1.A - Mahmoud and Ehab and the MEX
Problem - A - Codeforces

核心在于x之前的数肯定是有的,x是没有的
所以从0开始一直到x,如果哪个数没有就加上哪个数(操作数+1),如果有x就删去x(操作数+1)

AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110,M=1010;
int a[N];
bool st[M];
int ans;
int cnt;
int main()
{
int n, x;
cin >> n >> x;
for (int i =0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st[a[i]] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
if (!st[i]) ans++;
}
if (st[x]) ans++;
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}2.A - Beautiful Sequence
Problem - A - Codeforces

对于位置i的数,如果该数小于等于i,那么YES,否则NO

AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int a[N];
int idx[N];
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
bool flag;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
idx[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
flag = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i] <= idx[i]) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
//for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// cout << idx[i] << " " << a[i] << endl;
//}
if (flag) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}3.D. Remove Two Letters
Problem - D - Codeforces
题意是一个字符串,从中删除两个连续的字符,能得到多少个不同的字符串(注意是连续两个字符,我当时做题的时候不知道)
对于长度为n的字符串,无非就是删除1,2或2,3或3,4.....n-1,一共n-1种情况
所以什么情况下删除两个连续的字符时不会增加一个新的字符串呢?当遇到aba型时,删除ab和ba都会留下一个a,那么删除ab时增加了一个新的字符串,但是删除ba时没有增加新的字符串,所以只要从头遍历一遍,如果某字符与上上个字符相等,那么就不会增加一个新的字符串,否则增加一个新的字符串

AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
string s;
cin >> s;
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] == s[i - 2]) continue;
else ans++;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}4.D. Palindromes Coloring
Problem - D - Codeforces
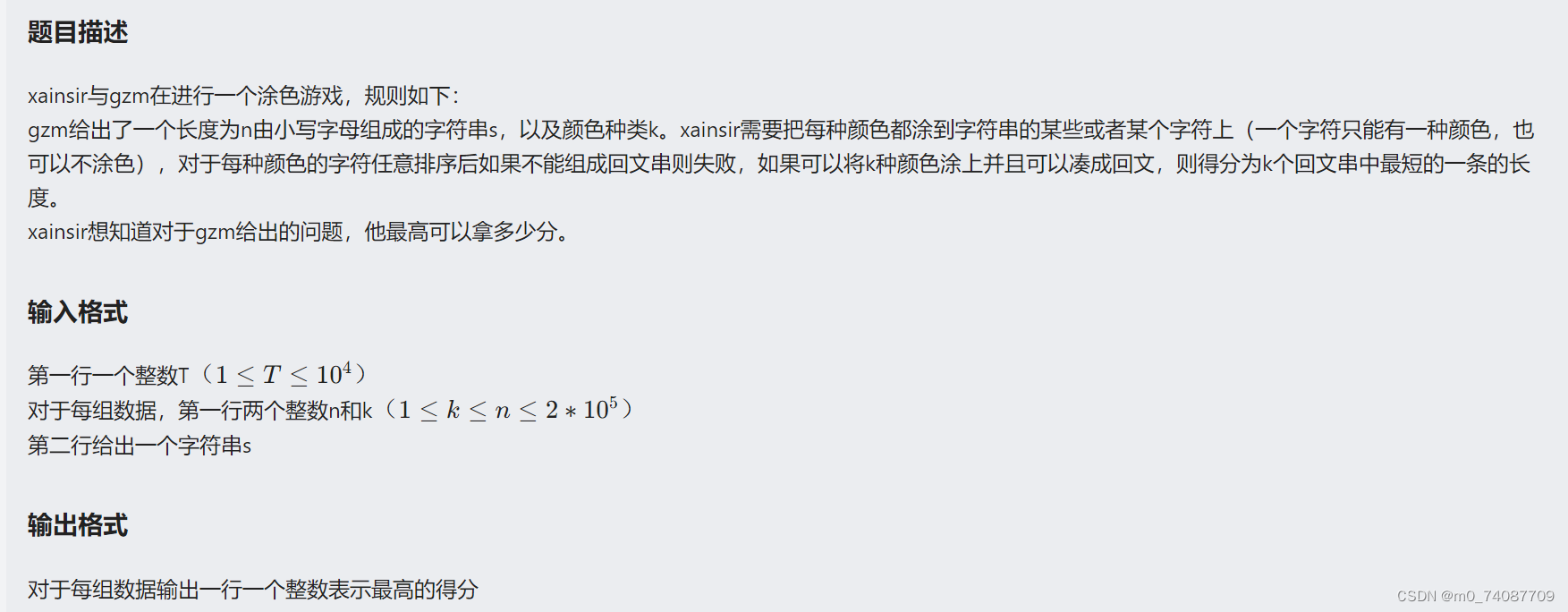
大致题意就是能否在一个字符串中找到k个分隔的回文串,并且使得这k个回文串最短的那个长度最大,输出长度
与顺序无关,那么只与数量有关,统计相同字符的元素的个数,cnt1记录一共有几对相同的元素(两两一对),cnt2记录一共有多少个字符是只有一个的
要想使得最短的长度最大,那么分配时要尽量满足平均
一共k组,每组基本字符数量是cnt1/k*2,剩下的没有用过字符只能以一个字符的方式加到每组中,使得每组仍能够是回文串并且最小长度的字符串能+1,那么剩下的字符个数得大于k

AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50;
int a[N];
int cnt1, cnt2;
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
string s;
cin >> s;
memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
cnt1 = 0;
cnt2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[s[i] - 'a' + 1]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) {
cnt1 += a[i] / 2;
cnt2 += a[i] % 2;
}
if ((cnt1 - cnt1 / k*k)*2+cnt2>=k) cout << cnt1 / k * 2 + 1 << endl;
else cout << cnt1 / k * 2 << endl;
}
return 0;
}5.D. Masha and a Beautiful Tree
Problem - D - Codeforces

用分治的思想,类似于归并排序,先排好左半边和右半边,然后将排好的左半边和右半边进行比较,看是否要交换两边的子树,每交换一次两边的子树ans++
最后排好后看是否是从1开始的递增序列,如果不是说明不能变成完美二叉树,则输出-1,否则输出ans
归并排序见(1条消息) 算法:排序_m0_74087709的博客-CSDN博客
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N];
int n;
int ans;
void dfs(int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
dfs(l, mid), dfs(mid + 1, r);
if (a[l] > a[r]) {
ans++;
for (int i = l; i <= mid; i++) {
swap(a[i], a[i - l + mid + 1]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
ans = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
dfs(1, n);
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[i +1]) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (!flag) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}6.E - Swap PlacesE - Swap Places


暂时不会,之后再补