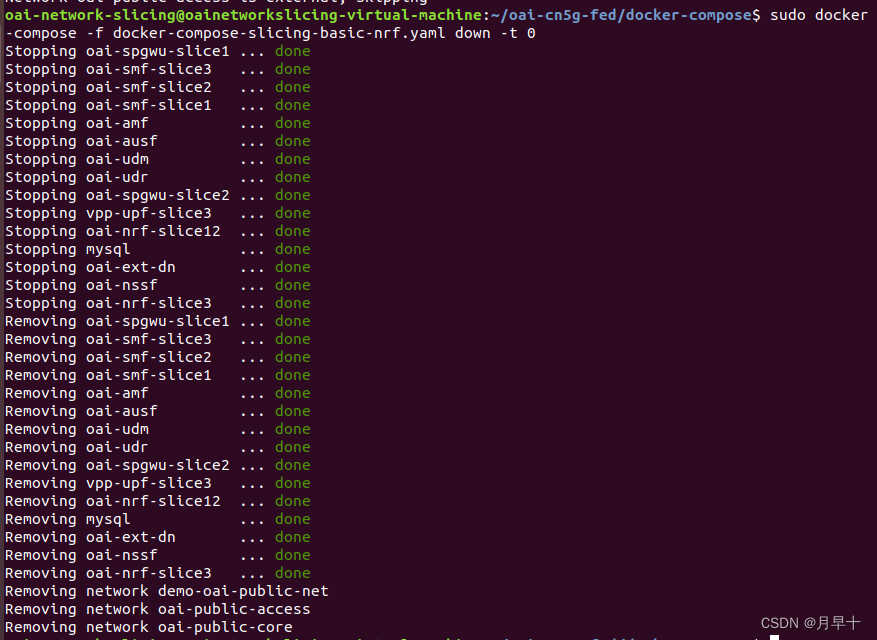
参考引用
- Point Cloud Library
- 黑马机器人 | PCL-3D点云
PCL点云库学习笔记(文章链接汇总)
1. 引言
-
点云分割是根据空间、几何和纹理等特征对点云进行划分,使得同一划分区域内的点云拥有相似的特征。点云的有效分割往往是许多应用的前提,例如:在逆向工程 CAD/CAM 领域,对零件的不同扫描表面进行分割,然后才能更好地进行孔洞修复、曲面重建、特征描述和提取,进而进行基于 3D 内容的检索、组合重用等。在激光遥感领域,同样需要对地面、物体首先进行分类处理,然后才能进行后期地物的识别、重建
-
总之,分割采用分而治之的思想,在点云处理中和滤波一样属于重要的基础操作,在 PCL 中目前实现了进行分割的基础架构,为后期更多的扩展奠定了基础,现有实现的分割算法是鲁棒性比较好的 Cluster 聚类分割和 RANSAC 基于随机采样一致性的分割
-
PCL 分割库包含多种算法,这些算法用于将点云分割为不同簇。适合处理由多个隔离区域空间组成的点云。将点云分解成其组成部分,然后可以对其进行独立处理。下面这两个图说明了平面模型分割(上)和圆柱模型分割(下)的结果

2. 平面模型分割
-
planar_segmentation.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h> #include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); // 生成 15 个无序点云,x,y 为随机数,z 为 1.0 cloud->width = 15; cloud->height = 1; cloud->points.resize(cloud->width * cloud->height); for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i) { cloud->points[i].x = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); cloud->points[i].y = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); cloud->points[i].z = 1.0; } // 将 points 中 0、3、6 索引位置的 z 值进行修改,将之作为离群值 cloud->points[0].z = 2.0; cloud->points[3].z = -2.0; cloud->points[6].z = 4.0; std::cerr << "Point cloud data: " << cloud->points.size() << " points" << std::endl; for (std::size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i) { std::cerr << " " << cloud->points[i].x << " " << cloud->points[i].y << " " << cloud->points[i].z << std::endl; } // 将输入的点云数据拟合成一个平面模型并返回该平面模型的系数 // coefficients 用于存储平面模型的系数;inliers 用于存储被拟合平面包含的点的索引 pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients); pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices); pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg; seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true); // 启用平面模型系数优化 seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE); // 设置模型类型为平面模型 seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC); // 采用 RANSAC 算法进行估计,因为 RANSAC 比较简单 // 设置点到平面距离的阈值,用于确定属于平面的点集 // 只要点到 z=1 平面距离小于该阈值的点都作为内点看待,而大于该阁值的则看做离群点 seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.01); seg.setInputCloud(cloud); // 开始分割 // 将符合条件的点集索引存储在 inliers 中,平面模型系数存储在 coefficients 中 seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients); if (inliers->indices.size() == 0) { PCL_ERROR("Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset."); return (-1); } // 此段代码用来打印出估算的平面模型的参数(以 ax+by+ca+d=0 形式) // 详见 RANSAC 采样一致性算法的 SACMODEL_PLANE 平面模型 std::cerr << "Model coefficients: " << coefficients->values[0] << " " << coefficients->values[1] << " " << coefficients->values[2] << " " << coefficients->values[3] << std::endl; std::cerr << "Model inliers: " << inliers->indices.size() << std::endl; for (std::size_t i = 0; i < inliers->indices.size(); ++i) { std::cerr << inliers->indices[i] << " " << cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].x << " " << cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].y << " " << cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].z << std::endl; } return 0; } -
配置文件 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5 FATAL_ERROR) project(planar_segmentation) find_package(PCL 1.2 REQUIRED) include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS}) link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS}) add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS}) add_executable (planar_segmentation planar_segmentation.cpp) target_link_libraries (planar_segmentation ${PCL_LIBRARIES}) -
编译并执行
$ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make $ ./planar_segmentation# 输出结果 Point cloud data: 15 points 0.352222 -0.151883 2 -0.106395 -0.397406 1 -0.473106 0.292602 1 -0.731898 0.667105 -2 0.441304 -0.734766 1 0.854581 -0.0361733 1 -0.4607 -0.277468 4 -0.916762 0.183749 1 0.968809 0.512055 1 -0.998983 -0.463871 1 0.691785 0.716053 1 0.525135 -0.523004 1 0.439387 0.56706 1 0.905417 -0.579787 1 0.898706 -0.504929 1 Model coefficients: 0 0 1 -1 Model inliers: 12 1 -0.106395 -0.397406 1 2 -0.473106 0.292602 1 4 0.441304 -0.734766 1 5 0.854581 -0.0361733 1 7 -0.916762 0.183749 1 8 0.968809 0.512055 1 9 -0.998983 -0.463871 1 10 0.691785 0.716053 1 11 0.525135 -0.523004 1 12 0.439387 0.56706 1 13 0.905417 -0.579787 1 14 0.898706 -0.504929 1

3. 圆柱体模型分割
本例介绍了如何采用 RANSAC 估计从带有噪声的点云中提取一个圆柱体模型,整个程序处理流程如下
- 过滤掉远于 1.5m 的数据点
- 估计每个点的表面法线
- 分割出平面模型(数据集中的桌面)并保存到磁盘中
- 分割圆出柱体模型(数据集中的杯子)并保存到磁盘中
- cylinder_segmentation.cpp
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
pcl::PCDReader reader; // PCD 文件读取对象
pcl::PassThrough<PointT> pass; // 直通滤波器
pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, pcl::Normal> ne; // 法线估算对象
pcl::SACSegmentationFromNormals<PointT, pcl::Normal> seg; // 分割器
pcl::PCDWriter writer; // PCD 文件写入对象
pcl::ExtractIndices<PointT> extract; // 点提取对象
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::Normal> extract_normals; // 法线提取对象
pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_filtered2(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals2(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients_plane(new pcl::ModelCoefficients), coefficients_cylinder(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers_plane(new pcl::PointIndices), inliers_cylinder(new pcl::PointIndices);
// 读取点云数据
reader.read("../data/table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd", *cloud);
std::cerr << "PointCloud has: " << cloud->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 构建直通滤波器去除伪 NaNs
pass.setInputCloud(cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass.setFilterLimits(0, 1.5);
pass.filter(*cloud_filtered);
std::cerr << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 估计点的法线
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
ne.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
ne.setKSearch(50);
ne.compute(*cloud_normals);
// 为平面模型创建分割对象,并设置所有参数
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true); // 启用平面模型系数(平面方程的系数)的优化
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE); // 设置模型类型为法向量估计的平面模型
// 设置法向量距离权重系数为 0.1,表示在拟合平面的时候更加注重法向量的一致性
// 即:使得拟合出来的平面法向量与原始点云法向量的夹角最小
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.03); // 设置距离阈值为 0.03,表示与平面拟合误差超过该值的点将被视为离群点
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals);
// 将拟合出来的平面模型系数存储到 coefficients_plane 中,同时将属于平面的点的索引存储到 inliers_plane 中
seg.segment(*inliers_plane, *coefficients_plane);
std::cerr << "Plane coefficients: " << *coefficients_plane << std::endl; // 输出拟合出来的平面模型系数到控制台
// 从输入点云中提取平面内点
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers_plane);
extract.setNegative(false);
// 将提取到的平面内点写入磁盘
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>());
extract.filter(*cloud_plane);
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points."
<< std::endl;
writer.write("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_plane.pcd", *cloud_plane, false);
// 去除平面内点,提取剩余的点
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud_filtered2);
extract_normals.setNegative(true);
extract_normals.setInputCloud(cloud_normals);
extract_normals.setIndices(inliers_plane);
extract_normals.filter(*cloud_normals2);
// 创建用于圆柱体分割的分割对象,并设置所有参数
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_CYLINDER); // 设置分割模型为圆柱体
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC); // 设置采用 RANSAC 算法进行参数估计
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1); // 设置表面法线权重系数
seg.setMaxIterations(10000); // 设置最大迭代次数 10000
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.05); // 设置内点到模型的最大距离 0.05m
seg.setRadiusLimits(0, 0.1); // 设置圆柱体的半径范围 0 ~ 0.1m
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered2);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals2);
seg.segment(*inliers_cylinder, *coefficients_cylinder);
std::cerr << "Cylinder coefficients: " << *coefficients_cylinder << std::endl;
// 将圆柱体内点写入磁盘
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered2);
extract.setIndices(inliers_cylinder);
extract.setNegative(false);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_cylinder(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>());
extract.filter(*cloud_cylinder);
if (cloud_cylinder->points.empty()) {
std::cerr << "Can't find the cylindrical component." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the cylindrical component: " << cloud_cylinder->points.size()
<< " data points." << std::endl;
writer.write("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_cylinder.pcd", *cloud_cylinder, false);
}
return 0;
}
-
配置文件 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5 FATAL_ERROR) project(cylinder_segmentation) find_package(PCL 1.2 REQUIRED) include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS}) link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS}) add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS}) add_executable (cylinder_segmentation cylinder_segmentation.cpp) target_link_libraries (cylinder_segmentation ${PCL_LIBRARIES}) -
编译并执行
$ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make $ ./cylinder_segmentation# 输出结果 PointCloud has: 307200 data points. PointCloud after filtering has: 139897 data points. Plane coefficients: header: seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id: values[] values[0]: 0.015758 values[1]: -0.838789 values[2]: -0.544229 values[3]: 0.527018 PointCloud representing the planar component: 126168 data points. Cylinder coefficients: header: seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id: values[] values[0]: 0.0585808 values[1]: 0.279481 values[2]: 0.900414 values[3]: -0.0129607 values[4]: -0.843949 values[5]: -0.536267 values[6]: 0.0387611 PointCloud representing the cylindrical component: 9271 data points.# 将三个点云在一个窗口内显示 $ pcl_viewer ../data/table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_plane.pcd table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_cylinder.pcd

4. 欧式聚类提取
- cluster_extraction.cpp
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/extract_clusters.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// 读取输入点云
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud_f(
new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
reader.read("./data/tabletop.pcd", *cloud);
std::cout << "PointCloud before filtering has: " << cloud->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl; //*
// 执行降采样滤波,叶子大小 1cm
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> vg;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
vg.setInputCloud(cloud);
vg.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);
vg.filter(*cloud_filtered);
std::cout << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 创建平面模型分割器并初始化参数
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.02);
int i = 0, nr_points = (int) cloud_filtered->points.size();
while (cloud_filtered->points.size() > 0.3 * nr_points) {
// 分割出剩余点云中最大的平面
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
// 执行分割,将分割出来的平面点云索引保存到 inliers 中
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size() == 0) {
std::cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl;
break;
}
// 从输入点云中取出平面内点
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract;
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers);
extract.setNegative(false);
// 得到与 cloud_plane 平面相关的点
extract.filter(*cloud_plane);
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 从点云中剔除这些平面内点,提取出剩下的点保存到 cloud_f 中,并重新赋值给 cloud_filtered
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud_f);
*cloud_filtered = *cloud_f;
}
// 为提取算法的搜索方法创建一个 KdTree 对象
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
tree->setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
/*
* cluster_indices 是一个 vector,包含多个检测到的簇的 PointIndices 的实例
* 因此,cluster_indices[0] 包含点云中第一个 cluster(簇)的所有索引
* 从点云中提取簇(集群),并将点云索引保存在 cluster_indices 中
*/
std::vector<pcl::PointIndices> cluster_indices;
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction<pcl::PointXYZ> ec;
// 如果搜索半径取一个非常小的值,那么一个实际独立的对象就会被分割为多个聚类;如果将值设置得太高,那么多个对象就会被分割为一个聚类
ec.setClusterTolerance(0.02); // 设置聚类搜索半径(搜索容差)为 2cm
ec.setMinClusterSize(100); // 每个簇(集群)的最小 大小,限制一个聚类最少需要的点数目
ec.setMaxClusterSize(25000); // 每个簇(集群)的最大 大小,限制一个聚类最多需要的点数目
ec.setSearchMethod(tree); // 设置点云搜索算法
ec.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); // 设置输入点云
ec.extract(cluster_indices); // 设置提取到的簇,将每个簇以索引的形式保存到 cluster_indices
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3D Viewer"));
// 将一个点云数据集中的点根据聚类结果,划分为多个簇,并可视化显示每个簇
int j = 0;
for (std::vector<pcl::PointIndices>::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin();
it != cluster_indices.end(); ++it) {
// 每次创建一个新的点云数据集,并将所有当前簇的点写入到点云数据集中
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
const std::vector<int> &indices = it->indices;
for (std::vector<int>::const_iterator pit = indices.begin(); pit != indices.end(); ++pit) {
cloud_cluster->points.push_back(cloud_filtered->points[*pit]);
}
// 输出当前簇所包含的点的数量
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j;
// 生成随机颜色
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerRandom<pcl::PointXYZ> single_color(cloud_cluster);
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud_cluster, single_color, ss.str());
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, ss.str());
j++; // 增加计数器 j,以便为下一个簇创建一个不同的名称
}
std::cout << "cloud size: " << cluster_indices.size() << std::endl;
viewer->addCoordinateSystem(0.5);
while (!viewer->wasStopped()) {
viewer->spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}
-
配置文件 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5 FATAL_ERROR) project(cluster_extraction) find_package(PCL 1.2 REQUIRED) include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS}) link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS}) add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS}) add_executable (cluster_extraction cluster_extraction.cpp) target_link_libraries (cluster_extraction ${PCL_LIBRARIES}) -
编译并执行
$ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make $ ./cluster_extraction# 输出结果 PointCloud before filtering has: 460400 data points. PointCloud after filtering has: 41049 data points. PointCloud representing the planar component: 20536 data points. PointCloud representing the planar component: 12442 data points. PointCloud representing the Cluster: 4857 data points. PointCloud representing the Cluster: 1386 data points. PointCloud representing the Cluster: 321 data points. PointCloud representing the Cluster: 291 data points. PointCloud representing the Cluster: 123 data points. cloud size: 5