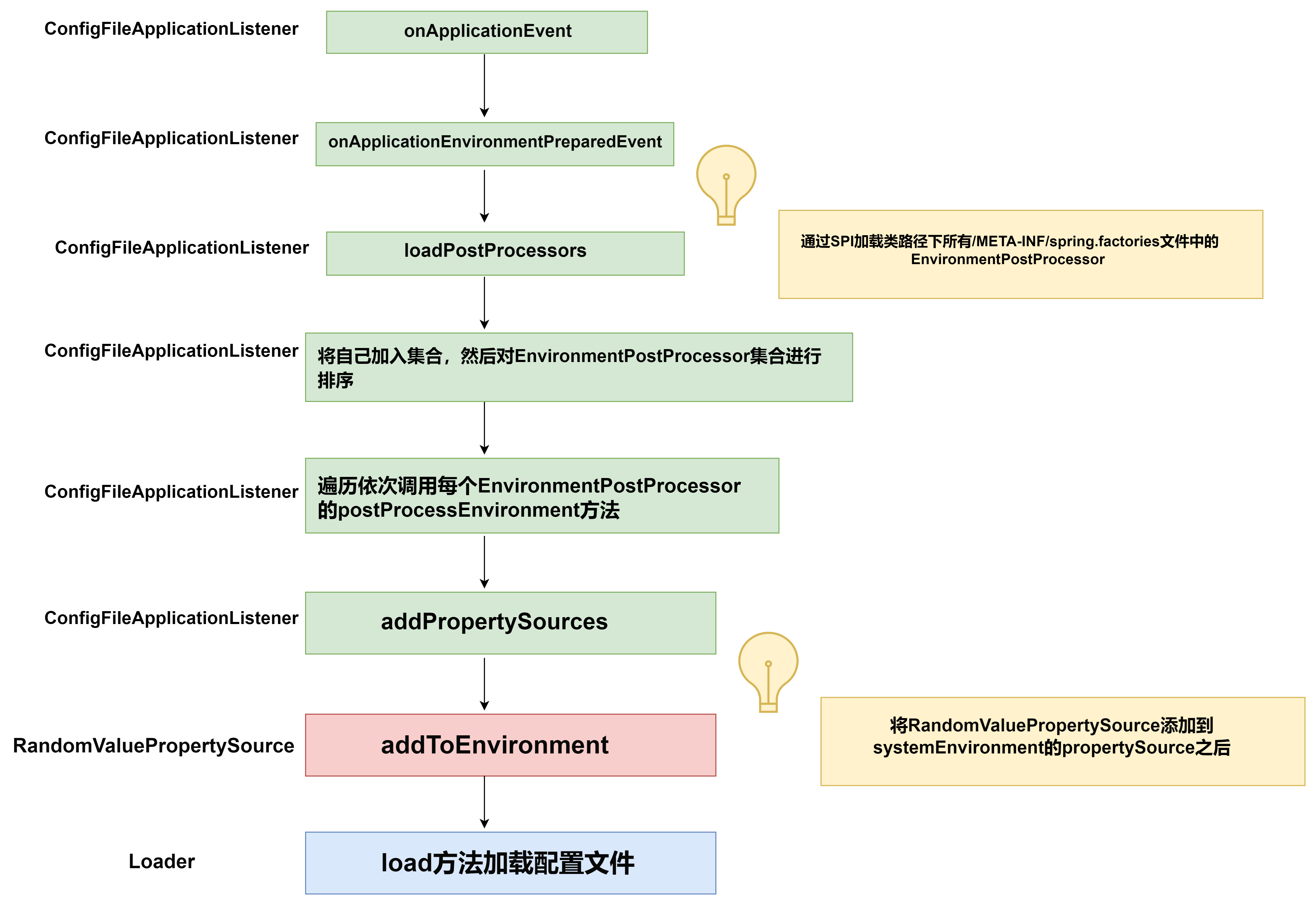
- ConfigFileApplicationListener的onApplicationEvent方法如下
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
//重点关注监听应用程序环境上下文准备好的这个事件处理逻辑
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
//一句话: 将SpringApplication中的defaultProperties对应的propertysource移动到属性源集合末尾
//即: 具有最低优先级 --- 上面一开始添加过
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
//SPI机制加载所有EnvironmentPostProcessor
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
//ConfigFileApplicationListener自己本身也是一个EnvironmentPostProcessor
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
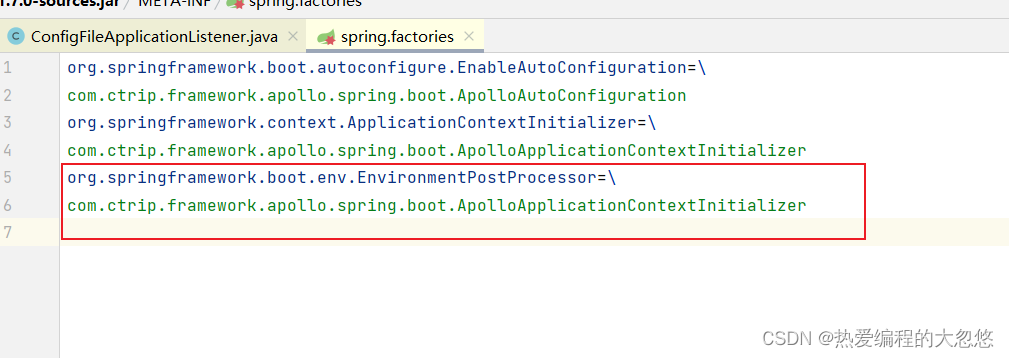
- Apollo在这里也添加了一个自定义的EnvironmentPostProcessor
- ConfigFileApplicationListener的postProcessEnvironment方法会调用addPropertySources方法
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}
//addPropertySources方法中,会首先向环境上下中添加一个随机数属性源
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
//创建一个Loader,调用其load方法,完成配置文件的加载
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
Loader加载配置文件
- Loader如何完成配置文件的加载,以及如何封装配置文件为PropertySource,然后加载到Environment的PropertySources集合中呢?
Loader(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.environment = environment;
//search and parse==> environment内部的propertySources集合的delegate
this.placeholdersResolver = new PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver(this.environment);
//加载配置的资源加载器
this.resourceLoader = (resourceLoader != null) ? resourceLoader : new DefaultResourceLoader(null);
//通过SPI机制加载PropertySourceLoader
this.propertySourceLoaders = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(PropertySourceLoader.class,
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
- 默认提供的两个实现如下 – 分别负责加载.yml,.yaml和.properties结尾的配置文件
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader
- load方法源码如下
void load() {
FilteredPropertySource.apply(this.environment, DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, LOAD_FILTERED_PROPERTY,
(defaultProperties) -> {
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//初始化profiles--从已有的propertySource集合中解析得到激活的profile
initializeProfiles();
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
//如果当前Profile是默认的,那么加入Environment的ActiveProfile集合
if (isDefaultProfile(profile)) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
//加载配置文件,并通过getNegativeProfileFilter过滤进行过滤
//过滤规则:
//1.如果传入的profile为null,那么过滤掉document的profiles不为空
//2.如果传入的profile不为null,那么过滤掉document的profile不等于传入的profile的
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter,
//将配置文件加载完毕后,回调此方法,用于将配置文件对应的PropertySource和Profile关系记录到loaded集合中
addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
//标记当前profile处理完毕
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
//加载配置文件,并通过getNegativeProfileFilter过滤进行过滤
//过滤规则: 1.如果传入的profile为null,那么过滤掉document的profiles不为空
//2.如果传入的profile不为null,那么过滤掉document的profile不等于传入的profile的
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
//将Loaded集合中记录的propertySource加入environment的propertySources集合中去
addLoadedPropertySources();
//向environment中添加通过解析配置文件得到的activeProfiles
applyActiveProfiles(defaultProperties);
});
}
- initializeProfiles负责尝试从已有的propertySource集合中解析得到激活的profile
private void initializeProfiles() {
// The default profile for these purposes is represented as null. We add it
// first so that it is processed first and has lowest priority.
this.profiles.add(null);
Binder binder = Binder.get(this.environment);
//获取spring.profiles.active和spring.profiles.include
Set<Profile> activatedViaProperty = getProfiles(binder, ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY);
Set<Profile> includedViaProperty = getProfiles(binder, INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY);
//获取Environment中已经存在的profile的,过滤掉了和上面两个重复的profile
List<Profile> otherActiveProfiles = getOtherActiveProfiles(activatedViaProperty, includedViaProperty);
//合并三个集合
this.profiles.addAll(otherActiveProfiles);
// Any pre-existing active profiles set via property sources (e.g.
// System properties) take precedence over those added in config files.
this.profiles.addAll(includedViaProperty);
addActiveProfiles(activatedViaProperty);
//如果我们没有通过命令行或者系统参数的形式配置spring.profiles.active
//那么添加defaultProflie到profiles集合中
if (this.profiles.size() == 1) { // only has null profile
for (String defaultProfileName : this.environment.getDefaultProfiles()) {
Profile defaultProfile = new Profile(defaultProfileName, true);
this.profiles.add(defaultProfile);
}
}
}
- 核心load方法
private void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
//默认springboot会去这几个路径下寻找配置文件
//classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/*/,file:./config/
getSearchLocations()
.forEach((location) -> {
//getSearchNames获取配置文件的前缀名,默认只有一个,为application
boolean isDirectory = location.endsWith("/");
Set<String> names = isDirectory ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES;
names.forEach((name) ->
//location目录路径有了,配置文件名有了,还差个后缀名
//load方法拼接上后缀,然后去定位配置文件
load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer));
});
}
- load重载方法
//location目录路径有了,配置文件名有了,还差个后缀名
//load方法拼接上后缀,然后去定位配置文件
private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory,
DocumentConsumer consumer) {
...
Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>();
//默认情况下能够处理.properties后缀,.yml后缀或者是.yaml后缀
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {
for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) {
if (processed.add(fileExtension)) {
//配置文件完整路径=目录名+文件名+后缀名
loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory,
consumer);
}
}
}
}
- loadForFileExtension定位加载配置文件
private void loadForFileExtension(PropertySourceLoader loader, String prefix, String fileExtension,
Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
//DocumentFilterFactory负责进行过滤
DocumentFilter defaultFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(null);
DocumentFilter profileFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile);
//如果说profile不为null,那么还会尝试根据:目录名+文件名+"-"+profile+后缀去定位配置文件
if (profile != null) {
String profileSpecificFile = prefix + "-" + profile + fileExtension;
load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, defaultFilter, consumer);
load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
// Try profile specific sections in files we've already processed
for (Profile processedProfile : this.processedProfiles) {
if (processedProfile != null) {
String previouslyLoaded = prefix + "-" + processedProfile + fileExtension;
load(loader, previouslyLoaded, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
}
}
}
//根据 目录名+文件名+后缀去定位配置文件
load(loader, prefix + fileExtension, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
}
- 真正加载配置文件的地方
private void load(PropertySourceLoader loader, String location, Profile profile, DocumentFilter filter,
DocumentConsumer consumer) {
//利用resourceLoader加载配置文件
Resource[] resources = getResources(location);
for (Resource resource : resources) {
try {
//如果配置文件不存在则continue--省略配置文件不存在或者不符合要求的几种情况判断
...
//配置文件存在--name作为propertySource的名字
String name = "applicationConfig: [" + getLocationName(location, resource) + "]";
//加载配置文件信息
List<Document> documents = loadDocuments(loader, name, resource);
//如果集合为空,则continue
...
// DocumentFilter进行过滤
List<Document> loaded = new ArrayList<>();
for (Document document : documents) {
if (filter.match(document)) {
//如果配置文件中指定了spring.profiles.active则进行记录
addActiveProfiles(document.getActiveProfiles());
//如果配置文件中指定了spring.profiles.include则进行记录
addIncludedProfiles(document.getIncludeProfiles());
loaded.add(document);
}
}
Collections.reverse(loaded);
if (!loaded.isEmpty()) {
//调用回调接口,进行propertySource合并处理
//加入ConfigFileApplicationListener的Map<Profile, MutablePropertySources> loaded
//集合中
loaded.forEach((document) -> consumer.accept(profile, document));
...
}
}
...
}
}
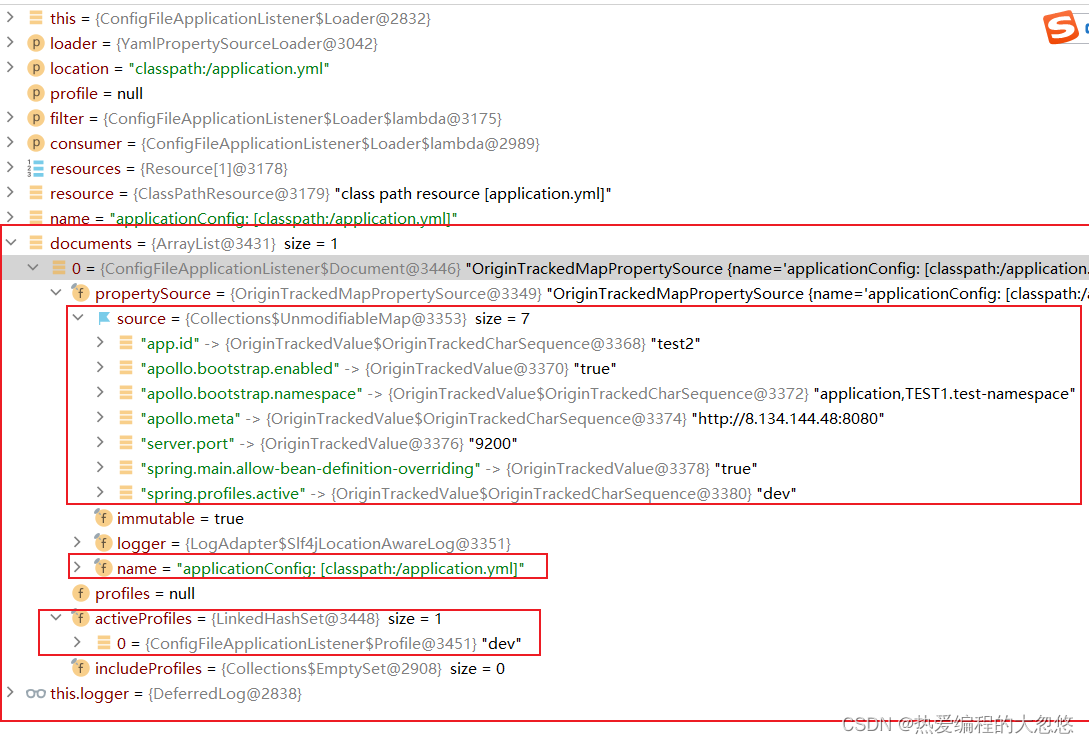
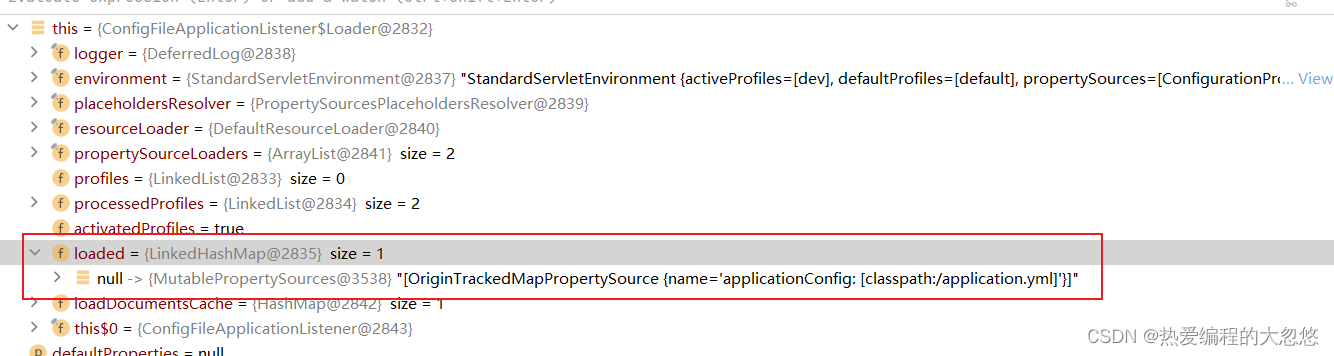
- 配置文件加载完毕后的效果

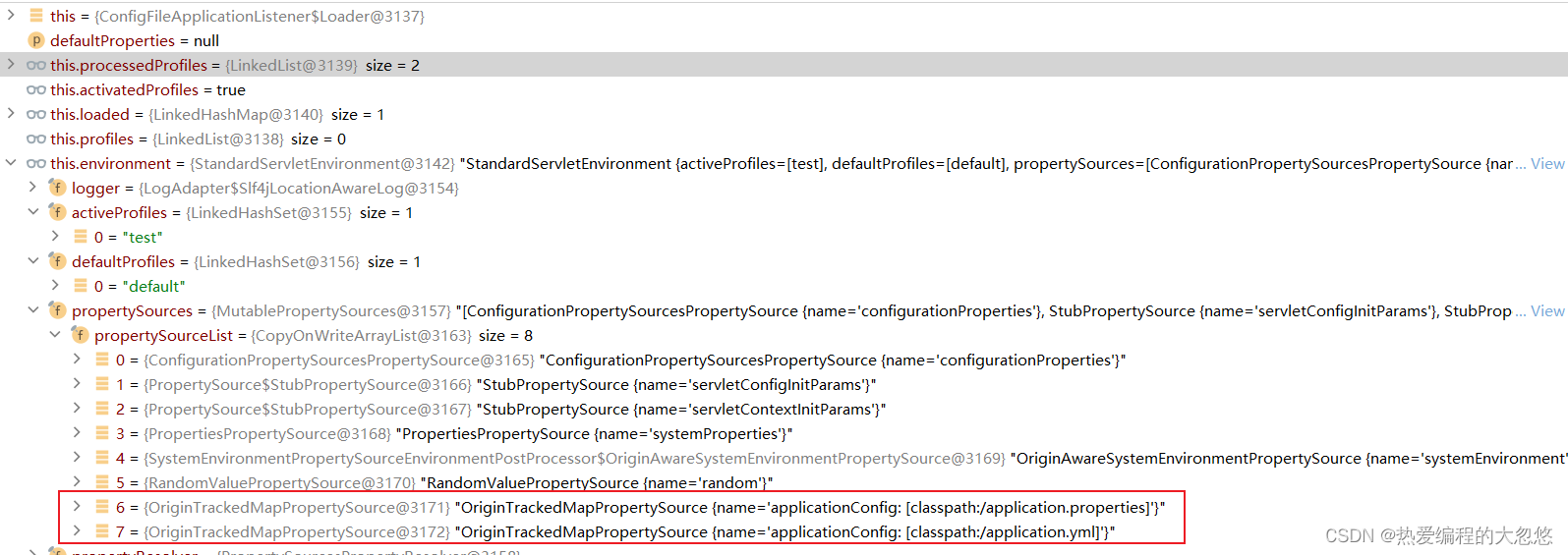
Apollo与SpringBoot整合原理
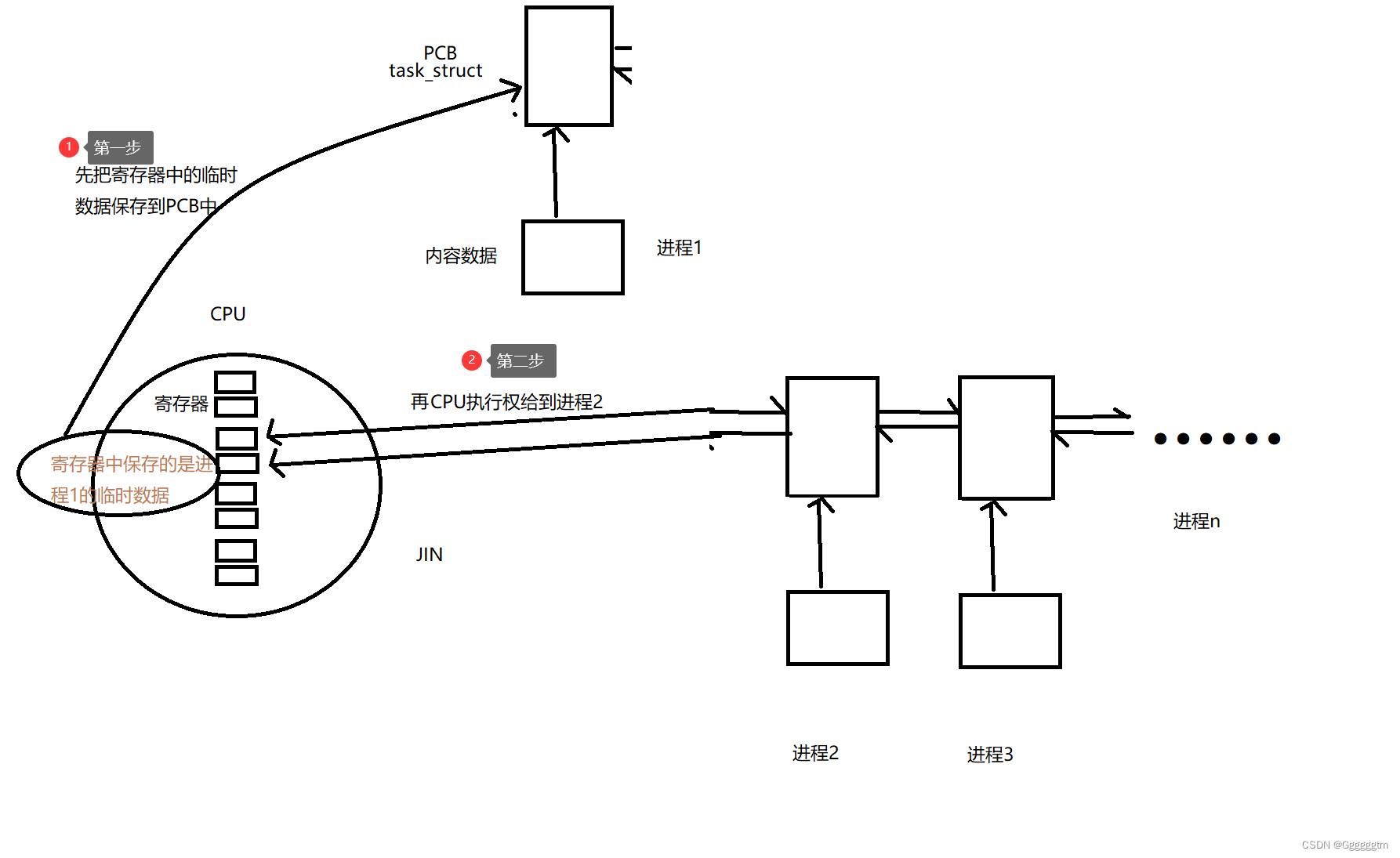
Apollo和Spring/Spring Boot集成的手段:在应用启动阶段,Apollo从远端获取配置,然后组装成PropertySource并插入到第一个即可,如下图所示:
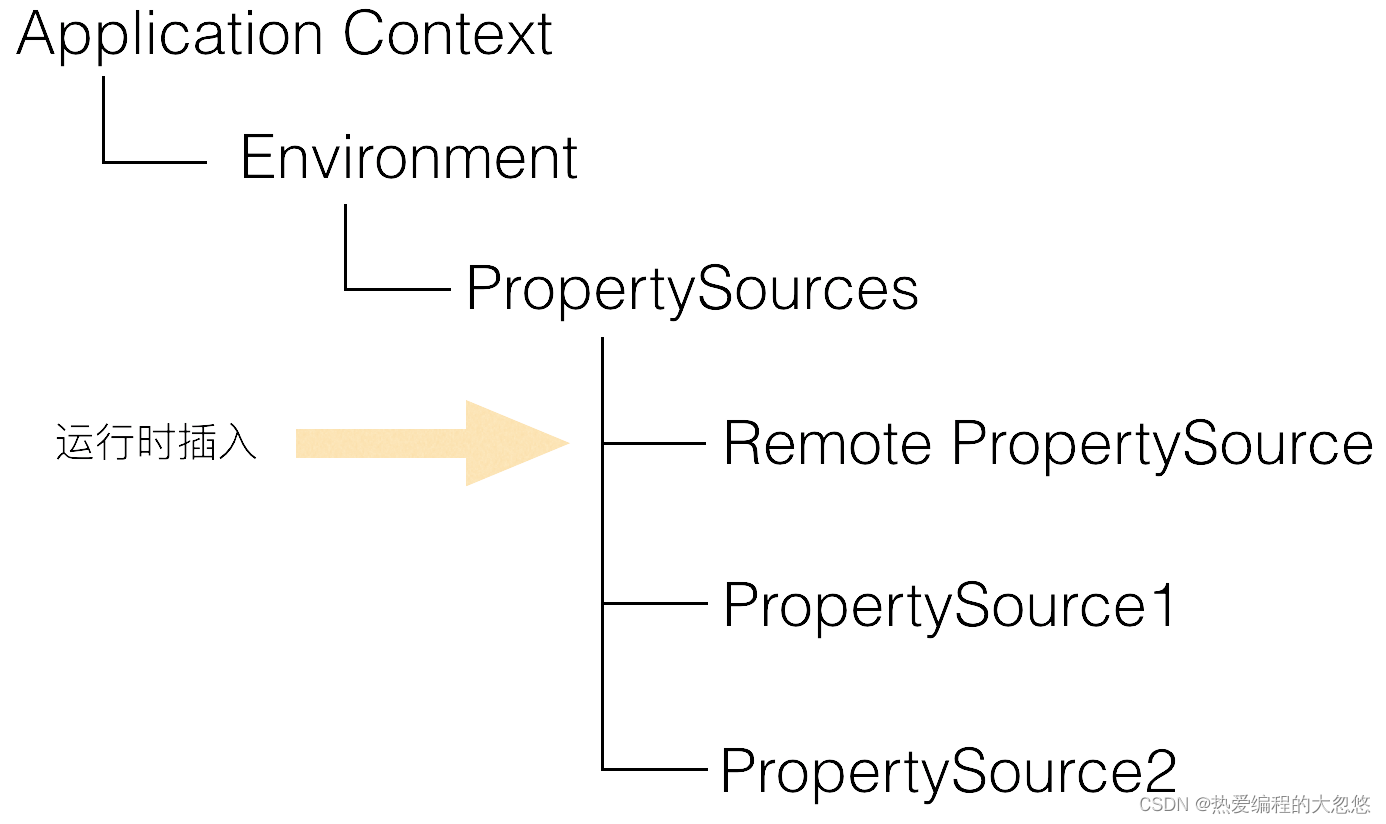
- apollo与spring整合的时候,是如何做到的呢?
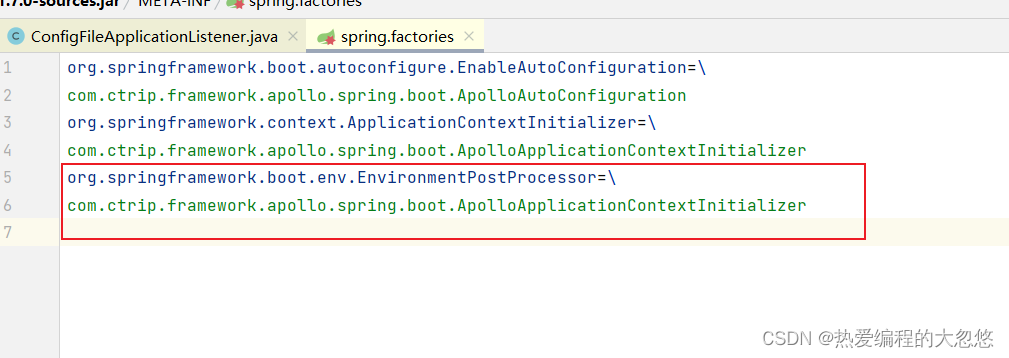
- 还记得上面看到的EnvironmentPostProcessor环境后置处理器嘛? 其实apollo在和Spring整合的时候就是添加了一个EnvironmentPostProcessor
Apollo在最开始的,是通过提供一个ApplicationContextInitializer,在prepareContext方法中会调用ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法,Apollo在此处完成命名空间配置拉取,然后包装成PropertySource加入环境上下文的属性源集合中。
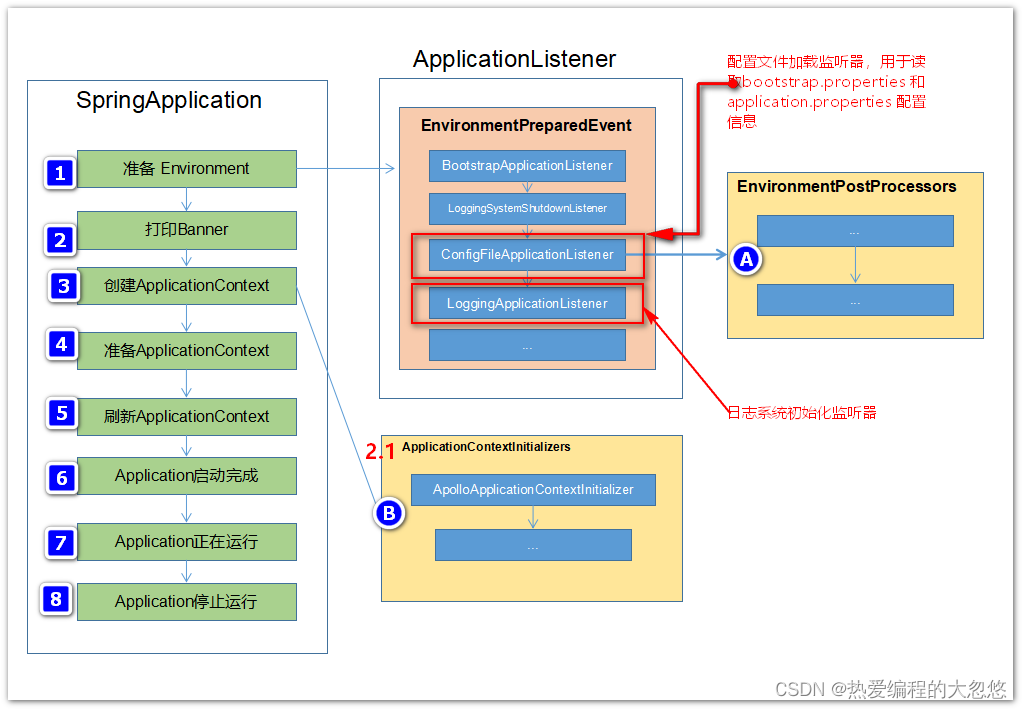
但是问题是加载配置信息的时机比日志系统初始化晚,如果要让logbak-spring.xml文件能够正常读取Apollo的配置,则有两种方案可供选择:
- 方案一:在ConfigFileApplicationListener 和LoggingApplicationListener之间插入一个监听器,用于初始化Apollo 配置信息;
这种方式在SpringBoot模式下想在这两者之间插入一个Listener 有点问题,Spring Boot 会将添加的Listener踢掉,目前还没弄清楚咋回事;另外这种插入方式和Listener的Order顺序有关,写死顺序不是很优雅;
- 方案二:实现一个EnvironmentPostProcessor,供ConfigFileApplicationListener在加载好bootstrap.properties 和application.properties之后加载Apollo的配置信息
这种方式比较好些,添加一个EnvironmentPostProcessor实现,然后在spring.factories里面指定即可
注意:
- 这种方式使得Apollo的加载顺序放到了日志系统加载之前,会导致Apollo的启动过程无法通过日志的方式输出(因为执行Apollo加载的时候,日志系统压根没有准备好呢!所以在Apollo代码中使用Slf4j的日志输出便没有任何内容)
详细参考github上提的pr: 增加EnvironmentPostProcessor处理,将Apollo配置加载提到初始化日志系统之前
- ApolloApplicationContextInitializer–>postProcessEnvironment
/**
* 为了能够尽可能早的在spring加载日志系统之前加载apollo配置,ApolloApplicationContextInitializer的postProcessEnvironment可以在ConfigFileApplicationListener被成功调用后执行
*
* 此时的处理顺序会如下所示:
* Load Bootstrap properties and application properties -----> load Apollo configuration properties ----> Initialize Logging systems
*/
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment configurableEnvironment, SpringApplication springApplication) {
//应始终首先初始化系统属性,例如 app.id --> 先从environment中取出app.id,apollo.meta等值
//设置进System系统属性集合中
initializeSystemProperty(configurableEnvironment);
//apollo.bootstrap.eagerLoad.enabled是否被设置为true
Boolean eagerLoadEnabled = configurableEnvironment.getProperty(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_BOOTSTRAP_EAGER_LOAD_ENABLED, Boolean.class, false);
//EnvironmentPostProcessor should not be triggered if you don't want Apollo Loading before Logging System Initialization
if (!eagerLoadEnabled) {
return;
}
//apollo.bootstrap.enabled属性为true才会启用apollo
Boolean bootstrapEnabled = configurableEnvironment.getProperty(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_BOOTSTRAP_ENABLED, Boolean.class, false);
if (bootstrapEnabled) {
initialize(configurableEnvironment);
}
}
protected void initialize(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
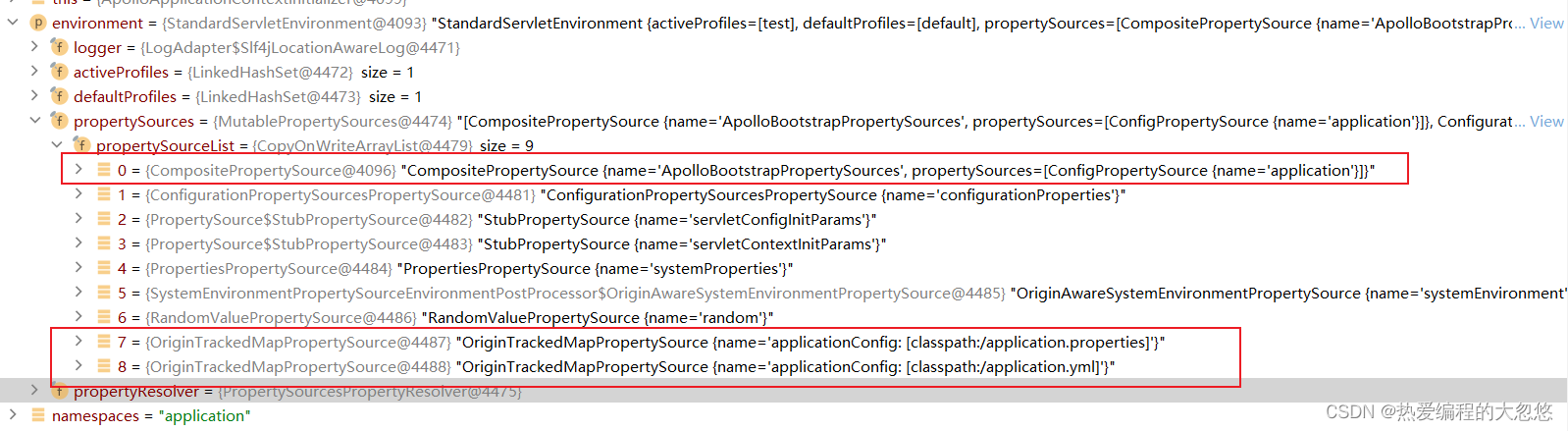
//apollo会向environment中新增一个名为ApolloBootstrapPropertySources的propertysource
if(environment.getPropertySources().contains(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
//already initialized
return;
}
//获取我们配置文件中配置的apollo.bootstrap.namespaces配置,如果没配置,默认加载的命名空间为application
String namespaces = environment.getProperty(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_BOOTSTRAP_NAMESPACES, ConfigConsts.NAMESPACE_APPLICATION);
logger.debug("Apollo bootstrap namespaces: {}", namespaces);
List<String> namespaceList = NAMESPACE_SPLITTER.splitToList(namespaces);
//创建一个名为ApolloBootstrapPropertySources的CompositePropertySource
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
//依次拉取各个命名空间下的配置
for (String namespace : namespaceList) {
Config config = ConfigService.getConfig(namespace);
//每个命名空间下的配置创建一个ConfigPropertySource接收
composite.addPropertySource(configPropertySourceFactory.getConfigPropertySource(namespace, config));
}
//将apollo对应的CompositePropertySource放在environment中PropertySources列表头部
//说明具有最高优先级
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(composite);
}
@Value注解的热更新原理
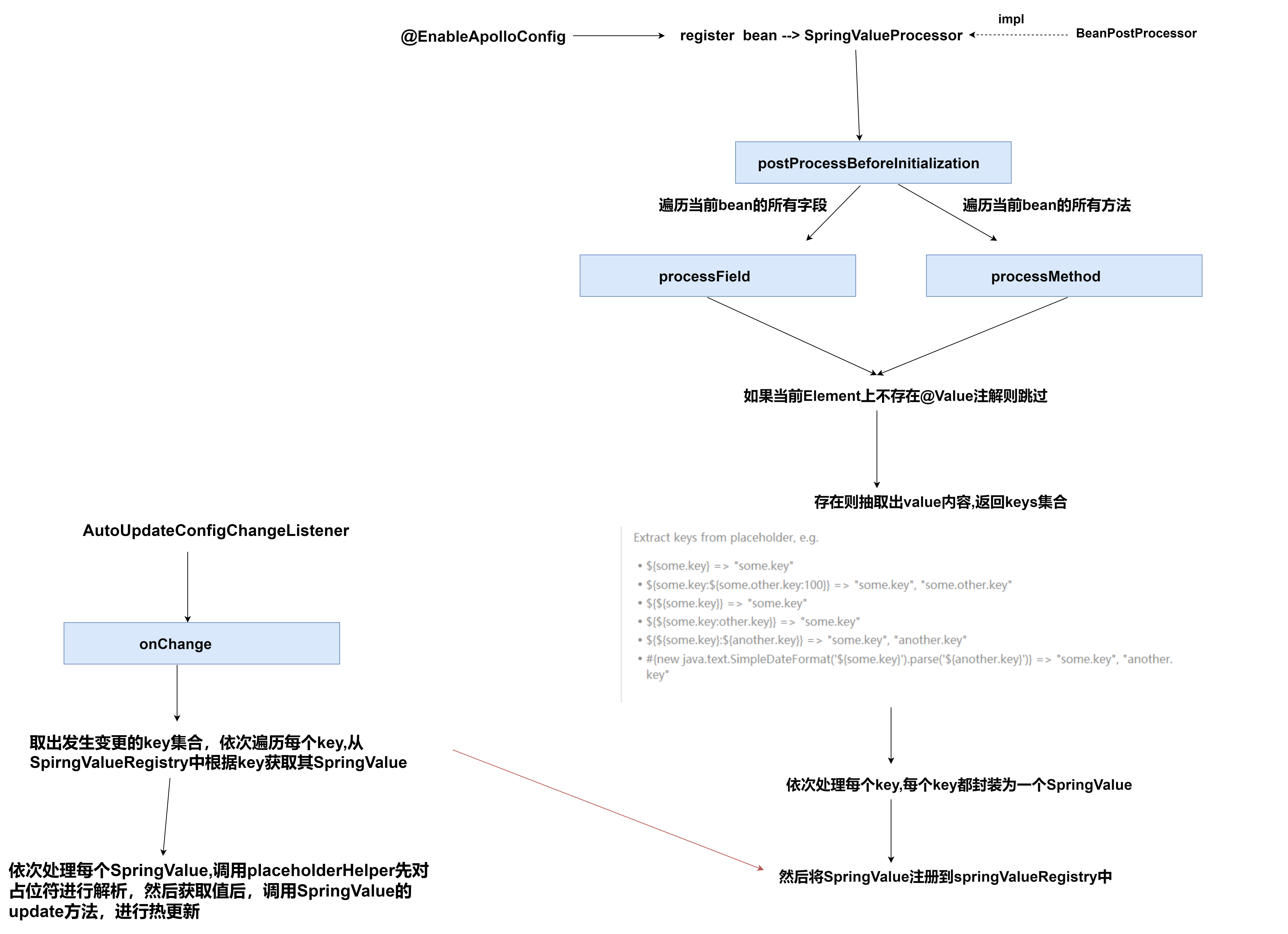
- SpringValue的update方法
public void update(Object newVal) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
if (isField()) {
injectField(newVal);
} else {
injectMethod(newVal);
}
}
private void injectField(Object newVal) throws IllegalAccessException {
Object bean = beanRef.get();
if (bean == null) {
return;
}
boolean accessible = field.isAccessible();
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(bean, newVal);
field.setAccessible(accessible);
}
private void injectMethod(Object newVal)
throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Object bean = beanRef.get();
if (bean == null) {
return;
}
methodParameter.getMethod().invoke(bean, newVal);
}