文章目录
- 标准输入流
- 标准输出流
- 字节打印流
- 字符打印流
- 案例--复制java文件(文件打印流版本)
- 对象序列化流
- 序列化流
- 反序列化流
- serialVersionID&transient
- Properties作为Map集合的使用
- Properties作为集合的特有方法
- Properties与IO流相结合的方法
- 案例--游戏次数
标准输入流

package heima;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class P312 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//public static final InputStream in:标准输入流
InputStream is =System.in;
// //1.只能输入字符
// int by;
// while ((by = is.read())!=-1){
// System.out.println((char) by);
// }
// //2.把字符转换为字符流
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
//3.实现字符流一次读取一行数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
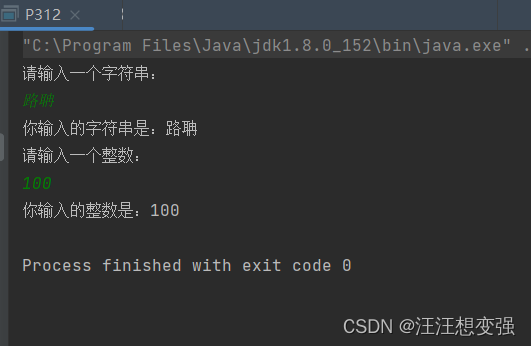
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println("你输入的字符串是:"+line);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int i = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("你输入的整数是:"+i);
}
}
输出:
自己实现太麻烦,java提供了一个供我们使用的方法
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in)
标准输出流

package heima;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class P313 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//pulic sattic final PrintStream out:标准输出流
PrintStream ps = System.out;
//能够方便地打印各种数据
// ps.print("hello");
// ps.print(100);
//
// ps.println("hello");
// ps.println(100);
//System.out的本质是一个字节输出流
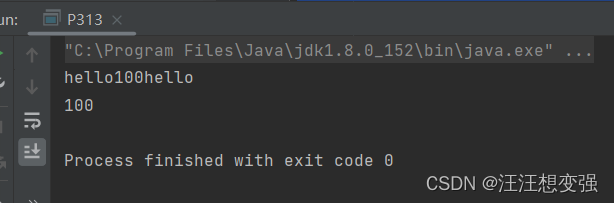
System.out.println("hello");
System.out.println(100);
System.out.println();
// System.out.print();
}
}
注意:直接System.out.print();不带参数,是错误的
字节打印流

转码:指转为对应的ASCII码
package heima;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class P314 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
//PrintStream(String fileName):使用指定的文件名创建新的打印流
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\ps.txt");
//写数据
//字节输出流有的方法
ps.write(97); //a
//使用特有方法写数据
ps.print(97); //97
//释放资源
ps.close();
}
}
字符打印流
package heima;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class P315 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
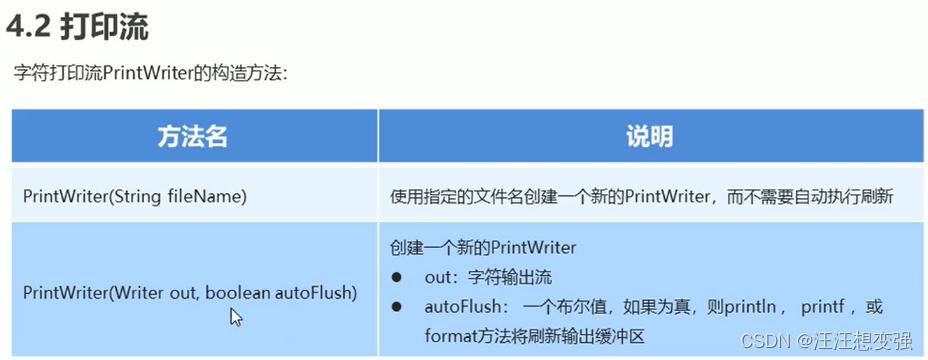
//PrintWriter(String fileName):使用指定的文件名创建一个新的PrintWriter,而不需要自动执行行的刷新
// PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\pw.txt");
//
// pw.write("hello");
// pw.write("\r\n");
// pw.flush();
// pw.write("world");
// pw.write("\r\n");
// pw.flush();
//
// pw.println("hello");//输出失败
// /*原因
// pw.write("hello");
// pw.write("\r\n");
// */
//PrintWriter (Writer out,boolean autoFlush):创建一个新的PrintWriter
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\pw.txt"),true);//true代表开启自动刷新flush()
pw.println("hello");
pw.println("world");
}
}
案例–复制java文件(文件打印流版本)
package heima;
import java.io.*;
public class P316 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
//根据数据源创建字符输入流对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2022.2.3\\study\\src\\heima\\P315.java"));
//根据目的地创建字符输出流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\ts.java"));
//读写数据,复制文件
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
//释放资源
bw.close();
br.close();
*/
//根据数据源创建字符输入流对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2022.2.3\\study\\src\\heima\\P315.java"));
//根据目的地创建字符输出流对象
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\te.java",true));
//读写数据,复制文件
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
pw.println(line);
}
//释放资源
pw.close();
br.close();
}
}
对象序列化流
序列化流

一定要在类中定义一个标记接口Serializable
package heima;
import heima.common.Student;
import java.io.*;
public class P317 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//ObjectOutputStream (OutputStream out):创建一个写入指定的OutputStrem的ObjectOutputStream
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream( "C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\oos.txt"));
//创建对象
Student s = new Student("小林",30);
//void writeObject(Object obj):将指定的对象写入ObjectOutputStream
oos.writeObject(s);
//释放资源
oos.close();
}
}
反序列化流
输出上面的序列流
package heima;
import heima.common.Student;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class P318 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//ObjectInputStream(InputStream in):创建从指定的InputStream读取的ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\oos.txt"));
//Objext readObject():从ObjectInputStream读取一个对象
Object obj = ois.readObject();
Student s = (Student) obj;
System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());
ois.close();
}
}
serialVersionID&transient

package heima;
import heima.common.Student;
import java.io.*;
public class P319 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
write();
// read();
}
//序列化
private static void write() throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\oos.txt"));
Student s = new Student("小林",30);
oos.writeObject(s);
oos.close();
}
//反序列化
private static void read() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\oos.txt"));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
Student s = (Student) obj;
System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());
ois.close();
}
}
对上述代码,若在read()执行后,改动类Student内容,再执行write()则报错。
原因
需要对Student进行如下改动:

Properties作为Map集合的使用

package heima;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class P320 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
//1.err --想当然的把Properties当作泛型
// Properties<String,String> prop = new Properties<String,String>();
Properties prop = new Properties();
//存储元素
prop.put("item01","小林");
prop.put("item02","小王");
prop.put("item03","小雨");
//遍历集合
Set<Object> keySet = prop.keySet();
for (Object key : keySet){
Object value = prop.get(key);
System.out.println(key+","+value);
}
}
}
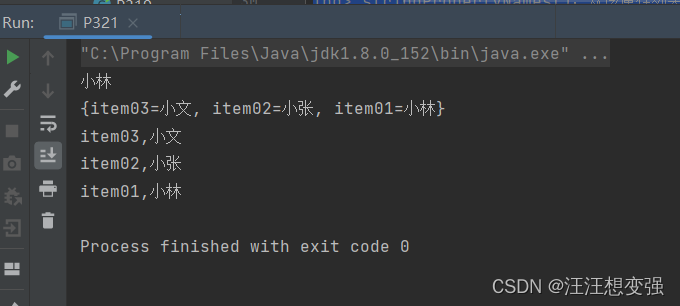
Properties作为集合的特有方法
package heima;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class P321 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Properties prop = new Properties();
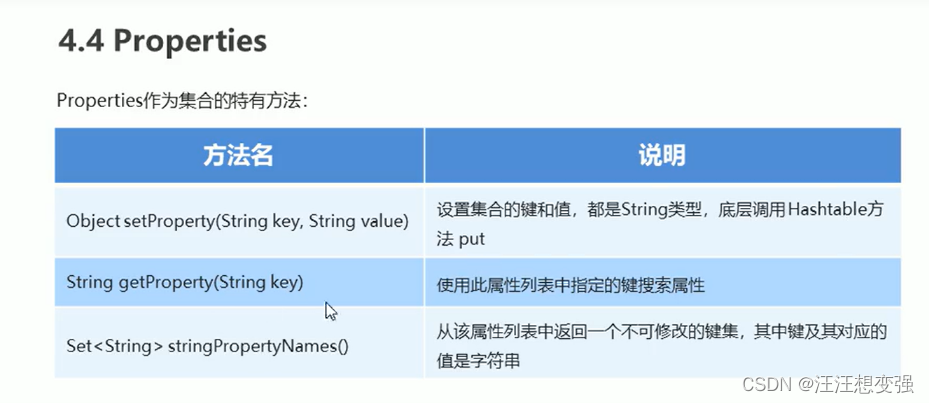
//Object setProperty(String key,String value):设置集合的键和值,都是String类型,底层调用Hashtable方法put
prop.setProperty("item01","小林");
/* 方法来源
Object setProperty(String key,String value){
return put(key,value);
}
Object put(Object key,Object value){
return map.put(key,value);
}
设计:把一个接受Object对象的方法,改为只能接受String对象,设计巧妙
*/
prop.setProperty("item02","小张");
prop.setProperty("item03","小文");
//String getProperty(String key):使用此属性列表中指定的键搜索属性
System.out.println(prop.getProperty("item01"));
System.out.println(prop);
//Set<String> stringPropertyNames():从该属性列表中返回一个不可修改的键集,其中键及其对应的值是字符串
Set<String> names = prop.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : names){
// System.out.println(key);//输出所以的键名
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key+","+value);//输出键和对应的值
}
}
}
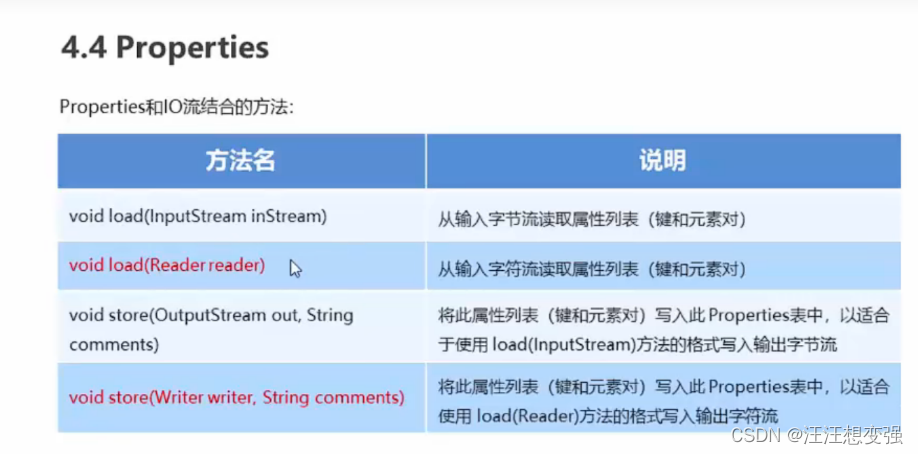
Properties与IO流相结合的方法
package heima;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class P322 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//把集合中的数据保存到文件
// myStore();
//把文件中的数据加载到集合
myLoad();
}
private static void myLoad() throws IOException, IOException {
Properties prop = new Properties();
//void load(Reader reader):
FileReader fr = new FileReader("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\fw.txt");
prop.load(fr);
fr.close();
System.out.println(prop);
}
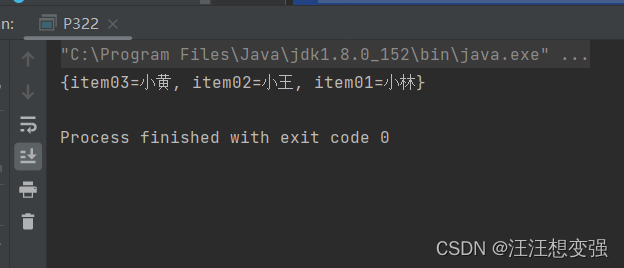
private static void myStore() throws IOException {
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("item01","小林");
prop.setProperty("item02","小王");
prop.setProperty("item03","小黄");
//void store(Writer writer,String comments):
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\fw.txt");
prop.store(fw,null);
fw.close();
}
}
输出:
先只执行myStore(),再只执行myLoad()
案例–游戏次数

package heima;
import heima.common.GuessNumber;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class P323 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//从文件中读取数据到Properties集合,用load()方法实现
Properties prop = new Properties();
FileReader fr = new FileReader("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\game.txt");
prop.load(fr);
fr.close();
//通过Properties集合获取到玩游戏的次数
String count = prop.getProperty("count");
int number = Integer.parseInt(count);
//判断次数是否到达3次了
if (number >= 3){
//如果到了
System.out.println("游戏试玩已结束,想玩请充值(www.itcast.cn)");
}else {
//继续玩游戏
GuessNumber.start();
//次数+1,重新写回文件,用Properties的store()方法实现
number++;
//String.valueOf():转换位字符串
prop.setProperty("count",String.valueOf(number));
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\路聃\\Desktop\\Java\\game.txt");
prop.store(fw,null);
fw.close();
}
}
}
//1 load
//2 store
GuessNumber.java
package heima.common;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GuessNumber {
private GuessNumber(){}
public static void start(){
//要完成猜数字的游戏,首先要有一个要猜的数字,使用随机数生成该数字,范围1到200
Random r = new Random();
int number = r.nextInt(100)+1;
while (true){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要猜的数字:");
int guessNumber = sc.nextInt();
//比较输入的数字喝系统产生的数据
if (guessNumber > number){
System.out.println("你猜的的数字"+guessNumber+"大了");
}else if (guessNumber <number){
System.out.println("你猜的数字"+guessNumber+"小了");
}else {
System.out.println("恭喜你猜中了");
break;
}
}
}
}
![[附源码]SSM计算机毕业设计血库管理系统JAVA](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/39641a460fa94577bb546996551b561f.png)