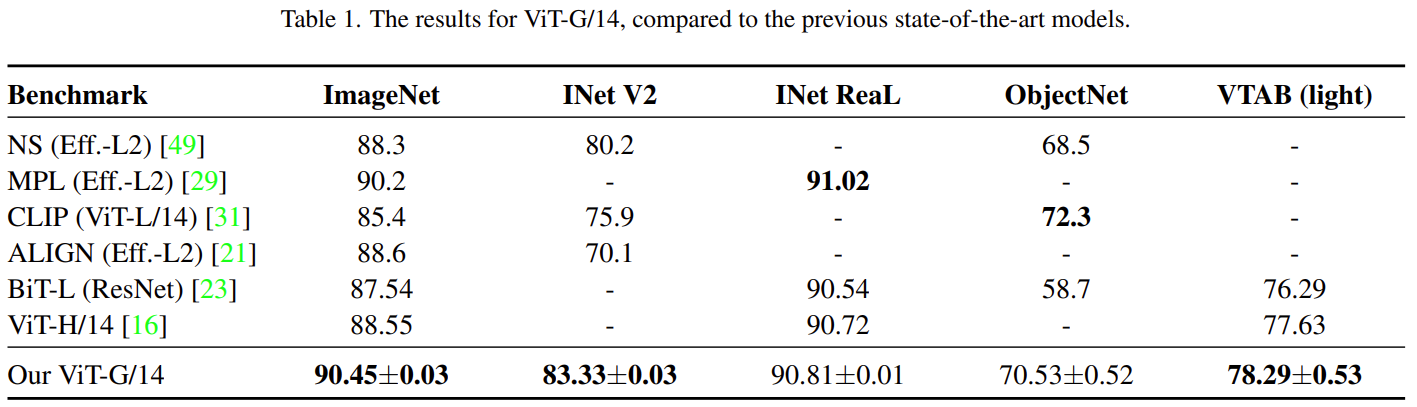
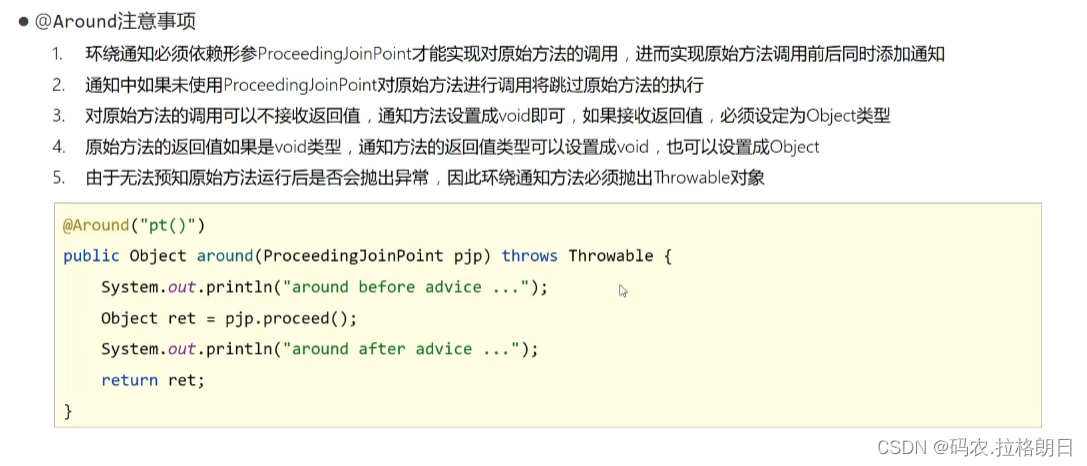
前言
*.properties文件,是 Java 支持的一种配置文件类型,并且 Java 提供了 properties 类来读取 properties 文件中的信息。文件中以键值对 "键=值"的形式,存储工程中会多次重复使用的配置信息,通过“Properties”类来读取这些信息,以实现“一次编写,多处调用;需要修改配置文件时,只修改一处即可”的效果。
本文介绍【读写 properties 文件】,【追加数据】,【实现有序读写】,【解决中文乱码】问题。
正文
一、Properties 类简介
Properties有一个特殊的作用,专门用来加载xxx.properties配置文件。Properties继承于Hashtable,表示了一个持久的属性集,可保存在流中或从流中加载。属性列表中,每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
- 常用方法:
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| public String getProperty(String key) | 用指定的键在此属性列表中搜索属性 |
| public Object setProperty(String key,String value) | 向Properties中增加属性,有则覆盖,没有则新增 |
| public void load(InputStream in) | 从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对) |
| public void load(Reader reader) | 按简单的面向行的格式从输入字符流中读取属性列表(键和元素对) |
| public void store(OutputStream out, String comments) | 将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出流 |
| public void store(Writer writer, String comments) | 将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出字符 |
二、读写 properties 文件
由于Properties继承于Hashtable,所以,当新增属性写入到 .properties 文件的时候,结果显示的顺序可能并不是我们当初set属性的顺序。这个问题要注意,我们再后面会解决。
- Properties继承于Hashtable

- 借助IO流,利用Properties类操作.properties文件
// .properties文件的相对路径
private static final String FILE_ADDRESS = "src/main/resources/application.properties";
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
log.info("test 接口调用:【开始】 --------------------");
this.writeIntoText(new Properties());
Properties prop = this.readFromText();
log.info("jdbc.username = " + properties.getProperty("jdbc.username"));
log.info("test 接口调用:【结束】 --------------------");
return "success";
}
/**
* 模拟向 properties 文件写入数据
*/
private void writeIntoText(Properties properties){
OutputStream output = null;
try {
output = new FileOutputStream(FILE_ADDRESS);
properties.setProperty("jdbc.driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
properties.setProperty("jdbc.url", "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf8");
properties.setProperty("jdbc.username", "root");
properties.setProperty("jdbc.password", "123456");
properties.store(output, "tjm modify");
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (output != null) {
try {
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 读取 properties 文件,返回 Properties 对象
*/
private Properties readFromText(){
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream input = null;
try {
input = new FileInputStream(FILE_ADDRESS);
properties.load(input);
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (input != null) {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return properties;
}- 运行上述代码会产生几个问题:
- 顺序是无序的,或者说是hash排序的,并不是set的顺序;
- 每次write,properties文件的数据都会被覆盖掉,只展示最新数据;
- 如果value里面包含中文,那一定会是乱码;
下面,我们就以此解决这几个问题。
三、解决追加、有序、乱码问题
2.1 实现有序读写
自定义一个PropertiesUtil类,该类继承自Properties。PropertiesUtil提供一个返回由key按照存入顺序组成的List的方法,getKeyList(),这样就可以解决有序写的问题。至于读嘛,也是一样的道理。
- 如何保证getKeyList()方法返回的就是有序的key组成的集合?
通过查询Properties方法的源码,发现:Properties.load()方法从.properties文件加载内容时,是按照文件顺序进行读取,而Properties.setProperty()方法底层调用的是父类HashTable.put()方法进行储存。
HashTable本身就是无序的,所以,解决办法就是让PropertiesUtil持有一个私有的可以有序存储key的集合,然后重写父类的put()方法,在方法体中照常通过super.put()进行属性的存储,同时将key添加到存储key的集合中。
再查源码,发现: Properties将当前对象的内容存放到指定的输出流的方法又2个,save()和store(),但是它们的底层逻辑都是一样的,都是通过调用Properties.keys()方法获取一个Enumeration,然后对该Enumeration进行遍历,依次将对应的key和value写入到输出流中。要保证写入是有序的,就要保证遍历keys()方法返回的Enumeration取出的元素key是有序的。
所以,得到最终的解决方法是:重写keys()方法,保证遍历Enumeration得到的key是有序的。

- PropertiesUtil类的完整代码如下:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @Description: Java Punk
* @Created: by JavaPunk on 2023/5/10 16:33
* @Version: 1.0.0
*/
public class PropertiesUtil extends Properties {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private List<Object> keyList = new ArrayList<Object>();
/**
* 默认构造方法
*/
public PropertiesUtil() {
}
/**
* 从指定路径加载信息到Properties
* @param path
*/
public PropertiesUtil(String path) {
try {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(path);
this.load(is);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("指定文件不存在!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 重写put方法,按照property的存入顺序保存key到keyList,遇到重复的后者将覆盖前者。
*/
@Override
public synchronized Object put(Object key, Object value) {
this.removeKeyIfExists(key);
keyList.add(key);
return super.put(key, value);
}
/**
* 重写remove方法,删除属性时清除keyList中对应的key。
*/
@Override
public synchronized Object remove(Object key) {
this.removeKeyIfExists(key);
return super.remove(key);
}
/**
* keyList中存在指定的key时则将其删除
*/
private void removeKeyIfExists(Object key) {
keyList.remove(key);
}
/**
* 获取Properties中key的有序集合
* @return
*/
public List<Object> getKeyList() {
return keyList;
}
/**
* 保存Properties到指定文件,默认使用UTF-8编码
* @param path 指定文件路径
*/
public void store(String path) {
this.store(path, "UTF-8");
}
/**
* 保存Properties到指定文件,并指定对应存放编码
* @param path 指定路径
* @param charset 文件编码
*/
public void store(String path, String charset) {
if (path != null && !"".equals(path)) {
try {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(path);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(os, charset));
this.store(bw, null);
bw.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("存储路径不能为空!");
}
}
/**
* 重写keys方法,返回根据keyList适配的Enumeration,且保持HashTable keys()方法的原有语义,
* 每次都调用返回一个新的Enumeration对象,且和之前的不产生冲突
*/
@Override
public synchronized Enumeration<Object> keys() {
return new EnumerationAdapter<Object>(keyList);
}
/**
* List到Enumeration的适配器
*/
private class EnumerationAdapter<T> implements Enumeration<T> {
private int index = 0;
private final List<T> list;
private final boolean isEmpty;
public EnumerationAdapter(List<T> list) {
this.list = list;
this.isEmpty = list.isEmpty();
}
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
// isEmpty的引入是为了更贴近HashTable原有的语义,在HashTable中添加元素前调用其keys()方法获得一个Enumeration的引用,
// 之后往HashTable中添加数据后,调用之前获取到的Enumeration的hasMoreElements()将返回false,但如果此时重新获取一个
// Enumeration的引用,则新Enumeration的hasMoreElements()将返回true,而且之后对HashTable数据的增、删、改都是可以在
// nextElement中获取到的。
return !isEmpty && index < list.size();
}
public T nextElement() {
if (this.hasMoreElements()) {
return list.get(index++);
}
return null;
}
}
}2.2 实现数据追加
在上面【读写 properties 文件】中简单介绍了写入的方法,因为每次都会 new Properties(),所以每次都会把源数据全部覆盖掉。清楚了原因,自然也就找到了解决办法:写入之前先将源文件加载出来,再进行有序的追加。
- 源码:先加载输入流,随后set新属性,最后store输出流
/**
* 模拟向 properties 文件追加写入数据
*/
private void addToText(){
// 将 PropertiesUtil 换成重写前的 Properties 类,最后写入的顺序是hash排序的
// Properties properties = new Properties();
PropertiesUtil properties = new PropertiesUtil();
InputStream input = null;
OutputStream output = null;
try {
// 先用输入流加载.properties文件
input = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_ADDRESS));
properties.load(new InputStreamReader(input));
// 输出流(FileOutputStream)对象,必须在Properties类加载(load)完以后创建(new)
output = new FileOutputStream(FILE_ADDRESS);
properties.setProperty("jdbc2.username", "PropertiesUtil Orderly test");
properties.store(output, "tjm modify");
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (output != null) {
try {
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (input != null) {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
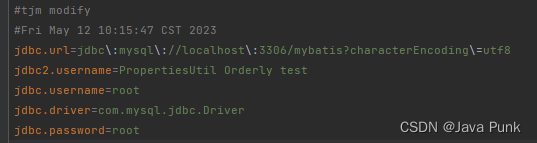
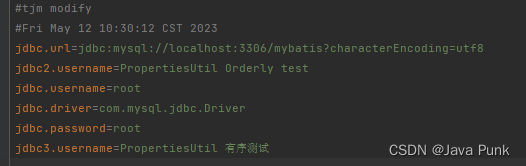
}- PropertiesUtil运行结果:

- Properties运行结果:
2.3 解决中文乱码
上面测试使用的都是中文,如果参数中包含【中文】,就会出现乱码问题,解决办法:输入输出时,设置【charsetName = "utf-8"】。
- 代码展示:
/**
* 模拟向 properties 文件追加写入数据
*/
private void addToText(){
// 将 PropertiesUtil 换成重写前的 Properties 类,最后写入的顺序是hash排序的
// Properties properties = new Properties();
PropertiesUtil properties = new PropertiesUtil();
InputStream input = null;
OutputStream output = null;
try {
// 先用输入流加载.properties文件
input = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_ADDRESS));
properties.load(new InputStreamReader(input, "utf-8"));
// 输出流(FileOutputStream)对象,必须在Properties类加载(load)完以后创建(new)
output = new FileOutputStream(FILE_ADDRESS);
properties.setProperty("jdbc3.username", "PropertiesUtil 有序测试");
properties.store(new OutputStreamWriter(output, "utf-8"), "tjm modify");
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (output != null) {
try {
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (input != null) {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 读取 properties 文件,返回 Properties 对象
*/
private Properties readFromText(){
PropertiesUtil properties = new PropertiesUtil();
InputStream input = null;
try {
input = new FileInputStream(FILE_ADDRESS);
properties.load(new InputStreamReader(input, "utf-8"));
log.info("举例说明:jdbc3.username = " + properties.getProperty("jdbc3.username"));
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (input != null) {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return properties;
}- 结果展示:
四、PropertiesConfiguration介绍
PropertiesConfiguration 是 Apache 帮我们实现按照文件的顺序读取properties文件的类,Properties类能做的它都能做。不仅如此,他还有许多方便实用的附加功能。
- 示例代码:功能展示
/**
* 模拟向 properties 文件写入数据
*/
private void setParam(){
try {
PropertiesConfiguration propsConfig = new PropertiesConfiguration(FILE_ADDRESS);
propsConfig.setEncoding("utf-8");
// 修改属性之后自动保存,省去了propsConfig.save()过程
propsConfig.setAutoSave(true);
// setProperty:遇到同名key会替换value,没有则新增
propsConfig.setProperty("set.name", "123456");
// addProperty:只会新增,即使遇到遇到同名key也不会替换
propsConfig.addProperty("add.name", "456789");
}catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 模拟向 properties 文件读取数据
*/
private void getParam(){
try {
PropertiesConfiguration propsConfig = new PropertiesConfiguration(FILE_ADDRESS);
propsConfig.setEncoding("utf-8");
String username = propsConfig.getString("jdbc.username");
log.info("举例说明:jdbc.username = " + username);
}catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}