目录
列表过滤
使用计算属性
使用watch监视属性
列表排序
Vue中数据原理
练习数据原理
Vue中数据原理总结
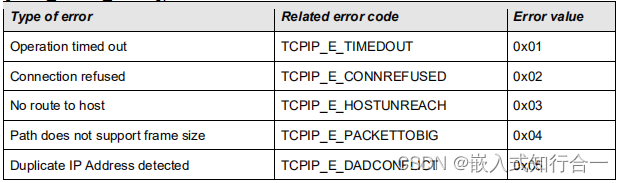
列表过滤
可以进行模糊搜索
使用计算属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-model="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--vue-->
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.7.0/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<div id="root">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入你想搜索的" v-model:value="searchWorld">
<li v-for="p in filterP" :key="p.id">
{{p.id}}--{{p.name}}--{{p.age}}--{{p.sex}}
</li>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
error:'',
searchWorld:'',
persons:[
{id:1,name:'蒋介石',age:"19岁",sex:'男'},
{id:2,name:'齐白石',age:"32岁",sex:'男'},
{id:3,name:'白居易',age:"42岁",sex:'男'},
{id:4,name:'介居齐',age:"30岁",sex:'女'}
],
},
computed: {
immediate: true,
filterP() {
//返回值作为计算属性的值
return this.persons.filter((p) => {
return p.name.indexOf(this.searchWorld) !== -1
})
}
}
});
console.log(vm)
</script>
<body>
</body>
</html>运行结果
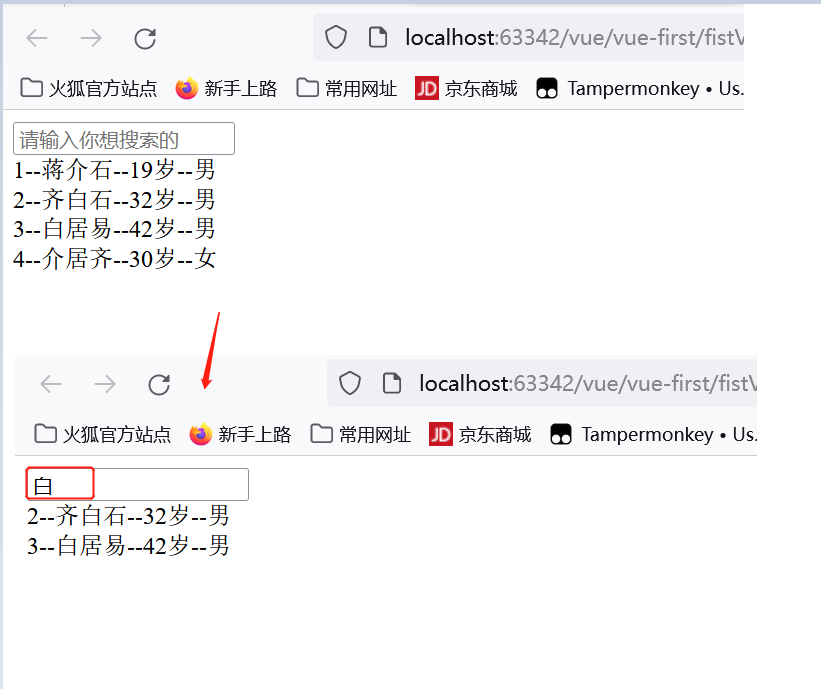
使用watch监视属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-model="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--vue-->
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.7.0/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<div id="root">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入你想搜索的" v-model:value="searchWorld"><span style="color: red" >{{error}}</span>
<span style="color: green" >{{mess}}</span>
<li v-for="p in filterP" :key="p.id">
{{p.id}}--{{p.name}}--{{p.age}}--{{p.sex}}
</li>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
mess:'',
error:'',
searchWorld:'',
persons:[
{id:1,name:'蒋介石',age:"19岁",sex:'男'},
{id:2,name:'齐白石',age:"32岁",sex:'男'},
{id:3,name:'白居易',age:"42岁",sex:'男'},
{id:4,name:'介居齐',age:"30岁",sex:'女'}
],
filterP:[],
},
watch: {
searchWorld: {
immediate: true,
handler(){
this.error=this.mess='',
this.filterP =this.persons.filter((p) => {
return p.name.indexOf(this.searchWorld)!== -1
})
if (this.filterP==''){
this.error='找不到'
}else {
this.mess="找到了"
}
}
}
}
});
console.log(vm)
</script>
<body>
</body>
</html>运行结果
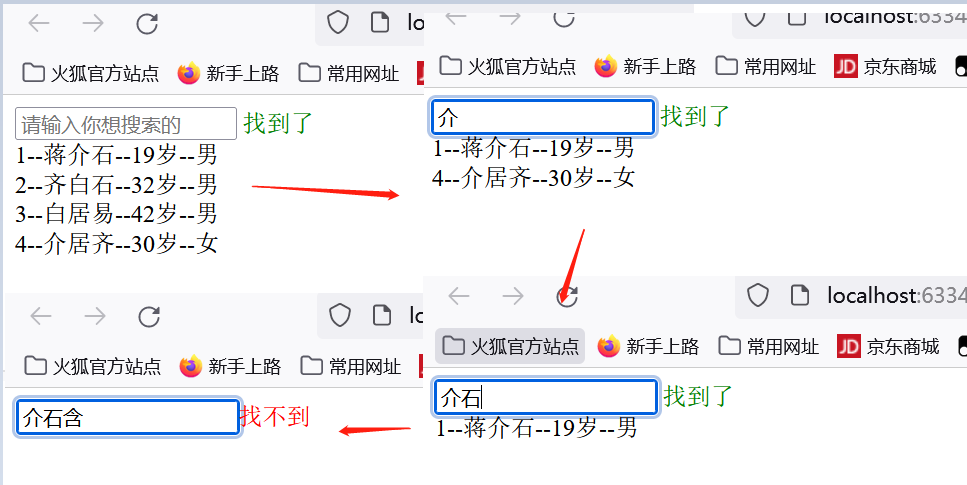
列表排序
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-model="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--vue-->
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.7.0/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<div id="root">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入你想搜索的" v-model:value="searchWorld">
<button @click="sortNum=1">年龄升序</button>
<button @click="sortNum=2">年龄降序</button>
<button @click="sortNum=0">原顺序</button>
<li v-for="p in filterP" :key="p.id">
{{p.id}}--{{p.name}}--{{p.age}}--{{p.sex}}
</li>
现在是:<span style="color: green">{{sortName}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
sortName:'原顺序',
sortNum:0,
searchWorld:'',
persons:[
{id:1,name:'蒋介石',age:19,sex:'男'},
{id:2,name:'齐白石',age:32,sex:'男'},
{id:3,name:'白居易',age:43,sex:'男'},
{id:4,name:'介居齐',age:23,sex:'女'}
],
},
computed: {
immediate: true,
filterP() {
//返回值作为计算属性的值,filter为过滤
const arrSort=this.persons.filter((p) => {
return p.name.indexOf(this.searchWorld) !== -1
})
this.sortName='原顺序'
//判断用户是否需要排序
if (this.sortNum!=0){
arrSort.sort((big,small)=>{
this.sortName= this.sortNum===1?'升序':'降序'
return this.sortNum===1?big.age-small.age: small.age-big.age
})
}
return arrSort
}
}
});
console.log(vm)
</script>
<body>
</body>
</html>arrSort.sort((big,small)=>big-small是升序排序,反之则为降序
运行结果

Vue中数据原理
练习数据原理
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--vue-->
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.7.0/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body >
<div id="root">
<h2>学生信息</h2>
学生姓名:{{student.name}}<br>
学生年龄:{{student.age}}<br/>
学生性别:{{student.sex}}<br/>
<h3>学生爱好:</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(h,index) of student.hobby" :key="index">
{{h}}
</li>
</ul><br/>
<h3>朋友们:</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(h,index) of student.friends" :key="index">
{{h.name}}-{{h.age}}
</li>
</ul><br/>
<button @click="student.age++">点击年龄加1</button>
<button @click="addSex">添加性别♀女</button>
<button @click="student.sex='男🚹'">切换为♂男</button>
<button @click.once="addFriend">添加一个🐻的朋友</button><br><br>
<button @click.once="changeFriend">改第一个朋友的名字</button>
<button @click="addHobby">添加一个游泳🏊爱好</button>
<button @click="changeHobby">修改第一个爱好为开车🚗</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
student:{
name:'小麻瓜🍉',
age:19,
hobby:['学习📕','吃饭🍚','睡觉😴💤'],
friends:[
{name:'吧不略',age:20},
{name:'皮',age:21}
]
},
},
methods: {
addSex(){
// Vue.set(this.student,'sex','女🚺')
vm.$set(this.student,'sex','女🚺')
},
addFriend(){
this.student.friends.unshift({name:'熊大',age:5})
},
changeFriend(){
this.student.friends[0].name='熊二'
},
addHobby(){
this.student.hobby.push('游泳🏊')
},
changeHobby(){
this.student.hobby.splice(0,1,"开车🚆")//从第0个开发,删一个,添加为开车
}
}
});
console.log(vm)
</script>
</body>
</html>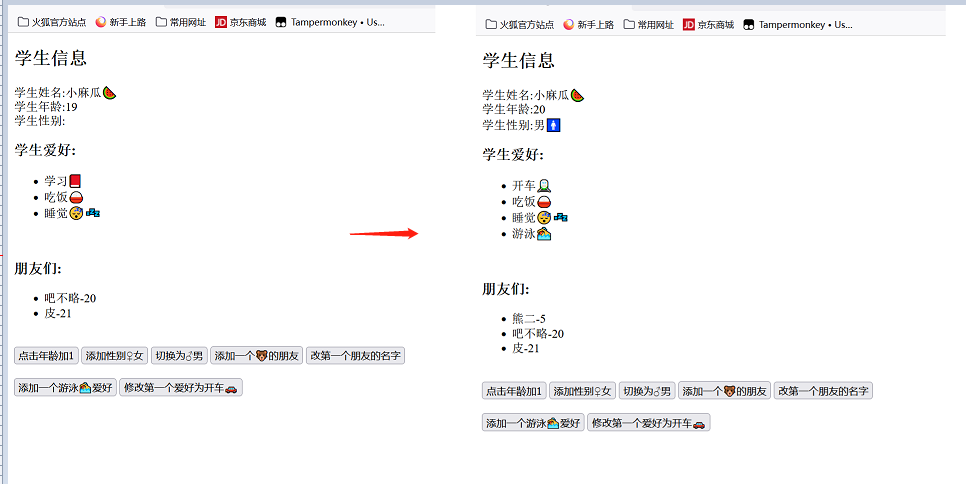
Vue中数据原理总结
1、vue会监视data中所有层次的数据。
2、如何监视对象中的数据?
- 通过setter实现监视,且要在new Vue时就传入要检测的数据。
- 对象中后追加的属性,Vue默认不作响应式处理(没有get set作为监视,vue检测不到数据的变化)
如需给后添加的属性做响应式,得使用vue提供的API:
Vue.set(target,propertyName/index,value)或vm.$set(target,propertyName/index,value)
- 第一个参数target是要添加目标位置,如vm._data.student
- 第二个参数propertyName是要添加的值或者如果前面的是数组,那这个就是索引,
- 第三个参数value是添加的值
3、如何监视数组中的数据?
通过包裹的数组跟心元素的方法实现,本质就是做了:
- 调用原生对应的方法对数组进行更新
- 重新解释模版,进而更新页面
4、在Vue修改数组中的某个元素一定要用如下方法:
- 使用这些API:push()、pop()、shift()、unshift()、splice()、sort()、reverse()
- Vue.set()或vm.$set()
特点注意:Vue.set()和vm.$set()不能给vm或vm的根数据对象_data添加属性




![[NLP] SentenceTransformers使用介绍](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b1132f4d07904512bc5382d4135d7f68.png)