文章目录
- 一、线程的状态
- 二、线程的常见属性
- 三、多线程编程
- Thread类常用构造方法
- 1.继承Thread类
- 2.实现Runnable接口
- 3.匿名内部类实现
- 4.lambda 表达式创建 Runnable 子类对象
- 四、线程的常见方法
一、线程的状态
//线程的状态是一个枚举类型 Thread.State
public class ThreadState {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Thread.State state : Thread.State.values()) {
System.out.println(state);
}
}
}
- NEW: 安排了工作, 还未开始行动
- RUNNABLE: 可工作的. 又可以分成正在工作中和即将开始工作.
- BLOCKED: 这几个都表示排队等着其他事情
- WAITING: 这几个都表示排队等着其他事情
- TIMED_WAITING: 这几个都表示排队等着其他事情
- TERMINATED: 工作完成了.
二、线程的常见属性
| 属性 | 获取方法 |
|---|---|
| ID | getId() |
| 名称 | getName() |
| 状态 | getState() |
| 优先级 | getPriority() |
| 是否后台线程 | isDaemon() |
| 是否存活 | isAlive() |
| 是否被中断 | isInterrupted() |
三、多线程编程
常见的多线程实现的方法有不下七种,我们这里介绍继承Thread类以及实现Runnable接口实现,我们接下来逐一介绍
Thread类常用构造方法
- Thread() // 创建线程对象
- Thread(Runnable target) //使用 Runnable 对象创建线程对象
- Thread(String name) //创建线程对象,并命名
1.继承Thread类
首先我们要清楚在Java代码中main方法可以认为是主线程
//通过继承Thread类来实现一个线程类
class MyThread extends Thread {
private int sum = 0;
public MyThread (int sum){
this.sum = sum;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("hello Thread"+sum);
}
}
}
public class Text1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化线程类对象
MyThread t1 = new MyThread(1);
//通过start来启动t线程,自动执行重写的run方法
t1.start();
//实例化线程类对象
MyThread t2 = new MyThread(2);
//通过start来启动t线程,自动执行重写的run方法
t2.start();
}
}
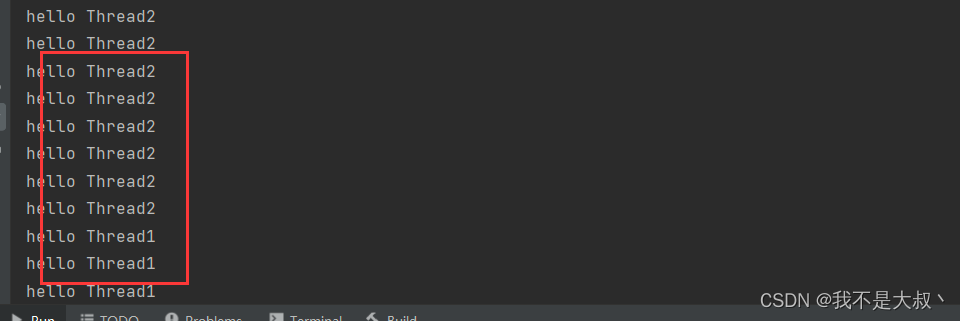
线程之间是并发执行的,因此我们打印的结果时而为2,时而为1,如下图:
2.实现Runnable接口
//实现 Runnable 接口
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
private int sum = 0;
public MyRunnable (int sum){
this.sum = sum;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("hello Thread"+sum);
}
}
}
public class Text2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建 Thread 类实例, 调用 Thread 的构造方法时将 Runnable 对象作为 target 参数
Thread t1 = new Thread(new MyRunnable(1));
Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyRunnable(2));
//调用t线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
3.匿名内部类实现
// 使用匿名类创建 Thread 子类对象
public class Text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("hello t1");
}
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("hello t2");
}
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
- 匿名内部类创建 Runnable 子类对象也是类似
4.lambda 表达式创建 Runnable 子类对象
//利用lambda表达式
public class Text4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
System.out.println("Thread t1");
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
System.out.println("Thread t2");
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
注:我们在日常生活中最常用的就是以lambda表达式实现的多线程编程
四、线程的常见方法
常见方法大概有:
- 启动线程:start()
- 等待线程:join()
- 获取线程引用:currentThread()
- 休眠线程:sleep(long millis)
- 线程中断: interrupt()、共享标记
简要说明:
1.调用start方法会直接运行我们创建的线程对象重写\实现的run方法
2.调用join方法的时候,会把该线程对象的优先级提高,先将该线程执行结束才会进行执行另一个线程
3.join方法可以带参数(long millis),意在表明只等待该线程一定时间,时间到优先级恢复,与其他线程同时执行
4.sleep方法目的是让线程暂停一定的时间再继续执行
5.线程中断我们后续会详细介绍,以及以上方法的进一步使用也会在后续详细介绍