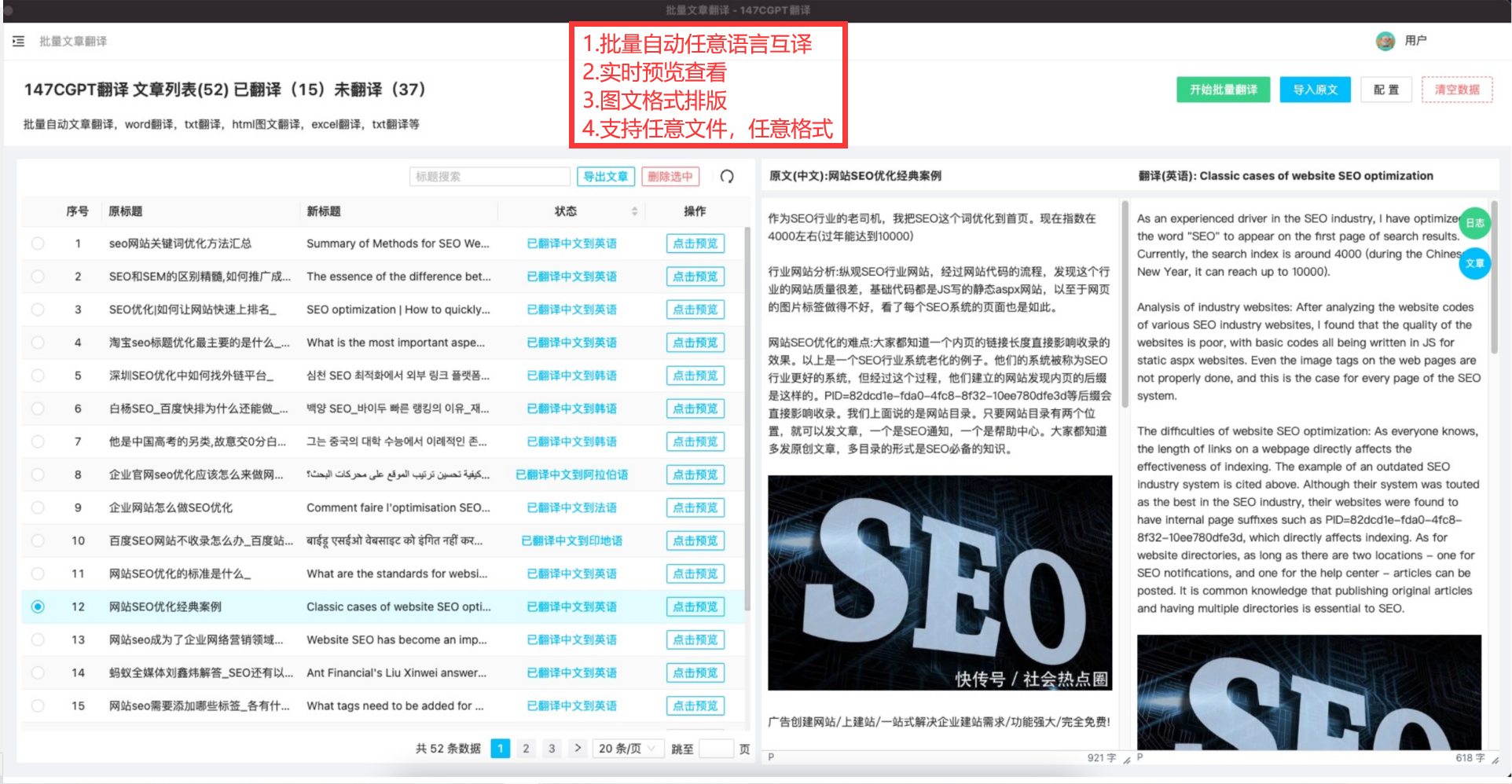
1. 图像加法
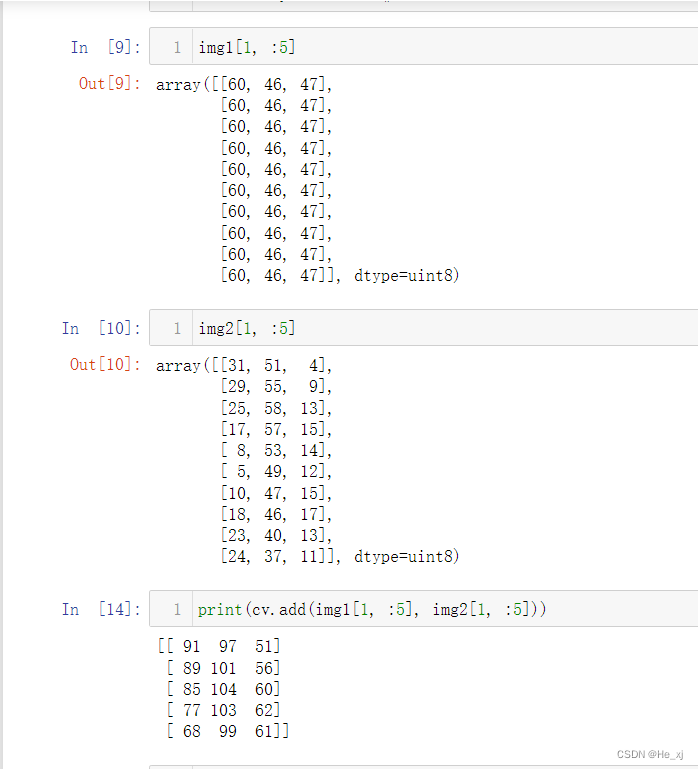
函数 cv.add(img1, img2)
参数中的img1 和 img2 应该是相同的深度和类型, 或者第二个图像可以是像素值
代码示例:
>>> x = np.uint8([250])
>>> y = np.uint8([10])
>>> print(cv.add(x,y)) #250 + 10 =260 => 255
[[255]]
>>> print(x + y)
[4]
可以注意到,如果二者的和大于最大像素值255那么opencv会将其自动置为255.
合成实例:
可以发现add函数就是普通的像素值相加
2.图像混合
cv.addWeighted(img1, alpha, img2, 1-alpha, gama)
这也是将图像相加,但是对图像赋予不同的权重,从而给出混合感或透明感。图像按以下等式添加:
g
(
x
)
=
(
1
−
α
)
f
0
(
x
)
+
α
f
1
(
x
)
+
g
a
m
a
g(x) = (1-\alpha)f_0(x)+\alpha f_1(x) + gama
g(x)=(1−α)f0(x)+αf1(x)+gama
- gama: 添加到每个总和的标量,默认为0
但是这个函数也是只能用两张相同大小的图片进行混合。
代码示例:
img1= cv.imread(img1.path)
img2= cv.imread(img2.path)
dst = cv.addWeighted(img1,0.7,img2,0.3,0)
cv.imshow('dst',dst)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
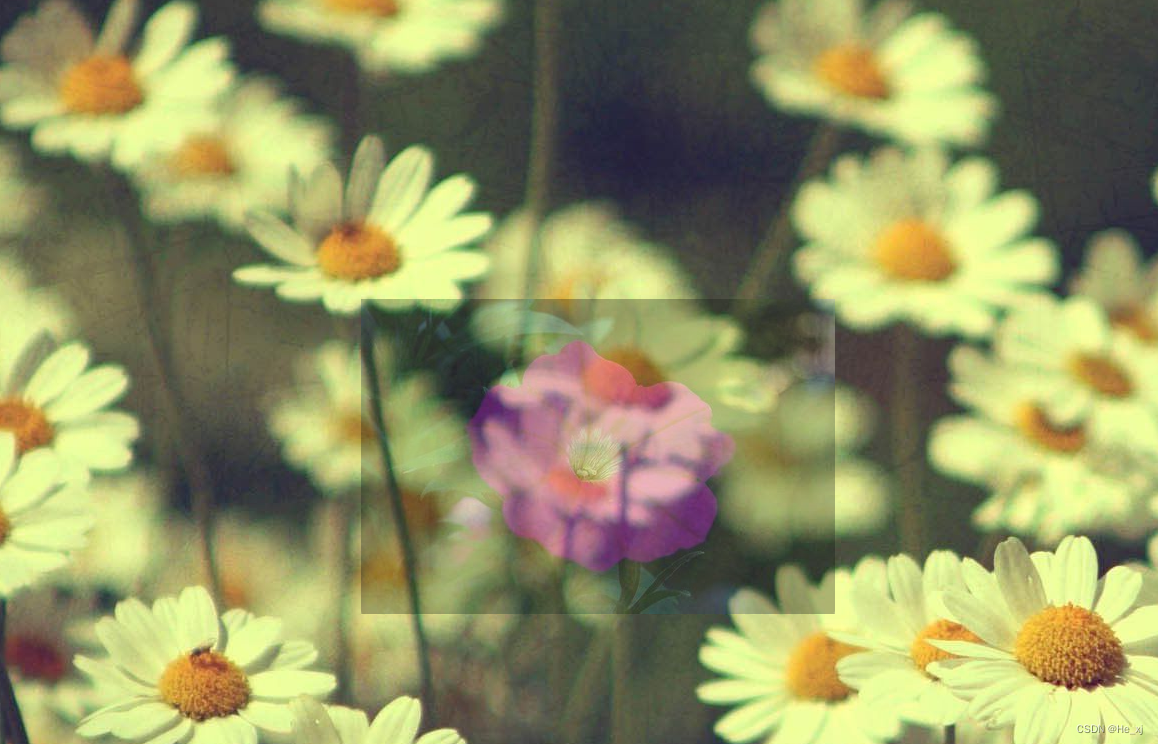
下面的代码表示将一个小的图片混合到大图片当中
# smaller img merge to bigger img
def addWeightedSmallImgToLargeImg(largeImg, alpha, smallImg, beta = 0, gamma=0.0, regionTopLeftPos=(0,0)):
# get the img's width and hight
bW, bH = largeImg.shape[1::-1]
sW, sH = smallImg.shape[1::-1]
# 是否偏移
x,y = regionTopLeftPos
if (sW>bW) or (sH>bH): # check the img is legal or not
raise ValueError(f"img2's size {smallImg.shape[1::-1]} must less than or equal to img1's size {largeImg.shape[1::-1]}")
else:
if (x+sW)>bW:
x = bW-sW
if (y+sH)>bH:
y = sH-bH
destImg = np.array(largeImg)
tmpSrcImg = destImg[y:y+sH,x:x+sW]
tmpImg = cv.addWeighted(tmpSrcImg, alpha, smallImg, beta, gamma)
destImg[y:y + sH, x:x + sW] = tmpImg
return destImg
# read img and show img's shape
img1 = cv.imread(r'images\flowers.jpg')
img2 = cv.imread(r'images\flo.jpg')
print(img1.shape)
print(img2.shape)
## show the img
new_img = addWeightedSmallImgToLargeImg(img1, 0.7, img2, 0.3, regionTopLeftPos=(640,500))
cv.imshow('merge image', new_img)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
效果如图:

主要思想来自 opencv 中文文档