使用BinaryDescriptor接口提取线条并将其存储在KeyLine对象中,使用相同的接口计算每个提取线条的描述符,使用BinaryDescriptorMatcher确定从不同图像获得的描述符之间的匹配。
opencv提供接口实现
线提取和描述符计算
下面的代码片段展示了如何从图像中检测出线条。LSD提取器使用LSD_REFINE_ADV选项进行初始化;其余参数保持默认值。使用全1掩码以接受所有提取的线条,最后使用随机颜色显示第0个八度的线条。
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv_modules.hpp>
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_FEATURES2D
#include <opencv2/line_descriptor.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/utility.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::line_descriptor;
using namespace std;
static const char* keys =
{ "{@image_path | | Image path }" };
static void help()
{
cout << "\nThis example shows the functionalities of lines extraction " << "furnished by BinaryDescriptor class\n"
<< "Please, run this sample using a command in the form\n" << "./example_line_descriptor_lines_extraction <path_to_input_image>" << endl;
}
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/* get parameters from comand line */
CommandLineParser parser( argc, argv, keys );
String image_path = parser.get<String>( 0 );
if( image_path.empty() )
{
help();
return -1;
}
/* load image */
cv::Mat imageMat = imread( image_path, 1 );
if( imageMat.data == NULL )
{
std::cout << "Error, image could not be loaded. Please, check its path" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
/* create a random binary mask */
cv::Mat mask = Mat::ones( imageMat.size(), CV_8UC1 );
/* create a pointer to a BinaryDescriptor object with deafult parameters */
Ptr<LSDDetector> bd = LSDDetector::createLSDDetector();
/* create a structure to store extracted lines */
vector<KeyLine> lines;
/* extract lines */
cv::Mat output = imageMat.clone();
bd->detect( imageMat, lines, 2, 1, mask );
/* draw lines extracted from octave 0 */
if( output.channels() == 1 )
cvtColor( output, output, COLOR_GRAY2BGR );
for ( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ )
{
KeyLine kl = lines[i];
if( kl.octave == 0)
{
/* get a random color */
int R = ( rand() % (int) ( 255 + 1 ) );
int G = ( rand() % (int) ( 255 + 1 ) );
int B = ( rand() % (int) ( 255 + 1 ) );
/* get extremes of line */
Point pt1 = Point2f( kl.startPointX, kl.startPointY );
Point pt2 = Point2f( kl.endPointX, kl.endPointY );
/* draw line */
line( output, pt1, pt2, Scalar( B, G, R ), 3 );
}
}
/* show lines on image */
imshow( "LSD lines", output );
waitKey();
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cerr << "OpenCV was built without features2d module" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#endif // HAVE_OPENCV_FEATURES2D
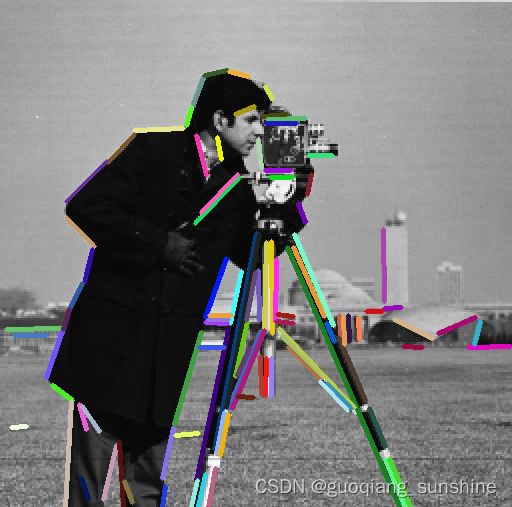

另一种提取线条的方法是使用LSDDetector类;这种类使用LSD提取器来计算线条。为了获得这个结果,只需使用上面看到的代码片段,通过修改行即可。
Here’s the result returned by LSD detector again on cameraman picture:

#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv_modules.hpp>
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_FEATURES2D
#include <opencv2/line_descriptor.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/utility.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::line_descriptor;
static const char* keys =
{ "{@image_path | | Image path }" };
static void help()
{
std::cout << "\nThis example shows the functionalities of lines extraction " << "and descriptors computation furnished by BinaryDescriptor class\n"
<< "Please, run this sample using a command in the form\n" << "./example_line_descriptor_compute_descriptors <path_to_input_image>"
<< std::endl;
}
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/* get parameters from command line */
CommandLineParser parser( argc, argv, keys );
String image_path = parser.get<String>( 0 );
if( image_path.empty() )
{
help();
return -1;
}
/* load image */
cv::Mat imageMat = imread( image_path, 1 );
if( imageMat.data == NULL )
{
std::cout << "Error, image could not be loaded. Please, check its path" << std::endl;
}
/* create a binary mask */
cv::Mat mask = Mat::ones( imageMat.size(), CV_8UC1 );
/* create a pointer to a BinaryDescriptor object with default parameters */
Ptr<BinaryDescriptor> bd = BinaryDescriptor::createBinaryDescriptor();
/* compute lines */
std::vector<KeyLine> keylines;
bd->detect( imageMat, keylines, mask );
/* compute descriptors */
cv::Mat descriptors;
bd->compute( imageMat, keylines, descriptors);
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cerr << "OpenCV was built without features2d module" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#endif // HAVE_OPENCV_FEATURES2D
Matching among descriptors
如果我们从两幅不同的图像中提取了描述符,那么可以在它们之间搜索匹配项。其中一种方法是将每个输入查询描述符与一个描述符进行精确匹配,并选择最接近的那个。
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv_modules.hpp>
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_FEATURES2D
#include <opencv2/line_descriptor.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/utility.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#define MATCHES_DIST_THRESHOLD 25
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::line_descriptor;
static const char* keys =
{ "{@image_path1 | | Image path 1 }"
"{@image_path2 | | Image path 2 }" };
static void help()
{
std::cout << "\nThis example shows the functionalities of lines extraction " << "and descriptors computation furnished by BinaryDescriptor class\n"
<< "Please, run this sample using a command in the form\n" << "./example_line_descriptor_compute_descriptors <path_to_input_image 1>"
<< "<path_to_input_image 2>" << std::endl;
}
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/* get parameters from command line */
CommandLineParser parser( argc, argv, keys );
String image_path1 = parser.get<String>( 0 );
String image_path2 = parser.get<String>( 1 );
if( image_path1.empty() || image_path2.empty() )
{
help();
return -1;
}
/* load image */
cv::Mat imageMat1 = imread( image_path1, 1 );
cv::Mat imageMat2 = imread( image_path2, 1 );
if( imageMat1.data == NULL || imageMat2.data == NULL )
{
std::cout << "Error, images could not be loaded. Please, check their path" << std::endl;
}
/* create binary masks */
cv::Mat mask1 = Mat::ones( imageMat1.size(), CV_8UC1 );
cv::Mat mask2 = Mat::ones( imageMat2.size(), CV_8UC1 );
/* create a pointer to a BinaryDescriptor object with default parameters */
Ptr<BinaryDescriptor> bd = BinaryDescriptor::createBinaryDescriptor( );
/* compute lines and descriptors */
std::vector<KeyLine> keylines1, keylines2;
cv::Mat descr1, descr2;
( *bd )( imageMat1, mask1, keylines1, descr1, false, false );
( *bd )( imageMat2, mask2, keylines2, descr2, false, false );
/* select keylines from first octave and their descriptors */
std::vector<KeyLine> lbd_octave1, lbd_octave2;
Mat left_lbd, right_lbd;
for ( int i = 0; i < (int) keylines1.size(); i++ )
{
if( keylines1[i].octave == 0 )
{
lbd_octave1.push_back( keylines1[i] );
left_lbd.push_back( descr1.row( i ) );
}
}
for ( int j = 0; j < (int) keylines2.size(); j++ )
{
if( keylines2[j].octave == 0 )
{
lbd_octave2.push_back( keylines2[j] );
right_lbd.push_back( descr2.row( j ) );
}
}
/* create a BinaryDescriptorMatcher object */
Ptr<BinaryDescriptorMatcher> bdm = BinaryDescriptorMatcher::createBinaryDescriptorMatcher();
/* require match */
std::vector<DMatch> matches;
bdm->match( left_lbd, right_lbd, matches );
/* select best matches */
std::vector<DMatch> good_matches;
for ( int i = 0; i < (int) matches.size(); i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance < MATCHES_DIST_THRESHOLD )
good_matches.push_back( matches[i] );
}
/* plot matches */
cv::Mat outImg;
cv::Mat scaled1, scaled2;
std::vector<char> mask( matches.size(), 1 );
drawLineMatches( imageMat1, lbd_octave1, imageMat2, lbd_octave2, good_matches, outImg, Scalar::all( -1 ), Scalar::all( -1 ), mask,
DrawLinesMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
imshow( "Matches", outImg );
waitKey();
imwrite("/home/ubisum/Desktop/images/env_match/matches.jpg", outImg);
/* create an LSD detector */
Ptr<LSDDetector> lsd = LSDDetector::createLSDDetector();
/* detect lines */
std::vector<KeyLine> klsd1, klsd2;
Mat lsd_descr1, lsd_descr2;
lsd->detect( imageMat1, klsd1, 2, 2, mask1 );
lsd->detect( imageMat2, klsd2, 2, 2, mask2 );
/* compute descriptors for lines from first octave */
bd->compute( imageMat1, klsd1, lsd_descr1 );
bd->compute( imageMat2, klsd2, lsd_descr2 );
/* select lines and descriptors from first octave */
std::vector<KeyLine> octave0_1, octave0_2;
Mat leftDEscr, rightDescr;
for ( int i = 0; i < (int) klsd1.size(); i++ )
{
if( klsd1[i].octave == 1 )
{
octave0_1.push_back( klsd1[i] );
leftDEscr.push_back( lsd_descr1.row( i ) );
}
}
for ( int j = 0; j < (int) klsd2.size(); j++ )
{
if( klsd2[j].octave == 1 )
{
octave0_2.push_back( klsd2[j] );
rightDescr.push_back( lsd_descr2.row( j ) );
}
}
/* compute matches */
std::vector<DMatch> lsd_matches;
bdm->match( leftDEscr, rightDescr, lsd_matches );
/* select best matches */
good_matches.clear();
for ( int i = 0; i < (int) lsd_matches.size(); i++ )
{
if( lsd_matches[i].distance < MATCHES_DIST_THRESHOLD )
good_matches.push_back( lsd_matches[i] );
}
/* plot matches */
cv::Mat lsd_outImg;
resize( imageMat1, imageMat1, Size( imageMat1.cols / 2, imageMat1.rows / 2 ), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR_EXACT );
resize( imageMat2, imageMat2, Size( imageMat2.cols / 2, imageMat2.rows / 2 ), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR_EXACT );
std::vector<char> lsd_mask( matches.size(), 1 );
drawLineMatches( imageMat1, octave0_1, imageMat2, octave0_2, good_matches, lsd_outImg, Scalar::all( -1 ), Scalar::all( -1 ), lsd_mask,
DrawLinesMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
imshow( "LSD matches", lsd_outImg );
waitKey();
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cerr << "OpenCV was built without features2d module" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#endif // HAVE_OPENCV_FEATURES2D
这段文本讨论了一种图像处理中的技术,即寻找最接近的k个描述符。描述符是一种用于描述图像特征的数学表示。在这种技术中,我们需要对先前的代码进行一些修改。
// prepare a structure to host matches
std::vector<std::vector<DMatch> > matches;
// require knn match
bdm->knnMatch( descr1, descr2, matches, 6 );
在上面的例子中,对于每个查询,返回最接近的6个描述符。在某些情况下,我们可以有一个搜索半径,查找距离输入查询最多为r的所有描述符。必须修改先前的代码:
// prepare a structure to host matches
std::vector<std::vector<DMatch> > matches;
// compute matches
bdm->radiusMatch( queries, matches, 30 );
这是一个从原始摄影师图像及其下采样(和模糊)版本提取描述符进行匹配的示例。
线特征基础实现
线特征优化实现


优化前后:里哟个均匀性质







![[echarts] legend icon 自定义的几种方式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ecc2c2dc938f43d394affbe376976a8b.png)