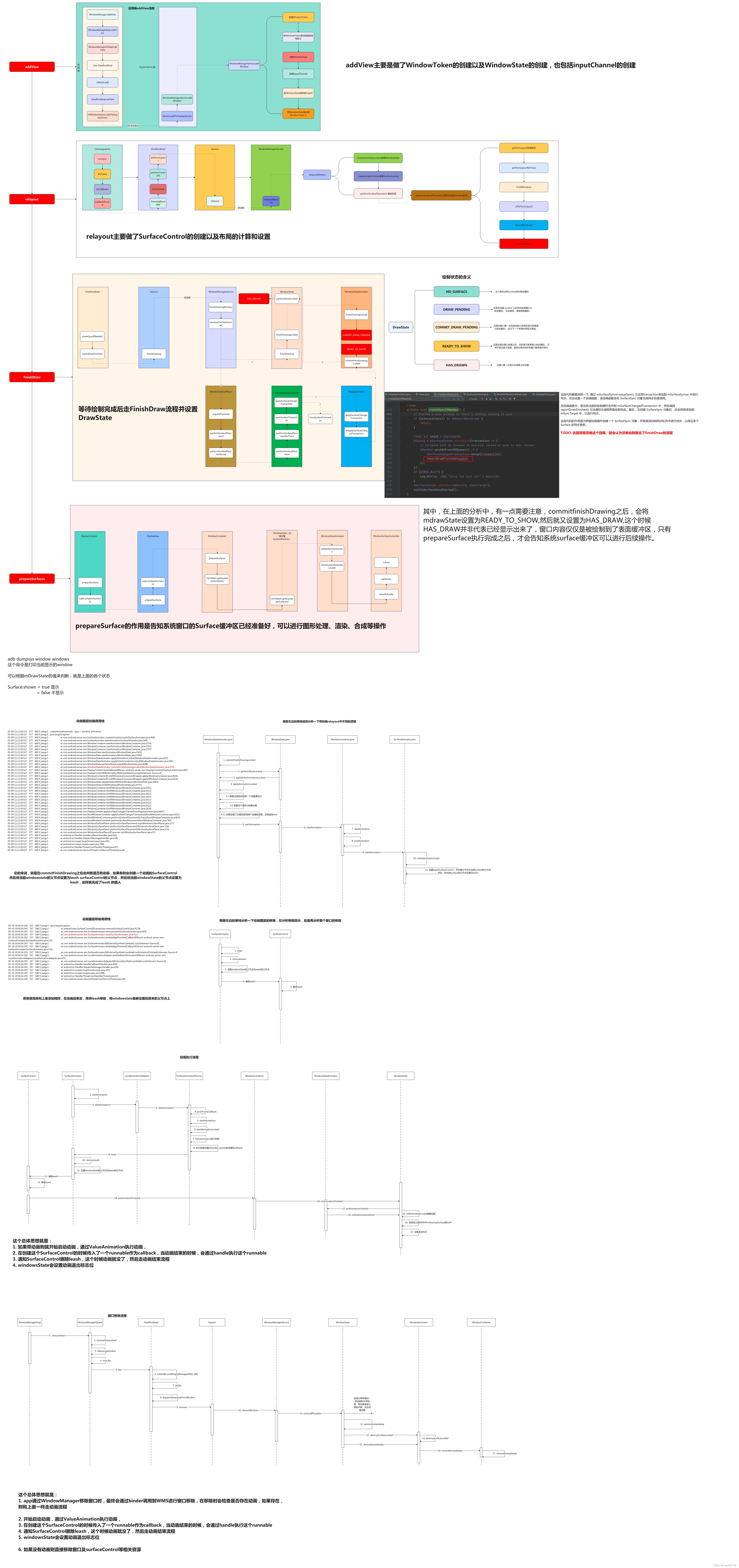
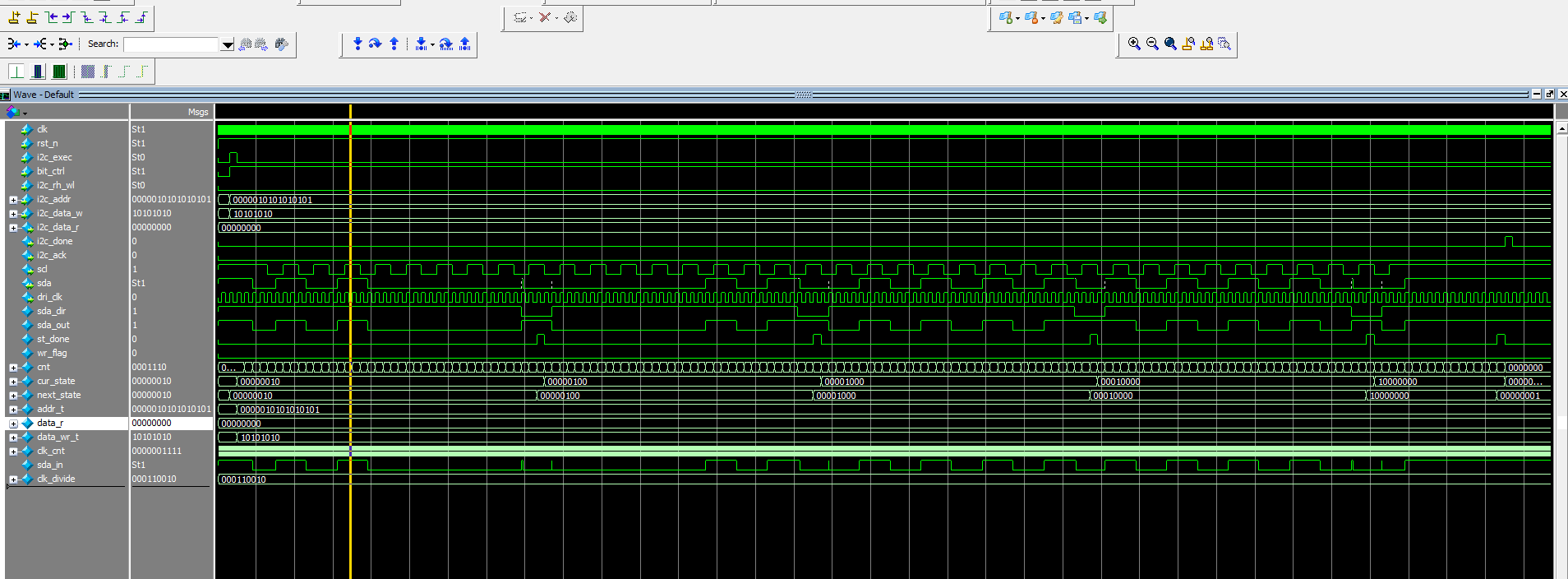
WMS 系统窗口添加流程
文章目录
- WMS 系统窗口添加流程
- 一. addView
- 二. addView代码分析
- 2.1 应用端调用WindowManager的addView
- 2.2 WindowManager的实现类是WindowManagerImpl
- 2.3 WindowManagerGlobal
- 2.4 setView
- 2.4 addToDisplayAsUser(Session.java)
- 2.5 addWindow(WindowManagerService.java)
- 2.6 WindowToken的创建
- 三. relayout
- 3.1 TraversalRunnable
- 3.2 doTraversal
- 3.3 performTraversals
- 3.4 relayoutWindow
- 3.4.1 relayout(Session)
- 3.4.1.1 relayoutWindow(WindowManagerService)
- 3.4.1.2 createSurfaceControl
- 3.4.2 performSurfacePlacement 强制布局
- 四. finishDraw
- 4.1 reportDrawFinished
- 4.2 finishDrawing(Session.java)
- 4.3 finishDrawingWindow(WindowManagerService.java)
- 4.4 WindowState.finishDraw
- 4.5 finishDrawingLocked(WindowStateAnimation.java)
- 4.6 requestTraversal(Windowurfaceplacer.java)
- 4.7 mPerformSurfacePlacement
- 4.8. performSurfacePlacement(WindowSurfacePlacer.java)
- 4.9 performSurfacePlacement
- 4.10 performSurfacePlacementLoop
- 4.11 mRoot.performSurfacePlacement
- 4.12 performSurfacePlacementNoTrace
- 4.13 applySurfaceChangesTransaction
- 4.14 applySurfaceChangesTransaction(DisplayContent)
- 4.15 mApplySurfaceChangesTransaction
- 4.16 commitFinishDrawingLocked(WindowAnimator)
- 4.17 performShowLocked
- 五. prepareSurface
- 5.1 prepareSurfaces
- 5.1.1 prepareSurfaces
- 5.1.2 prepareSurfaces(WindowContainer)
- 5.1.3 prepareSurfaces(WindowState)
- 5.1.4 mWinAnimator.prepareSurfaceLocked
- 5.1.5 showSurfaceRobustlyLocked
- 5.1.6 showRobustly
- 5.1.7 closeSurfaceTransaction
- 六. 高清大图
千里马framework学习笔记
环境: android 13
分析系统窗口添加流程,以悬浮窗为例
整体步骤分为四个,如下:
- addView
- relayout
- finishraw
- prepareurfaces
一. addView
主要流程如下:
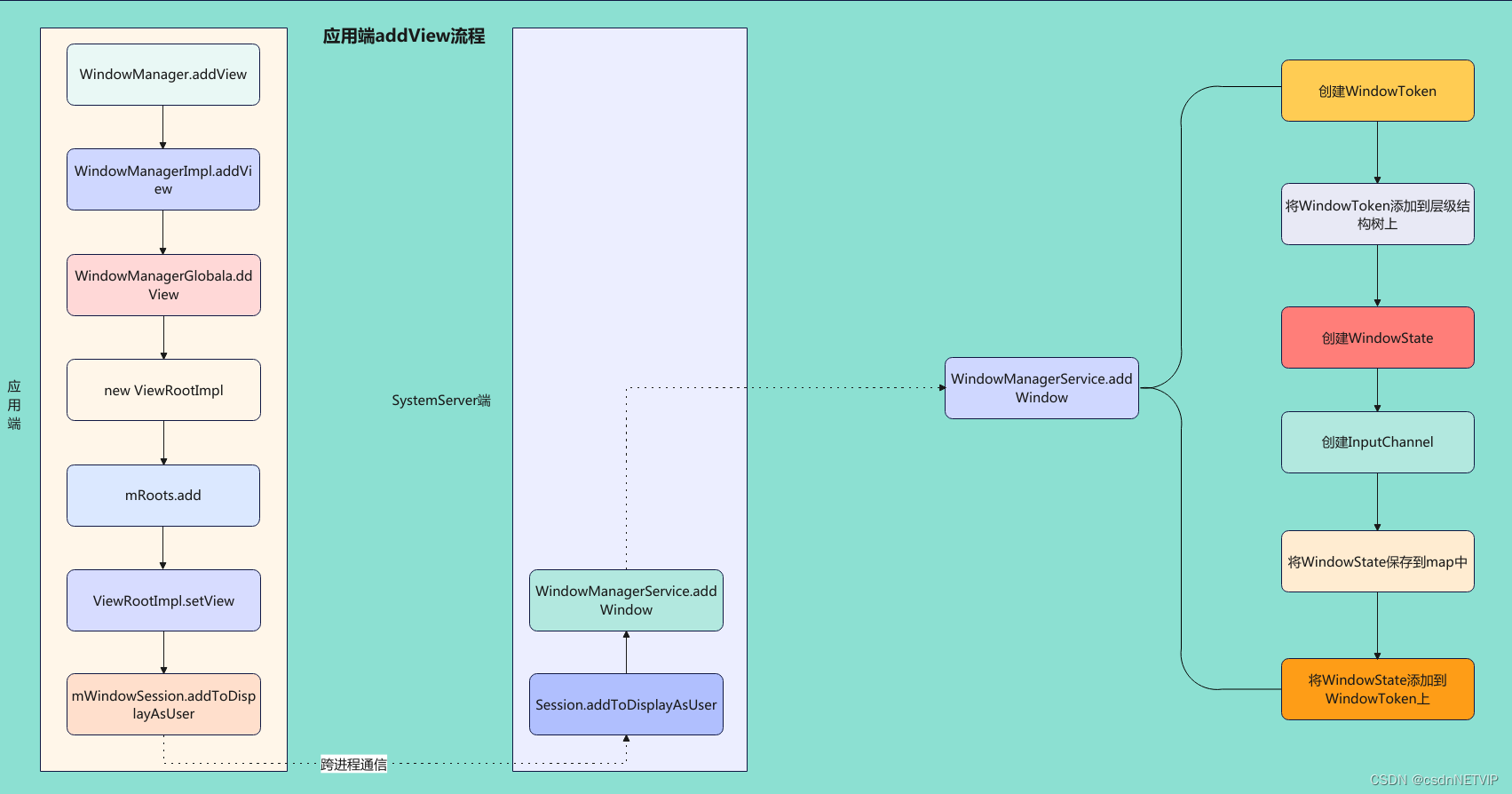
先说结论:addView主要做了什么?
addView 创建了WindowToken以及WindowState
其中也包括InputChannel的创建(事件相关)
二. addView代码分析
2.1 应用端调用WindowManager的addView
WindowManager mWindowManager;
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
mWindowManager.addView(mLayout, mLayoutParams);
2.2 WindowManager的实现类是WindowManagerImpl
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyTokens(params);
// 这里又调用了WindowManagerGlobal的addview
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplayNoVerify(), mParentWindow,
mContext.getUserId());
}
2.3 WindowManagerGlobal
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow, int userId) {
// ... 省略若干容错代码
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
if (parentWindow != null) {
// 一些参数调整
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);
}
// ... 省略一些代码
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
// ... 仅保留主要代码
IWindowSession windowlessSession = null;
if (windowlessSession == null) {
// 创建ViewRootImpl
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
}
// 设置View的参数
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
// 将view保存到一个集合中 ArrayList<View> mViews = new ArrayList<View>();
mViews.add(view);
// 将 root 也添加到集合中 ArrayList<ViewRootImpl> mRoots = new ArrayList<ViewRootImpl>();
mRoots.add(root);
// 将参数也添加到集合中 ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams> mParams = new ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams>();
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
// TODO 重点,这里就是将view添加到WMS中的入口
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView, userId);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
2.4 setView
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView,
int userId) {
synchronized (this) {
// 这里view是不为null的一般
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
// ... 省略部分非主体代码
// 下面就是InputChannel的创建了,这个和事件相关,不在这里分析
InputChannel inputChannel = null;
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
inputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
try {
// 调用session的addToDisplayAsUser将window添加到wms
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId,
mInsetsController.getRequestedVisibilities(), inputChannel, mTempInsets,
mTempControls);
}catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
} finally {
if (restore) {
attrs.restore();
}
}
// ... 省略非主体代码
2.4 addToDisplayAsUser(Session.java)
public int addToDisplayAsUser(IWindow window, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, int userId, InsetsVisibilities requestedVisibilities,
InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState,
InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls) {
// 这里直接调用了WMS的addWindow,Session只是一个代理罢了(binder通信)
return mService.addWindow(this, window, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId, userId,
requestedVisibilities, outInputChannel, outInsetsState, outActiveControls);
}
2.5 addWindow(WindowManagerService.java)
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility,
int displayId, int requestUserId, InsetsVisibilities requestedVisibilities,
InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState,
InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls) {
WindowState parentWindow = null;
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final int type = attrs.type;
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
// 根据displayId获取displayContent,一般为0,手机一般一个屏幕
final DisplayContent displayContent = getDisplayContentOrCreate(displayId, attrs.token);
// ... 省略容错代码
ActivityRecord activity = null;
final boolean hasParent = parentWindow != null;
// 窗口不存在的时候这里是获取不到的
WindowToken token = displayContent.getWindowToken(
hasParent ? parentWindow.mAttrs.token : attrs.token);
// If this is a child window, we want to apply the same type checking rules as the
// parent window type.
final int rootType = hasParent ? parentWindow.mAttrs.type : type;
boolean addToastWindowRequiresToken = false;
final IBinder windowContextToken = attrs.mWindowContextToken;
// 这里一般为null
if (token == null) {
// token的创建,在创建的时候就将它挂载到层级结构树上了
token = new WindowToken.Builder(this, binder, type)
.setDisplayContent(displayContent)
.setOwnerCanManageAppTokens(session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow)
.setRoundedCornerOverlay(isRoundedCornerOverlay)
.build();
}
// windowState的创建
final WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token, parentWindow,
appOp[0], attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid, userId,
session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow);
res = ADD_OKAY;
win.attach();
// 保存window 方便查找 StateHashMap<IBinder, WindowState> mWindowMap = new HashMap<>();
mWindowMap.put(client.asBinder(), win);
// 将windowState添加到windowToken下面
win.mToken.addWindow(win);
}
// ... 省略非主体部分
return res;
}
2.6 WindowToken的创建
protected WindowToken(WindowManagerService service, IBinder _token, int type,
boolean persistOnEmpty, DisplayContent dc, boolean ownerCanManageAppTokens,
boolean roundedCornerOverlay, boolean fromClientToken, @Nullable Bundle options) {
super(service);
token = _token;
windowType = type;
mOptions = options;
mPersistOnEmpty = persistOnEmpty;
mOwnerCanManageAppTokens = ownerCanManageAppTokens;
mRoundedCornerOverlay = roundedCornerOverlay;
mFromClientToken = fromClientToken;
if (dc != null) {
// 这里,将windowToken添加到层级结构树上
dc.addWindowToken(token, this);
}
}
到此为止,addView部分,流程结束
三. relayout
主要流程如下图:
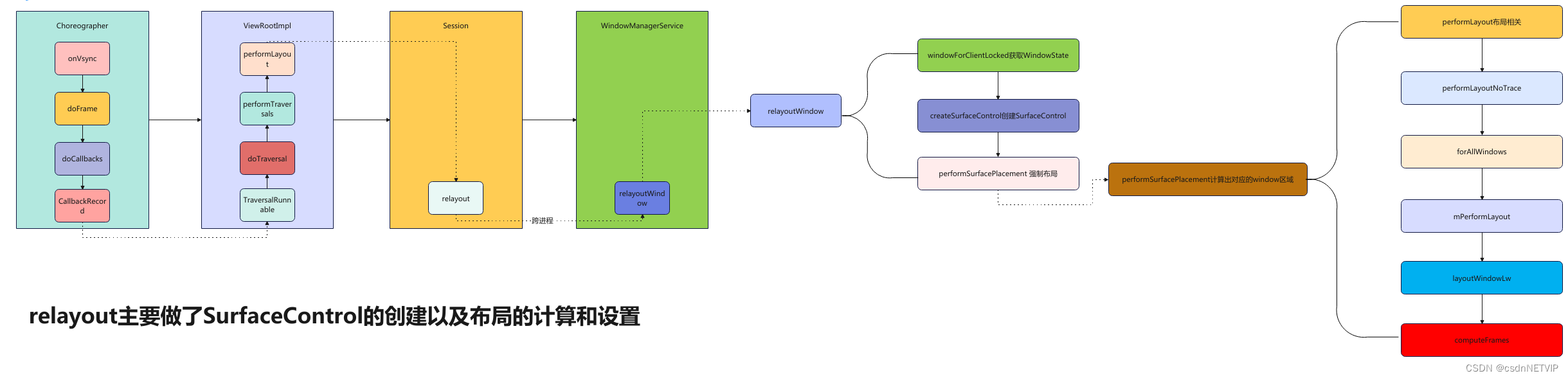
在收到Vsync信号时会执行ViewRootImpl中的TraversalRunnable方法
3.1 TraversalRunnable
// 这是一个runnable,会执行其中的run方法
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// 如上图,执行doTraversal
doTraversal();
}
}
3.2 doTraversal
void doTraversal() {
if (mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = fals;
// 紧接着执行performTraversals,这些方法都是一路调下去的,也没啥好解释的
performTraversals();
}
}
3.3 performTraversals
// 这个方法太长,删除了部分不重要的
private void performTraversals() {
// ... 省略部分代码
// 对window进行布局
relayoutResult = relayoutWindow(params, viewVisibility, insetsPending);
final boolean dragResizing = mPendingDragResizing;
if (mSyncSeqId > mLastSyncSeqId) {
mLastSyncSeqId = mSyncSeqId;
if (DEBUG_BLAST) {
Log.d(mTag, "Relayout called with blastSync");
}
reportNextDraw();
mSyncBuffer = true;
}
// ... 省略部分代码
}
3.4 relayoutWindow
private int relayoutWindow(WindowManager.LayoutParams params, int viewVisibility,
boolean insetsPending) throws RemoteException {
int relayoutResult = 0;
// 获取窗口配置
WindowConfiguration winConfig = getConfiguration().windowConfiguration;
// 根据参数对window布局
relayoutResult = mWindowSession.relayout(mWindow, params,
requestedWidth, requestedHeight, viewVisibility,
insetsPending ? WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_INSETS_PENDING : 0,
mTmpFrames, mPendingMergedConfiguration, mSurfaceControl, mTempInsets,
mTempControls, mRelayoutBundle);
final int maybeSyncSeqId = mRelayoutBundle.getInt("seqid");
if (maybeSyncSeqId > 0) {
mSyncSeqId = maybeSyncSeqId;
}
if (mTranslator != null) {
mTranslator.translateRectInScreenToAppWindow(mTmpFrames.frame);
mTranslator.translateRectInScreenToAppWindow(mTmpFrames.displayFrame);
mTranslator.translateInsetsStateInScreenToAppWindow(mTempInsets);
mTranslator.translateSourceControlsInScreenToAppWindow(mTempControls);
}
mInsetsController.onStateChanged(mTempInsets);
mInsetsController.onControlsChanged(mTempControls);
mPendingAlwaysConsumeSystemBars =
(relayoutResult & RELAYOUT_RES_CONSUME_ALWAYS_SYSTEM_BARS) != 0;
final int transformHint = SurfaceControl.rotationToBufferTransform(
(mDisplayInstallOrientation + mDisplay.getRotation()) % 4);
return relayoutResult;
}
3.4.1 relayout(Session)
public int relayout(IWindow window, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int requestedWidth, int requestedHeight, int viewFlags, int flags,
ClientWindowFrames outFrames, MergedConfiguration mergedConfiguration,
SurfaceControl outSurfaceControl, InsetsState outInsetsState,
InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls, Bundle outSyncSeqIdBundle) {
// 这里又调用到了WMS中的relayoutWindow
int res = mService.relayoutWindow(this, window, attrs,
requestedWidth, requestedHeight, viewFlags, flags,
outFrames, mergedConfiguration, outSurfaceControl, outInsetsState,
outActiveControls, outSyncSeqIdBundle);
return res;
}
3.4.1.1 relayoutWindow(WindowManagerService)
public int relayoutWindow(Session session, IWindow client, LayoutParams attrs,
int requestedWidth, int requestedHeight, int viewVisibility, int flags,
ClientWindowFrames outFrames, MergedConfiguration mergedConfiguration,
SurfaceControl outSurfaceControl, InsetsState outInsetsState,
InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls, Bundle outSyncIdBundle) {
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
// 获取windowState,这就是前面保存起来的windowState
final WindowState win = windowForClientLocked(session, client, false);
final DisplayContent displayContent = win.getDisplayContent();
final DisplayPolicy displayPolicy = displayContent.getDisplayPolicy();
WindowStateAnimator winAnimator = win.mWinAnimator;
if (shouldRelayout) {
// TODO: 重点,创建SrufaceControl
result = createSurfaceControl(outSurfaceControl, result, win, winAnimator);
}
// 强制布局
mWindowPlacerLocked.performSurfacePlacement(true /* force */);
return result;
}
3.4.1.2 createSurfaceControl
private int createSurfaceControl(SurfaceControl outSurfaceControl, int result,
WindowState win, WindowStateAnimator winAnimator) {
// 声明一个本地的变量
WindowSurfaceController surfaceController;
// 开始创建
surfaceController = winAnimator.createSurfaceLocked();
// 如果不为null则创建成功
if (surfaceController != null) {
// 赋值给outSurfaceControl,这个是传出参数,传进来是空的,这里就将重新指向了新创建的surfaceControl
surfaceController.getSurfaceControl(outSurfaceControl);
ProtoLog.i(WM_SHOW_TRANSACTIONS, "OUT SURFACE %s: copied", outSurfaceControl);
}
return result;
}
这个函数执行完,SurfaceControl就创建好了,接着我们往回退
3.4.2 performSurfacePlacement 强制布局
final void performSurfacePlacement(boolean force) {
int loopCount = 6;
do {
mTraversalScheduled = false;
// 这里调用栈很深,可以跟着上面的流程图走一遍
performSurfacePlacementLoop();
mService.mAnimationHandler.removeCallbacks(mPerformSurfacePlacement);
loopCount--;
} while (mTraversalScheduled && loopCount > 0);
mService.mRoot.mWallpaperActionPending = false;
}
到此,relayout也结束了
四. finishDraw
主流程图如下:
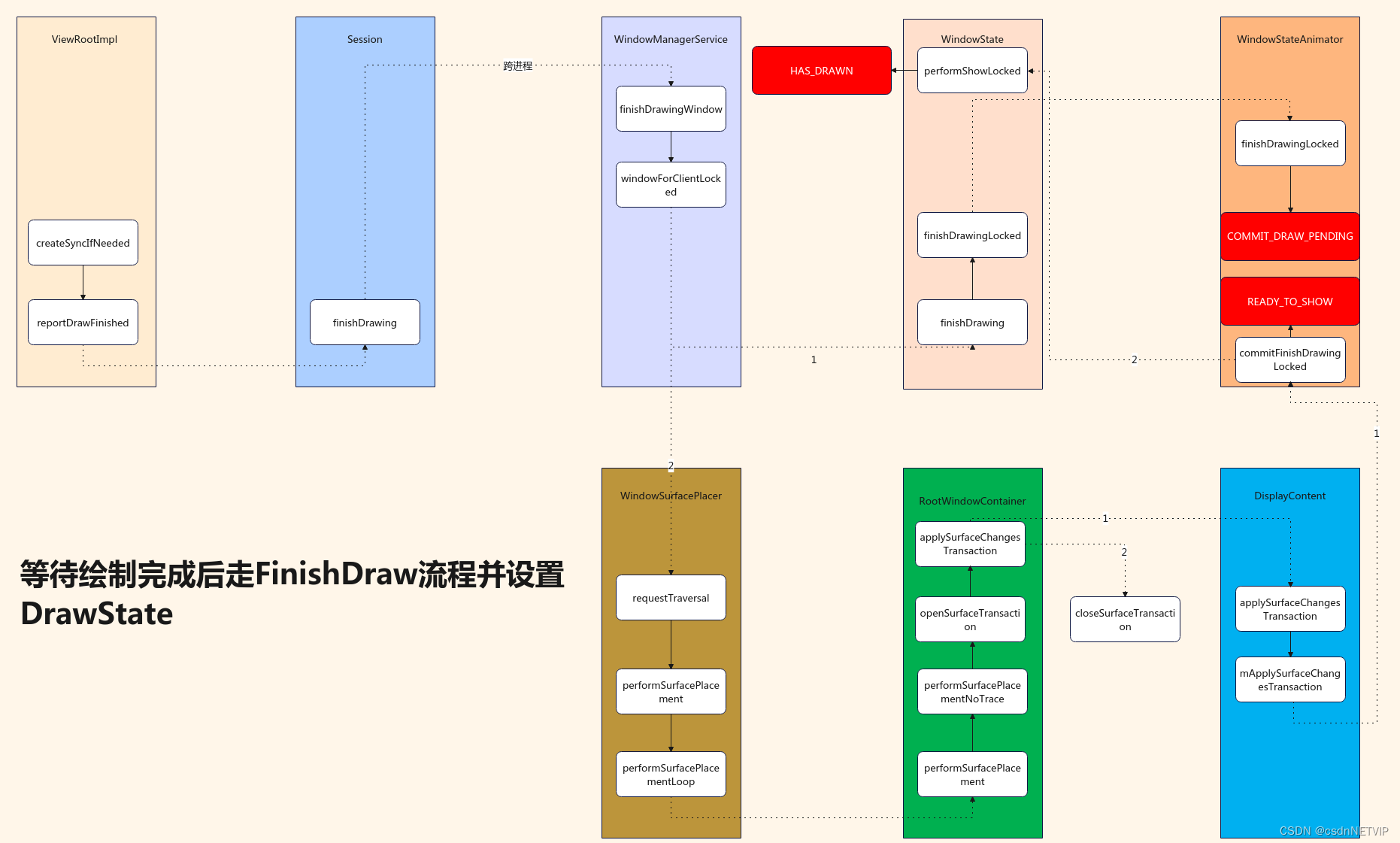
当layout完成之后,wms会通知应用开始绘制,应用端绘制完成之后会告知wms已经绘制完成,wms会将根据状态将surface提交给surfaceflinger进行合成。
其中,绘制状态如下:
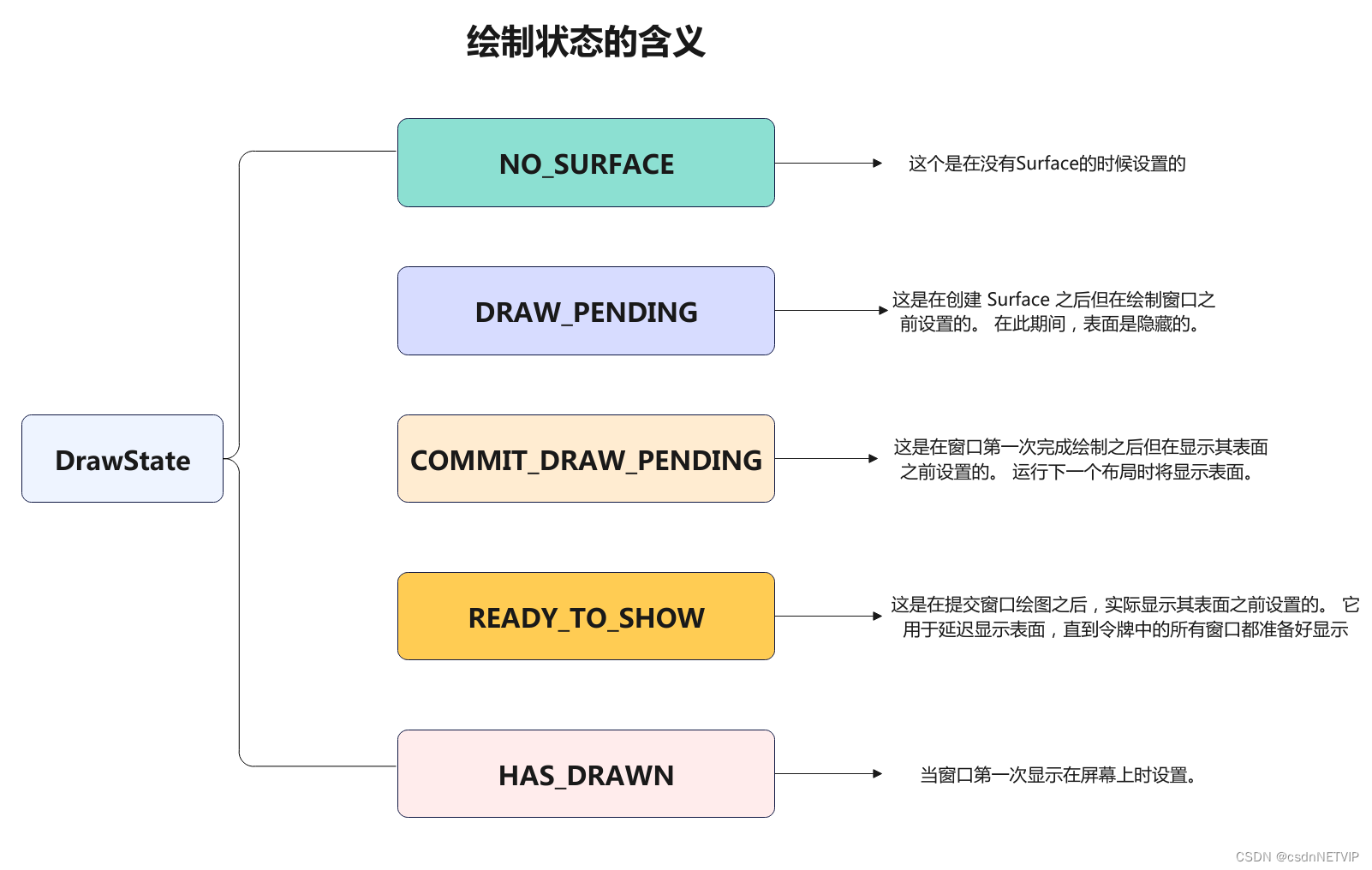
没有surface的时候,处于NO_SURFACE状态,经过relayout后,创建了surfaceControl,就变成了DRAW_PENDING
上面的流程图,其中reportDrawFinished是回调方法,当绘制完成之后会回调到这里,看流程图的时候需要注意,并不是顺序往下调用的。
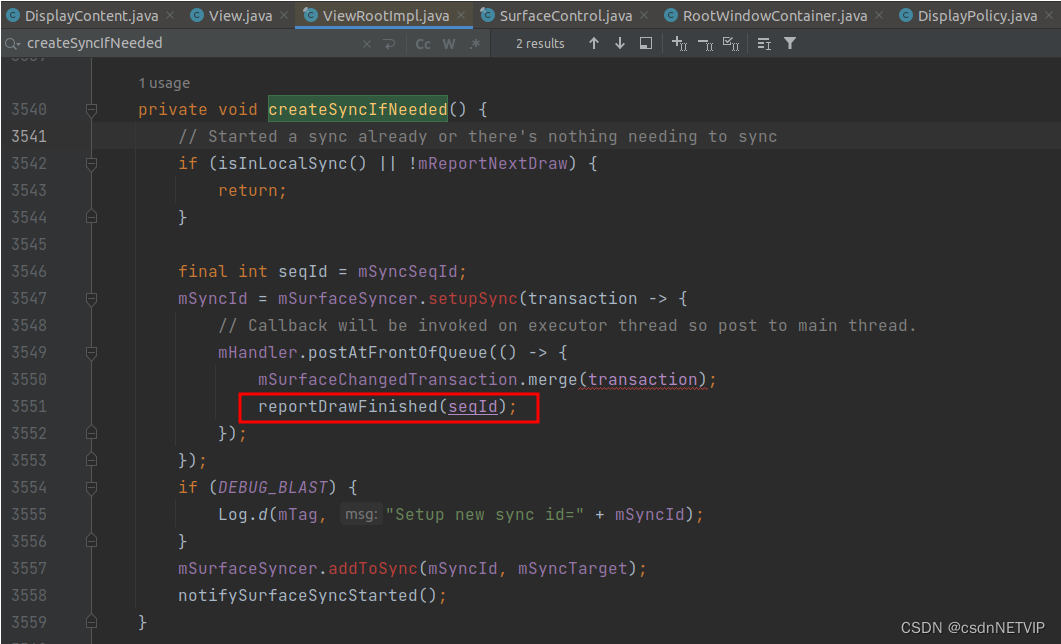
这段代码着重说明一下, 通过 mSurfaceSyncer.setupSync() 方法将transaction添加到 mSurfaceSyncer 中进行同步。还会设置一个回调函数,该回调函数会在 SurfaceSync 对象完成同步后被调用。
在回调函数中,首先将当前的绘制操作合并到 mSurfaceChangedTransaction 中,然后调用 reportDrawFinished() 方法通知主线程界面绘制完成。最后,在创建 SurfaceSync 对象后,还会将其添加到 mSyncTarget 中,以进行同步。
这段代码的作用是为界面绘制操作创建一个 SurfaceSync 对象,并将其添加到同步队列中进行同步,以保证多个 Surface 的同步更新。
TODO: 这里容易忽略这个回调。就会认为没有绘制就走了finishDraw的流程,所以一定记得是绘制完成了才走的这里
4.1 reportDrawFinished
private void reportDrawFinished(int seqId) {
// 调用session的finishDrawing
mWindowSession.finishDrawing(mWindow, mSurfaceChangedTransaction, seqId);
}
4.2 finishDrawing(Session.java)
public void finishDrawing(IWindow window,
@Nullable SurfaceControl.Transaction postDrawTransaction, int seqId) {
// 这里又直接调用了wms的finishDrawingWindow,和上面一样,其实就可以看出来了,Session其实就是应用端和WMS沟通的代理
mService.finishDrawingWindow(this, window, postDrawTransaction, seqId);
}
4.3 finishDrawingWindow(WindowManagerService.java)
void finishDrawingWindow(Session session, IWindow client,
@Nullable SurfaceControl.Transaction postDrawTransaction, int seqId) {
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
// 获得windowstate
WindowState win = windowForClientLocked(session, client, false);
// 调用windowState的finishDrawing
if (win != null && win.finishDrawing(postDrawTransaction, seqId)) {
win.setDisplayLayoutNeeded();
mWindowPlacerLocked.requestTraversal();
}
}
}
4.4 WindowState.finishDraw
boolean finishDrawing(SurfaceControl.Transaction postDrawTransaction, int syncSeqId) {
if (mOrientationChangeRedrawRequestTime > 0) {
// ... 省略
final boolean layoutNeeded =
mWinAnimator.finishDrawingLocked(postDrawTransaction, mClientWasDrawingForSync);
mClientWasDrawingForSync = false;
// We always want to force a traversal after a finish draw for blast sync.
return !skipLayout && (hasSyncHandlers || layoutNeeded);
}
4.5 finishDrawingLocked(WindowStateAnimation.java)
boolean finishDrawingLocked(SurfaceControl.Transaction postDrawTransaction,
boolean forceApplyNow) {
// 前面就知道,当创建完成SurfaceControl之后,DrawState就会变成DRAW_PENDING,这里符合条件
if (mDrawState == DRAW_PENDING) {
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_DRAW,
"finishDrawingLocked: mDrawState=COMMIT_DRAW_PENDING %s in %s", mWin,
mSurfaceController);
if (startingWindow) {
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_STARTING_WINDOW, "Draw state now committed in %s", mWin);
}
// 这里直接赋值为COMMIT_DRAW_PENDING
mDrawState = COMMIT_DRAW_PENDING;
layoutNeeded = true;
}
return layoutNeeded;
}
根据流程图,回到wms
4.6 requestTraversal(Windowurfaceplacer.java)
void requestTraversal() {
// 接下来执行mPerformSurfacePlacement
mService.mAnimationHandler.post(mPerformSurfacePlacement);
}
源码就是这样的,一层一层的,我们只需要关注重点就行,主体流程不需要记忆,这里仅仅是按照源码分析,因为不同的版本,源码会有不同的差异,但主体思想一般不会有大改动。
4.7 mPerformSurfacePlacement
private class Traverser implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
// 执行这个方法
performSurfacePlacement();
}
}
}
4.8. performSurfacePlacement(WindowSurfacePlacer.java)
final void performSurfacePlacement() {
performSurfacePlacement(false /* force */);
}
4.9 performSurfacePlacement
final void performSurfacePlacement(boolean force) {
if (mDeferDepth > 0 && !force) {
mDeferredRequests++;
return;
}
int loopCount = 6;
do {
mTraversalScheduled = false;
// 执行这个,其实和前面都一样了
performSurfacePlacementLoop();
mService.mAnimationHandler.removeCallbacks(mPerformSurfacePlacement);
loopCount--;
} while (mTraversalScheduled && loopCount > 0);
mService.mRoot.mWallpaperActionPending = false;
}
4.10 performSurfacePlacementLoop
private void performSurfacePlacementLoop() {
mService.mRoot.performSurfacePlacement();
}
4.11 mRoot.performSurfacePlacement
void performSurfacePlacement() {
Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "performSurfacePlacement");
try {
// 继续执行这里
performSurfacePlacementNoTrace();
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
}
}
4.12 performSurfacePlacementNoTrace
void performSurfacePlacementNoTrace() {
// 打开一个事物
mWmService.openSurfaceTransaction();
try {
// 执行这个函数
applySurfaceChangesTransaction();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Unhandled exception in Window Manager", e);
} finally {
// 关闭一个事物
mWmService.closeSurfaceTransaction("performLayoutAndPlaceSurfaces");
}
}
4.13 applySurfaceChangesTransaction
private void applySurfaceChangesTransaction() {
final int count = mChildren.size();
for (int j = 0; j < count; ++j) {
final DisplayContent dc = mChildren.get(j);
// 执行这里
dc.applySurfaceChangesTransaction();
}
}
4.14 applySurfaceChangesTransaction(DisplayContent)
void applySurfaceChangesTransaction() {
// 执行 mApplySurfaceChangesTransaction
forAllWindows(mApplySurfaceChangesTransaction, true /* traverseTopToBottom */);
}
4.15 mApplySurfaceChangesTransaction
private final Consumer<WindowState> mApplySurfaceChangesTransaction = w -> {
// 执行这里
final boolean committed = winAnimator.commitFinishDrawingLocked();
};
4.16 commitFinishDrawingLocked(WindowAnimator)
boolean commitFinishDrawingLocked() {
// TODO 这里将状态修改为READY_TO_SHOW
mDrawState = READY_TO_SHOW;
boolean result = false;
final ActivityRecord activity = mWin.mActivityRecord;
if (activity == null || activity.canShowWindows()
|| mWin.mAttrs.type == TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING) {
// 对于系统窗口来讲,会走这里
result = mWin.performShowLocked();
}
return result;
}
4.17 performShowLocked
boolean performShowLocked() {
// 赋值状态为HAS_DRAWN
mWinAnimator.mDrawState = HAS_DRAWN;
return true;
}
其中,在上面的分析中,有一点需要注意,commitfinishDrawing之后,会将mdrawState设置为READY_TO_SHOW,然后就又设置为HAS_DRAW,这个时候HAS_DRAW并非代表已经显示出来了,窗口内容仅仅是被绘制到了表面缓冲区,只有prepareSurface执行完成之后,才会告知系统surface缓冲区可以进行后续操作。
五. prepareSurface
主流程如下图:
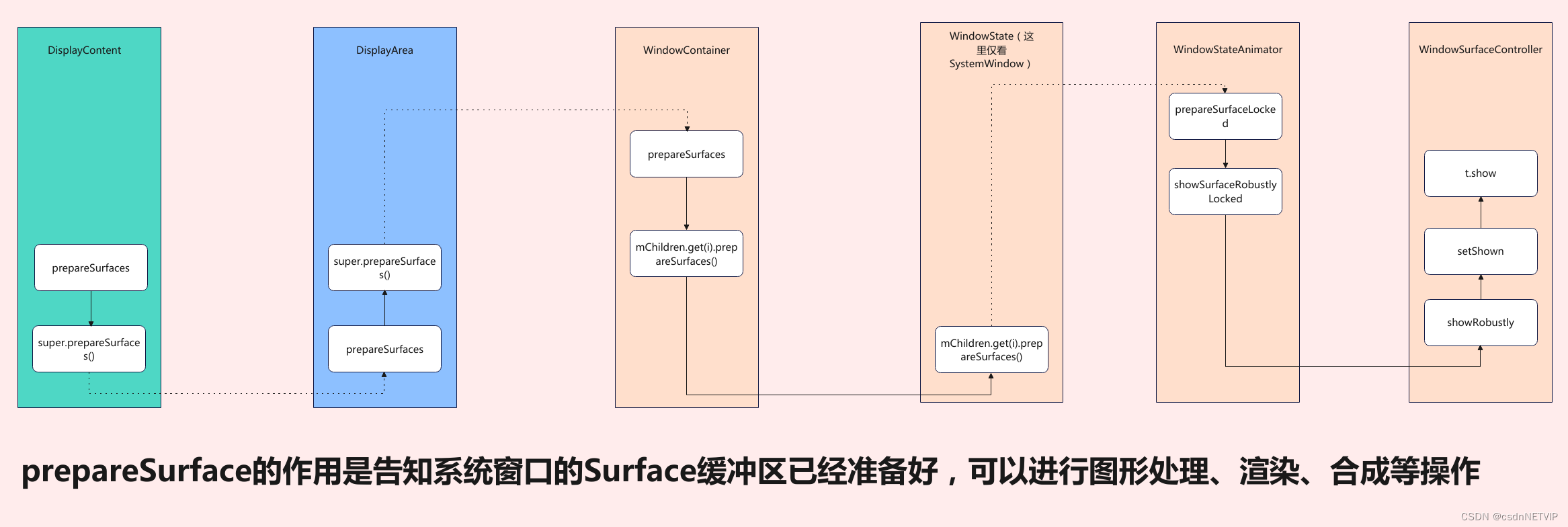
5.1 prepareSurfaces
在HAS_DRAW之后,回到前面的commitfinishDrawing之后的逻辑
void prepareSurfaces() {
try {
final Transaction transaction = getPendingTransaction();
// 执行父类的prepareSurfaces
super.prepareSurfaces();
// TODO: Once we totally eliminate global transaction we will pass transaction in here
// rather than merging to global.
SurfaceControl.mergeToGlobalTransaction(transaction);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
}
}
5.1.1 prepareSurfaces
void prepareSurfaces() {
mDimmer.resetDimStates();
// 继续prepareSurfaces
super.prepareSurfaces();
}
5.1.2 prepareSurfaces(WindowContainer)
void prepareSurfaces() {
// If a leash has been set when the transaction was committed, then the leash reparent has
// been committed.
mCommittedReparentToAnimationLeash = mSurfaceAnimator.hasLeash();
for (int i = 0; i < mChildren.size(); i++) {
// 执行mChildren的prepareSurfaces
mChildren.get(i).prepareSurfaces();
}
}
5.1.3 prepareSurfaces(WindowState)
void prepareSurfaces() {
// 执行这里
mWinAnimator.prepareSurfaceLocked(getSyncTransaction());
super.prepareSurfaces();
}
5.1.4 mWinAnimator.prepareSurfaceLocked
void prepareSurfaceLocked(SurfaceControl.Transaction t) {
final WindowState w = mWin;
if (!hasSurface()) {
// There is no need to wait for an animation change if our window is gone for layout
// already as we'll never be visible.
if (w.getOrientationChanging() && w.isGoneForLayout()) {
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION, "Orientation change skips hidden %s", w);
w.setOrientationChanging(false);
}
return;
}
computeShownFrameLocked();
if (w.isParentWindowHidden() || !w.isOnScreen()) {
hide(t, "prepareSurfaceLocked");
mWallpaperControllerLocked.hideWallpapers(w);
// If we are waiting for this window to handle an orientation change. If this window is
// really hidden (gone for layout), there is no point in still waiting for it.
// Note that this does introduce a potential glitch if the window becomes unhidden
// before it has drawn for the new orientation.
if (w.getOrientationChanging() && w.isGoneForLayout()) {
w.setOrientationChanging(false);
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION,
"Orientation change skips hidden %s", w);
}
} else if (mLastAlpha != mShownAlpha
|| mLastHidden) { // 窗口在没有显示之前都是隐藏的,创建surface的时候置位true
mLastAlpha = mShownAlpha;
ProtoLog.i(WM_SHOW_TRANSACTIONS,
"SURFACE controller=%s alpha=%f HScale=%f, VScale=%f: %s",
mSurfaceController, mShownAlpha, w.mHScale, w.mVScale, w);
boolean prepared =
mSurfaceController.prepareToShowInTransaction(t, mShownAlpha); // 设置一下alpha
if (prepared && mDrawState == HAS_DRAWN) {
if (mLastHidden) {
// 执行这里
if (showSurfaceRobustlyLocked(t))
}
}
}
5.1.5 showSurfaceRobustlyLocked
private boolean showSurfaceRobustlyLocked(SurfaceControl.Transaction t) {
// 执行showRobustly
boolean shown = mSurfaceController.showRobustly(t);
}
5.1.6 showRobustly
boolean showRobustly(SurfaceControl.Transaction t) {
// 这里就告诉系统我们已经可以显示了
t.show(mSurfaceControl);
return true;
}
5.1.7 closeSurfaceTransaction
关闭事物
六. 高清大图