前言
本博客中的例子和文字大部分来源于书籍《mysql必会知识》,后续会根据更多的书籍不断完善此笔记。
插入操作
可以这种方式向数据库插入两条数据,mysql和pg都支持这种写法。在实战中我们应该更多的使用这种写法,因为数据库的批量操作会比一条一条执行效率更高。
INSERT INTO demo VALUES('1001','liyong'),('1002', 'daipeng');
INSERT INTO demo(id,name) VALUES('1003','liyong'),('1004', 'daipeng');
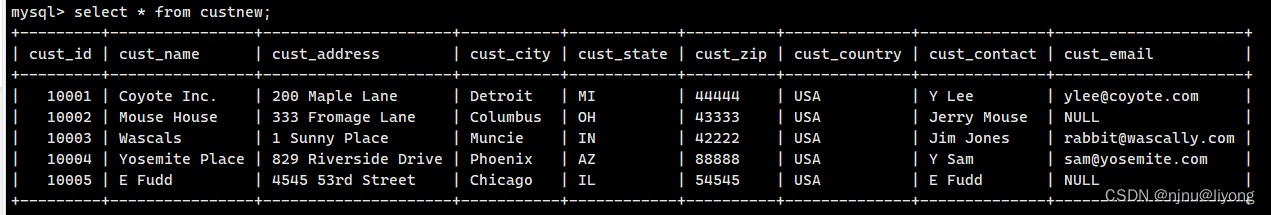
我们可以基于现有的数据直接插入select查询的数据,下面我新建一个表custnew。然后将customers里面的数据插入到custnew里面。
insert into custnew(cust_id,cust_contact,cust_email,cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_country) select cust_id,cust_contact,cust_email,cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_country from customers;
更新操作
这里我们记录一个写法,可能不常用
下面这条语句是一个批量更新,默认情况下如果一行更新的时候发生错误,则整个update会恢复之前的原来的值。
update customers set cust_name = 'demo';
#如果使用了ignore 那么其中的一些更新还是会生效
update ignore customers set cust_name = 'demo';
表操作
创建表
CREATE TABLE customers
(
cust_id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
cust_name char(50) NOT NULL ,
cust_address char(50) NULL ,
cust_city char(50) NULL ,
cust_state char(5) NULL ,
cust_zip char(10) NULL ,
cust_country char(50) NULL ,
cust_contact char(50) NULL ,
cust_email char(255) NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (cust_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
注:
这里要注意一下引擎的问题。如果省略ENGINE=语句,则使用默认引擎(很可能是MyISAM),多数SQL语句都会默认使用它。但并不是所有语句都默认使用它,这就是为什么ENGINE=语句很重要的原因(也就是为什么本书的样列表中使用两种引擎的原因)。 以下是几个需要知道的引擎:
InnoDB是一个可靠的事务处理引擎,它不支持全文本搜索;
MEMORY在功能等同于MyISAM,但由于数据存储在内存(不是磁盘)中,速度很快(特别适合于临时表);
MyISAM是一个性能极高的引擎,它支持全文本搜索,但不支持事务处理。
非常重要的是如果你表和表需要通过外键进行连接,那么这两个表必须使用同一种类型的引擎。
增加一个列
alter table vendors add vend_phone char(20);
删除一个列
alter table vendors drop column vend_phone;
定义外键
ALTER TABLE orderitems ADD CONSTRAINT fk_orderitems_orders FOREIGN KEY (order_num) REFERENCES orders (order_num);
重命名表
rename table custnew to customers2;
视图
下面是关于视图创建和使用的一些最常见的规则和限制。
与表一样,视图必须唯一命名(不能给视图取与别的视图或表相同的名字)。
对于可以创建的视图数目没有限制。
为了创建视图,必须具有足够的访问权限。这些限制通常由数据库管理人员授予。 视图可以嵌套,即可以利用从其他视图中检索数据的查询来构造一个视图。
ORDER BY可以用在视图中,但如果从该视图检索数据SELECT中也含有ORDER BY,那么该视图中的ORDER BY将被覆盖。
视图不能索引,也不能有关联的触发器或默认值。
视图可以和表一起使用。例如,编写一条联结表和视图的SELECT语句。
创建视图
create view productcustomers as select cust_name,cust_contact,prod_id from customers,orders,orderitems where customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id and orderitems.order_num = orders.order_num;
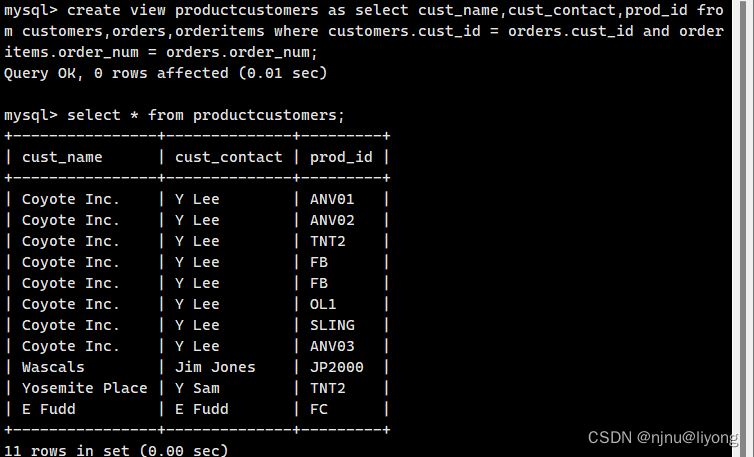
查看创建视图的语句
show create view productcustomers;
先drop在create
create OR replace view productcustomers as select cust_name,cust_contact,prod_id from customers,orders,orderitems where customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id and orderitems.order_num = orders.order_num;
删除视图
drop view productcustomers;
更新视图:
视图的更新,最终更新的是构成视图的基本表的数据。
并非所有视图都是可更新的。基本上可以说,如果MySQL不能正确地确定被更新的基数据,则不允许更新(包括插入和删除)。这实际上意味着,如果视图定义中有以下操作,则不能进行视图的更新:
分组(使用GROUP BY和HAVING);
联结;
子查询;
并;
聚集函数(Min()、Count()、Sum()等);
DISTINCT; 导出(计算)列。



![Prompt learning 教学[基础篇]:prompt基本原则以及使用场景技巧助力你更好使用chatgpt,得到你想要的答案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/cd93c27a13c217e61c77559a5d1d0010.png)